큰그림
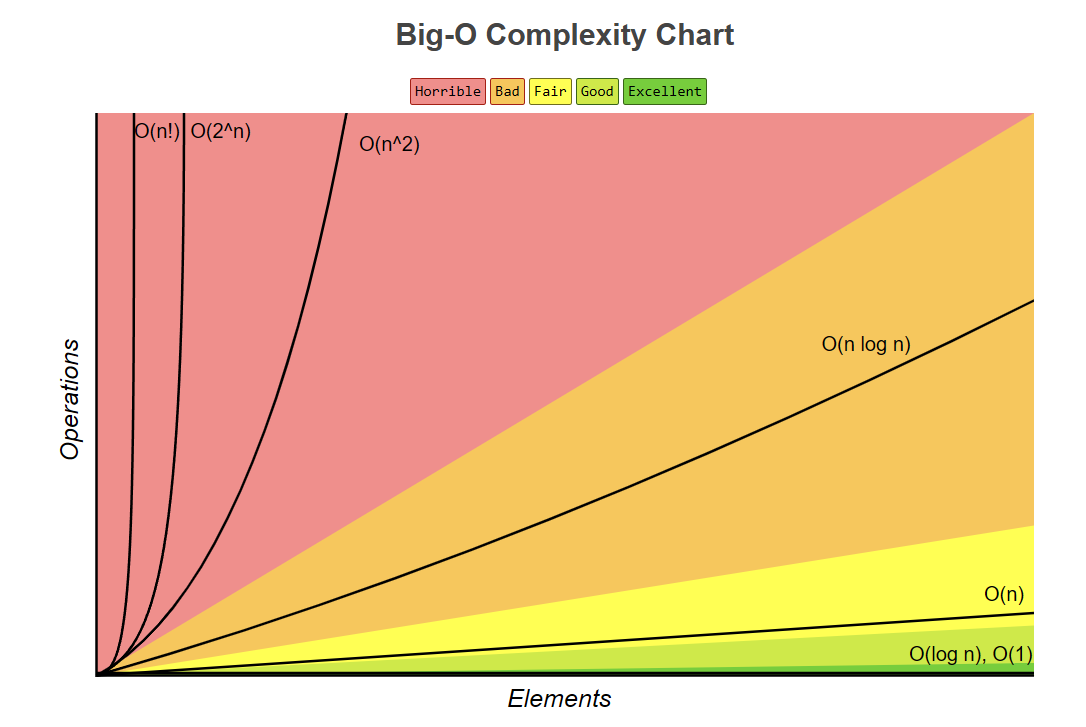
- 빅오 표기법(Big-O Notation)은 시간 복잡도와 매우 밀접하게 관련이 있습니다. 빅오 표기법은 알고리즘의 성능을 분석할 때 사용되며, 주로 입력 크기와 관련하여 알고리즘의 실행 시간이 어떻게 변하는지를 표현합니다.
- 빅오 표기법은 알고리즘의 효율성을 평가하는 중요한 도구로, 알고리즘의 최악의 경우 실행 시간을 나타내는 데 주로 사용됩니다. 이는 개발자가 알고리즘을 선택하고 최적화하는 데 있어서 매우 유용한 정보를 제공합니다.
- 시간 복잡도는 특정 알고리즘이 주어진 입력 크기(n)에 따라 얼마나 많은 시간(연산 수)을 필요로 하는지를 나타내며, 이를 빅오 표기법을 사용하여 나타냅니다.
예를 들어:- O(1): 상수 시간 복잡도
입력 크기와 상관없이 항상 일정한 시간이 걸리는 알고리즘입니다. 예를 들어, 배열의 첫 번째 요소를 읽는 작업.- O(n): 선형 시간 복잡도
입력 크기에 비례하여 시간이 증가하는 알고리즘입니다. 예를 들어, 배열의 모든 요소를 한 번씩 순회하는 작업.- O(n^2): 이차 시간 복잡도
입력 크기에 따라 시간이 제곱 비례로 증가하는 알고리즘입니다. 예를 들어, 중첩된 반복문을 사용하는 작업.- O(log n): 로그 시간 복잡도
입력 크기가 커질수록 시간이 느리게 증가하는 알고리즘입니다. 예를 들어, 이진 탐색.- O(n log n): 선형 로그 시간 복잡도
입력 크기와 로그의 곱에 비례하여 시간이 증가하는 알고리즘입니다. 예를 들어, 효율적인 정렬 알고리즘인 퀵 정렬, 합병 정렬.
Stack
Baek_10828_Stack
- push X: 정수 X를 스택에 넣는 연산이다.
- pop: 스택에서 가장 위에 있는 정수를 빼고, 그 수를 출력한다. 만약 스택에 들어있는 정수가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
- size: 스택에 들어있는 정수의 개수를 출력한다.
- empty: 스택이 비어있으면 1, 아니면 0을 출력한다.
- top: 스택의 가장 위에 있는 정수를 출력한다. 만약 스택에 들어있는 정수가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
class MyStack{
//데이터를 저장할 수 있는 int형 배열이 멤버변수로 정의
private int[] mystack;
private int top_position;
//스택의 top의 위치값, top_position변수값이 0이라는 것은 스택이 비어있다는 뜻
//(마이스택에 저장된 데이터갯수기때문에)
//MyStack클래스 내부에서 데이터를 저장하기 위한 공간(스택처럼 활용)
public MyStack(int size) {
this.mystack = new int[size];
}
//push, pop, top, empty, size 메소드 정의
// push X: 정수 X를 스택에 넣는 연산이다.
public void push(int data) {
mystack[top_position] = data;
top_position++;
// System.out.println("배열의 갯수:"+mystack.length);
// System.out.println("top_position:"+top_position);
}
public int size() {
return this.top_position;
}
public int top() {
if(top_position==0) {
return -1;
}else {
return mystack[top_position-1];
}
}
public int pop() {
int result = 0;
if(empty()==1) {//스택이 비어있으면
result = -1;
}else {
top_position = top_position -1;
result = mystack[top_position];
}
return result;
}
public int empty() {
int result = 0;
if(top_position==0) {
result = 1;
}else {
result = 0;
}
return result;
}
}
public class Baek_10828_Stack {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//MyStack의 메소드를 호출해서 테스트케이스 데이터를 입력받아 처리했을때 출력형식처럼 출력되도록 작업하기
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int count = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
MyStack stack = new MyStack(count);
for(int i=0;i<count;i++) {
String line = br.readLine();//한줄 전체 line을 입력받아 String 리턴
String[] arr = line.split(" ");//2개입력시 line[0], line[1]나옴// 1개입력시 line[0]
switch(arr[0]) {
case "push" :
int data = Integer.parseInt(arr[1]);
stack.push(data);
break;
case "pop" :
System.out.println(stack.pop());
break;
case "empty" :
System.out.println(stack.empty());
break;
case "size" :
System.out.println(stack.size());
break;
case "top" :
System.out.println(stack.top());
break;
}
}
}
}- 스캐너로 하니 시간초과 -> 버퍼드리더로 변경
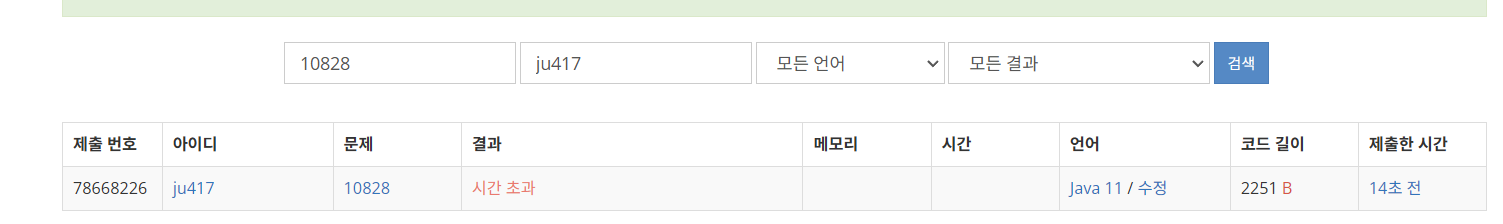
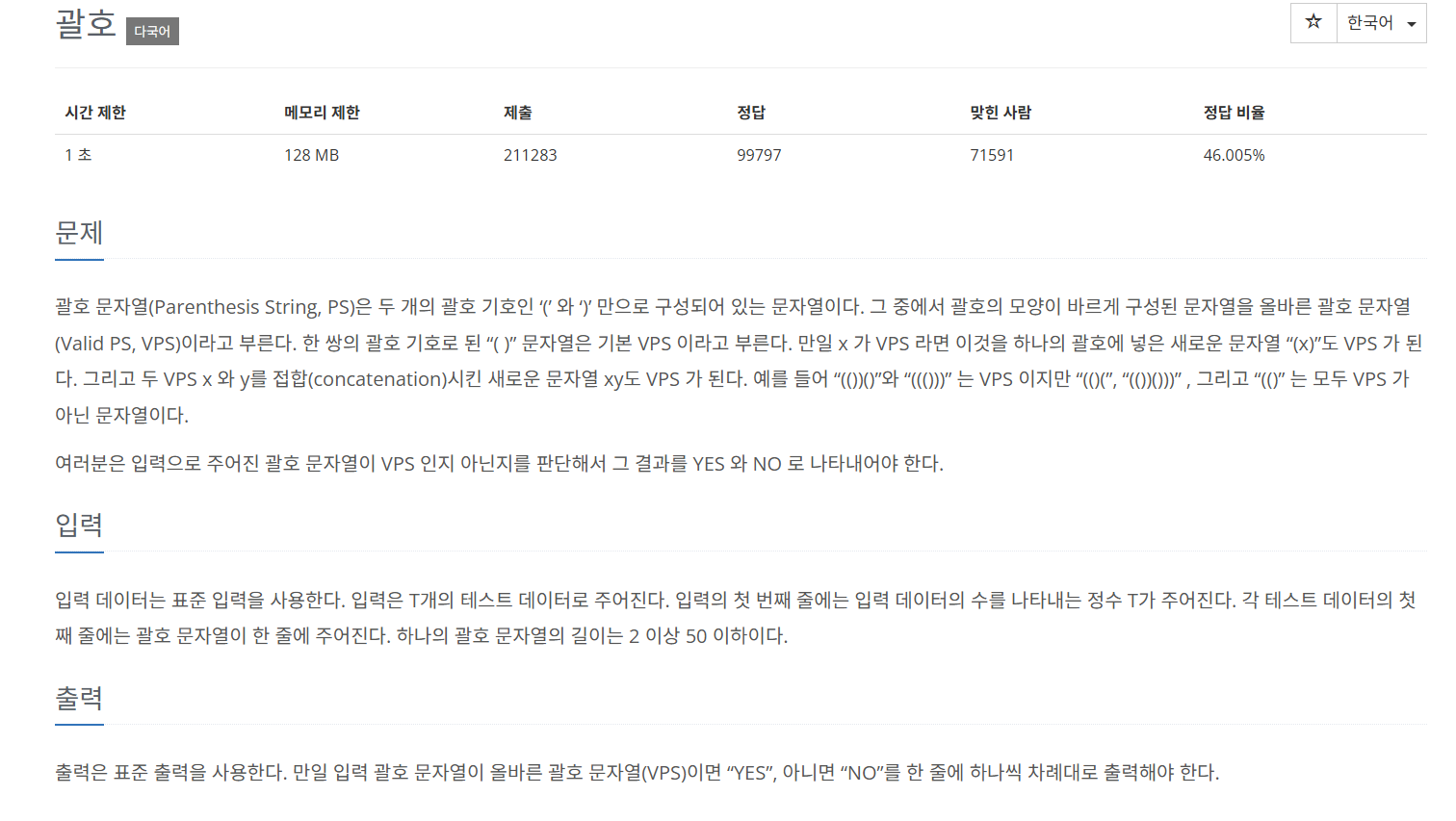
Baek_9012_Stack
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Baek_9012_Stack {
public static String checkVPS(String inputdata) {
String result = "YES";
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();//한문자로 뜯어서 봐야해서 캐릭터....
for(char c:inputdata.toCharArray()) {
if(c=='(') {
stack.push(c);
}else {
//pop을 하려고 하는데 만약 스택이 비어있으면 오류상황
if(stack.empty()) {
result = "NO";
}else {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
//작업이 모두 완료된 상태에서 스택에 데이터가 남아있으면 오류상황
if(!stack.empty()) {
result = "NO";
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int count = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i=0;i<count;i++) {
System.out.println(checkVPS(br.readLine()));
}
}
}Queue
교재 144p~
QueueAPITest
- rear : 큐의 가장 끝쪽 데이터가 삽입되는 위치
- front : 큐의 가장 앞쪽
- add : 큐의 rear에 데이터를 삽입
- poll : front부분에 저장된 데이터를 삭제
- peak : 큐의 맨 앞 부분 즉 front에 있는 데이터를 확인
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueAPITest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//큐에 데이터를 저장하기
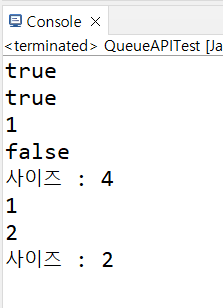
System.out.println(queue.add(1));//실행완료 true, 작업이 처리되지않으면 Exeption발생
System.out.println(queue.offer(2));//실행완료 true, 작업이 처리되지않으면 false
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());
System.out.println("사이즈 : "+queue.size());
System.out.println(queue.poll());//front의 요소를 꺼내고 결과를 출력(비어있으면 null)
System.out.println(queue.remove());//front의 요소를 꺼내고 결과를 출력(비어있으면 Exeption발생)
System.out.println("사이즈 : "+queue.size());
}
}
미션 / QueueExam / 10845문제
- 1번부터 10번까지 큐에 추가하고 데이터가 추가된 큐를 배열로 변환해서 출력하기
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
queue.add(i);
}
int[] arr = new int[queue.size()];//로직으로 한것
for(int i=0;i<=arr.length;i++) {
arr[i] = queue.poll();
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
Object[] arr2 = queue.toArray();//메소드로 한것
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
}
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>()
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();처럼 Queue 인터페이스의 구현체로 LinkedList를 사용하는 이유는 다음과 같습니다:
- 인터페이스와 구현체 분리: Queue는 인터페이스로, 이를 구현하는 여러 클래스가 있습니다. LinkedList는 Queue 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스 중 하나입니다. 이를 통해 나중에 구현체를 쉽게 변경할 수 있습니다.
- LinkedList의 특성: LinkedList는 Queue 인터페이스를 구현하고 있으며, 큐의 기본적인 동작을 수행할 수 있는 메서드를 제공합니다. LinkedList는 노드 기반의 자료 구조로, 삽입과 삭제가 빠릅니다. 큐는 보통 삽입과 삭제가 빈번하게 일어나는 자료 구조이므로, LinkedList가 적합합니다.
- 유연성: LinkedList는 Queue뿐만 아니라 Deque 인터페이스도 구현하고 있습니다. 따라서 필요에 따라 Deque의 기능(예: 양방향 큐)도 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 다른 구현체: Queue 인터페이스를 구현하는 다른 클래스들도 있습니다. 예를 들어, PriorityQueue는 우선순위 큐를 구현한 클래스입니다. 상황에 따라 다른 구현체를 사용할 수 있지만, LinkedList는 일반적인 FIFO(First-In-First-Out) 큐로 사용하기에 적합합니다.
- 요약하면, LinkedList는 큐로 사용하기 적합한 자료 구조로, 삽입과 삭제가 효율적이며, Queue 인터페이스를 구현하여 큐의 모든 기능을 제공합니다. 따라서 Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();와 같이 사용하는 것이 일반적입니다.
Baek_2164_Queue
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Baek_2164_Queue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()) ;
//1부터 N까지 큐에 저장
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++) {
queue.add(i);
}
while(queue.size()>1) {//한장남을때까지 반복작업
queue.poll();
queue.add(queue.poll());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(queue.toArray()));
}
System.out.println(queue.peek());
}
}
Programmers_120803
class Solution {
public int solution(int num1, int num2) {
int answer = num1 - num2;
return answer;
}
}
//두 수의 차
public class Programmers_120803 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution sol = new Solution();
System.out.println(sol.solution(2, 3));
System.out.println(sol.solution(100, 2));
}
}Programmers_120821
- 정수가 들어 있는 배열 num_list가 매개변수로 주어집니다.
- num_list의 원소의 순서를 거꾸로 뒤집은 배열을 return하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요
- 수도코드
- 배열을 탐색할 수 있도록 반복문을 실행
- 매개변수 num_list [0]에서부터 하나씩 꺼내기
- answer 마지막 index에서 데이터 넣어주기
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution2 {
public int[] solution(int[] num_list) {
int[] answer = new int[num_list.length];//이부분
int j = num_list.length-1;
for(int i=0;i<num_list.length;i++){
answer[j] = num_list[i];
j--;//이부분이 막혔음
}
return answer;
}
}
//배열뒤집기
public class Programmers_120821 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution2 sol = new Solution2();
int[] test1 = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sol.solution(test1)));
}
}과제
첫번째과제 스택의 응용문제 풀기 (과제 : 10799)
두번째과제 - 선형검색
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SequenceSearchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner key = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = {77,19,22,23,7,4,5};
System.out.println("찾을숫자: ");
int searchValue = key.nextInt();
//찾는 숫자는 배열에서 6번 위치에 있습니다
//찾는 숫자는 배열에 없습니다
search(arr, searchValue);
}
//searchValue의 위치를 리턴, 없으면 -1을 리턴하기
public static int search(int[] arr, int searchValue) {
return 0;
}
}본 포스팅은 멀티캠퍼스의 멀티잇 백엔드 개발(Java)의 교육을 수강하고 작성되었습니다.
