Virtual Memory
Motivation:

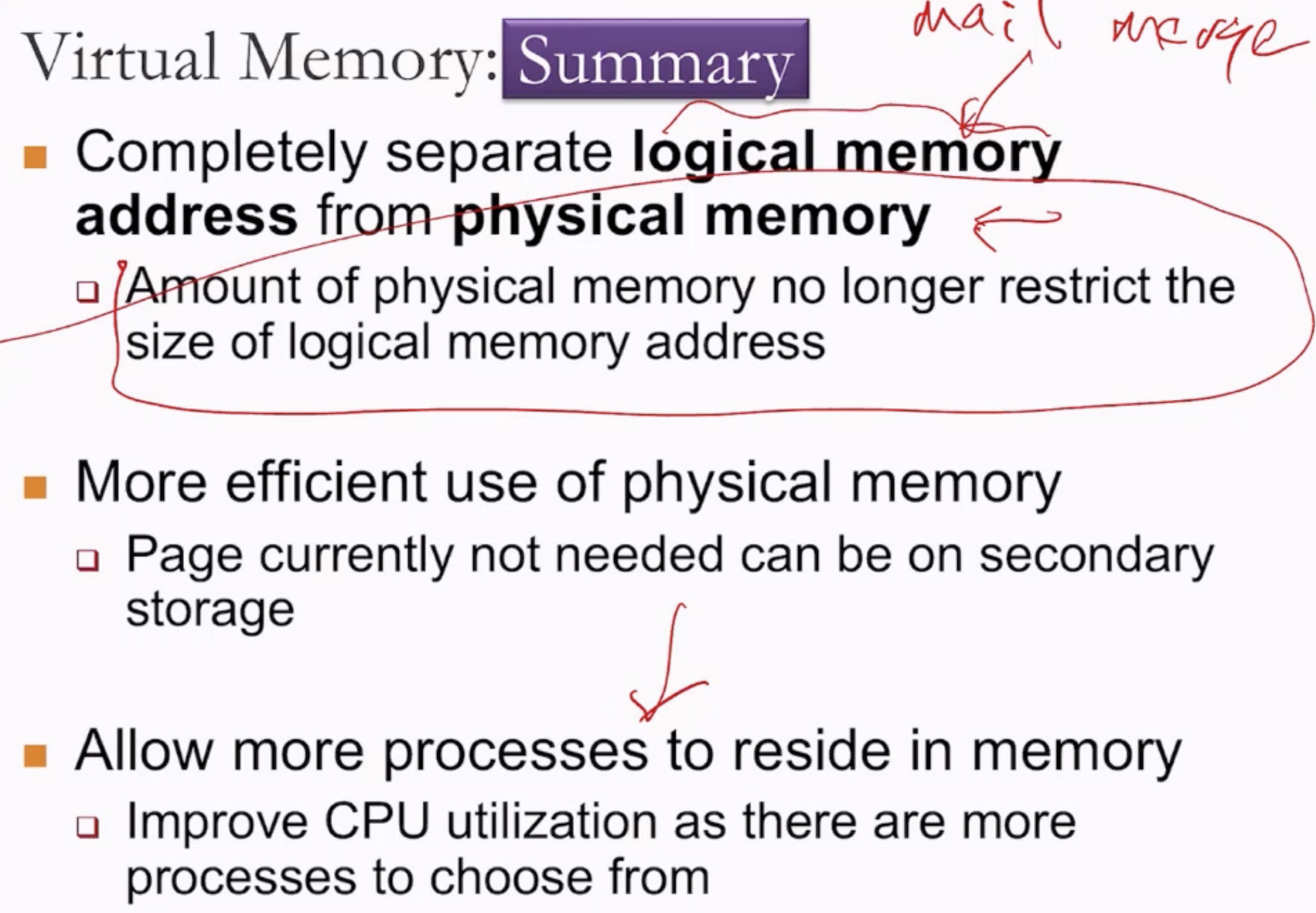
- What if the physical memory does not have enough space to store all the data required for a process?
Solution:
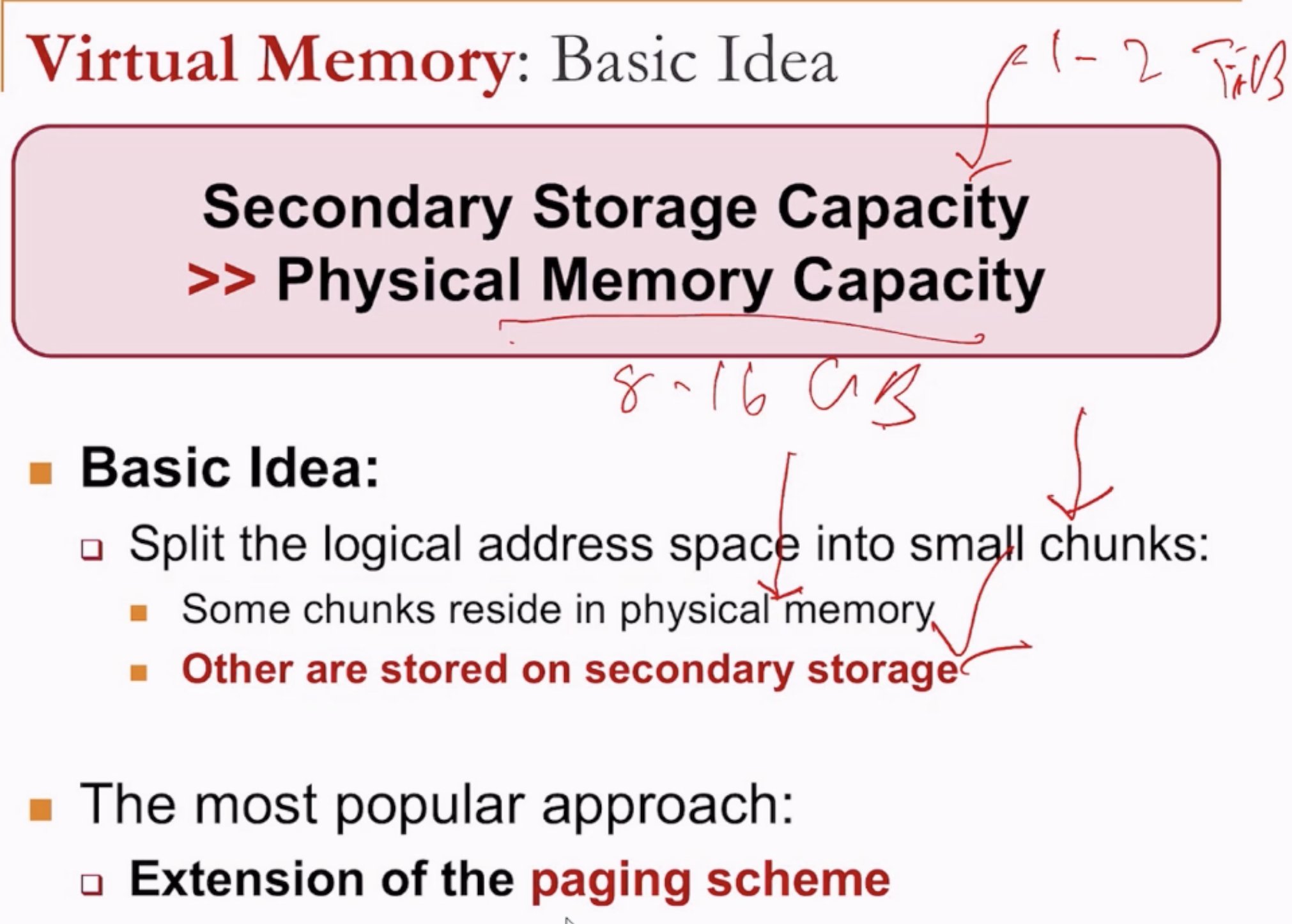
- By splitting the logic address space into chunks, saving some in physical memory and some in secondary storage (hard disk).
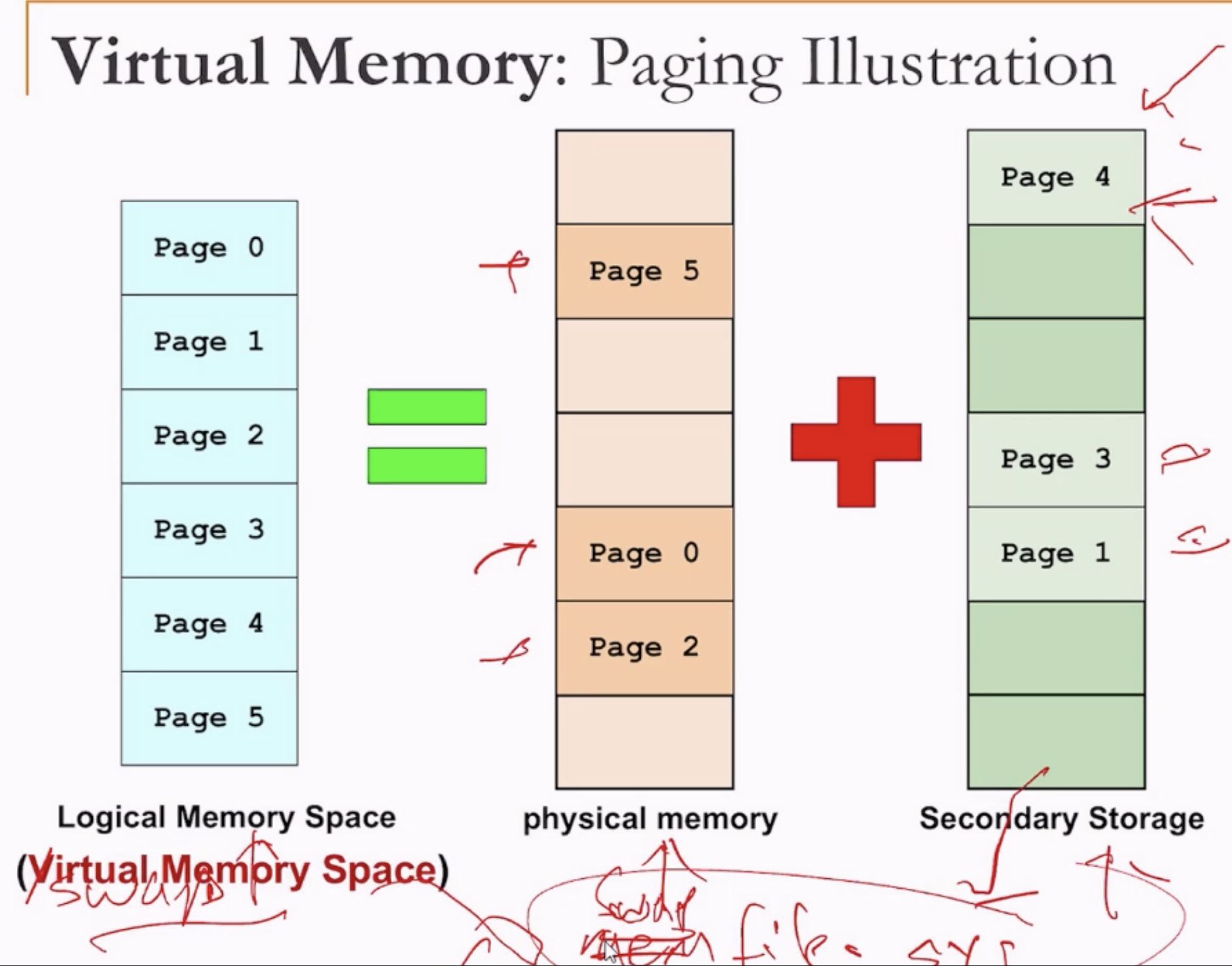
- In Windows the process pages are stored in memfile - or some gigantic file, while in macOs or linux it is stored in /swap partition.
- The name is virtual because the logical address space may no longer correspond to something that is physically available.
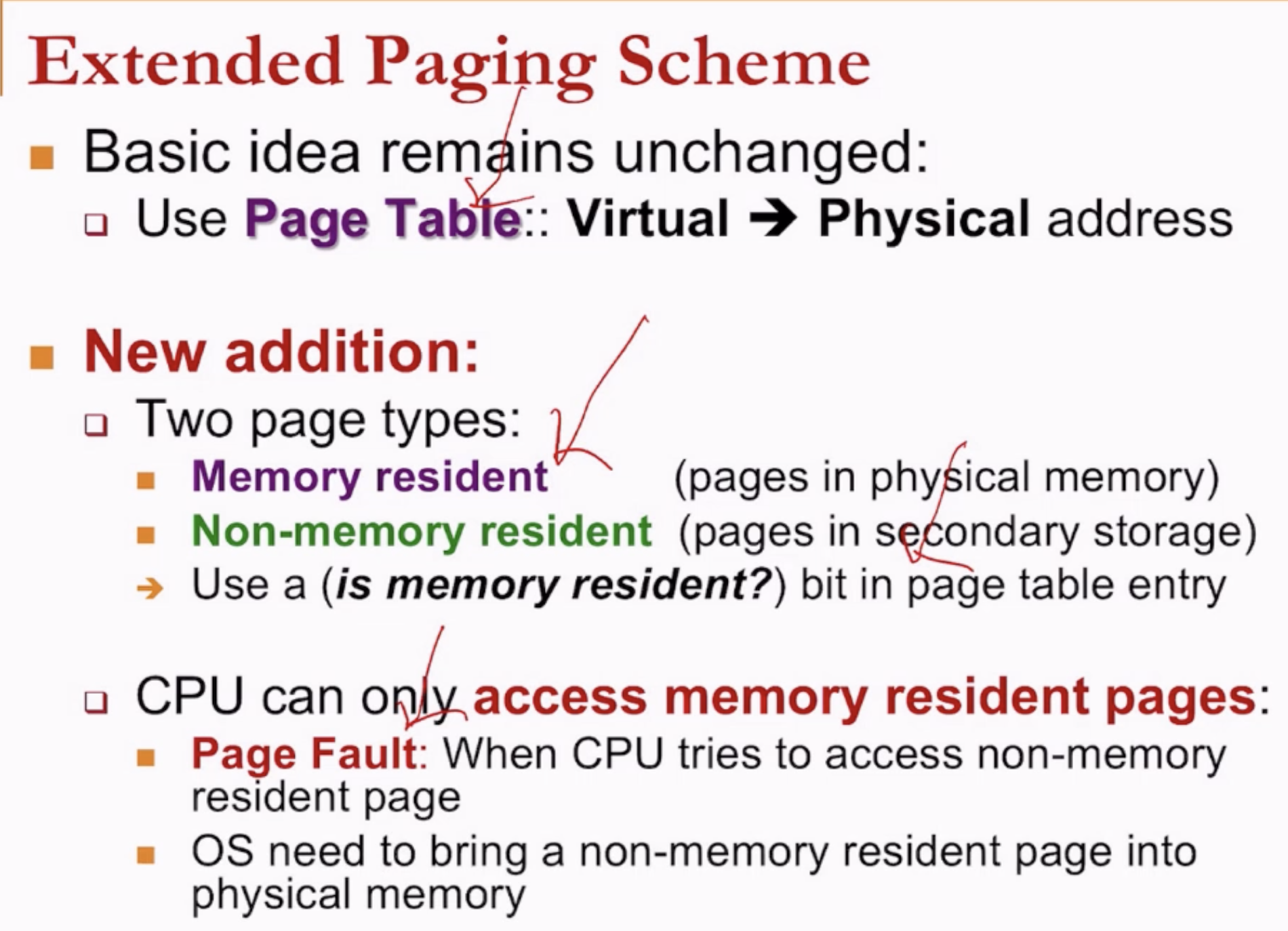
- Another bit in the page table that indicates whether the page is in physical memory or secondary storage.
- Loading an instruction from a page requires it to be in the physical memory.
- Page Fault mechenism will trigger something in the OS to bring a non-memory resident page into physical memory.
Page Fault

- Need extra data structures that tell me where the page X is in the drive.
- Step 1 is done by hardware, the rest is done by OS.
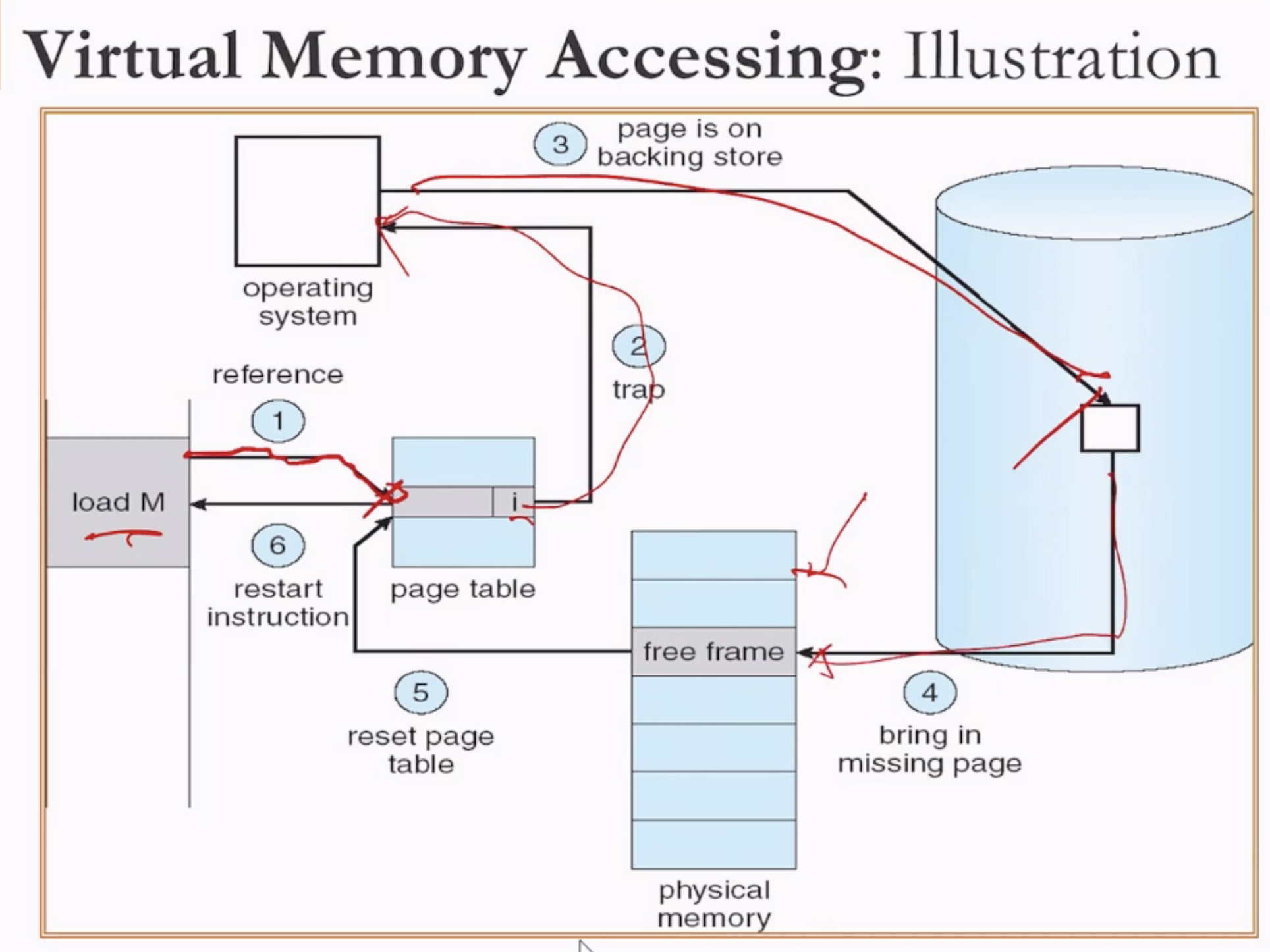
- Checks the page table: if doesn't exist, trap for OS to look for the page in the secondary storage, bring back to physical memory.

- Looking it up in the secondary storage requires a lot of time.
- Thrashing is when things are taking too much time.
- However, due to the principle of locality, we know that page fault is unlikely.

- Temporal: A memory address which is used is likely to be used again.
- Spatial: Memory addresses that are close to a used address is likely to be used.
- More process in memory means more CPU utilization - When one process is block on I/O, other processes can still be executed.
Demand Paging

- Less footprint of process -> more processes in memory -> better utilization of CPU.
What is a footprint in terms of processes? - Takes a long time to load every page onto the memory;
- but how would we know which page is useful if we don't load them? (instruction needs to be loaded first to be executed)

- Cascading effect: one page fault in a process may cause another page fault in another process, and another. This can cause thrashing.
