✅ 오늘 한 일
- Project BCA
📝 배운 것들
🏷️ IK 알고리즘 종류
① FABRIK (Forward And Backward Reaching Inverse Kinematics)
가장 널리 사용되는 IK 알고리즘 중 하나로, 목표 위치에 도달할 때까지 반복적으로 보정하는 방식입니다.
- Forward Pass (정방향 단계): 손에서부터 어깨 방향으로 목표 위치에 맞게 이동
- Backward Pass (역방향 단계): 어깨에서 손 방향으로 이동하면서 최종 보정
➡️ FABRIK은 부드러운 움직임을 제공하고 빠른 계산이 가능하므로 게임에서 많이 사용됩니다.
② CCD (Cyclic Coordinate Descent)
반복적으로 각 관절을 회전시키면서 목표에 가까워지도록 조정하는 방법입니다.
- 가장 끝에 있는 뼈(손)를 먼저 목표 위치로 이동
- 하나씩 부모 방향으로 관절을 회전하며 목표에 맞춰 조정
- 반복하면서 오차를 줄임
➡️ CCD는 간단하지만 세밀한 조정이 필요하며, 때로는 부자연스러운 움직임을 초래할 수 있음.
③ Jacobian Inverse Kinematics
- 수학적으로 더 정교한 방법으로, 각 관절의 이동을 수학적으로 계산하여 목표 위치에 도달하는 방법
- 자코비안 행렬(Jacobian Matrix) 을 사용하여 관절이 움직여야 하는 방향을 계산
- 매우 정확하지만, 실시간으로 계산하기에는 연산량이 많아 게임보다는 CG 영화에서 많이 사용
➡️ 게임보다는 물리 시뮬레이션, 애니메이션 제작에서 많이 활용됨.
🎮 Project BCA
로봇 팔 IK 로직 구현
코드로 구현하는게 불가능한 건 아닌데, 너무 지저분한거 아닌가 싶어서 다른 방법 없는지 추가 조사.
- 유니티 자체 IK 솔루션 OnAnimatorIK() : Humanoid에서만 작동함
- FABRIK, CCD 등 : 관절들이 같은 평면 상에 있지 않아서 되는지 안되는지 모르겠음
- gpt한테 물어보니 같은 평면 상에 있는 걸 전제로 한 알고리즘들이라 안 될 것 같다고는 함
- 그래도 일단 적용해보거나 해결책(같은 평면 상에 피벗 위치시킨다거나)을 찾을 수도 있겠지만, 적용하는데 시간이 너무 오래 걸릴 것 같음
- 어찌저찌 적용한다고 해도 답을 한 번에 구하는게 아니라 continous하게 구하는 방식이라 애니메이션을 내가 원하는대로 제어하기 어려울 것 같음
- 조금 귀찮아도 내가 뭘 하는지 정확히 알고 있는 해결책이 나와 있는 상황에서 굳이 다른 방법 써볼 것 까진 없을듯
- IK 알고리즘들 자체는 나중에 더 공부해보면 좋을듯

o1이 원 교점 수식을 간단하게 바꿔줬다.
o1 원본 코드
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public static class CircleIntersectionSolver
{
public static List<Vector2> FindCircleIntersections(
Vector2 center1, float radius1,
Vector2 center2, float radius2)
{
List<Vector2> intersectionPoints = new List<Vector2>();
float d = Vector2.Distance(center1, center2);
if (d > radius1 + radius2) return intersectionPoints;
if (d < Mathf.Abs(radius1 - radius2)) return intersectionPoints;
if (Mathf.Approximately(d, 0f) && Mathf.Approximately(radius1, radius2)) return intersectionPoints;
float a = (radius1*radius1 - radius2*radius2 + d*d) / (2f * d);
float h = Mathf.Sqrt(radius1*radius1 - a*a);
Vector2 m = center1 + a * (center2 - center1).normalized;
Vector2 perp = Perp(center2 - center1).normalized;
Vector2 i1 = m + perp * h;
Vector2 i2 = m - perp * h;
if (Mathf.Approximately(h, 0f))
{
intersectionPoints.Add(i1);
}
else
{
intersectionPoints.Add(i1);
intersectionPoints.Add(i2);
}
return intersectionPoints;
}
private static Vector2 Perp(Vector2 v)
{
// (x, y) -> (-y, x)
return new Vector2(-v.y, v.x);
}
}
두 원 교점 구하는 클래스
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class TestCircleIntersection3D : MonoBehaviour
{
[Header("Circle 1 (in 3D)")]
public Vector3 center1_3D = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
public float radius1 = 2f;
[Header("Circle 2 (in 3D)")]
public Vector3 center2_3D = new Vector3(2, 0, 0);
public float radius2 = 2f;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
// (1) 실제로는 3D 씬에 그리지만, "XY 평면"에 원을 배치한다고 가정.
// => CircleIntersectionSolver는 Vector2로 처리하므로, x-y만 취급
Vector2 c1_2D = new Vector2(center1_3D.x, center1_3D.y);
Vector2 c2_2D = new Vector2(center2_3D.x, center2_3D.y);
// (2) 3D 씬에서 WireSphere 그리기 (시각적으로는 구)
Gizmos.color = Color.yellow;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(center1_3D, radius1);
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(center2_3D, radius2);
// (3) 교점 계산 (2D 로직)
List<Vector2> intersectionPoints = CircleIntersectionSolver.FindCircleIntersections(
c1_2D, radius1, c2_2D, radius2
);
// (4) 교점들을 3D에 구로 표시 (z=0 평면에 놓인다고 가정)
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
foreach (Vector2 ip in intersectionPoints)
{
// 2D 좌표 -> 3D 좌표 (z=0)
Vector3 ip3D = new Vector3(ip.x, ip.y, 0);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(ip3D, 0.05f);
}
}
}테스트용 기즈모 그려주는 클래스
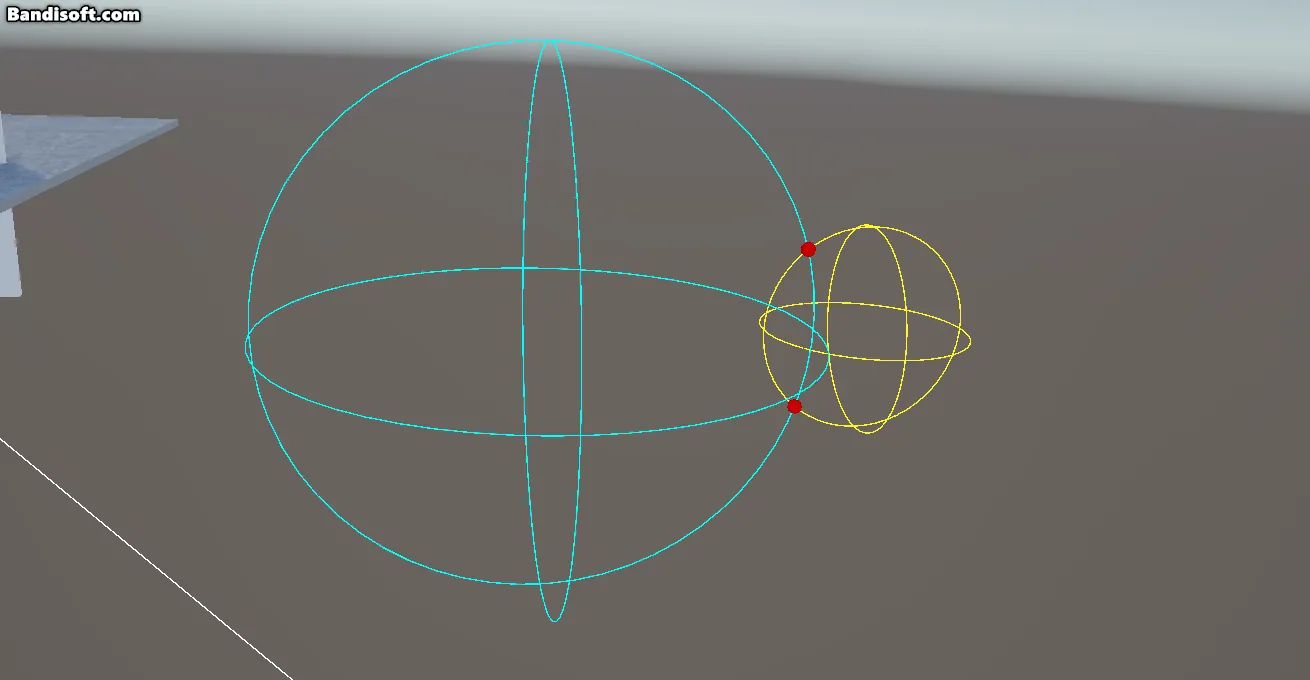
재밌다
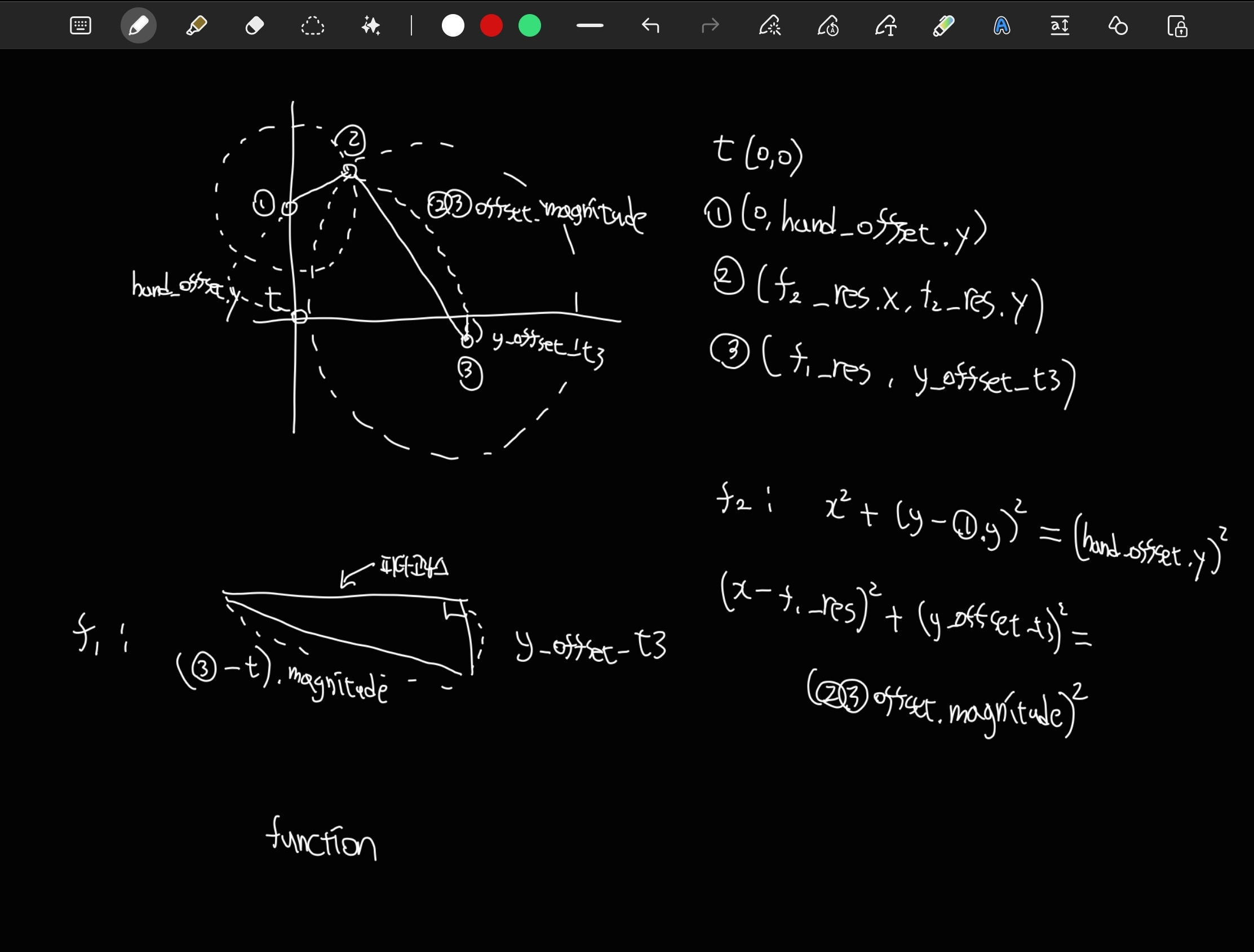
각도 기준점 issue
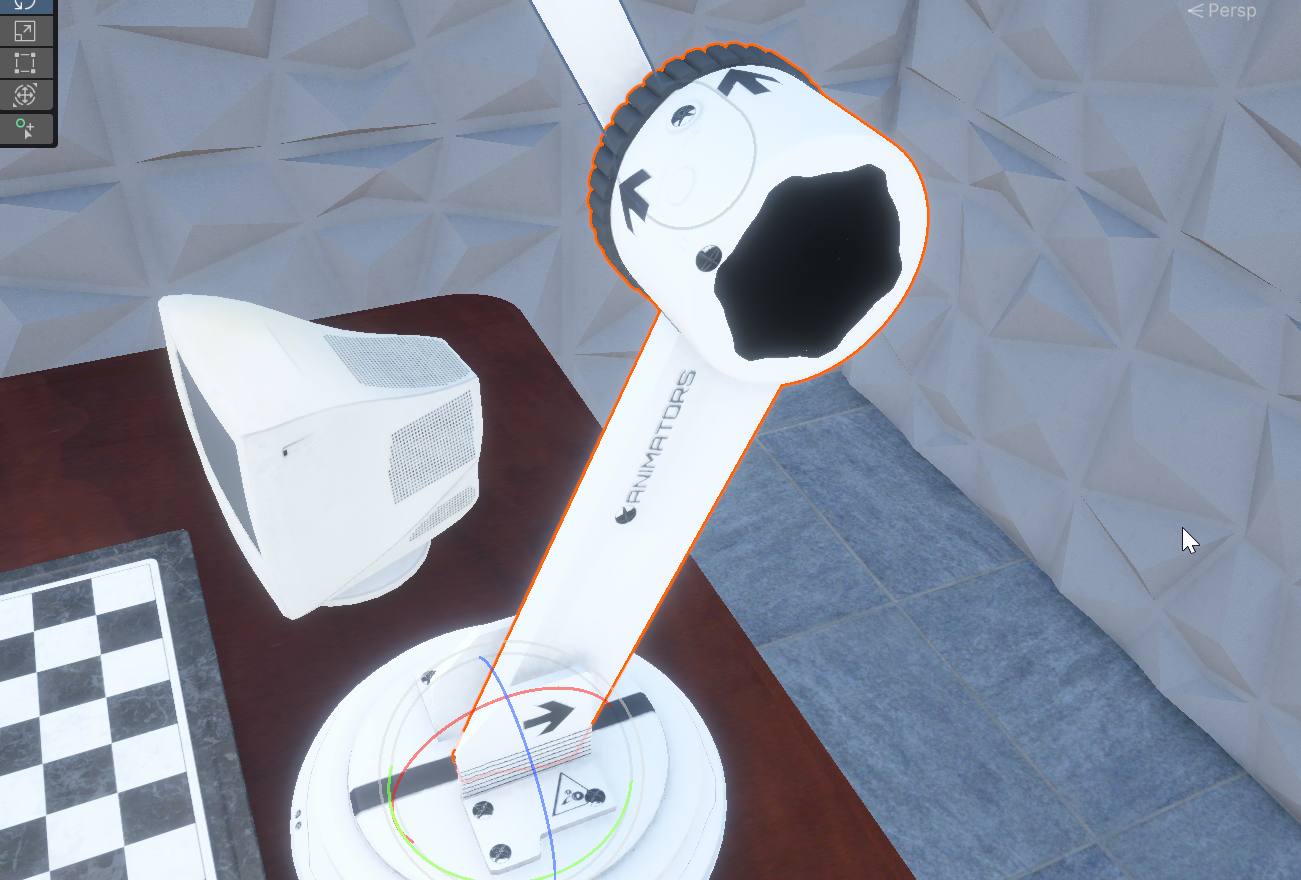

현재는 이 상태가 해당 파트가 로컬 좌표계 기준 rotation이 0,0,0일 때이다.
이렇게 되면 이론적으로 얼마만큼 돌려야 하는지 각도를 구했다고 하더라도,
실제로 각 파트의 rotation 수치가 얼마나 돼야하는지 알 수가 없다.
해결과정
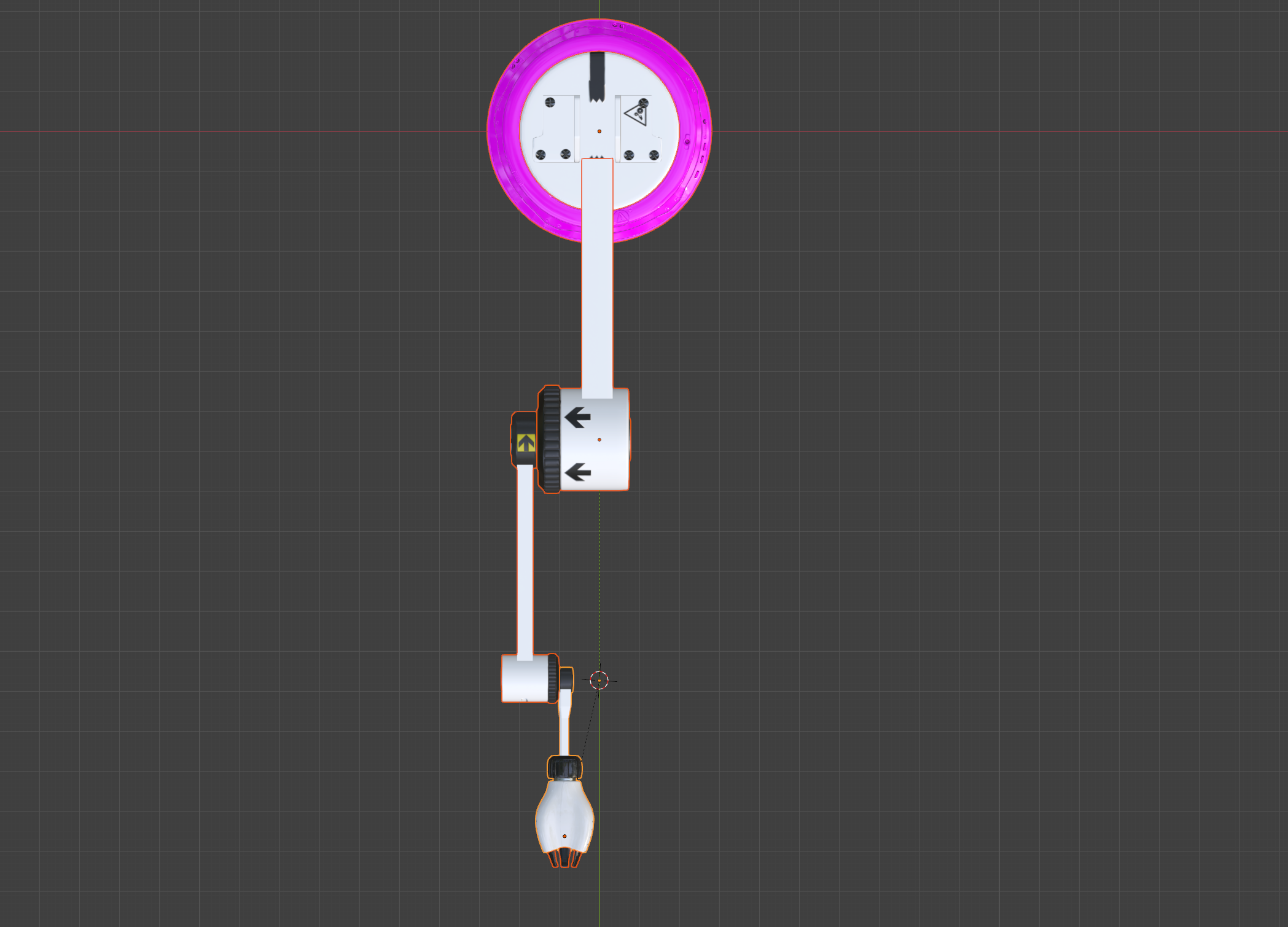
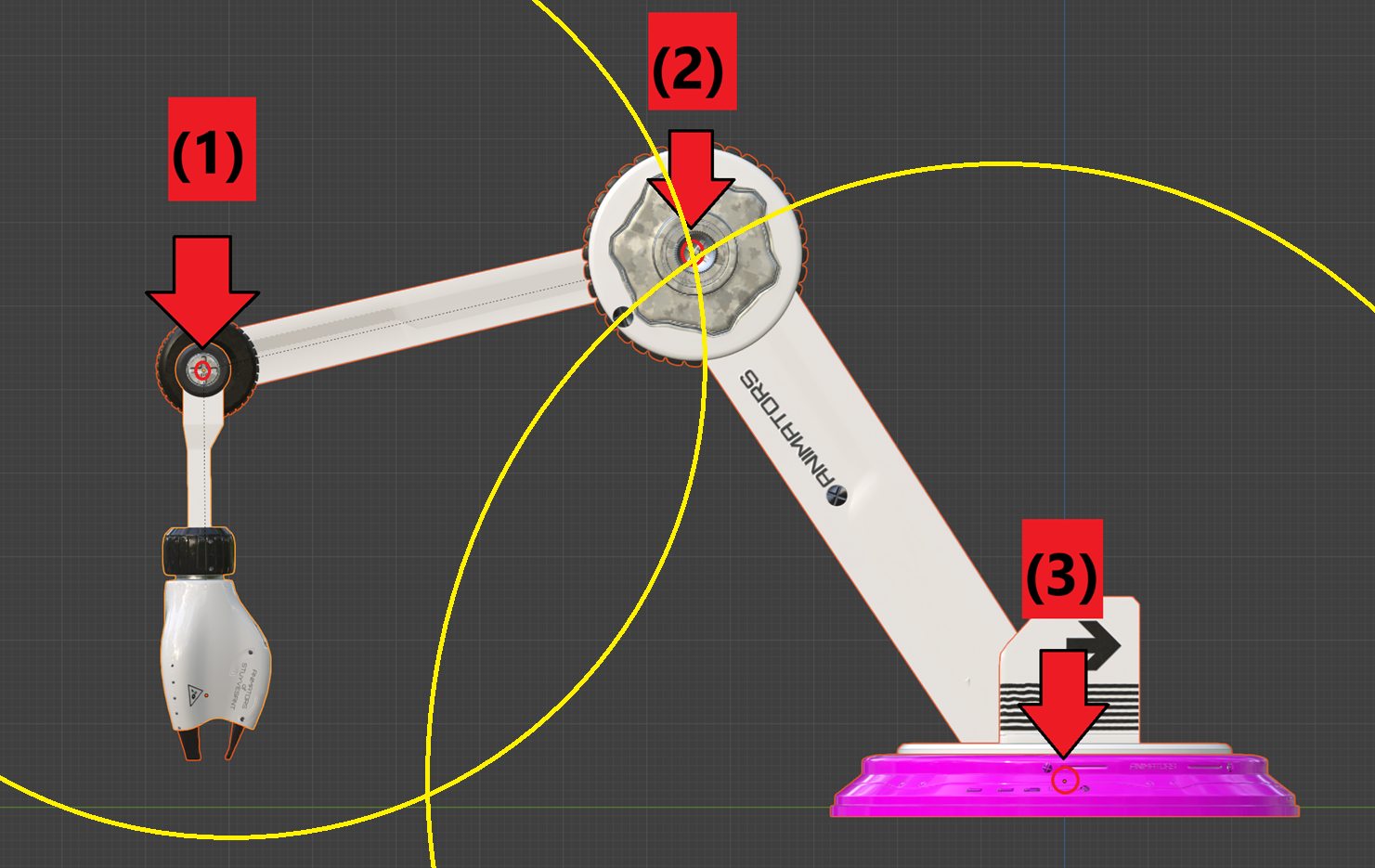
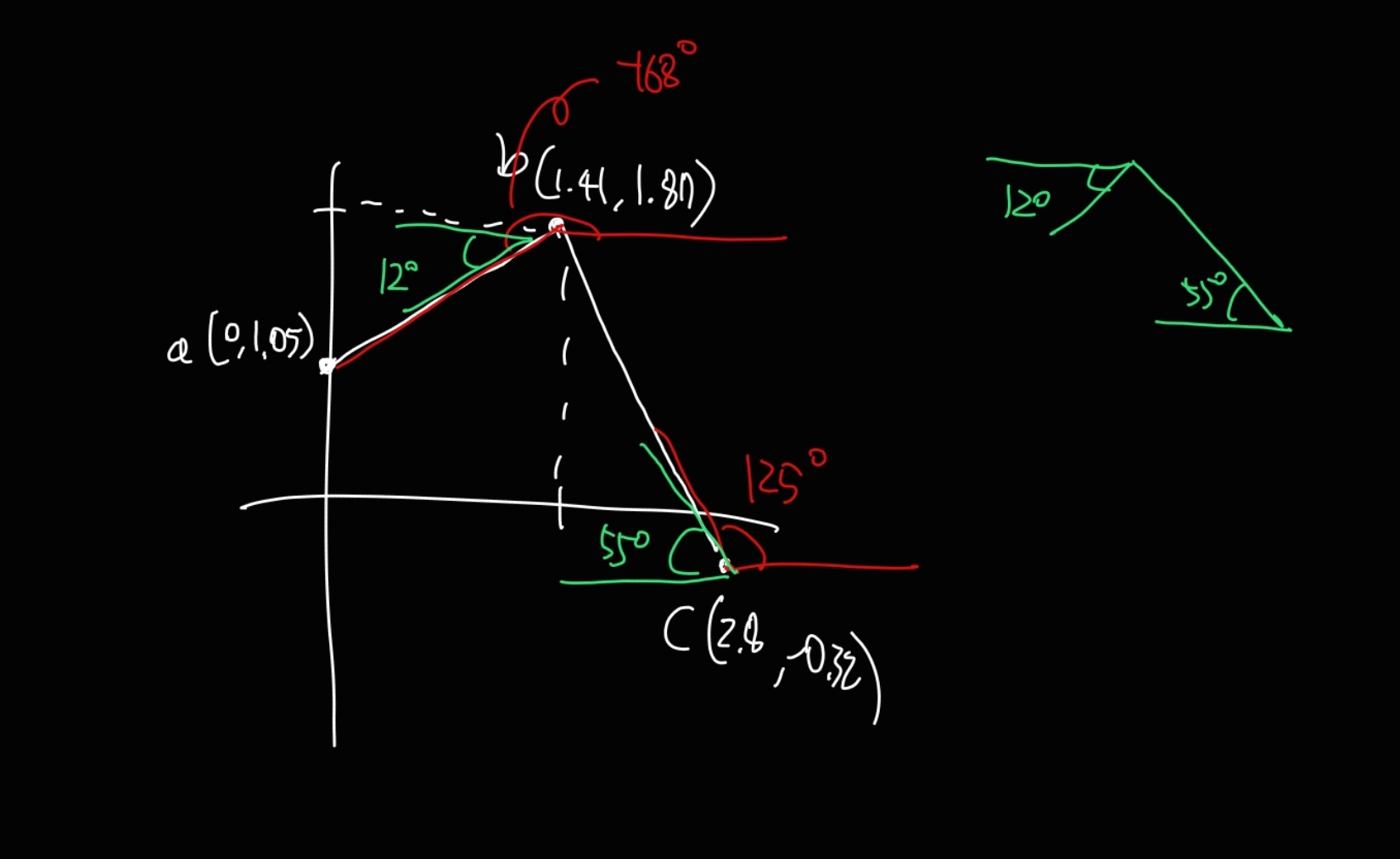
모델링을 수정하여 불필요한 오프셋 연산을 최소화했다.
- 모델링의 파트 별 중심점들이 한 평면에 있어야 한다. 그래야 오프셋 계산이 줄어든다
- 유니티 로컬 좌표계 기준 rotation 0,0,0으로 설정하면 부모와 일직선을 이루어야 한다. 첫번째 파트는 월드 좌표계 기준 rotation 0이어야 한다. 그래야 부모의 각도를 기준으로 자식의 각도를 설정할 수 있다.
- N > View > 3D Cursor에서 커서의 Location을 설정할 수 있다
- 모델의 중심들이 z축에 나열되도록 수정
- Ctrl+A > Rotation해야 기본 각도 정보를 수정 가능
코드 추가 수정 필요한 부분
- 각도를 구하는 연산을 추가한 뒤, 점이 아니라 각도의 배열을 반환한다.
- 손이 팔의 중심선에서 약간 벗어나 있다. 유니티에서 타겟의 자식 오브젝트를 만든 뒤 오프셋만큼 위치시키면 된다.
atan2는 180도를 넘어가면 -180부터 시작
완성
using UnityEngine;
public class RoboticArm : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField] private Transform target_for_math;
[SerializeField] private Transform target_to_reach;
[SerializeField] private Transform y_axis_part;
[SerializeField] private Transform x_axis_part;
[SerializeField] private Transform x_axis_part_2;
[SerializeField] private Transform hand_part;
[SerializeField] private Transform tongs_part;
private float hand_offset;
private float r1;
private float r2;
void Start()
{
hand_offset = -tongs_part.localPosition.y * 110;
r1 = (hand_part.position - x_axis_part_2.position).magnitude;
r2 = (x_axis_part_2.position - x_axis_part.position).magnitude;
}
public void SetTarget()
{
}
void Update()
{
if (target_for_math == null) return;
Sync_Y_Rotation();
Adjust_X_Axis_Angles();
}
private void Sync_Y_Rotation()
{
Vector3 direction = target_for_math.position - y_axis_part.position;
direction.y = 0; // 불연속적 계산 방지
float angle = Vector3.SignedAngle(Vector3.forward, direction, Vector3.up);
y_axis_part.rotation = Quaternion.Euler(-90, angle, 0);
}
private void Adjust_X_Axis_Angles()
{
(float angle2, float angle3) = Find_Angle_Set();
if (float.IsNaN(angle2) || float.IsNaN(angle3)) return;
x_axis_part.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(angle2, 0, 0);
x_axis_part_2.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(angle3, 0, 0);
float angle1 = 90 - angle2 - angle3;
hand_part.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(angle1, 0, 0);
}
private (float, float) Find_Angle_Set()
{
Vector2 a = new Vector2(0, hand_offset);
float y_offset_c = x_axis_part.position.y - target_for_math.position.y;
float offset_c = (target_for_math.position - x_axis_part.position).magnitude;
float x_c = GetHeight(y_offset_c, offset_c);
Vector2 c = new Vector2(x_c, y_offset_c);
Vector2 b = FindCircleIntersections(a, r1, c, r2);
float angle2 = -1 * (180 - GetAngleBetweenPoints(c, b));
float angle3 = GetAngleBetweenPoints(b, a) + 180 - angle2;
return (angle2, angle3);
}
private float GetHeight(float mit_byun, float bit_byun)
{
return Mathf.Sqrt(bit_byun * bit_byun - mit_byun * mit_byun);
}
/// <summary>
/// 두 원의 교점을 구하여 높이가 높은 쪽을 Vector2로 반환합니다.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="center1">첫 번째 원의 중심</param>
/// <param name="radius1">첫 번째 원의 반지름</param>
/// <param name="center2">두 번째 원의 중심</param>
/// <param name="radius2">두 번째 원의 반지름</param>
private Vector2 FindCircleIntersections(
Vector2 center1, float radius1,
Vector2 center2, float radius2)
{
float d = Vector2.Distance(center1, center2);
float a = (radius1 * radius1 - radius2 * radius2 + d * d) / (2 * d);
float h = Mathf.Sqrt(radius1 * radius1 - a * a);
Vector2 direction = (center2 - center1).normalized;
Vector2 m = center1 + a * direction;
Vector2 perp = new Vector2(-direction.y, direction.x);
Vector2 i1 = m + perp * h;
return i1;
}
float GetAngleBetweenPoints(Vector2 p1, Vector2 p2)
{
Vector2 dir = p2 - p1; // 방향 벡터 구하기
float angleRad = Mathf.Atan2(dir.y, dir.x); // atan2(y, x) 사용
float angleDeg = angleRad * Mathf.Rad2Deg; // 라디안을 도(degree)로 변환
return angleDeg;
}
}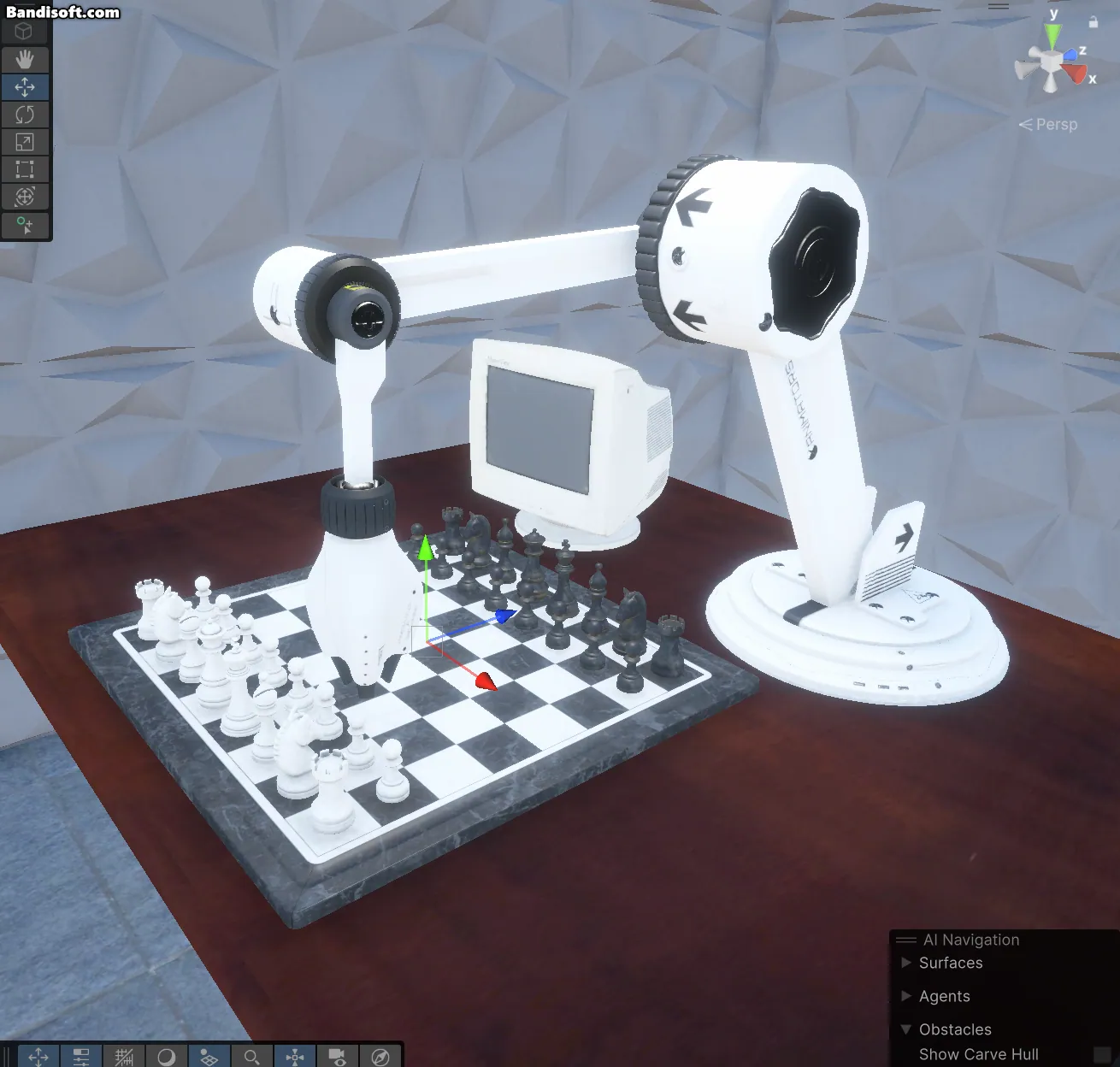
아직 오프셋 조정해야 하는 부분 있지만, 사실상 완성.
o1이 짜준 원 교점 구하는 코드에서 간결함을 위해 경우의 수를 전부 날려버렸는데,
그 때문인지 팔이 아래로 굽혀져야 하는 상황에선 오류가 뜸.
물론 그렇게 되면 로봇팔 쪽에 있는 흑 기물들에 닿아서 뭔가 이상해보일 것 같긴 함.
이건 유니티에서 크기 좀 더 키워서 간단하게 해결함.
보호 구문도 추가.
