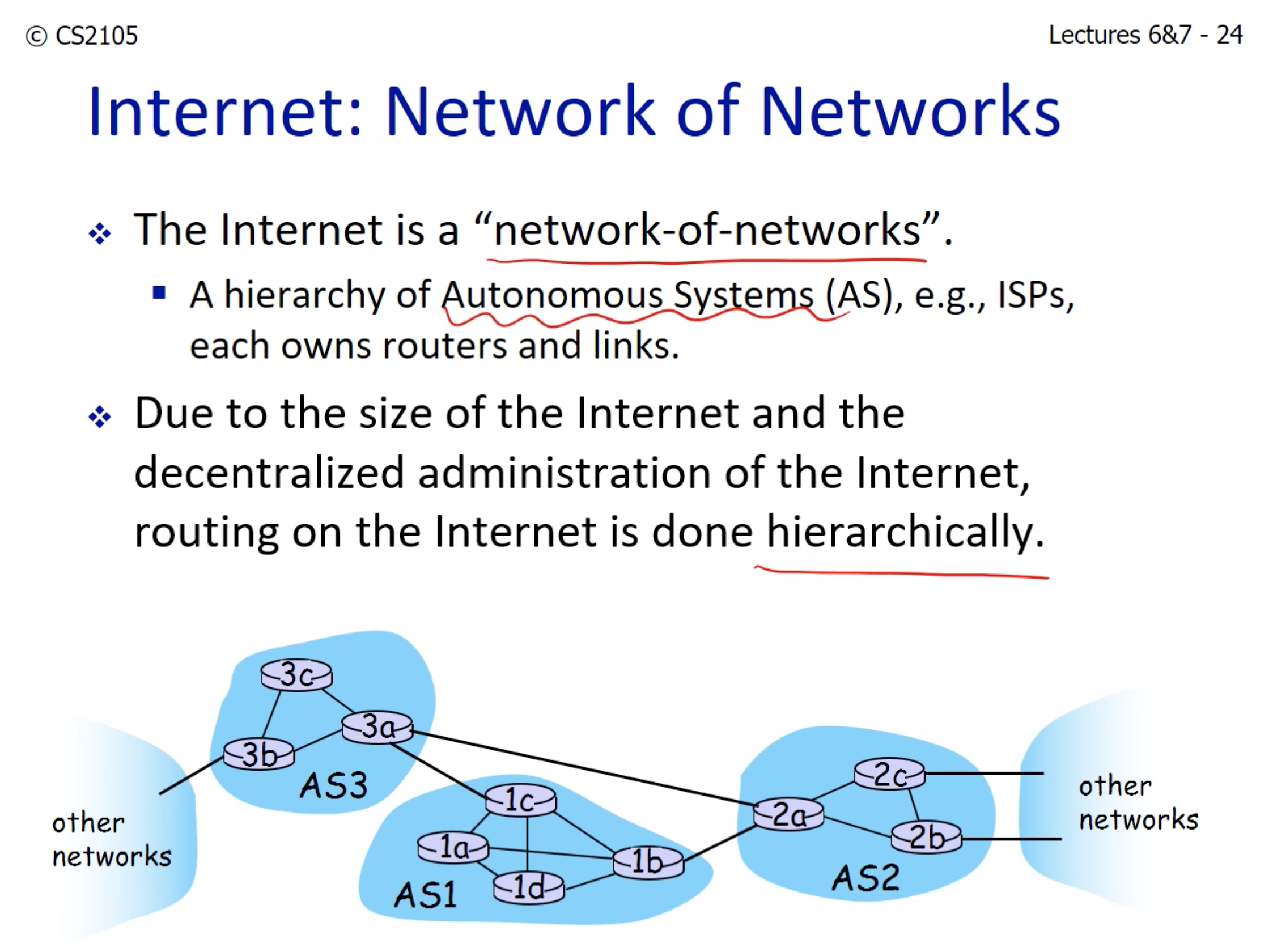
- Because not one organization owns all the networks, the routing is done in a hierarchical way.
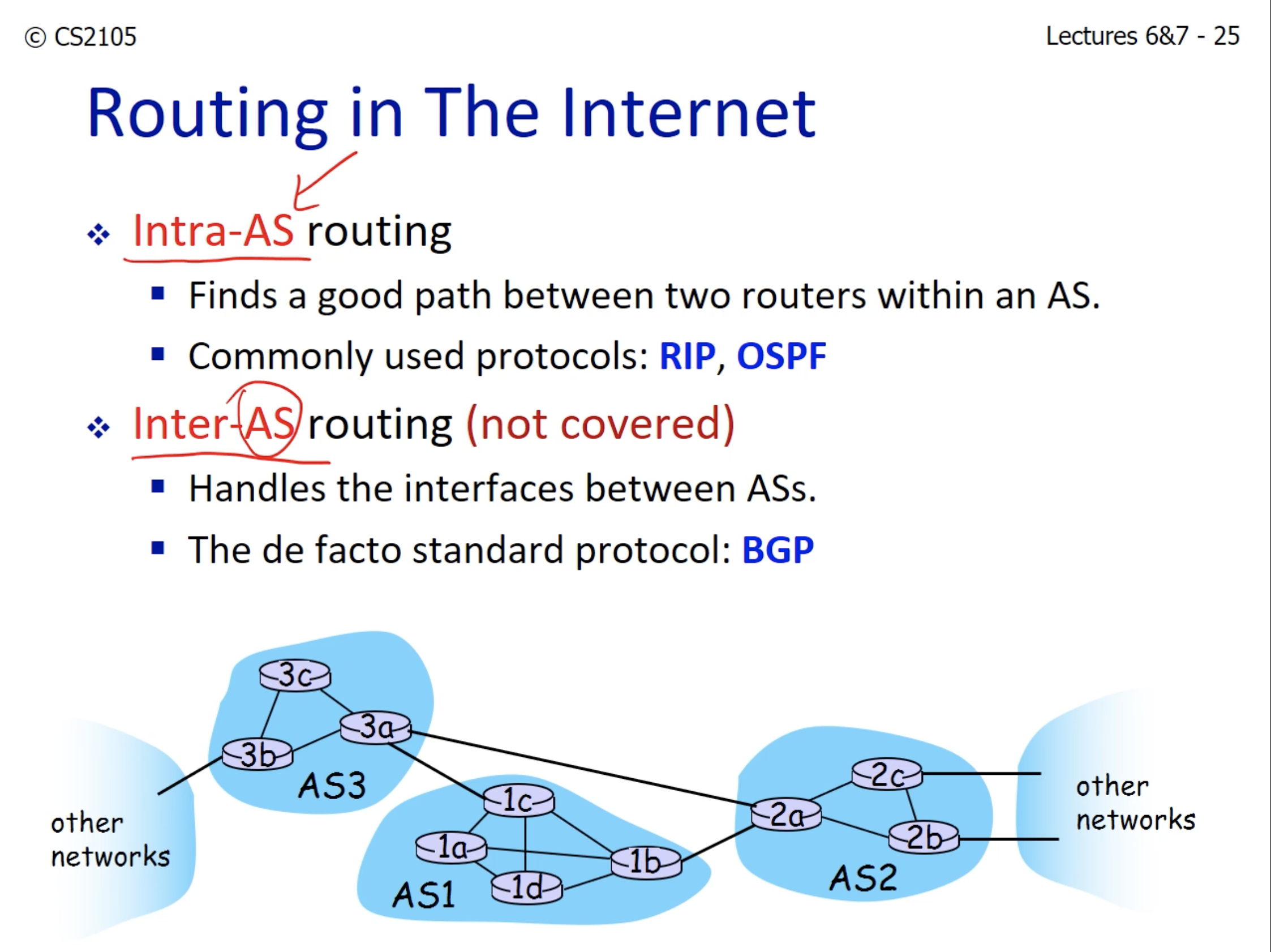
- Intra-AS: When routing is done within the same network. ex) Using desktop connected with campus network to use LumiNUS.
- Inter-AS: When packet goes through multiple networks before it reaches the destination.
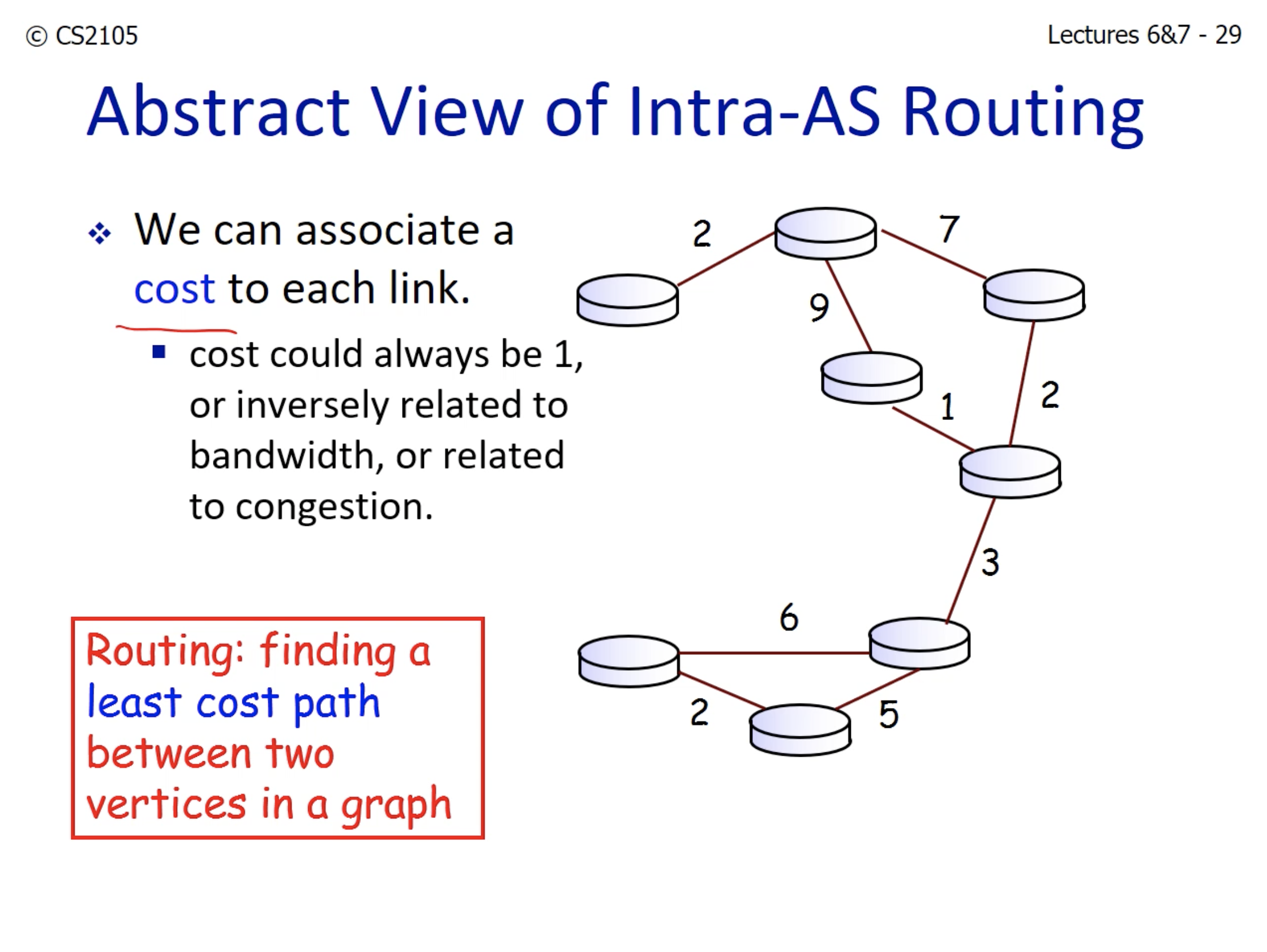
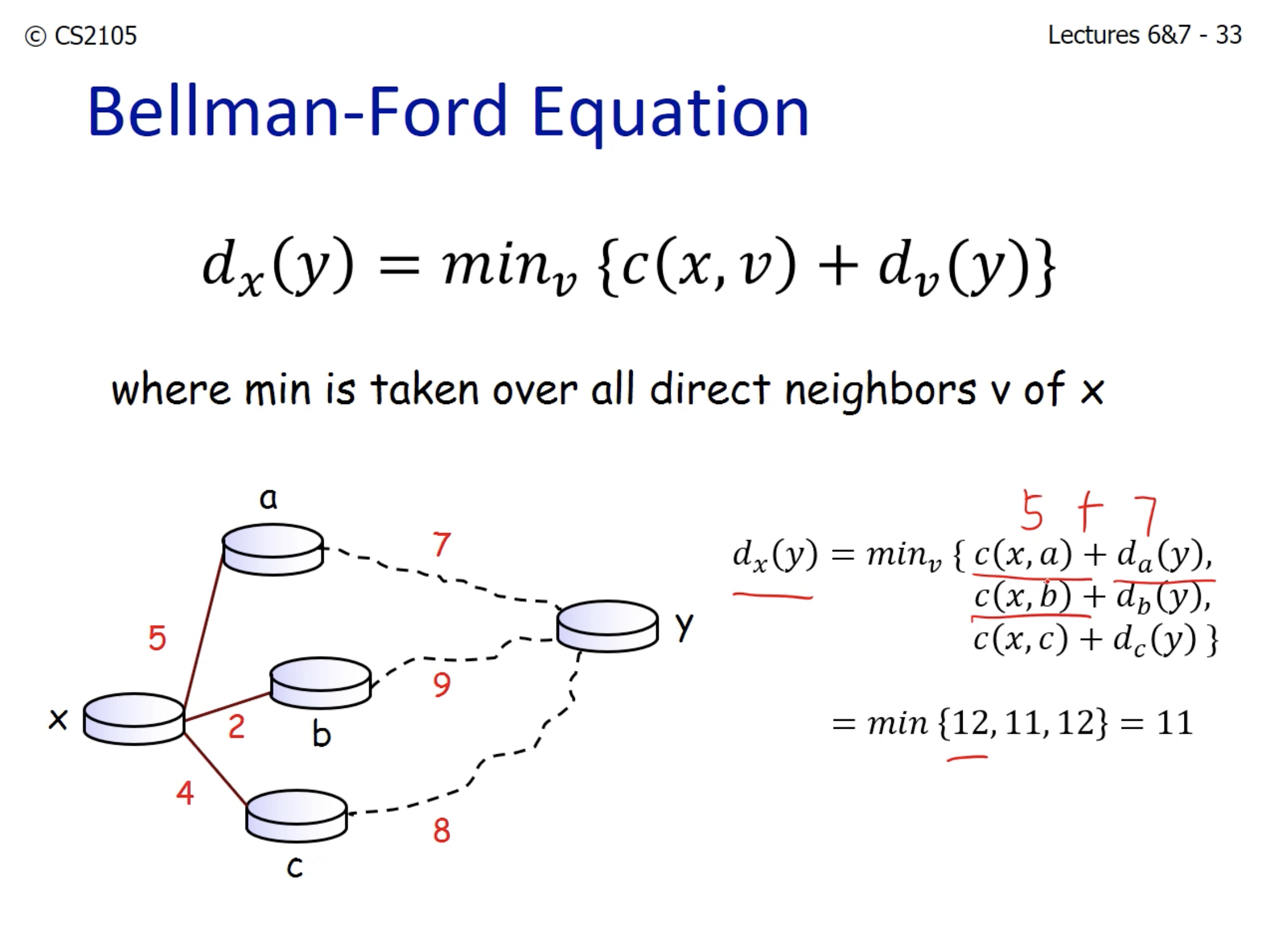
- In CS2105, every link has a cost. The problem is to find the path with the least amount of cost (Bellman-Ford algorithm)
Routing Algorithms
- "link state" algorithm
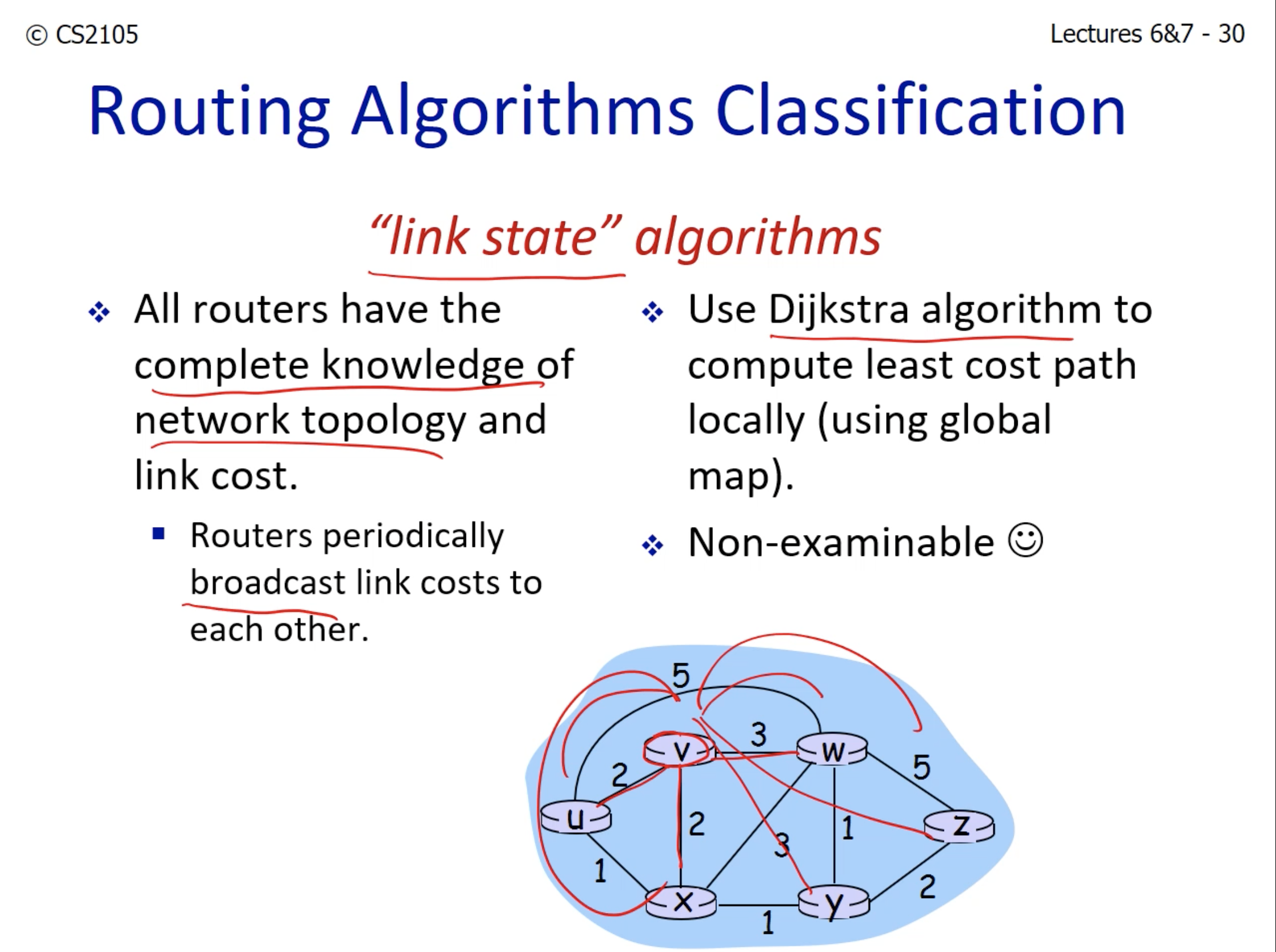
- Every router broadcasts the costs of the links that it is connected to.
- Every router has clear view of the network topology and link cost.
- Then we use Dijkstra's algorithm to compute the least cost path.
- "Distance vector" algorithm
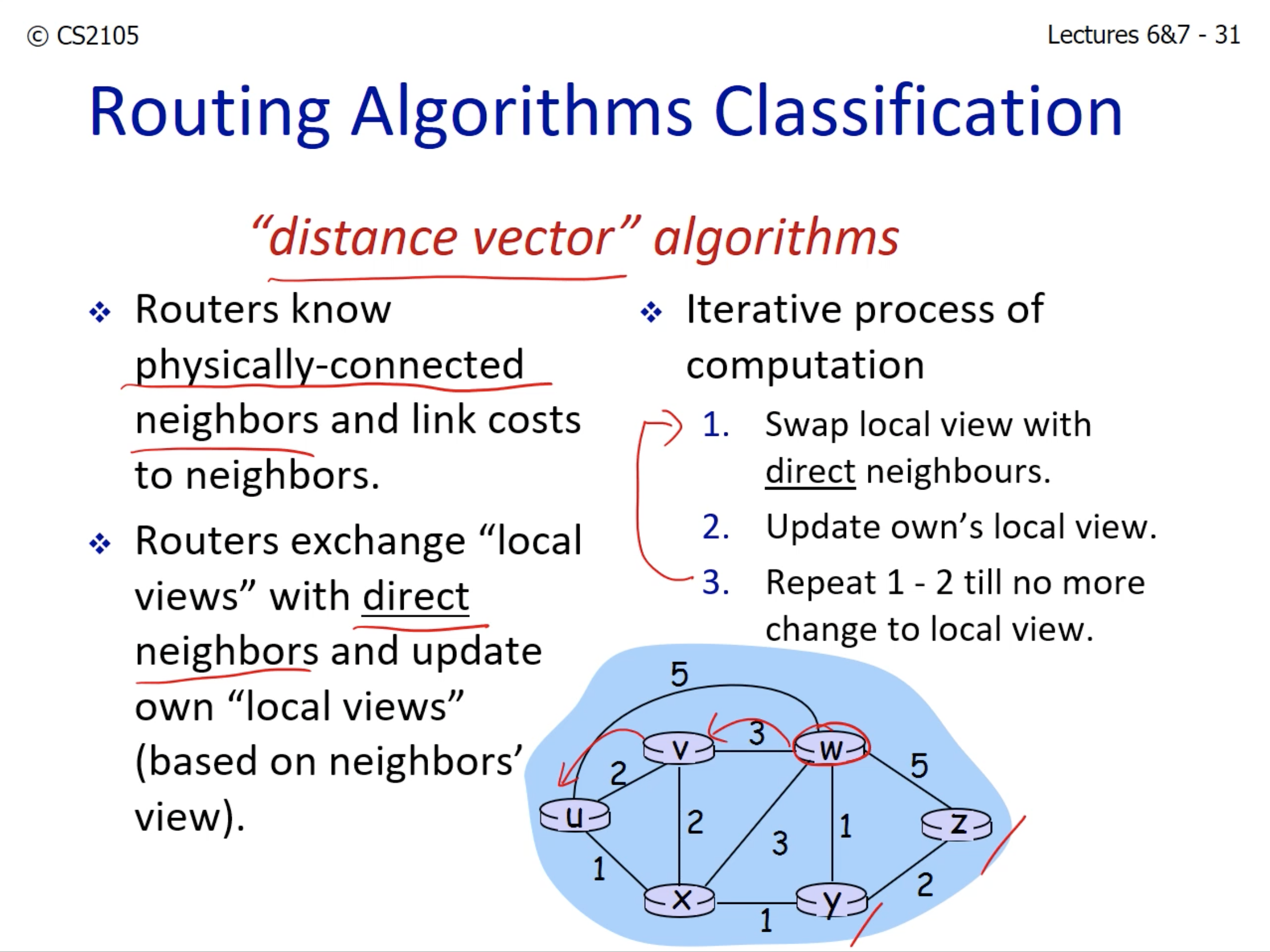
- Routers exchange the "local views" (link costs) with its direct neighbors.
- The global view of the costs get iteratively better.
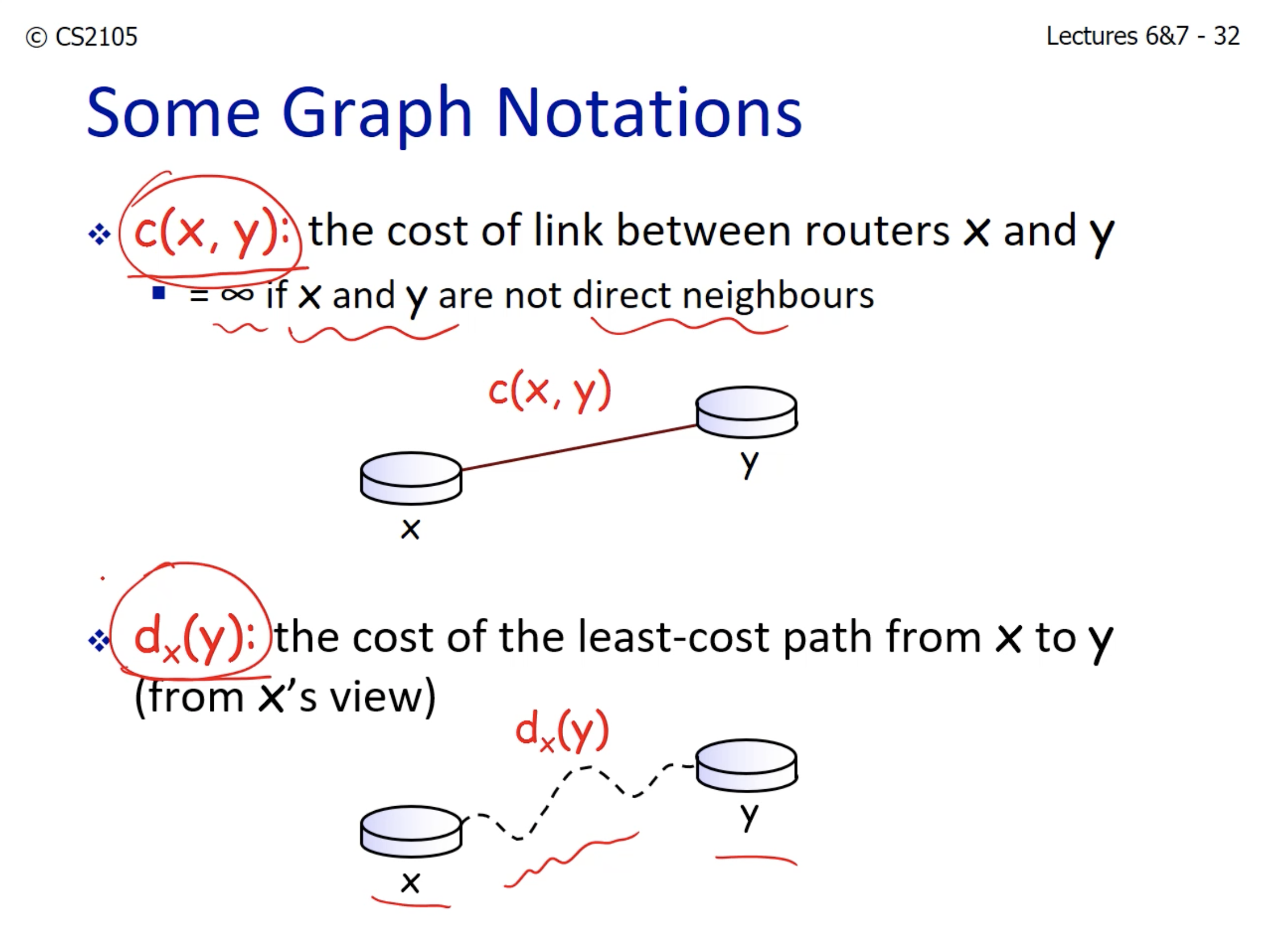
- C (x, y) is fact.
- D_x(y) is computed.
Bellman-Ford Equation:
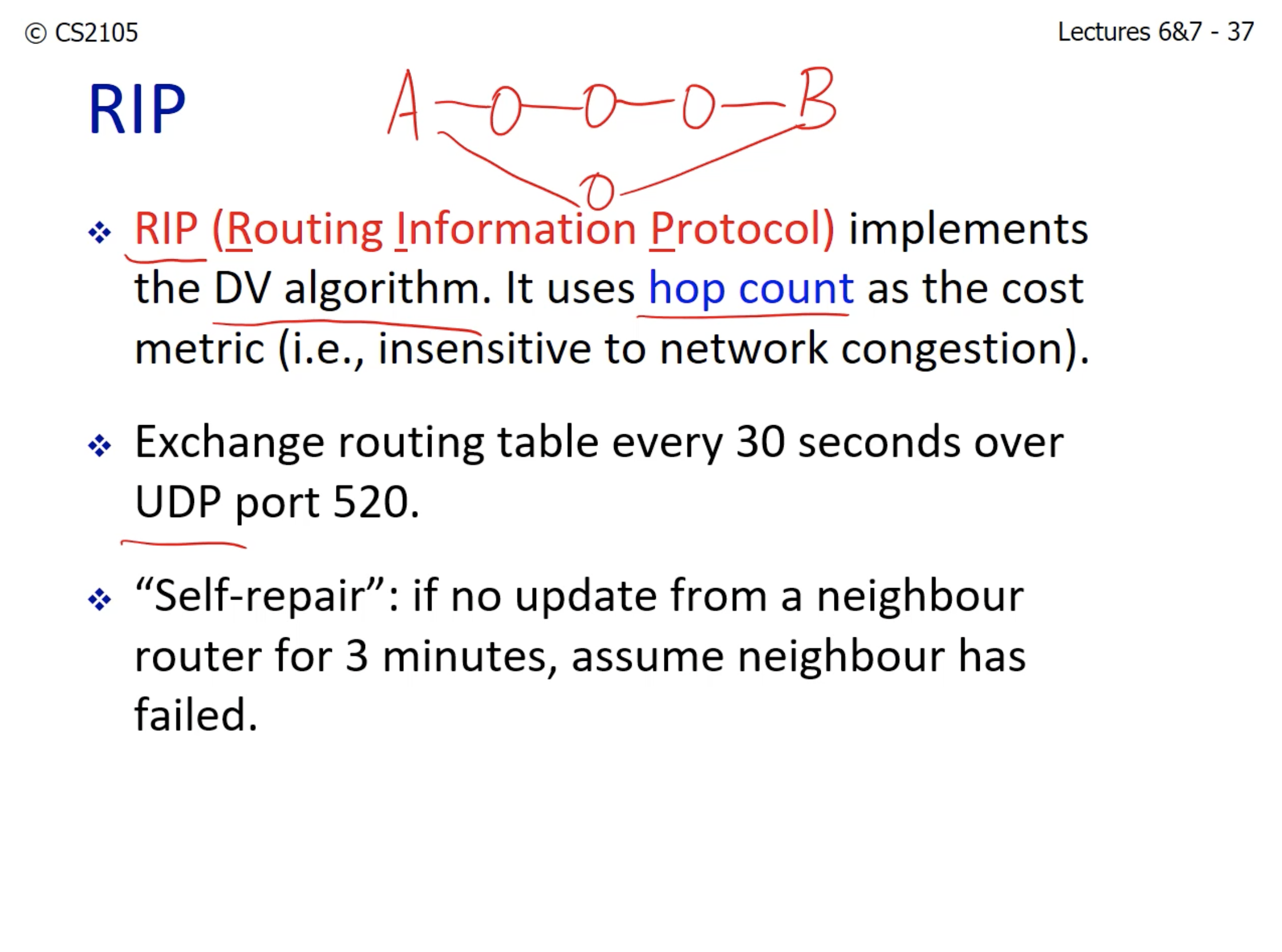
- RIP is insensitive to network congestion:
- In the diagram drawn above, there is one 4-hop path and 2-hop path.
- Even if 2-hop path is more congested than the 4-hop path, the router will still choose 2-hop path.
- UDP is used because TCP will have to make 3-way handshake everytime an information is being sent, which takes up too much time.
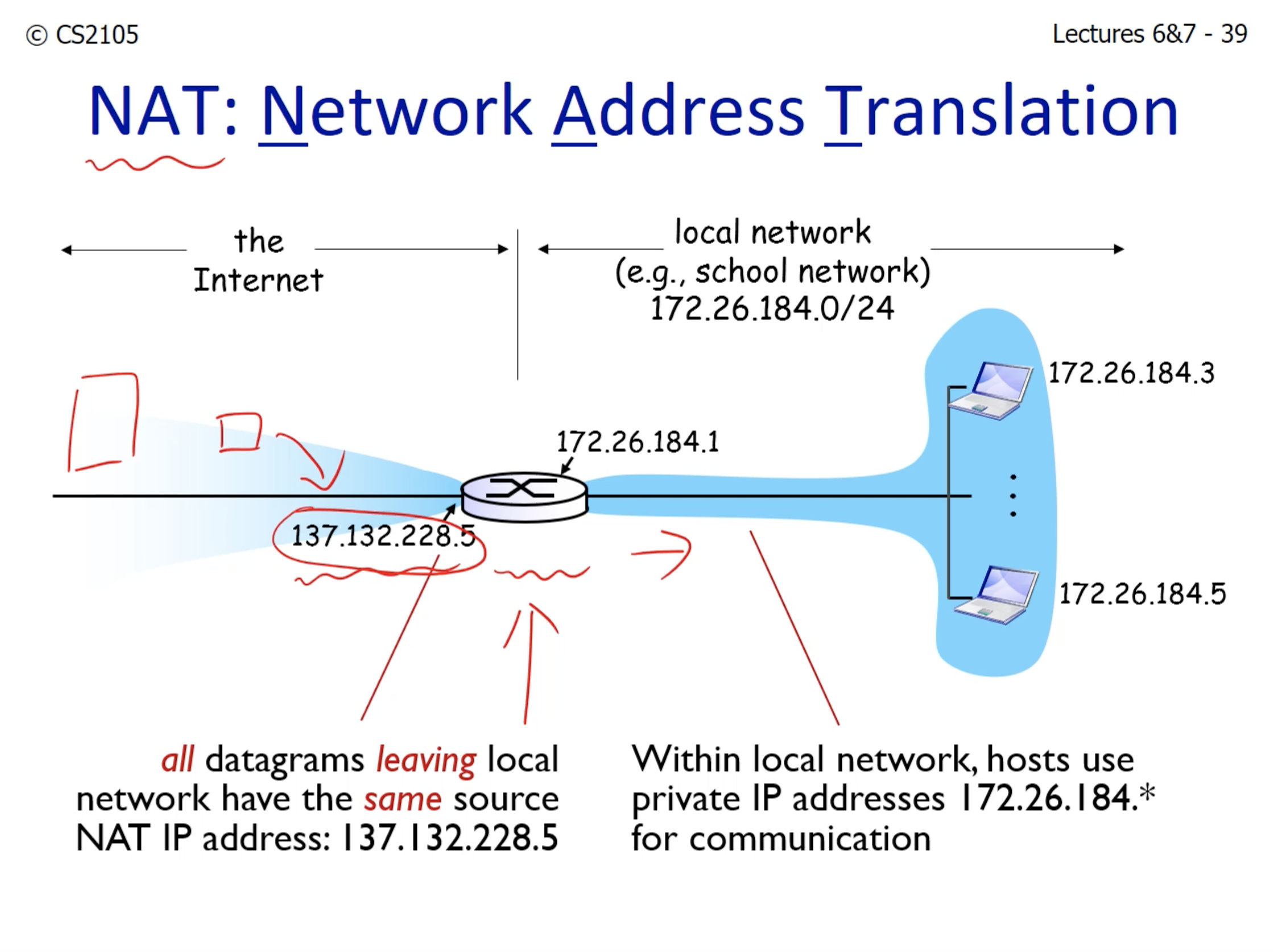
- NAT sits at the boundary between public and private IP.
- It helps translates the private IP address to a public one.
- This is necessary because for example, NTU and NUS computers can have the same private IP address. If it tries to send a packet to facebook, the facebook does not know where to send the reply packet to.
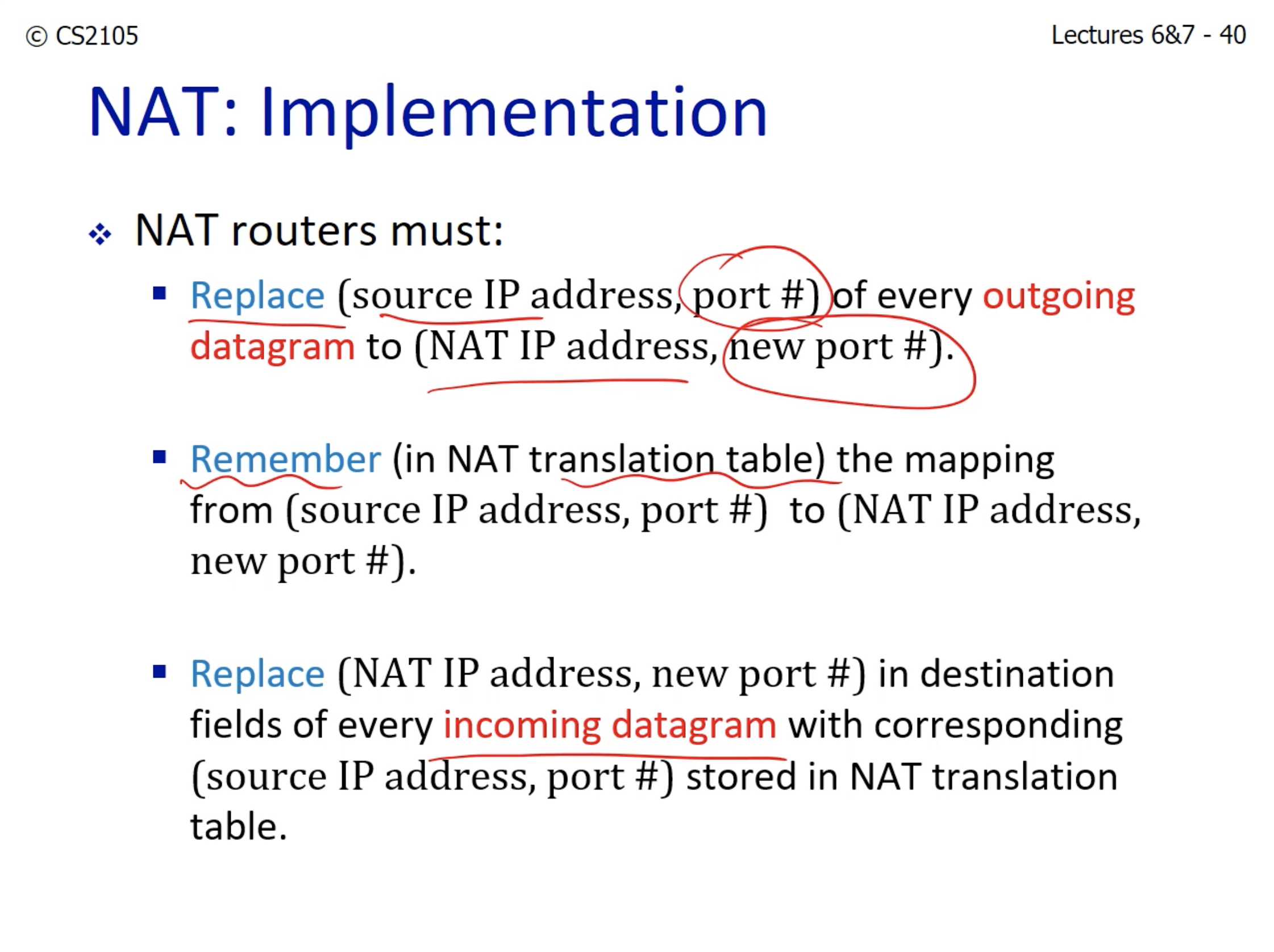
- The NAT router must remember the port number of the source as well.
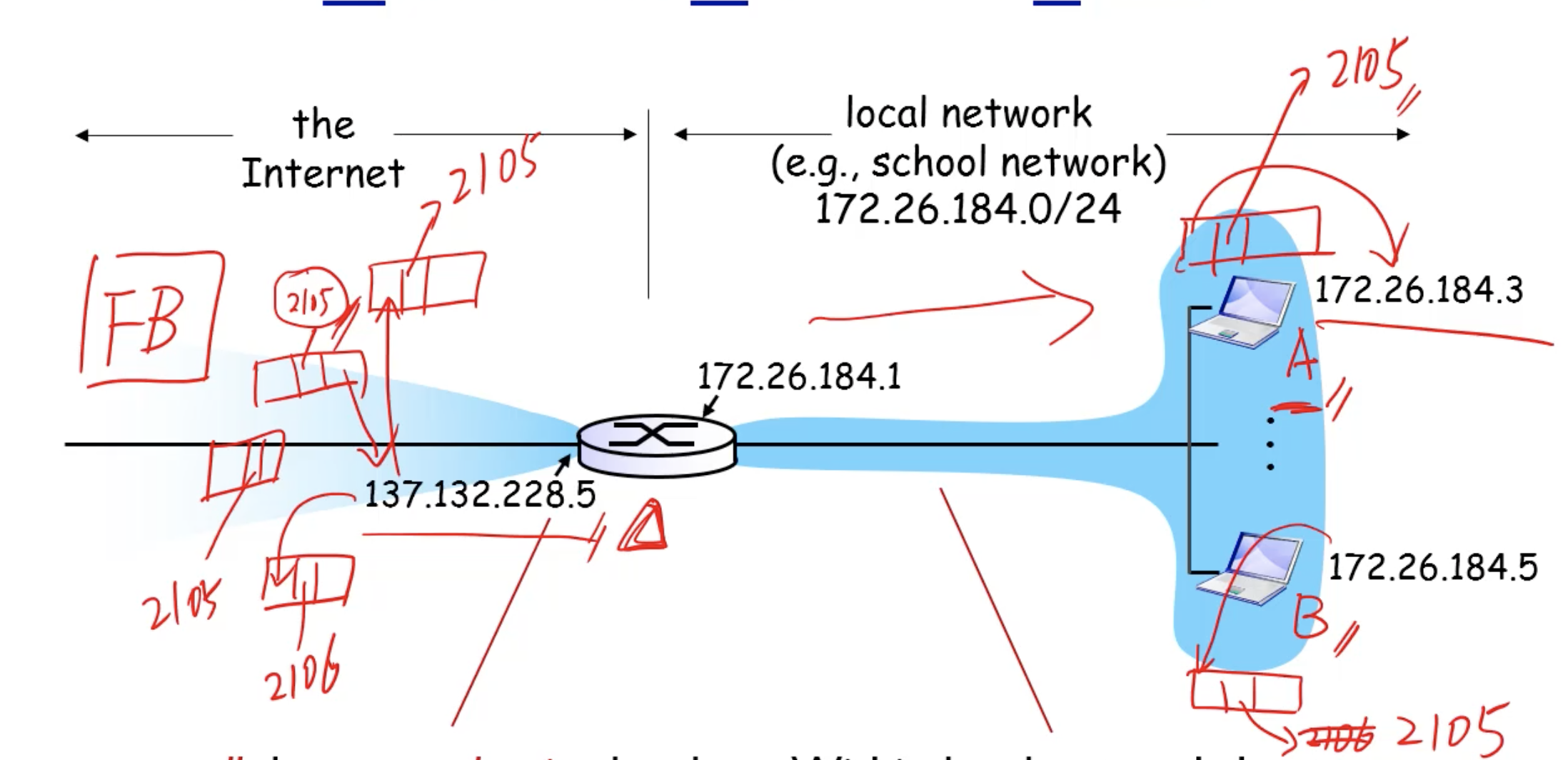
- The diagram shows why port numbers must be remembered.
- The two computers A and B may have the same public IP address after going through NAT router.
- The only difference the router can tell when it receives reply packets is the port number.
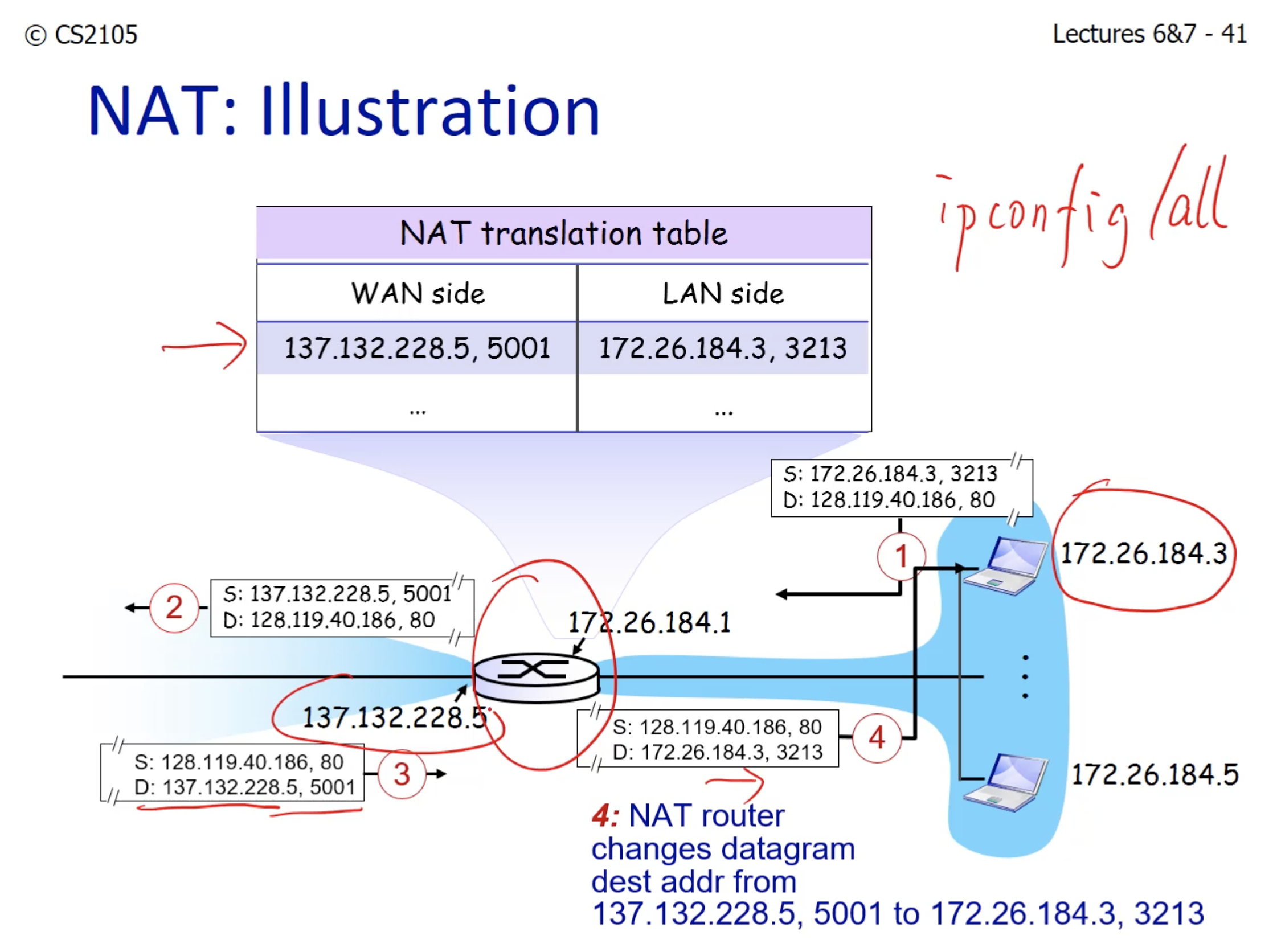
- LAN: Local Area Network
- WAN: Wide Area Network.
- ipconfig /all to view all my private addresses.

Understanding how data flows in networks is crucial, and using effective routing programs can simplify this process. They help optimize paths, manage traffic efficiently, and ensure reliable performance across complex systems.