임시 객체
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class String
{
public:
String()
{
cout << "String() : " << this << endl;
strData = NULL;
len = 0;
}
String(const char *str)
{
cout << "String(const char *) 생성자 호출" << this << endl;
len = strlen(str);
alloc(len);
strcpy(strData, str);
}
//매게변수로 String 클래스 타입을 받는것.
String(const String &ref)
{
cout << "String(String &ref) 생성자 호출" << endl;
len = ref.len;
alloc(len);
strcpy(strData, ref.strData);
}
~String()
{
cout << "~String(): " << this << endl;
release();
strData = NULL;
}
//복사 대입 연산자
String &operator=(const String &rhs)
{
cout << "String &operator = (const String&) : " << this << endl;
if (this != &rhs)
{
release();
len = rhs.len;
alloc(len);
strcpy(strData, rhs.strData);
}
return *this;
}
char *GetstrData() const
{
return strData;
}
int Getlen() const
{
return len;
}
//복사 생성자
void SetStrData(const char *str)
{
cout << "void setStrData(const char*) : " << this << ", " << str << endl;
len = strlen(str);
alloc(len);
strcpy(strData, str);
}
private:
void alloc(int len)
{
strData = new char[len + 1];
cout << "strData allocated : " << (void *)strData << endl;
}
void release()
{
delete[] strData;
if (strData)
cout << "strData released: " << (void *)strData << endl;
}
char *strData;
int len;
};
String getName()
{
cout << " ===== 2 =====" << endl;
// res 라는 객체 생성
String res("Jinchoel");
cout << " ===== 3 =====" << endl;
return res;
}
int main()
{
//매게변수가 없는 생성자를 가진 객체 'a' 생성
String a;
cout << " ===== 1 =====" << endl;
// a라는 변수에 getName 함수의 결과를 할당.
// 복사 대입 연사자 ('=') 호출.
a = getName();
cout << " ===== 4 =====" << endl;
}-
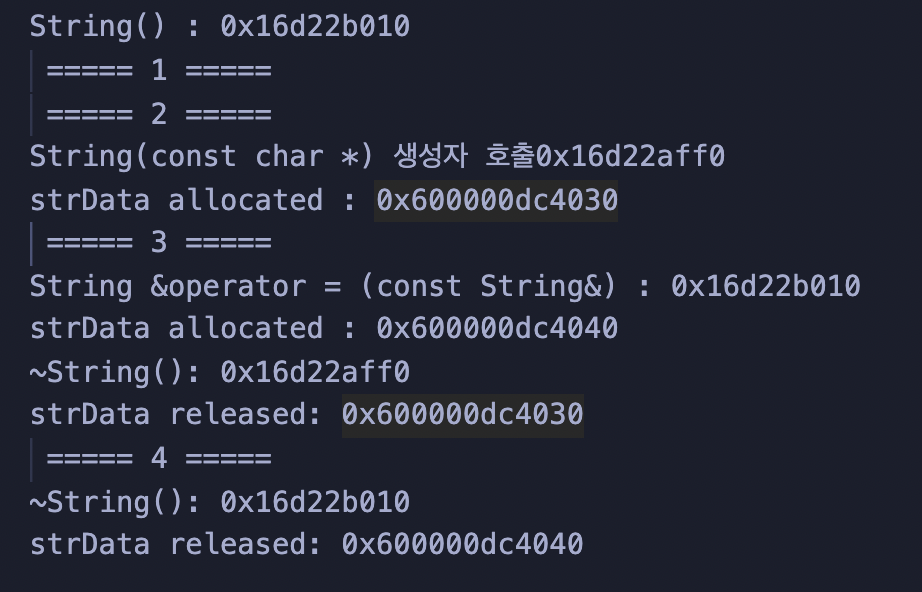
해당 코드 실행시 a가 대입연산자를 통해서 함수(getName())의 결과를 할당받으면서 '복사생성자' 실행됨.
-
getName 함수 내에서 return res 실행 후 res 는 소멸.
-
그러면 어떻게 a는 getName이 반환하는 res를 할당받을 수 있을까 ?
-
따라서 getName이 리턴되는 순간 새로운 retrun값을 받는 새로운 변수 필요. -> 이름이 없음 : 임시객체
-
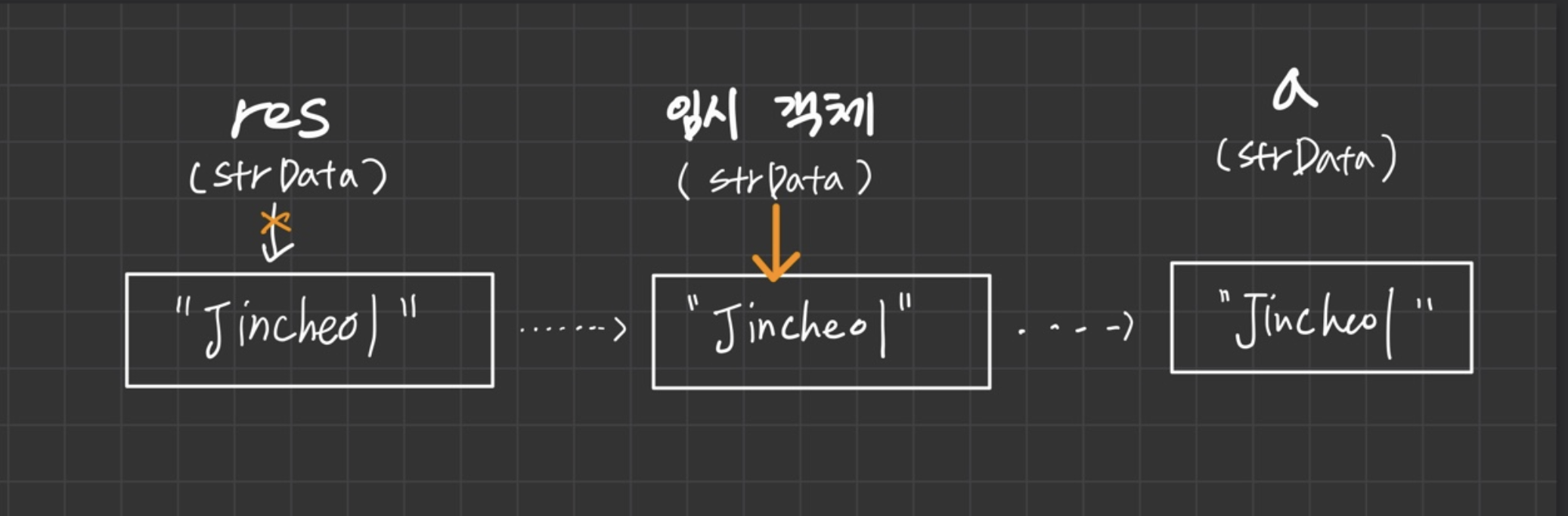
res 가 임시객체 안으로 들어감.
-
그 후 임시객체가 a로 흘러들어감.
-
임시객체가 a로 복사가되면 임무를 끝마쳤으므로 임시객체는 사라짐.
-
총 2번의 깊은 복사 이루어짐 ( res -> 임시객체 , 임시객체 -> a)
-
하지만 res, 임시객체는 a=getName() 코드 실행시 사라질 불필요한 객체들.
-
따라서 객체간의 복사를 깊은복사가 아닌 '얕은복사'로 이루어지게 만듦.
이동 시멘틱
'이동'이라는 컨셉을 가지고 얕은 복사 손쉽게 구현하기
- res 가 strData를 복사하고 임시객체가 strData를 복사하는 등의 반복된 복사가 이루어지는 것이 아닌 strData가 일종의 이동을 행하면서 각 객체에 strData를 할당하는 방식.
r-value

int f() { retrun 5; }- 임시객체(5) 에 특정한 값을 할당할 수 없으므로 결과적으로 임시객체는 r-value다.
&&r (r-value 참조자)

이동생성자 & 이동 대입 연산자
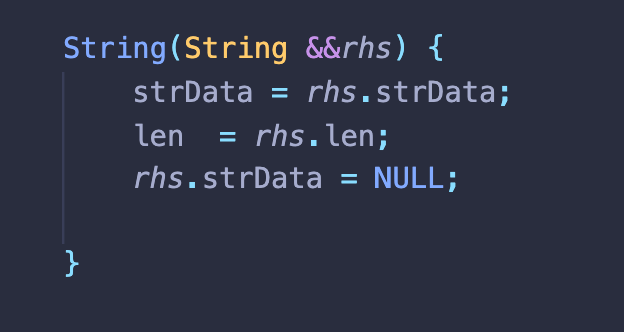
1) 이동생성자
- String res는 l-value이지만 res가 반환되는 동안에 잠시동안 r-value로 간주돼( 그렇게 돼야만 r-value 참조자로 res를 받을 수 있음) 임시객체로 복사가 되는 과정에서 res는 우변에만 올 수 있는 r-value이므로 r-value참조를 매개변수로 받는 생성자 String(String &&rhs)가 호출된다.
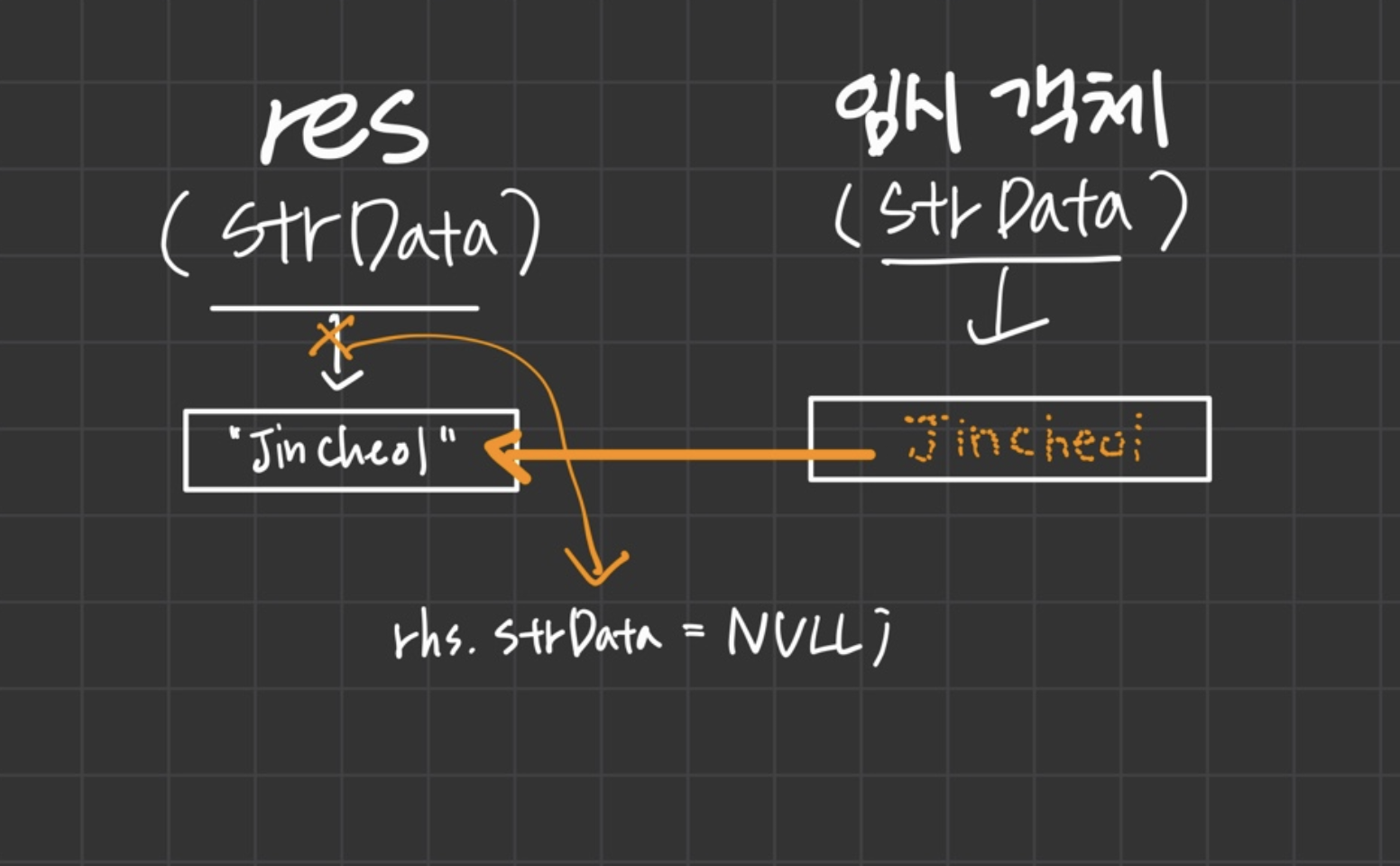
- 임시객체는 res 객체가 가르키고 있는 값을 똑같이 가르킴
- 그리고 기존 res 객체에 존재하는 strData의 값과의 연결은 끊어짐.
- 그러므로 delete[]strData가 수행되도 임시객체가 가져온 strData의 값과는 아무런 영향을 끼치지 못함.
- 결과적으로 임시 객체는 strData를 가르키게 돼며 해당 문자열은 살아남게됨.
----> 이동시멘틱의 기본적 원리
2) 이동 대입 연산자

- rhs.strData = strData 는 얕은복사 실행.
- return *this 의 이유는 String a = b= c ;와 같이 연쇄적으로 등호를 사용하는 경우를 대비.
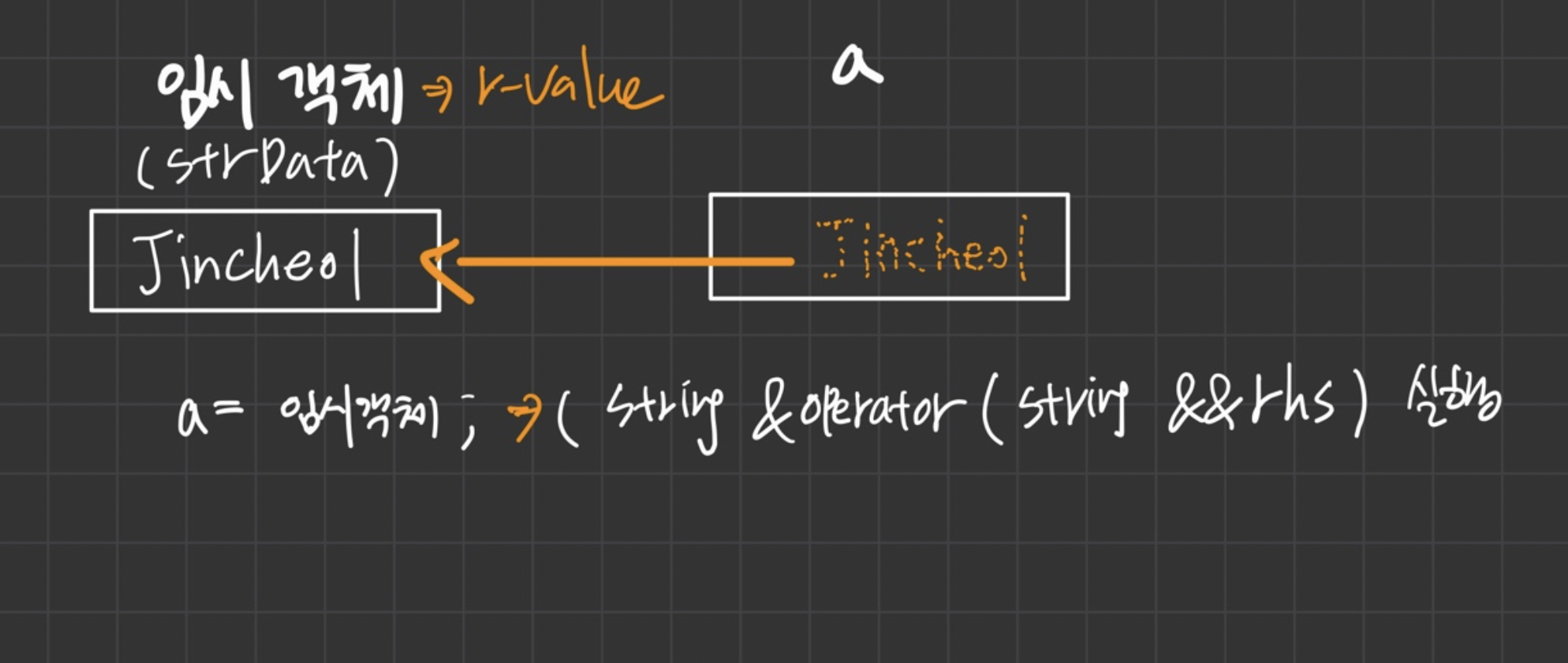
정리 : res, 임시객체는 r-value로 간주되기 때문에 String(String &&rhs), String & operatr=(String &&rhs)((r-value를 매게변수로 받음)) 에서 볼 수 있는 &&rhs와 같은 매게변수가 호출이된다.