- 단일 재귀 호출
재귀 호출은 함수 안에 함수를 넣는 것이다. 그러면 함수가 무한히 반복되니 빠져나오는 구문을 적는 것이 중요하다. 그 중 하나는 if문을 작성하는 것이다.
void CountDown(int n);
int main()
{
CountDown(4);
}
void CountDown(int n)
{
cout << "카운트 다운..." << n << endl;
if (n > 0)
CountDown(n - 1);
cout << n << ": Kaboom!" << endl;
}실행 결과.
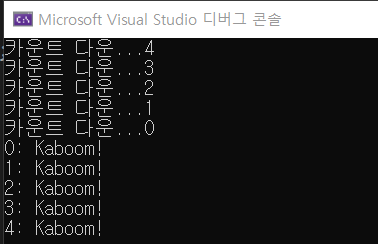
이런 재귀 함수의 재밌는 특징은, if 구문 이전의 코드는 순차적으로 진행되지만, 이후의 코드는 반대로 거슬러 올라간다는 점이다.
- 다중 재귀 호출
다중 재귀 호출은 하나의 작업을 여러 개로 나누어서 반복적으로 할 때 유용하다. 대표적인 것이 바로 피보나치 수열이다.
int Fibonacci(int n);
int main()
{
cout << Fibonacci(7) << endl;
}
int Fibonacci(int n)
{
if (n <= 2)
return 1;
return Fibonacci(n - 1) + Fibonacci(n - 2);
}1,1,2,3,5,8,13....이렇게 이전의 두 숫자를 더한 값이 다음 값이 되는 피보나치 수열의 특징은 다중 재귀 함수로 구현하기 딱 알맞은 예제이다.
