1. Question
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n x n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return the number of distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Example 1:
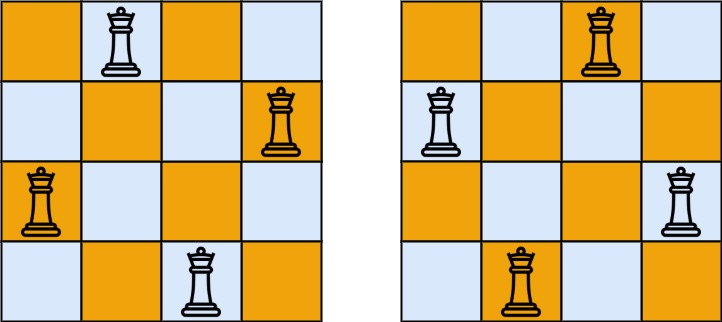
Input: n = 4
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown.Example 2:
Input: n = 1
Output: 12. Thoughts
divide the expression into left and right.
Using recursion, calculate left and right.
Use Memoization and set conversion for optimization
3. Tips learned
4. My solution
class Solution:
def is_big (self,x,y,a,b):
if a > x:
return True
elif a == x:
if b < y:
return True
return False
def removed(self, set_xy,x,y):
discard_list = set()
for x_from_set,y_from_set in set_xy:
if self.is_big(x,y,x_from_set,y_from_set) or x_from_set == x or y_from_set ==y or abs(y-y_from_set) == abs(x-x_from_set):
discard_list.add((x_from_set,y_from_set))
return set_xy - discard_list
def select_possible(self,set_xy,n,trial):
if n == trial:
return len(set_xy)
count = 0
for x,y in set_xy:
count += self.select_possible(self.removed(set_xy,x,y),n,trial+1)
return count
def totalNQueens(self, n: int) -> int:
set_xy = set((x,y) for x in range(n) for y in range(n))
return self.select_possible(set_xy,n,1)8/8 cases passed (1201 ms)
Your runtime beats 5.01 % of python3 submissions
Your memory usage beats 21.00 % of python3 submissions (16.82 MB)