요약
- 쓰레드와 쓰레드씽크 연습
- 쓰레드 프로그래밍방법 : 쓰레드 클래스 상속, 러너블 인터페이스 하위클래스작성해서 쓰레드 클래스 생성해서 사용
- 익명이너클래스 : 이름이 없는 클래스를 정의하고 바로 생성해서 사용할 수 있도록 작업
- 쓰레드 우선순위, 기타 메소드들
- 데몬쓰레드는 메인클래스 종료시 같이 종료되게 작업 가능데몬쓰레드 설명
- 쓰레드 종료방법 : 임의의 변수(flag변수:boolean,int,..)를 선언, 인터럽트 발생시켜 현재상태 확인후 작업
- 쓰레드 씽크 : 모든 쓰레드가 공유하는 객체(공유자원), 메소드파일, 실행파일, 쓰레드상속파일
- synchronized : 하나의 쓰레드가 공유객체의 메소드를 사용하는 동안 다른 쓰레드가 접근할 수 없도록 lock을 적용
- 연습할 파일
* 쓰레드 : ThreadExam01, RunnableExam01, BeepPrintExam_Thread, ThreadExam02- 씽크 : ThreadSyncTest01,ThreadSyncTest02
Thread
ThreadTest01
자바에서 쓰레드 프로그래밍 하는 방법
- thread클래스를 상속받아 사용하는 방법
1) thread 클래스를 상속(extend)받는다.
2) thread 클래스에 정의되어있는 run메소드를 오버라이딩해서 동시에 실행하고싶은 기능(thread프로그램으로 처리하고싶은 내용)을 정의
=> run메소드를 직접 호출하지 않는다.
3) 쓰레드 클래스에 정의되어있는 start메소드를 호출한다
=> start메소드를 호출하면 JVM내부에 스케줄러에 의해서 적절한 시점에 run메소드가 호출된다
class ThreadDemo01 extends Thread{
ThreadDemo01(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
//thread프로그래밍으로 실행하고싶은 내용을 정의
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) {
System.out.print(i+"("+getName()+")"+"\t");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);//0.5초 쉬게 하기
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%5==0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("*****메인시작********");
ThreadDemo01 t1 = new ThreadDemo01("t1");
ThreadDemo01 t2 = new ThreadDemo01("t2");
// t1.run(); ---쓰레드 작업이 아니라 단순 메소드 call
// t2.run();
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("*****메인종료********");
}
}
ThreadExam01

class AlphaThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {//run메소드 오버라이드 해야함
for(char i ='A';i<='Z';i++) {
System.out.print(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class DigitThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {//run메소드 오버라이드 해야함
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++) {
System.out.print(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%10==0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadExam01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AlphaThread a = new AlphaThread();
DigitThread d = new DigitThread();
a.start();
d.start();
}
}
RunnableTest01
자바에서 쓰레드 프로그래밍을 하는 방법
- Thread클래스를 상속받아서 작성 -> ThreadTest에서 확인
- 이미 상속받고있는 클래스가 있어서 상속못받을때, Thread클래스를 상속해서 쓰레드 프로그래밍을 할 수 없으므로 Runnable 인터페이스의 하위클래스를 작성하고 이 클래스를 이용해서 Thread클래스를 생성해서 사용하는 방법
1) Runnable인터페이스를 상속(구현)
2) run메소드를 오버라이딩해서 쓰레드 프로그래밍으로 처리하고싶은 내용을 정의한다
3) 쓰레드를 시작하는 곳에서 Runnable객체를 생성하고 이를 이용해서 Thread객체를 생성
=> Runnable 하위객체 생성
=> Thread객체를 생성하면서 Runnable하위객체를 매개변수로 전달
4) Thread객체의 start메소드를 호출
class RunnableDemo01 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) {
//getName은 Thread클래스에 정의되어있는 메소드이므로 Runnable에서는 사용할 수 없다
//Thread.currentThread()를 이용해면 현재 실행중인 쓰레드 객체를 리턴받아서 호출
System.out.print(i+"("+Thread.currentThread().getName()+")"+"\t");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);//0.5초 쉬게 하기
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%5==0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
public class RunnableTest01 {
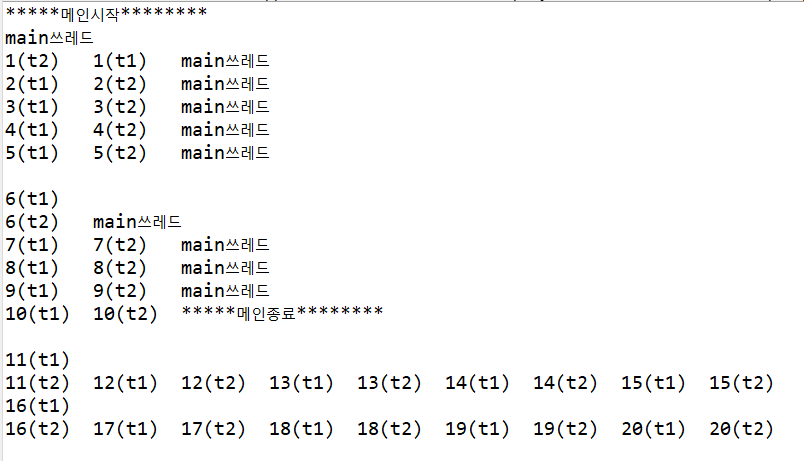
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("*****메인시작********");
//1.러너블 하위객체를 생성
RunnableDemo01 obj = new RunnableDemo01();
//2.생성한 러너블 하위객체를 이용해서 쓰레드 객체를 생성
Thread t1 = new Thread(obj,"t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new RunnableDemo01(),"t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
System.out.println("main쓰레드");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("*****메인종료********");
}
}
RunnableExam01
- ThreadExm01에서 작업한 내용을 러너블 인터페이스를 구현하는 코드로 변경
- 클래스 이름 겹치지 않게 AlphaRunnable,DigitRunnable
class AlphaRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(char a ='A';a<='Z';a++) {
System.out.print(a);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class DigitRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++) {
System.out.print(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(i%10==0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
public class RunnableExam01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new AlphaRunnable());
Thread t2 = new Thread(new DigitRunnable());
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}RunnableTest02_Inner/익명이너클래스
- Runnable을 implements하는 이름이 없는 클래스를 정의하고 바로 생성해서 사용할 수 있도록 작업
=>생성하면서 바로 정의해서 사용할 수 있음 - 객체를 생성하면서 생성자 내부에서 바로 클래스를 정의하고 있음
- new Runnable() {}는 Runnable의 하위클래스를 바로 정의해서 생성
- 바로 정의해서 메모리에 올려서 다른 클래스의 매개변수로 전달할 것이므로 이름이 필요없다.
- 익명클래스(익명이너클래스)라 부름
=> 람다, 안드로이드, GUI프로그램같이 이벤트 드리븐 방식의 코드를 구현할 때 사용
public class RunnableTest02_Inner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("메인시작");
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) {
System.out.print("익명이너클래스");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
System.out.println("메인종료");
}
}
BeepPrintExam & BeepPrintExam_Thread
- 쓰레드를 사용하지 않는 경우
- beep와 print를 같이 출력
public class BeepPrintExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}- beep와 print가 같이 실행될 수 있게 쓰레드를 이용해서 작업
- 익명inner클래스를 사용
public class BeepPrintExam_Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toolkit toolkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
toolkit.beep();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("띵");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}ThreadPriortyTest/우선순위
- 쓰레드의 우선순위 738p
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//시간지연을 위한 코드 - 프로그램이 실행되는 시간을 표현
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
}
System.out.println(getName()+"쓰레드의 우선순위->"+getPriority());
}
}
//지금은 그냥 쓰레드에서 처리하는 일 없이 쓰레드의 우선순위만 출력
public class ThreadPriortyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//숫자가 클수록 우선순위가 높다
System.out.println(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
System.out.println(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
System.out.println(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
//CPU의 성능을 판단하는 기준 중 하나가 코어의 수
//연산을 여러개의 코어가 처리하기 때문에 코어수가 많으면 빠르게 처리할 수 있다.
System.out.println("코어수:"+Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
MyThread t = new MyThread();
t.start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//쓰레드의 우선순위를 변경할수있다
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
MyThread t = new MyThread();
t.setName("t"+i);
if(i==7) {
t.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
}
t.start();
}
}
}
ThreadMethodTest
public class ThreadMethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("쓰레드이름:"+t.getName());
System.out.println("실행중인쓰레드의갯수:"+Thread.activeCount());
//아무일도 하지않는 쓰레드 만들기
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
Thread t2 = new Thread("t"+i);
System.out.println(t2.getName());
t2.start();
}
System.out.println("실행중인쓰레드의갯수:"+Thread.activeCount());
//console창에 찍히는 타이밍이 달라서, 이미끝난건 반영안됨
}
}
DaemonThreadTest
- 일반쓰레드는 메인쓰레드와 상관없이 자신의 작업이 종료되어야 종료되는 쓰레드
- 데몬쓰레드로 만드는 작업을 하면 메인쓰레드가 종료될때 같이 종료될 수 있도록 작업할 수 있다.
- 데몬쓰레드는 특별한 종류의 쓰레드이고 백그라운드에서 실행되는 쓰레드를 만들때 사용
class MyThread2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
System.out.println(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class DaemonThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("*****메인시작********");
MyThread2 t = new MyThread2();
t.setDaemon(true);//데몬쓰레드로 설정한거//false는 안한거랑 같음
//데몬쓰레드로 만드는 작업은 start 되기 전에 작업
t.start();//데몬쓰레드여도 실행자체는 스타트를 써야함.
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("*****메인종료********");
}
}
StopThreadTest01
스레드 중지하기
한번 start된 스레드는 절대 다시 실행할 수 없다.
->스레드는 일회용
[스레드를 종료]
- 임의의 변수(flag변수)를 선언해서 종료하는방법
- 변수에 저장된 값에 따라서 작업을 처리할 목적으로 선언하는 변수(실행 or 종류 -boolean,int,..)
- 변수값을 체크(오래걸리는 작업인 경우에 중간에 stop할 수 있도록 처리)
class StopThread extends Thread{
//현재 상태값을 저장할 수 있는 변수
private boolean state = true;
//기본값작업안하면 펄스라서 처리
public void run() {
while(state) {
System.out.println("현재쓰레드의 상태: 실행중~~~");
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("현재쓰레드의 상태:종료상태");
}
//스레드의 현재 상태값이 저장된 변수를 변경할 수 있는 메소드
public void stopThread() {
state = false;
}
}
public class StopThreadTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("*****메인시작********");
StopThread t = new StopThread();
t.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//쓰레드 실행을 제어하는 변수인 쓰레드객체의 state를 변경하면서 쓰레드를 종료
t.stopThread();
System.out.println("*****메인종료********");
}
}
StopThreadTest02
[스레드를 종료]
- 인터럽트를 발생시키고 현재 상태를 확인한 후 작업하기
class StopThread02 extends Thread{
public void run() {
//인터럽트가 발생되지 않는동안 실행할 수 있도록 처리
try {
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
//와일문은 인터럽트발생되어도 실행되니까 빠져나올수있게 트라이문안으로
System.out.println("현재쓰레드의 상태: 실행중~~~");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
}finally {
System.out.println("현재쓰레드의 상태:종료상태");
}
}
}
public class StopThreadTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("*****메인시작********");
StopThread02 t = new StopThread02();
t.start();
System.out.println("쓰레드이름 :"+t.getName());
//인터럽트가 발생되면 true, 그렇지 않으면 false
System.out.println("인터럽트 상태 :"+t.isInterrupted());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//인터럽트를 발생시키는 작업
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("인터럽트상태:"+t.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("인터럽트상태:"+t.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("인터럽트상태:"+t.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("*****메인종료********");
}
}
ThreadStateTest
public class ThreadStateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t = new MyThread();
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());//처음스레드가 만들어졌을때 상태
t.start();
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());//실행될때
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("쓰레드의 상태:"+t.getState());//종료된후
}
}
ThreadExam02
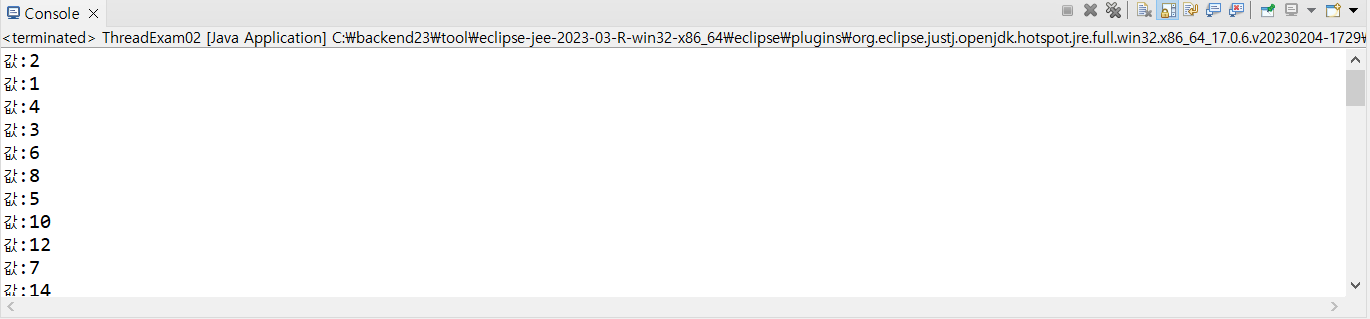
- 1부터100까지 짝수를 출력하는 스레드
- 0.1초 sleep
- 값이 50이 넘어가면 스레드가 종료될 수 있도록 처리(flag변수를 이용해서 종료)
- 1부터 1000까지 홀수를 출력하는 스레드
- 0.2초 sleep
- 70이 넘어가면 스레드가 종료될수있도록 처리(interrupt를 발생시키고 작업)
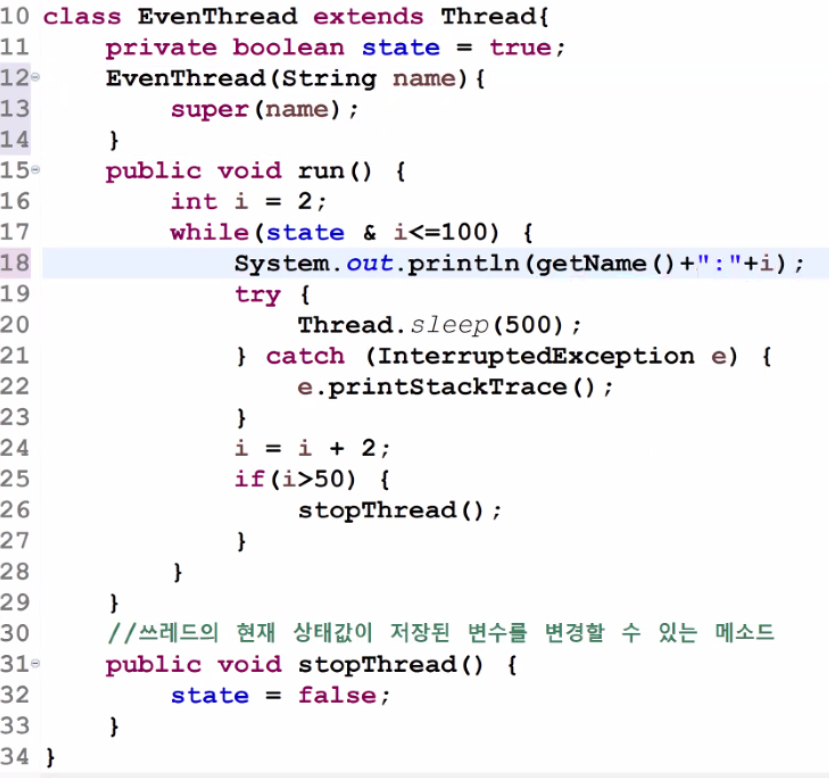
class EvenThread extends Thread{
private boolean state = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 2;
while (state &i<=100) {
System.out.println("값:"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i = i+2;
if(i>50) {
stopThread();
}
}
}
//쓰레드의 현재 상태값이 저장된 변수를 변경할 수 있는 메소드
public void stopThread() {
state = false;
}
}
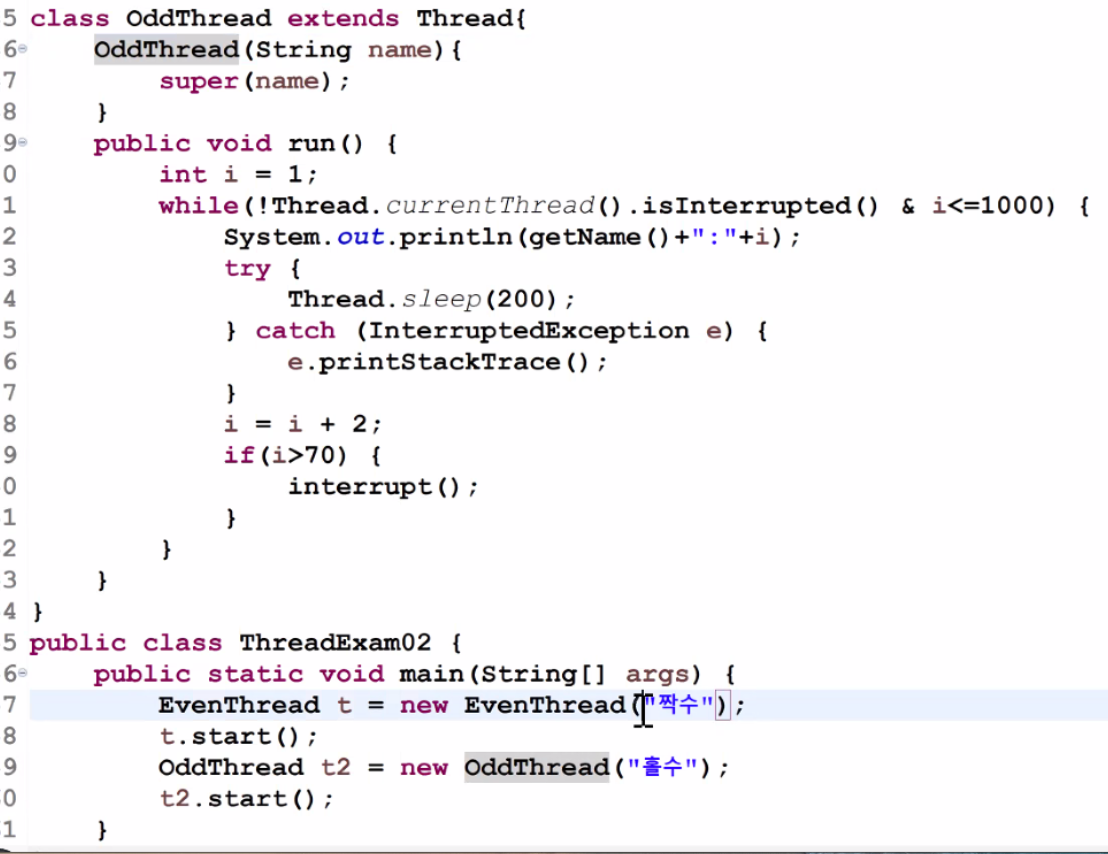
class OddThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 1;
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() & i<=1000) {
System.out.println("값:"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
i = i +2;
if(i>70) {
interrupt();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadExam02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EvenThread t = new EvenThread();
t.start();
OddThread t2 = new OddThread();
t2.start();
}
}
이렇게 할 수도 있다..~
Thread.Sync
ThreadSyncTest01+Toilet,User
- synchronized를 메소드 전체에 추가하기 위해서 메소드 선언부에 추가하면 하나의 쓰레드가 공유객체의 메소드를 사용하는 동안 다른 쓰레드가 접근할 수 없도록 lock을 적용 ->전체에 걸면 성능저하.. 무거움
- 메소드 전체가 아니라 일부에만 lock처리를 하고싶은 경우
synchronized (공유객체) {
쓰레드들이 고유하게 처리해야 하는 일
}
모든 쓰레드가 공유하는 객체(공유자원)
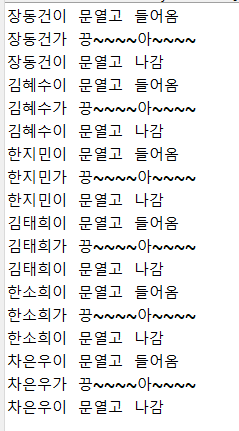
public class Toilet {
//synchronized 빼면 무작위로됨
public synchronized void open(String name) {//name은 공유객체를 사용하ㄴㄴ 쓰레드의 이름
System.out.println(name+"이 문열고 들어옴");
for(int i=1;i<=100000000;i++) {
if(i==10000) {
System.out.println(name+"가 끙~~~~아~~~~");
}
}
System.out.println(name+"이 문열고 나감");
}
}public class User extends Thread{
String name;
Toilet toilet;
public User(String name, Toilet toilet) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.toilet = toilet;
}
@Override
public void run() {
toilet.open(name);
}
}//여러쓰레드가 객체를 공유해서 사용하는 경우 발생할 수 있는 문제점
//->synchronized를 Toilet에 줘서 하나씩
public class ThreadSyncTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//쓰레드에서 공유해서 사용할 객체 생성
Toilet toilet = new Toilet();
//공유객체를 사용하게 될 쓰레드들을 생성
User user1 = new User("장동건",toilet);
User user2 = new User("차은우",toilet);
User user3 = new User("한소희",toilet);
User user4 = new User("김태희",toilet);
User user5 = new User("한지민",toilet);
User user6 = new User("김혜수",toilet);
user1.start();
user2.start();
user3.start();
user4.start();
user5.start();
user6.start();
//들어오고 나가고 속도 다름
}
}
ThreadSyncTest02, Account, Obj, AccountTransferThread, AccountSumThread
계좌이체를 여러번 처리하면서 공유객체에 셋팅된 계좌의 정보가 어떻게 변경되는지 살펴보기
- 쓰레드생성 후 테스트해보기
- 계좌이체하는 쓰레드 B에서 출금해서 A에 입금하는 작업을 20번 처리하는 쓰레드
1000000만원을 출금했습니다.
1000000만원을 입금했습니다. - 두 계좌의 잔액을 더해서 출력하는 쓰레드 5번
총 잔액 => __
- 쓰레드 시작
동기화처리가 되지않은경우 계좌이체쓰레드가 출금한 상태에서 더하는 쓰레드가 Obj를 사용하게 되면
5900만원이 출력
- 동기화처리
잔액은 늘 6000만원으로 출력
public class ThreadSyncTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//공유객체를 생성 - 계좌이체 정보를 셋팅할 객체
Obj obj = new Obj();
obj.acc1 = new Account("111-222-333", 10000000,"김서연");
obj.acc2 = new Account("777-888-999", 50000000,"장동건");
AccountTransferThread t1 = new AccountTransferThread(obj);//쓰레드로 만들기
Thread t2 = new Thread(new AccountSumThread(obj));//러너블로 만들기
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}전에 만든거 단순히 가져온거
public class Account {
private String accId;
private long balance;
private String ownerName;
public Account() {
}
public Account(String accId, long balance, String ownerName) {
super();
this.accId = accId;
this.balance = balance;
this.ownerName = ownerName;
}
//입금하기
public void deposit(long amount) {
balance = balance + amount;
}
//출금하기
public void withdraw(long amount) {
balance = balance - amount;
}
public String getAccId() {
return accId;
}
public void setAccId(String accId) {
this.accId = accId;
}
public long getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(long balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getOwnerName() {
return ownerName;
}
public void setOwnerName(String ownerName) {
this.ownerName = ownerName;
}
}공유객체 - 계좌이체에 필요한 두 계좌의 정보를 가지고 있는 객체
public class Obj {
Account acc1;//김서연계좌 - 이체를 받을 계좌
Account acc2;//장동건계좌 - 이체할 계좌
//공유객체에 메소드를 직접정의하고 사용하는 경우
public synchronized void 계좌이체() {
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) {
acc2.withdraw(1000000);
System.out.println("100만원을 출금했습니다.");
acc1.deposit(1000000);
System.out.println("100만원을 입금했습니다.");
}
}
public synchronized void 출금하기() {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
long total = acc1.getBalance()+acc2.getBalance();
System.out.println("총잔액=>"+total);
}
}
}public class AccountTransferThread extends Thread{
Obj obj; //공유객체
public AccountTransferThread(Obj obj) {
super();
this.obj = obj;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//공유객체의 메소드를 호출
obj.계좌이체();
}
}public class AccountSumThread implements Runnable{
Obj obj; //공유객체
public AccountSumThread(Obj obj) {
super();
this.obj = obj;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//공유객체의 메소드를 호출
obj.출금하기();
}
}
본 포스팅은 멀티캠퍼스의 멀티잇 백엔드 개발(Java)의 교육을 수강하고 작성되었습니다.
