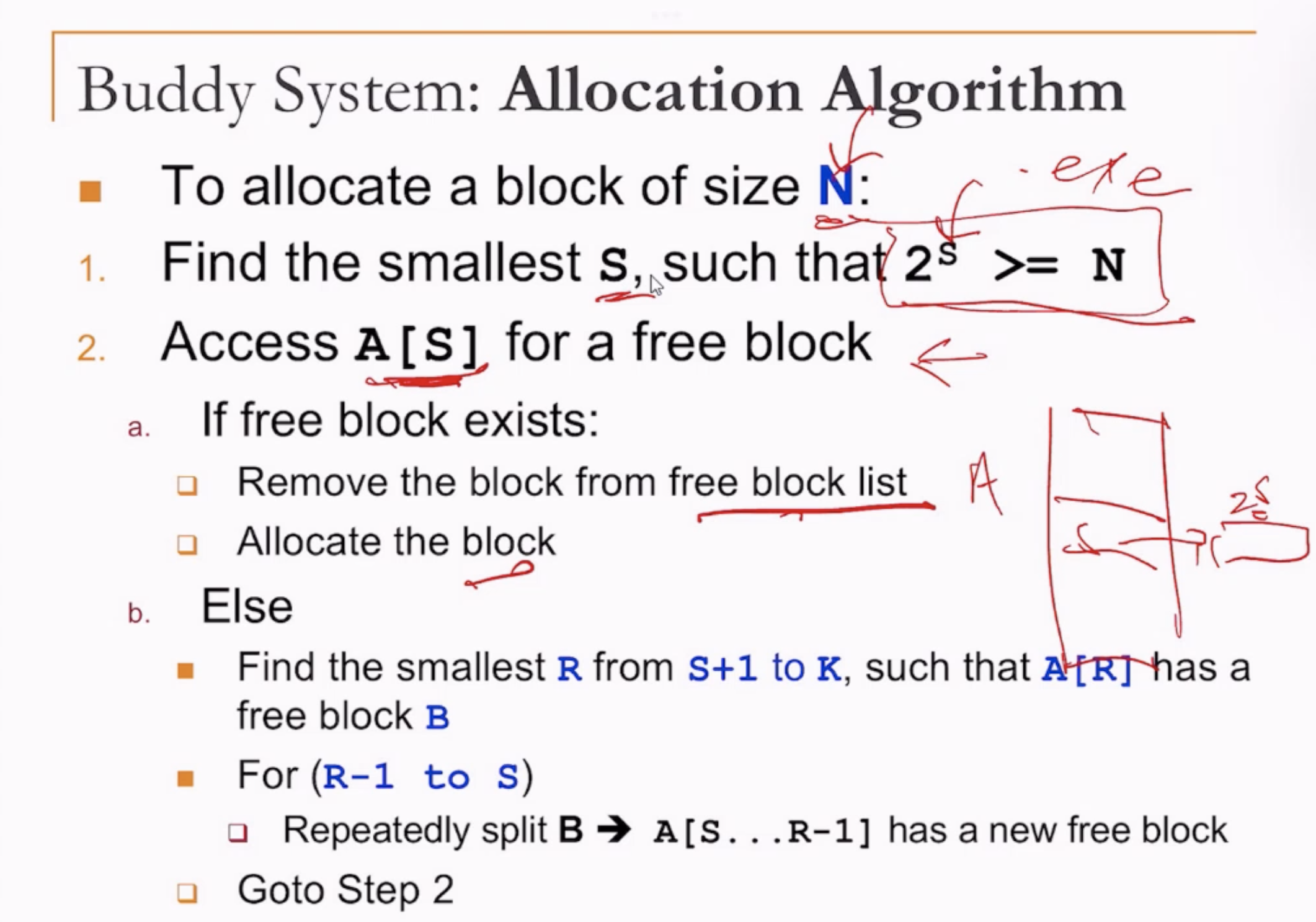
- size N comes from the software calculating approximately how much memory is needed for the program execution.
- A[s] keeps the available blocks of size 2 ^ (s).
- If the best fit block is unavailable, then find the smallest available block that fits the size N, then split.
- If it is the size of S + 2, then can split to two of size S + 1.
- Then the entry A[S+1] will have a block of size S + 1, since one of the blocks will be splitted again to size S to fit the N.
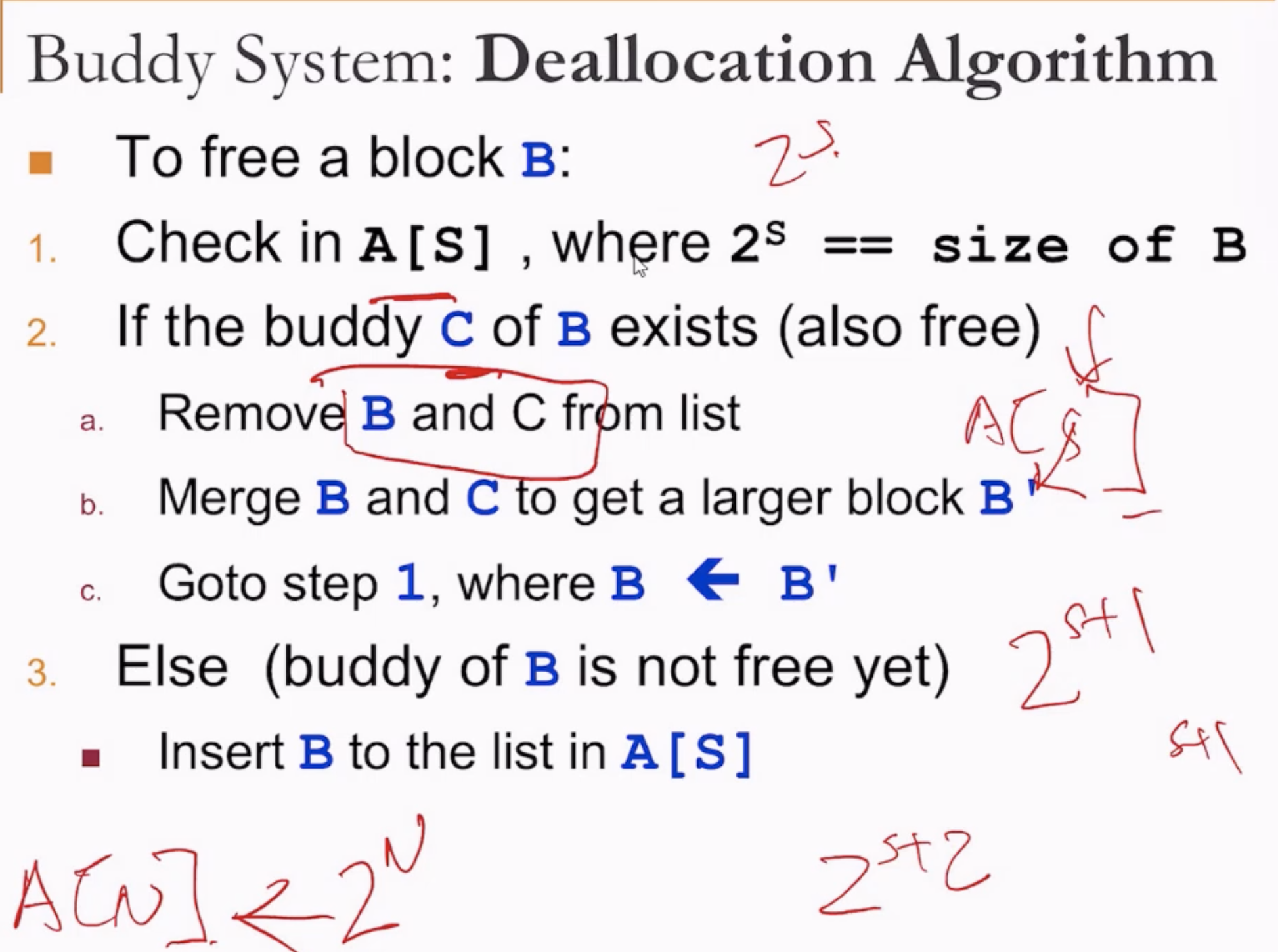
- Then when deallocating, see if A[S] has a free block.
- If A[S] is not empty, then merge and check if A[S+1] is not empty, repeating the process.
- If A[S] is empty, then just put into A[S].
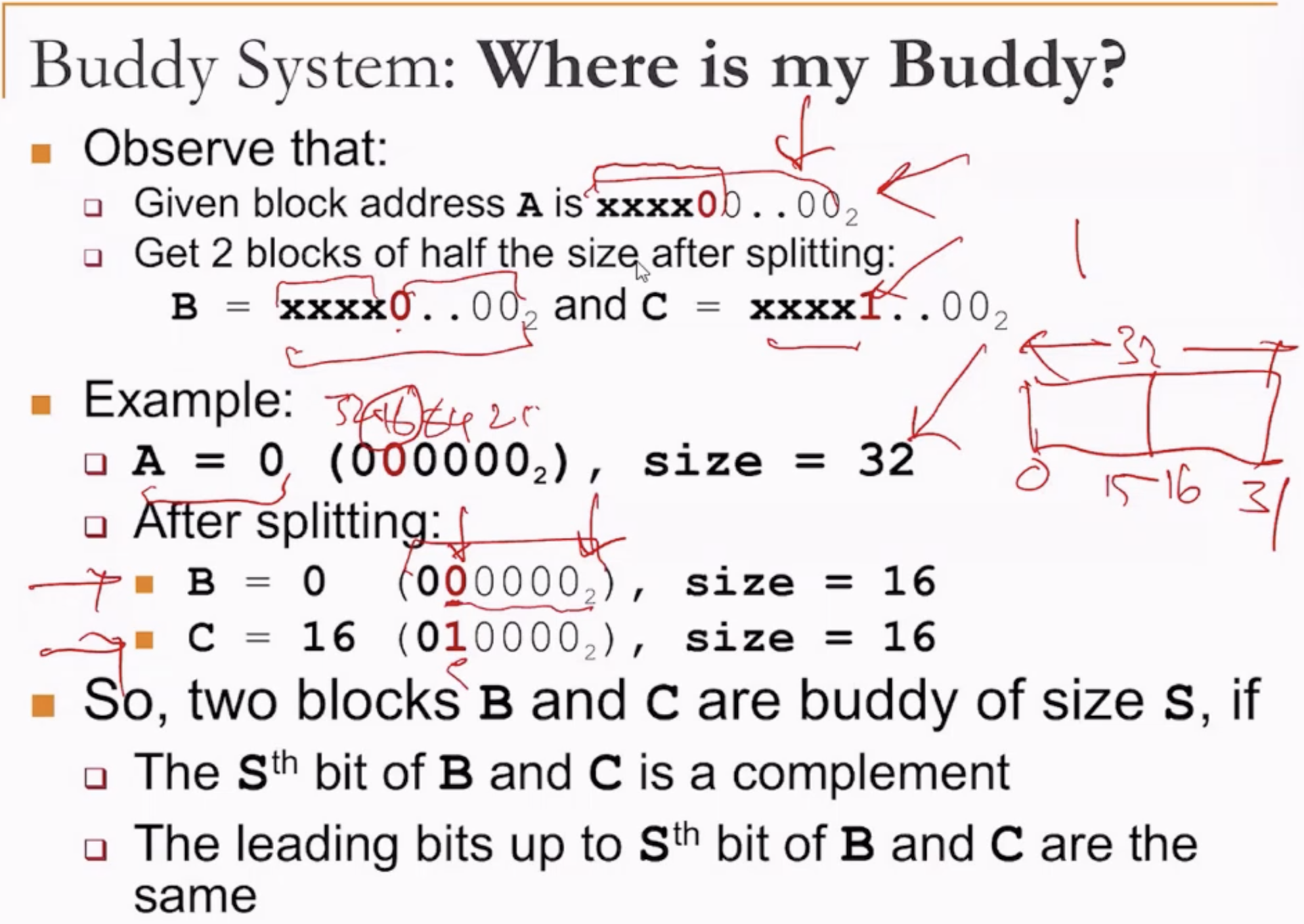
Disjoint Memory
- A process does not have to occupy a contiguous block of memory -> It can be disjointed.
Paging
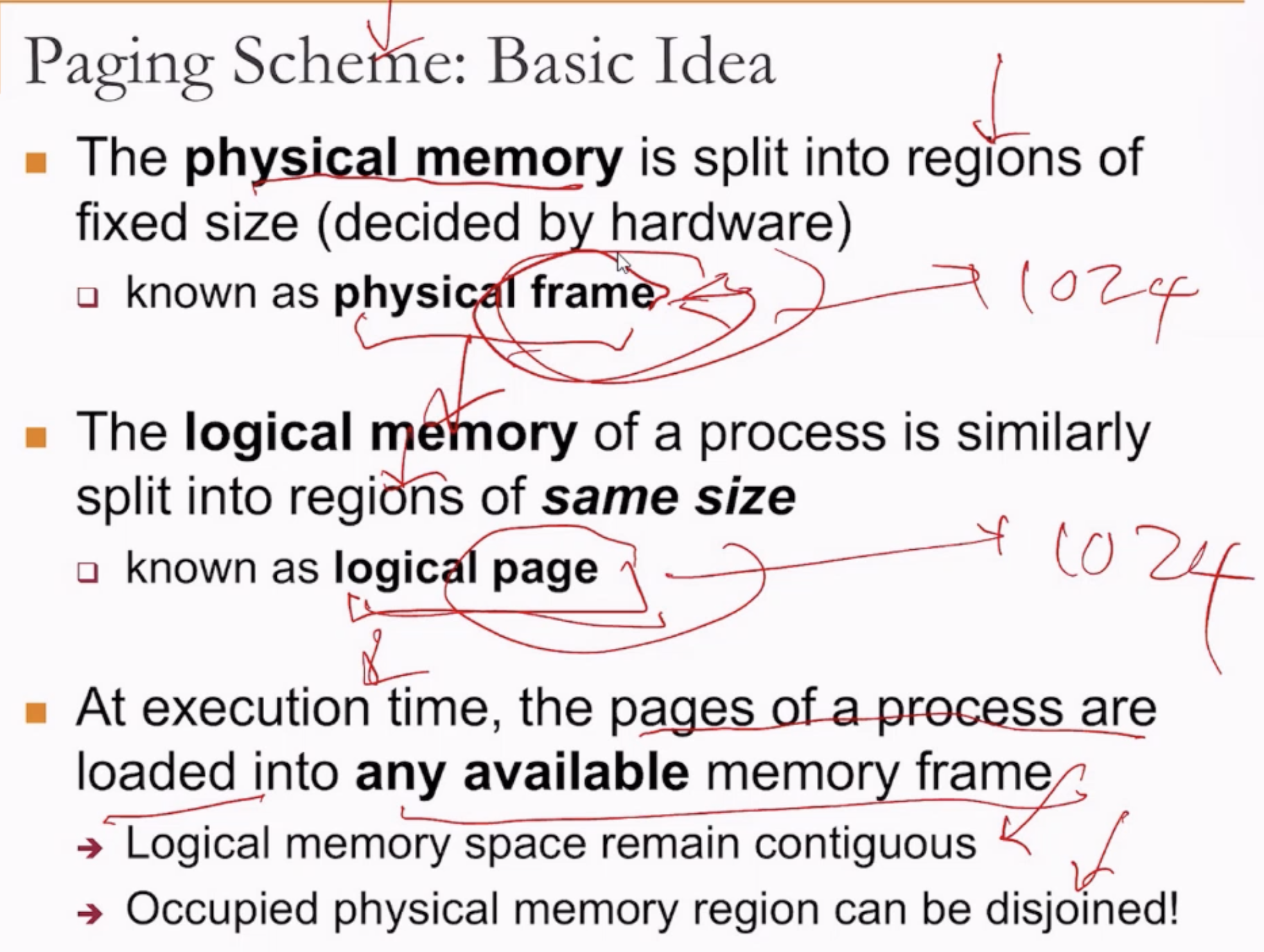
- It is most likely that the processes will not have one contiguous block of memory that can fit everything in.
- It is more likely that the memory is scattered.
- Frame refers to physical memory space.
- Physical memory vs logical memory?
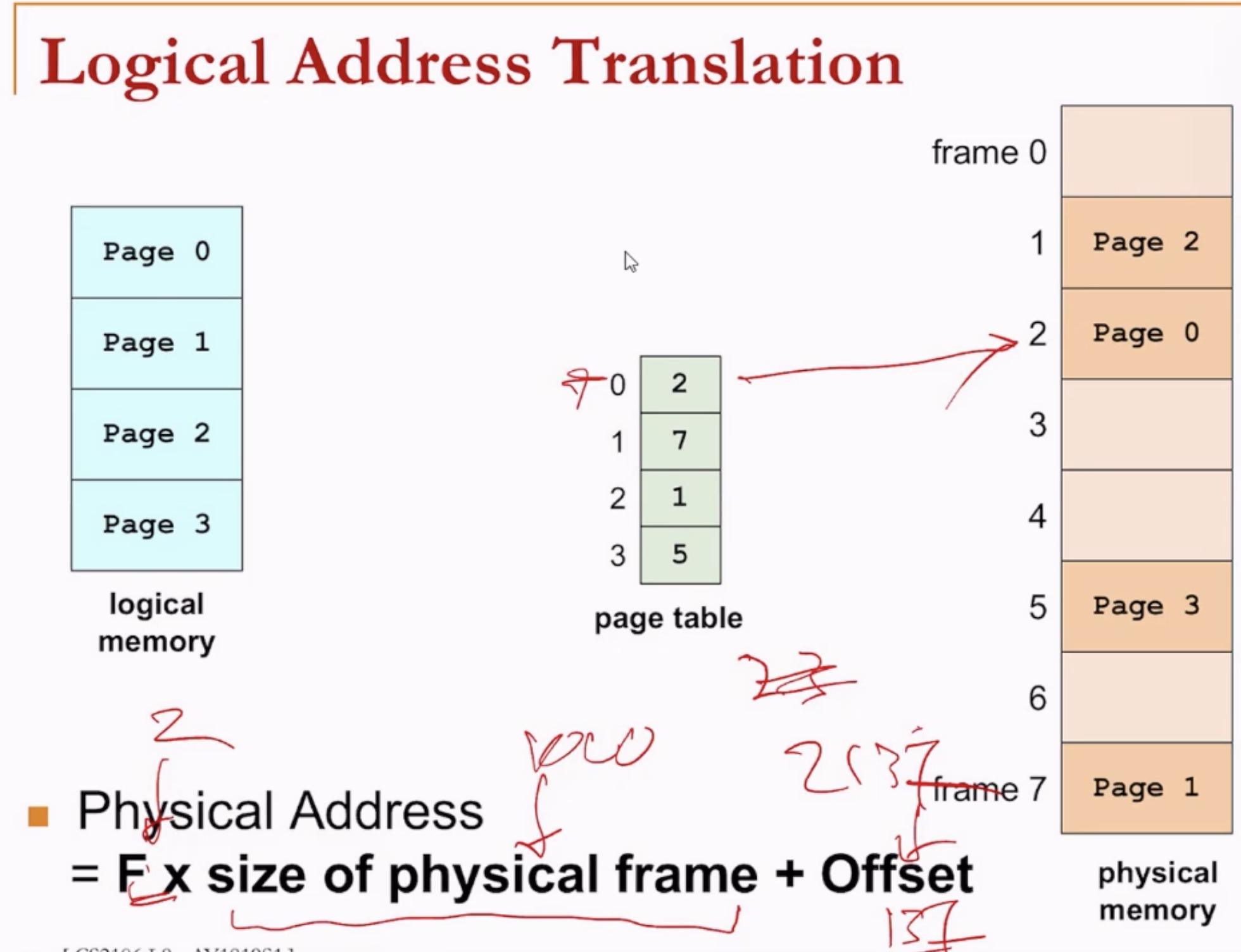
- Logical address 137 would belong to physical addres 2137.
- The page size is 1000.
- Then 137 belongs to page 0.
- On page table page 0 corresponds to frame 2.
- The physical address is then 2 * 1000 (because one frame corresponds to one page) + 137 (offset).
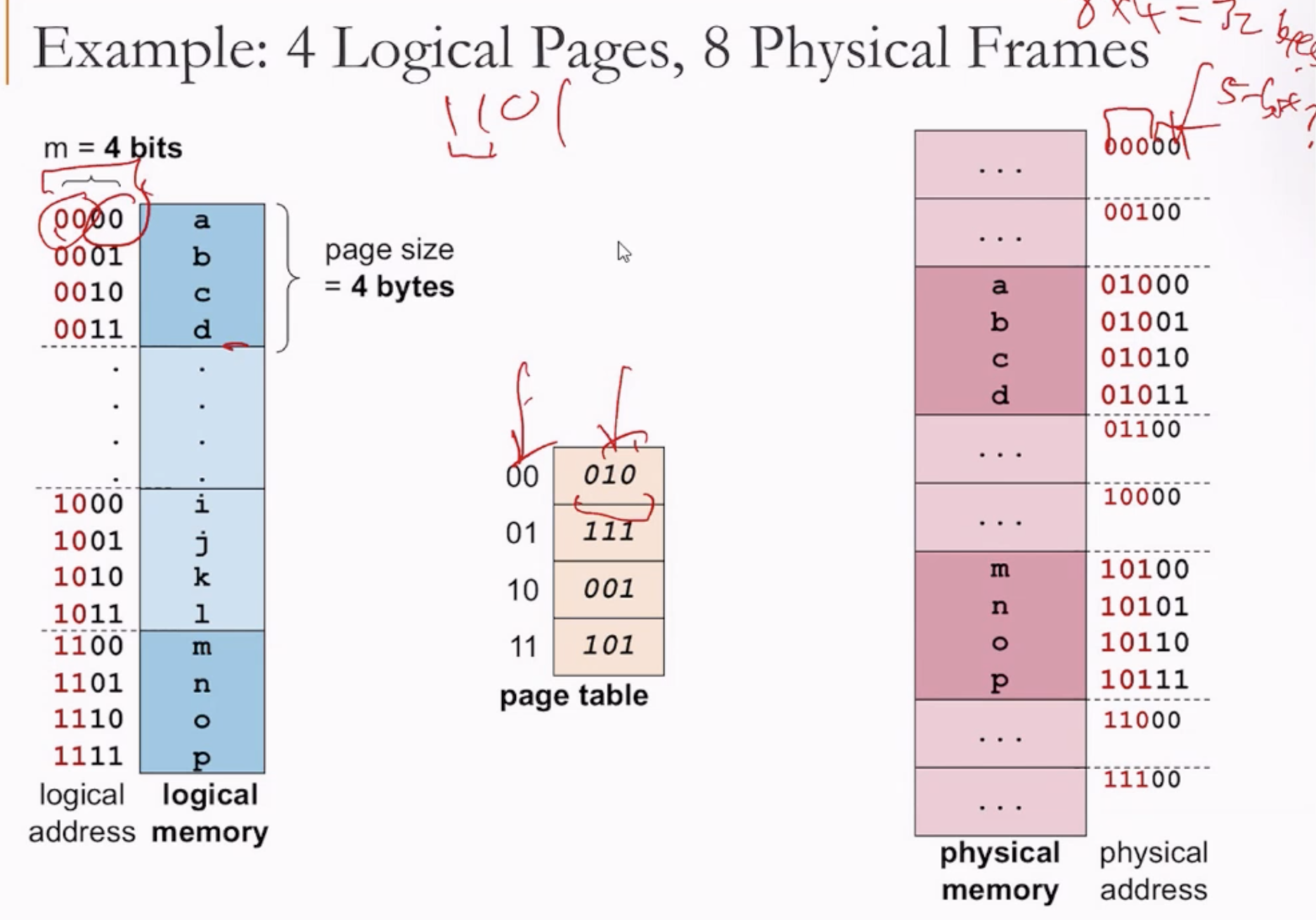
- Logical Memory <-> Physical Memory:
- The first 2 bits are the page number, the other bits are offset (in the case above).
- Each page number will take one block in the page table.
- Page number is translated to corresponding frame numbers.
- The offset bits are concatenated.
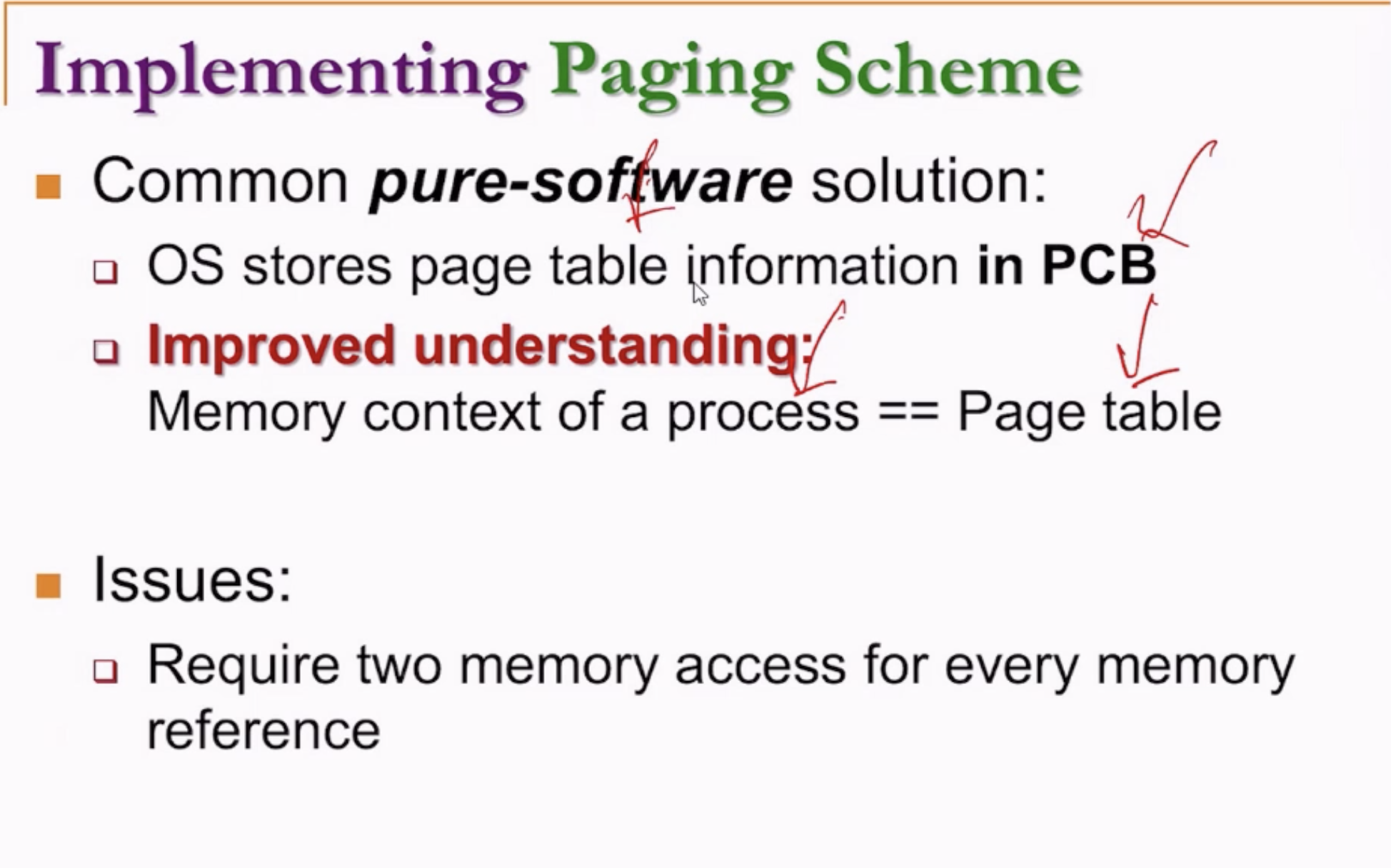
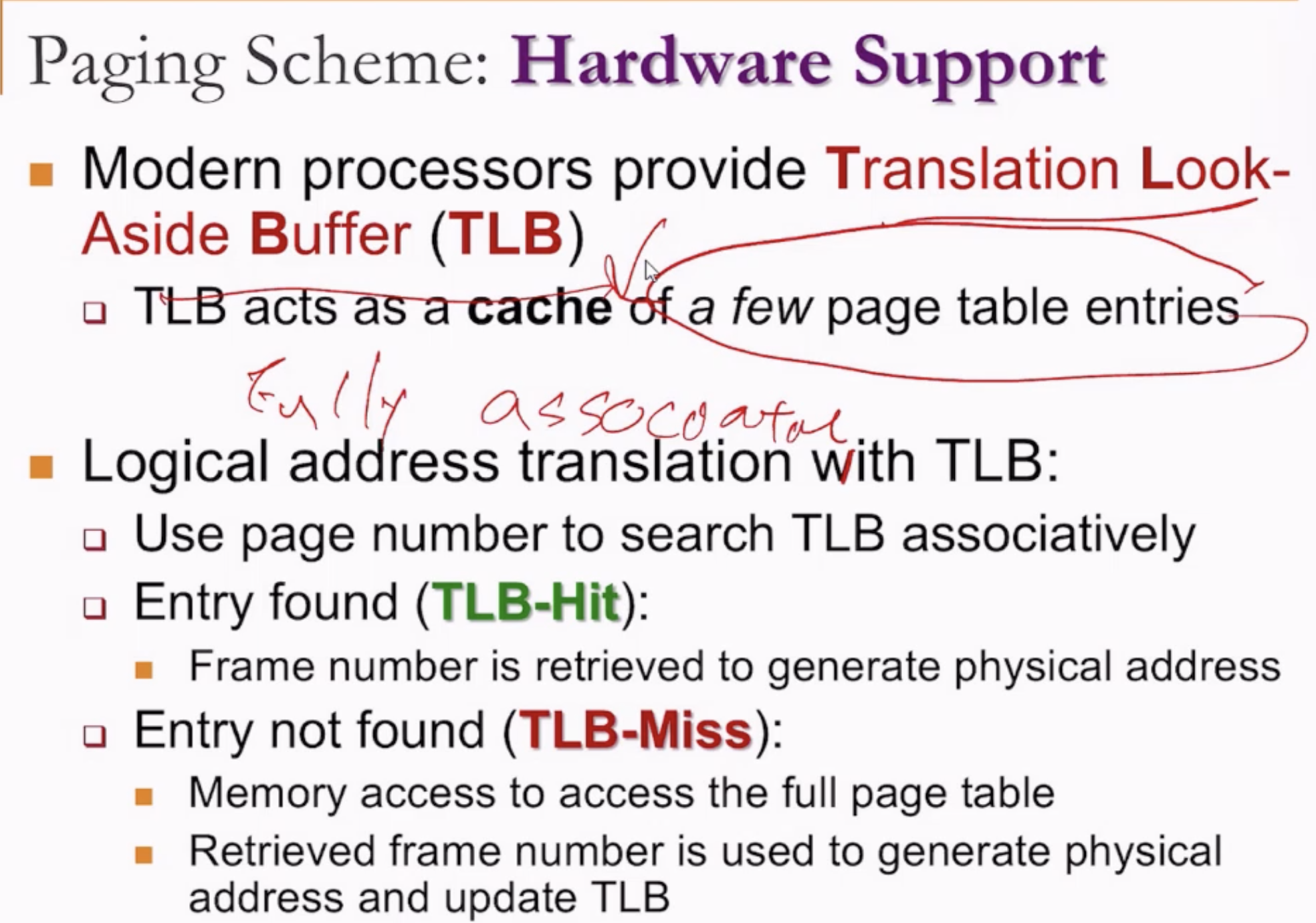
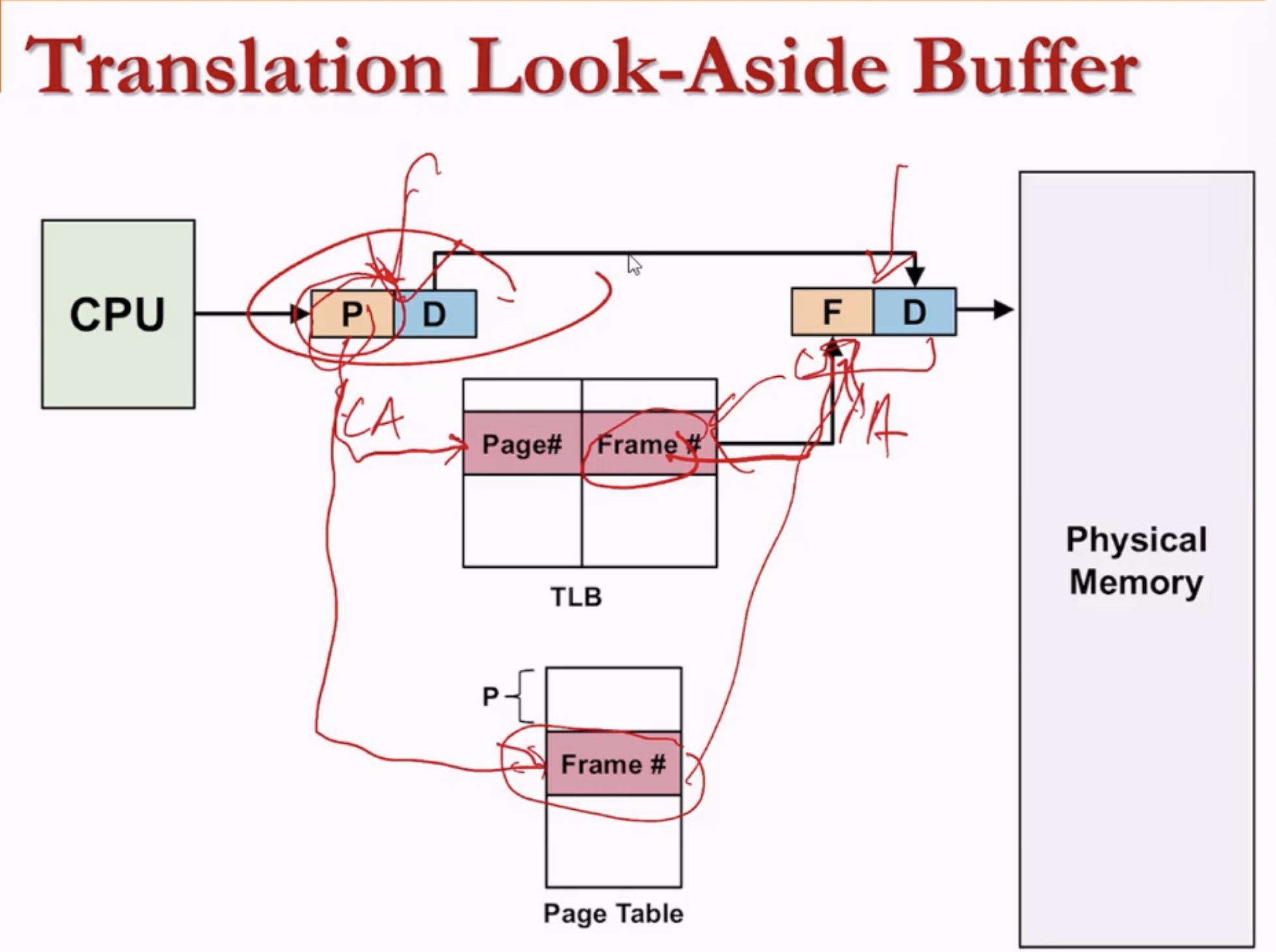
- The CPU would look for the frame # corresponding to the page # in a TLB first.
- If the entry exists, frame # is used.
- If not, the CPU would then look for it in the main page table in PCB, update the TLB, then use the frame #.
- Fully associative caches? TLB?
Page Sharing and Copy-On-Write

- Two or more processes can share the same physical memory spaces by assigning them the same page tables.
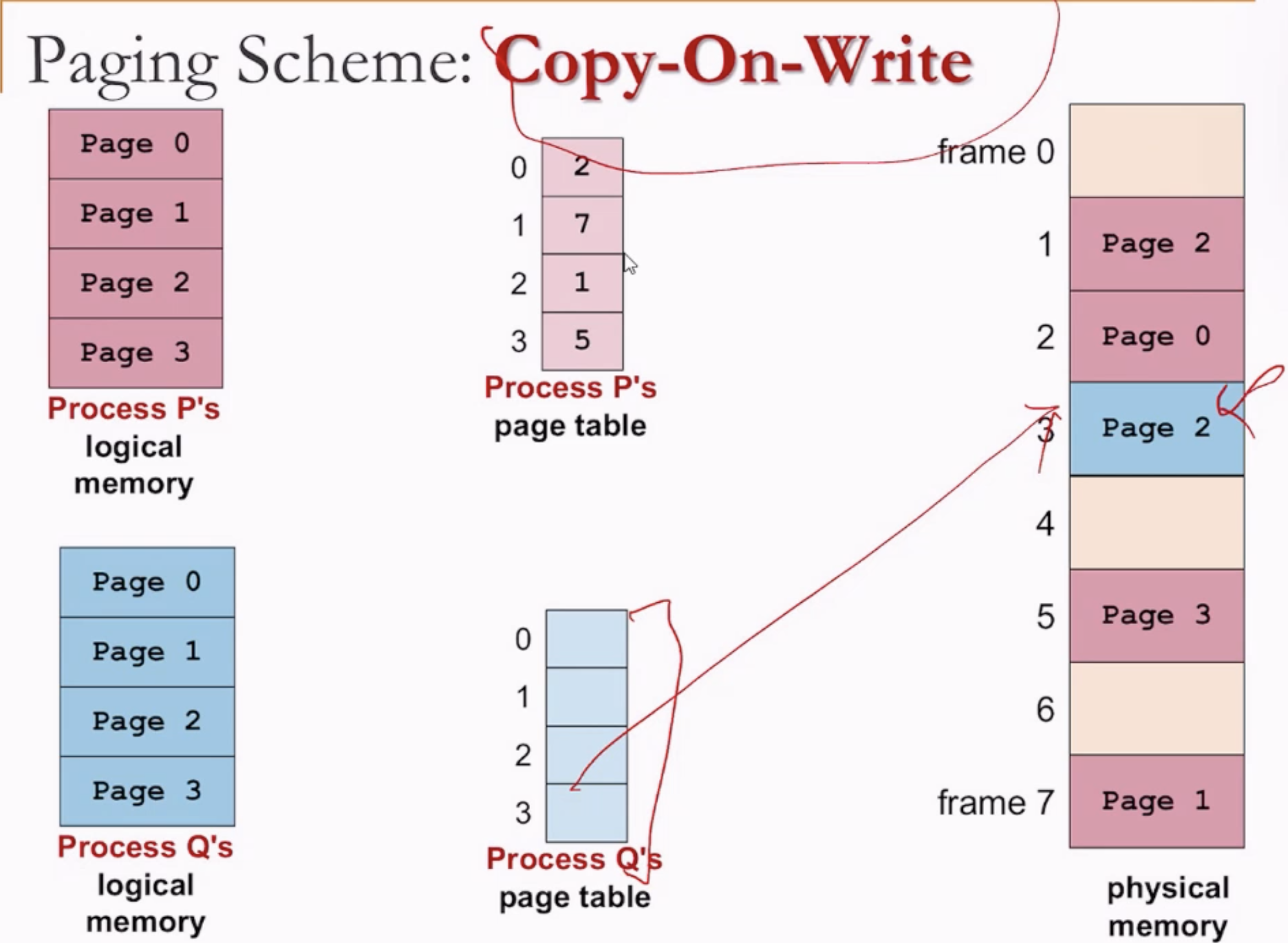
- Fork().
- When forked, they originally share the same values, but when one process makes a change, the value is copied to an empty frame.
