1. Question
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the kth largest element in the array.
Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Can you solve it without sorting?
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2
Output: 5Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6], k = 4
Output: 42. Thoughts
- Use Heap to track largest element
- After going through all element, heap pop kth time to get the kth largest element
3. Tips learned
From :
https://littlefoxdiary.tistory.com/3
3.1. What is Heap
A heap is a tree with specific rules and is based on a fully binary tree designed to speed up operations to find maximum and minimum values.
Hip property: If A is the parent node of B, there is a large or small relationship between the key value of A and the key value of B
Minimum heap: The key value of the parent node is always smaller than the key value of the child node
Maximum heap: The key value of the parent node is always greater than the key value of the child node
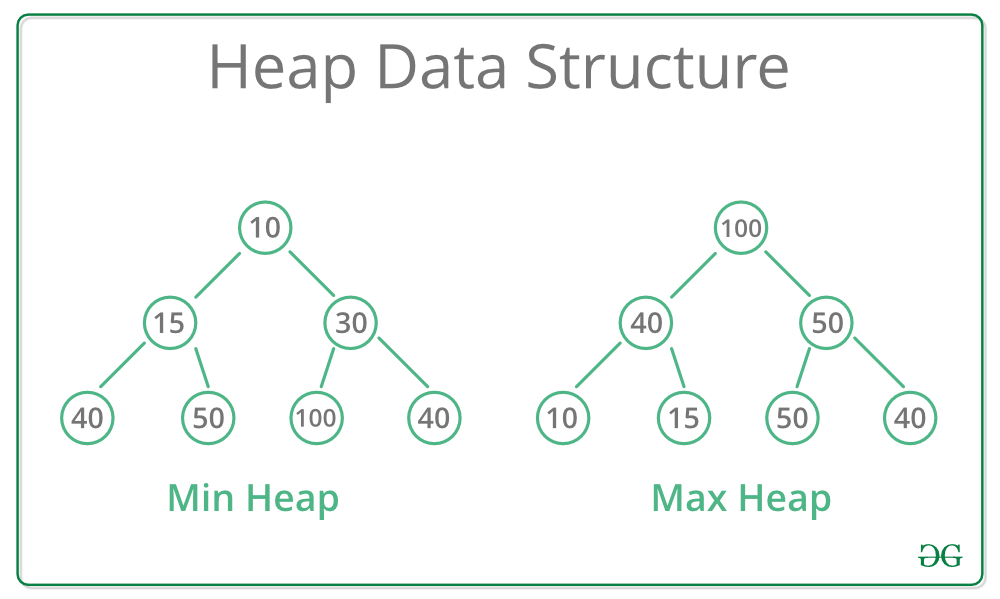
Due to these properties, the node with the lowest (or highest) priority always comes to the root in the heap, which can be used to implement abstract data types such as priority queues.
At this time, the magnitude relationship of the key value is established only between parents/children, and the magnitude relationship is not determined between the sibling nodes.
3.2. How to use Heap in Python
heapq in python uses minimum heap
Basically:
#Init Heap
heap = []
#Add element to heap
heapq.heappush(heap, 1)
# Delete smallest element to heap
heapq.heappop(heap)To make list to heap:
tmp = [7, 5, 8, 3]
heapq.heapify(tmp)To Make Maximum heap, put minus:
import heapq
nums = [4, 1, 7, 3, 8, 5]
heap = []
for num in nums:
heapq.heappush(heap, (-num, num))
while heap:
print(heapq.heappop(heap)[1])4. My solution
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
heap = []
for num in nums:
heapq.heappush(heap, -num)
for _ in range(k - 1):
heapq.heappop(heap)
return -heapq.heappop(heap)
41/41 cases passed (481 ms)
Your runtime beats 77.73 % of python3 submissions
Your memory usage beats 72.96 % of python3 submissions (29.6 MB)5. AI Solution and Improvements
Your solution using a heap is a good approach for finding the kth largest element without sorting the entire array. However, it can be optimized further. In your current implementation, you are negating each element and using a min-heap. This works but can be simplified by using a max-heap directly, which Python's heapq module does not directly support. However, you can simulate a max-heap by pushing tuples into the heap, with the first element of the tuple being the negative of the number.
Here's an improved version of your code:
import heapq
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
heap = []
# Build a heap of size k
for num in nums[:k]:
heapq.heappush(heap, num)
# For the rest of the elements, if the element is larger than the smallest in the heap, replace it
for num in nums[k:]:
if num > heap[0]:
heapq.heappushpop(heap, num)
# The root of the heap is the kth largest element
return heap[0]In this improved approach:
- We build a min-heap with the first
kelements of the array. This heap will hold theklargest elements seen so far. - For each remaining element in the array, if it is larger than the smallest element in the heap (which is the heap's root), we replace the smallest element with the current element using
heapq.heappushpop(). - The root of the heap (heap[0]) will be the kth largest element.
This approach is more efficient because it maintains a heap of size k instead of the entire array size, reducing the memory usage and potentially improving the time complexity for large inputs.
