MST (최소 신장 트리)
- 그래프에서 최소 비용 문제
1. 모든 정점을 연결하는 간선들의 가중치의 합이 최소가 되는 트리
2. 두 정점 사이의 최소 비용의 경로 찾기
- 신장 트리
- n개의 정점으로 이루어진 무방향 그래프에서 n개의 정점과 n-1개의 간선으로 이루어진 트리
- 최소 신장 트리(Minimum Spanning Tree)
- 무방향 가중치 그래프에서 신장 트리를 구성하는 간선들의 가중치의 합이 최소인 신장 트리
SWEA 3124. 최소 스패닝 트리
https://swexpertacademy.com/main/code/problem/problemDetail.do?contestProbId=AV_mSnmKUckDFAWb
크루스칼 알고리즘
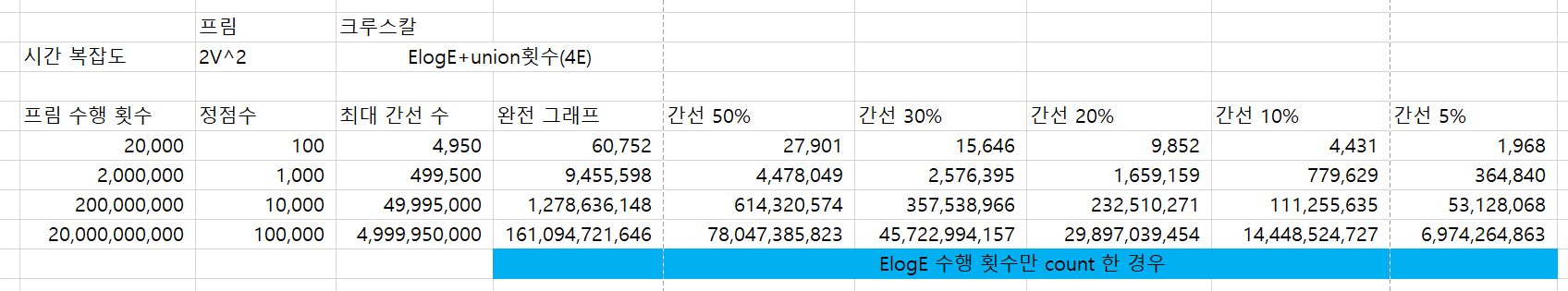
- 간선 중심으로 최소 신장 트리를 구하는 알고리즘 (간선이 적을 때 프림 알고리즘보다 유리)
- 간선들을 가중치의 오름차순 정렬하여 가장 작은 간선 선택
- 그 간선이 지금까지 만들어진 MST와 사이클을 형성한다면 제외, 아니면 MST에 추가
- 모든 간선에 대해 반복
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 시간 : 2,044ms, 메모리 : 116,936KB
*/
public class Kruskal {
// 간선 정보 클래스
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
// 우선 순위 큐 활용
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
}
static int T, V, E, from, to, weight;
static long answer;
static int[] parents;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> pq;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
StringBuilder sb;
T = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for (int t = 1; t <= T; t++) {
sb = new StringBuilder();
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
answer = 0;
V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 부모 노드 세팅
parents = new int[V + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < V + 1; i++) {
parents[i] = i;
}
// 간선 정보 입력
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
weight = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
pq.offer(new Edge(from, to, weight));
}
// 사이클 확인 (union-find)
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Edge now = pq.poll(); // 가중치가 가장 작은 간선
// 부모 노드가 다를때만 (사이클X)
if(find(now.from) != find(now.to)){
union(now.from, now.to);
answer += now.weight;
}
}
sb.append("#").append(t).append(" ").append(answer);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
// 합치기
static void union(int v, int u){
int pv = find(v);
int pu = find(u);
if(pv < pu)
parents[pu] = pv;
else
parents[pv] = pu;
}
// 부모 노드 찾기
static int find(int v){
if(parents[v] == v) return v;
return parents[v] = find(parents[v]); // 경로 압축
}
}프림 알고리즘
- 정점 중심으로 최소 신장 트리를 구하는 알고리즘 (정점이 적을 때 크루스칼 알고리즘보다 유리)
- 임의의 정점 선택
- 그 정점과 인접한 정점을 잇는 간선 중 가중치가 가장 낮은 간선 선택
- 그 간선이 연결하는 정점 선택, 모든 정점에 대해 2번 과정 반복
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/**
* 시간 : 3,417ms, 메모리 : 204,624KB
*/
public class Prim {
static class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
int to;
int weight;
public Node(int to, int weight) {
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
}
static int T, V, E, from, to, weight;
static long answer;
static List<Node>[] lists;
static boolean[] visited;
static PriorityQueue<Node> pq;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
StringBuilder sb;
T = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for (int t = 1; t <= T; t++) {
sb = new StringBuilder();
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
answer = 0;
V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
E = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists = new List[V + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < V + 1; i++) {
lists[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
visited = new boolean[V + 1];
pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 간선 정보 입력 (정점 연결리스트)
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
weight = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists[from].add(new Node(to, weight));
lists[to].add(new Node(from, weight));
}
int cnt = 0;
pq.offer(new Node(1, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()){
Node now = pq.poll();
// 이미 방문한 정점이라면 탐색 X
if(visited[now.to]) continue;
visited[now.to] = true;
answer += now.weight;
// 모든 노드 확인 완료
if (++cnt == V) break;
// 연결되어 있는 방문하지 않은 정점 큐에 추가
for (Node next : lists[now.to]) {
if(visited[next.to]) continue;
pq.offer(next);
}
}
sb.append("#").append(t).append(" ").append(answer);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
}시간 복잡도