.jpg)
async / await
aync과 await을 사용해서 비동기 처리를 할 수 있으며, Promise 객체를 사용하는 것 보다 좀 더 간결하다.
async 키워드
function 앞에 쓰며, async를 붙이는 경우 항상 promise를 반환한다.
아래 예시와 같이 이행된 프라미스가 반환된다.
const myfunc = async () => {
return 'Good'
}
myfunc().then()명시적으로 promise를 반환해서 쓸 수도 있다.
const myfunc = async () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Good!!!')
});
}
myfunc().then()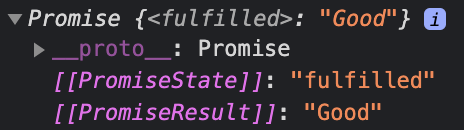
await 키워드
await은 async 함수에서만 작동하며, 비동기 처리 코드 앞에 쓴다. await를 만나면 promise 처리가 될 때까지 기다리고 결과는 이후 반환된다.
async와 await의 사용
async function 함수명() {
await 비동기 함수명()
}resultFunc()는 async 키워드를 앞에 붙여 promise를 반환하는 함수가 된다.
자바스크립트는 읽어가다가 await를 만나면 promise가 이행될 때 까지 기다리므로 2초 뒤에 result가 출력된다.
function promiseFunc() {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('1,2,3')
},2000)
});
}
async function resultFunc() {
let result = await resultFunc(); //프라미스가 이행될 때 까지 기다린다.
console.log(result);
}예외처리
async / await 에러처리는 try-catch로 많이 처리한다.
- try-catch 특징
try안에 있는 것들을 실행하다가 에러가 발생하면 뒤에 것 실행안하고 catch로 넘어간다.
const myfunc = (err) => {
console.log('Start');
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout( () => {
if(!err) {
resolve()
} else {
reject()
}
},2000);
});
}fulfilled 상태
아래는 resolve()가 호출되어 이행 상태일 때 promise를 반환하기 때문에 2초 뒤에 hello1이 출력, 2초 뒤에 hello2가 출력, 2초 뒤에 hello3가 출력된다.
await을 만나면 이행될 때 까지 기다리는 특성 때문에 task3가 처리 되기까지 6초가 걸린다.
const run = async () => {
try {
const task1 = await myfunc(false);
console.log("hello1");
const task2 = await myfunc(false);
console.log("hello2");
const task3 = await myfunc(false);
console.log("hello3"); //<- 6초 걸림
console.log("hello3");
} catch(err) {
console.log(new Error('에러'));
}
}
run()failed 상태
task1의 await은 작동이 되어 promise 이행이 끝나면 hello1을 출력하고, task2의 await을 실행시키는데 reject()를 불러와 실패 상태가 되므로 catch()의 에러 메세지를 반환하고 종료해버린다.
let run = async () => {
try {
const task1 = await myfunc(false);
console.log("hello1");
const task2 = await myfunc(true);
console.log("hello2");
const task3 = await myfunc(false);
console.log("hello3"); //<- 6초 걸림
console.log("hello3");
} catch(err) {
console.log(new Error('에러'));
}
}
run()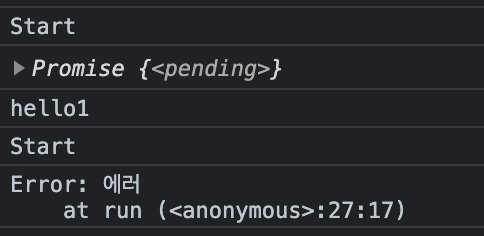
막간 퀴즈
-
await 키워드 다음에 등장하는 함수 실행은, 어떤 타입을 리턴할 경우에만 의미가 있나요?
promise를 리턴해야만 의미가 있다. -
await 키워드를 사용할 경우, 어떤 값이 리턴되나요?
Promise가 리턴된다.
