1. 버블 정렬(O(n^2))
두 인접한 데이터의 크기를 비교하여 정렬한다.
ex) 백준 2750번
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
// 버블 정렬
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int temp;
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << a[i] << "\n";
}
return 0;
}2. 선택 정렬(O(n^2))
첫 기준 인덱스 값을 선택하여 그것을 나머지와 하나하나 비교하며 정렬한다.
ex) 백준 1427번
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
string str;
cin >> str;
vector<int> a(str.size());
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
a[i] = stoi(str.substr(i, 1));
}
// 선택 정렬
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
int maxIdx = i, tmp;
for (int j = i; j < str.size(); j++) {
if (a[maxIdx] < a[j]) {
tmp = a[maxIdx];
a[maxIdx] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
cout << a[i];
}
return 0;
}3. 삽입 정렬(O(n^2))
정렬된 데이터 범위에 정렬되지 않은 데이터를 적절한 위치에 삽입하여 정렬하는 방식이다.
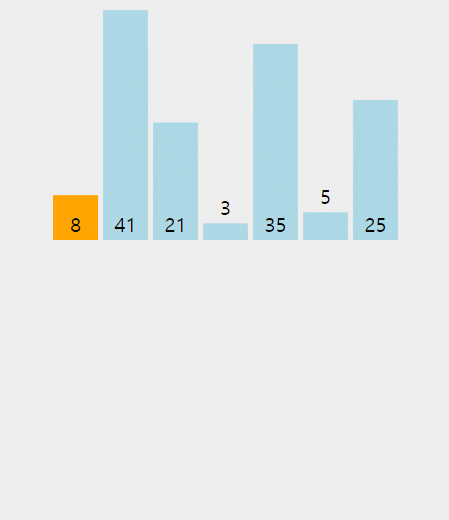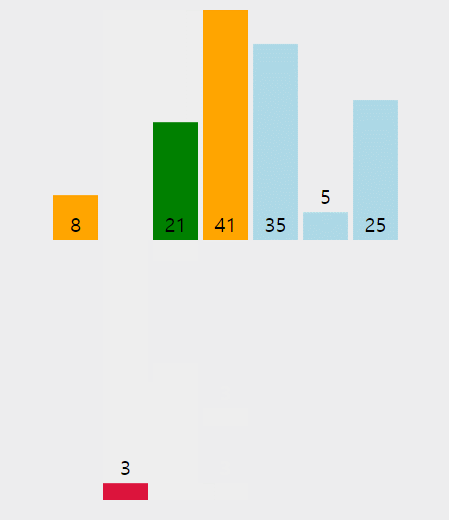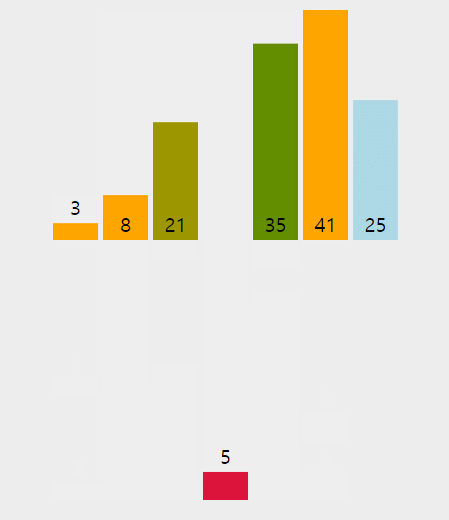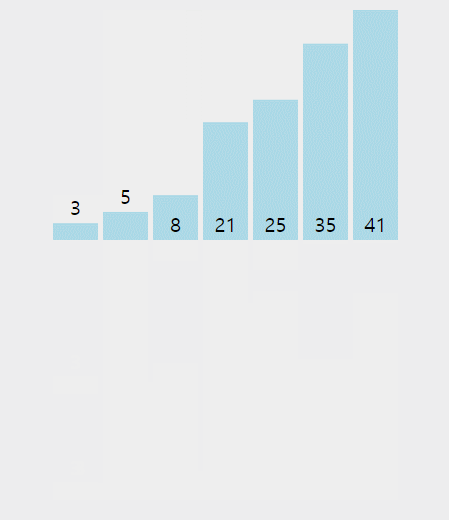
ex) 삽입정렬 구현 코드
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[10] = { 3,6,7,1,4,2,9,0,5,8 };
// 삽입 정렬
void insertion_sort(int a[])
{
int key, j, i;
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++) { // 1
key = a[i];
// shift, 앞의 값이 key보다 크면 뒤로 넘긴다.
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0 && a[j] > key; j--) {
a[j + 1] = a[j];
}
// key보다 작으면, 작은 a[j]의 뒤 index 배열에 key를 대입한다.
// 어차피 앞 부분은 배열이 되어있으므로, 작은 a[j]의 앞 부분은
// 신경쓰지 않아도 된다.
a[j + 1] = key; //3
}
}
int main()
{
insertion_sort(a);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}자료 : VisuAlgo.NET
