
React Query의 도입 이전
-
프로젝트에서는 활성화 되어있는 모집파티를 실시간으로 Update하는 과정이 필요했다. Socket.io를 이용하여 클라이언트와 서버의 실시간 연동을 통해 클라이언트들의 실시간성 유지하였다.
-
클라이언트에서는 모임을 생성하면 소켓서버에 이벤트를 방출한다. 이벤트를 감지한 소켓서버는 DB를 Update하고, 소켓과 연결된 클라이언트들에게 이벤트를 방출한다.
-
서버소켓에서 방출한 이벤트를 감지한 클라이언트들은 콜백으로 모집중인 파티, 내가찜한 파티의 전역상태를 최신으로 Update하는 과정을 통해 실시간으로 변하는 데이터를 받아 올 수 있었다.
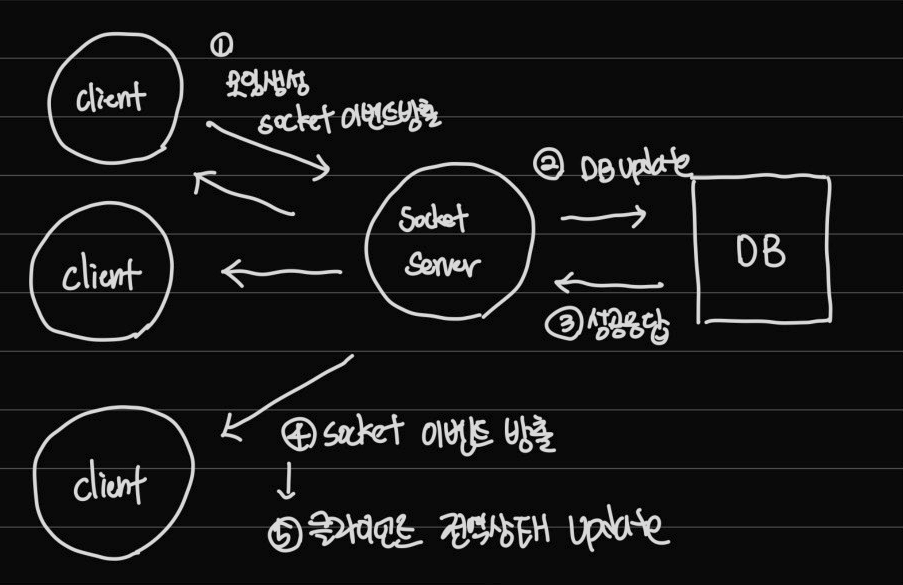
- 모집중인 파티정보와, 내가찜한파티정보는 여러 컴포넌트에서 사용했기 때문에 Redux의 전역상태로 관리하였다. 비동기 요청을 처리하기 위해서 Redux-toolkit의 createasyncthunk를 사용하였다.
// partySlice.ts
import { createSlice, createAsyncThunk } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import { get } from '../api/API';
import type { Party } from '../pages/MainPage/Type';
const initialState: { myPartyList: Party[]; activePartyList: Party[] } = {
myPartyList: [],
activePartyList: [],
};
export const getMyPartyList = createAsyncThunk('party/host', async (_, { rejectWithValue }) => {
try {
const res = await get('/api/parties/liked-party');
if (!res) {
throw new Error('에러!');
}
return res;
} catch (err) {
rejectWithValue(err);
}
});
export const getActivePartyList = createAsyncThunk(
'party/active',
async (_, { rejectWithValue }) => {
try {
const parties = await get('/api/parties');
if (!parties) {
throw new Error('에러!');
}
return parties;
} catch (err) {
rejectWithValue(err);
}
},
);
const partySlice = createSlice({
name: 'party',
initialState,
reducers: {},
extraReducers: (builder) => {
builder.addCase(getMyPartyList.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
const lists = [...action.payload];
const newList = lists.map((list: Party) => {
if (list.likedNum !== list.partyLimit) return list;
list.isComplete = 1;
return list;
});
state.myPartyList = [...action.payload];
});
builder.addCase(getMyPartyList.rejected, (state, action) => {
state.myPartyList = [];
});
builder.addCase(getActivePartyList.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
state.activePartyList = [...action.payload];
});
builder.addCase(getActivePartyList.rejected, (state, action) => {
state.activePartyList = [];
});
},
});
export default partySlice;React Query의 도입
-
카카오페이 Tech에서 React Query를 도입한 글을 보게 되었다. 프로젝트에서도 Redux를 이용해 서버상태를 관리하는데에 여러 단점이 존재하였기 때문에 리팩토링 과정에서 React Query를 도입하기로 결정하였다.
-
현재 Redux를 통해 비동기데이터를 관리하는데 프로젝트에서 발생하는 단점들은 다음과 같다.
- Boilerplate 코드가 너무 많다.
- 클라이언트 전역상태를 관리하는 부분과 서버상태를 관리하는 부분이 하나의 store에 존재한다.
- 불필요한 API호출이 발생한다.
-
Redux는 상태를 읽기전용으로 취급하고, 하나의 store에서만 action과 Reducer를 통해 데이터가 변경되기 때문에 복잡한 상태를 체계적으로 관리 할 수 있다.
-
하지만 기본적으로 작성해야 하는 Boilerplate 코드가 너무 많다. 그래서 코드를 보면 한눈에 로직이 들어오지 않는 단점이 있다.
-
API를 호출하는 과정에서도 Loading, Error, update 같은 상태들을 state로 관리하였는데 데이터가 변경된 후 state를 변경함으로써, useEffect를 통해 api를 재 호출하는 과정으로 새로운 데이터를 받아왔다.
-
또한 비동기 데이터까지 처리하는 경우 하나의 store에서 서버상태와 클라이언트 상태를 모두 관리해야 한다는 단점이 발생한다. 성격이 다른 데이터를 한곳에서 변경하는 것은 코드적인 관점에서 좋지 않다.
-
Redux 자체는 클라이언트의 전역상태를 관리하기 위한 라이브러리이지, 서버의 상태를 관리하기 위한 라이브러리가 아니므로, Loading, Error와 같은 서버상태를 개발자가 알아서 지정해줘야 한다. 이는 협업시에도 개발자의 생산성을 떨어트린다.
React Query 도입이후 장점
- Boilerplate 코드 삭제
- Redux를 사용함으로써 작성해야 했던 Boilerplate 코드들을 삭제 할 수 있었다.
- API 호출 상태의 체계적인 관리
- React Query가 없을때에는 Loading, Error, update 같은 상태들을 state로 관리하였다.
// foodDetail.tsx
const [isLoading, setLoading] = useState<boolean>(true);
const [update, setUpdated] = useState<boolean>(false);
const [shopState, setShopState] = useState<ShopState>(initialShopState);
const [commentState, setCommentState] = useState<CommentState[]>([]);
const [menuState, setMenuState] = useState<MenuState[]>([]);
const fetchCommentState = async (shopId: number) => {
const commentState = await getComment(shopId);
setCommentState(commentState);
};
const fetchShopState = async (shopId: number) => {
const [shopState, menuState] = await Promise.all([getShop(shopId), getMenu(shopId)]);
setShopState(shopState);
setMenuState(menuState);
};
const fetchInitialData = async () => {
await fetchCommentState(shopId);
await fetchShopState(shopId);
setLoading(false); // 데이터 fetching후 loading상태 변경
};
const updateCommentState = useCallback(() => {
setUpdated((current) => !current);
}, []); // prop으로 전달 > 하위 컴포넌트에서 실행
useEffect(() => {
fetchInitialData();
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
fetchCommentState(shopId);
}, [update]); // update상태가 변경되었다면 다시 data Refetching함.
// CommentList.tsx
const handleDelete = async (e: React.MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>, commentId: number) => {
await deleteComment(commentId);
updateCommentState();
}; // 댓글 삭제후 refetch- React Query의 useQuery는 query의 상태를 loading, error, success, idle로 정의한다.
- idle상태는 쿼리가 data가 비어있는 상태 즉 {enabled : false} 상태로 쿼리가 호출되었을때 이 상태로 시작한다.
- query의 상태가 data가 fetching 되는 과정에서 알아서 변경되기 때문에 개발자가 따로 처리 해 줄 필요가 없다.
- refetching이 필요할때는 invalidateQueries() 함수를 통해 쿼리를 무효화 시켜서 데이터를 업데이트 하는 과정으로 api를 호출 할 수 있다. 자세한 코드는 다음 Post에서 작성하겠다.
- 캐싱기능을 통한 불필요한 API 호출 최소화
- 캐싱기능을 활용해 불필요한 API 호출을 줄 일 수 있었다. 캐싱에 관한 내용은 다음 POST에서 작성하겠다.
- 서버 데이터의 분리
- React Query는 서버데이터를 관리하기 위한 tool로 ReactQueryDevtools를 제공한다. 이를 통해 현재 데이터가 stale한지 fresh한지, refetching 되고있는지 등 서버데이터 상태를 관리 할 수 있었다.
ref)
