Background
Relational model:
1) mathematical relation(set) concept을 사용
2) set theory(집합 이론)과 first-order predicate logic(1차 술어 논리)에 theoretical basis를 둔다.
- First-order logic: 술어는 functions 또는 다른 술어가 아닌 개별 개체에만 적용된다.
(e.g., "Socrates is mortal." (O), "Being beautiful is good." (X))
RELATIONAL MODEL CONCEPTS
Relational Model Concepts: "Informal" Definitions
Relation
: "sets"를 기반으로 한 수학적인 개념 (set: element간 중복이 없는 집합), relational model에서 database => a collection of relations
-
relation은 값들의 table(informal) 또는 records의 flat file처럼 보인다.

-
relation은 일반적으로 rows(informal)들의 set을 포함한다.
- 각 row의 data elements는 entity or relationship에 상응하는 facts를 표현
- formal model에서는 row를 tuple이라고 한다.
-
각 column은 해당 column에 저장되는 data items의 의미를 전달하는 column header(informal)를 가진다.
- formal model에서는 column을 attribute라고 한다.
Formal Informal Relation Table Tuple Row Attribute Column header
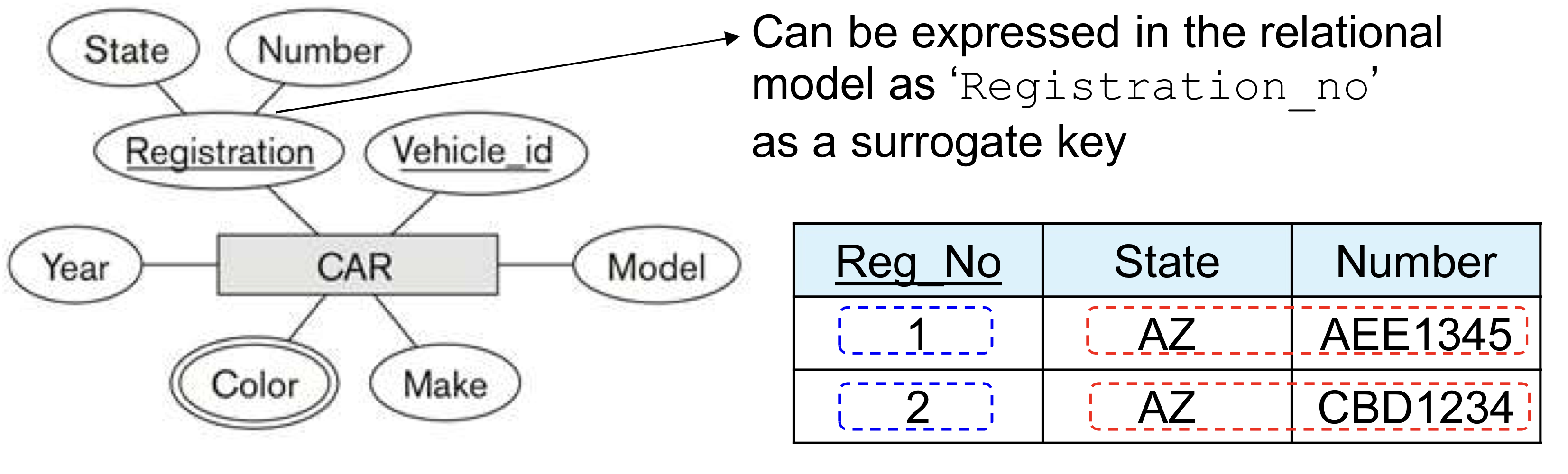
Key of a relation (Most Important)
: 각 row는 table에 존재하는 row를 유일하게 구분하는 data "element"의 값을 가지고, 이를 "key"라고 한다.
- STUDENT table의 key attribute는 ? Student_Number (Name 또한 중복이 없다면 key 가능)
- 가끔 row_id나 sequential number가 key로 사용될 수 있는데, 이를 surrogate (or artificial) key라고 한다. table 안에서 row를 식별하기 위한 간단한 용도이다.
- 여기서 알 수 있는 점은, Key attribute라고 하여 무조건 의미가 있는 attribute를 사용하는 것은 아니다.
Relational Model Concepts: "Formal" Definitions - Schema
relation의 schema
: relation을 묘사하기 위해 로 표기
- : relation name
: list of attributes - relation 의 degree (or arity): 의 attributes의 수
Example:
CUSTOMER (Cust-id, Cust-name, Addr, Phone#)
- What's the relation name? Customer
- Defined over the four attributes: what? (Cust-id, Cust-name, Addr, Phone#)
- What's the degree of relation? 4
Domain
: 각 attributes는 valid values 집합의 domain을 가진다.
- E.g., Cust-id의 domain: 6 digit numbers -> 6자리 숫자만을 취급
(C.f. unsigned int의 domain: (0 ~ )) -> not negative
Relational Model Concepts: "Formal" Definitions - Tuple
Tuple
: relation schema를 따르고 있는 instance로, 값들의 ordered set. ('<...>' 로 표기)
tuple의 각 값들은 appropriate domain(schema의 attribute가 가지는 domain)으로부터 나온다.
CUSTOMER relation(table)의 tuple(row)는 다음과 같다
: <632895, "홍길동", "대구 북구 대학로 80 IT-5 41566", "053-950-6372">
4개의 attribute(=relation degree)를 가지고 있어서 4-tuple이라고 부른다.
relation은 tuple들의 set

Relational Model Concepts: "Formal" Definitions - Domain
Domain
:atomic(indivisible)한 values의 set
- logical definition or name을 가진다.
- E.g., "Korea_cell_phone_numbers"는 일반적으로 11 digit phone numbers의 집합으로 나타나고, 01로 시작하고, 한국에서 유효하다.
- 정의된 data type or data format을 가진다.
- Ex1) "Korea_cell_phone_numbers"는 (01X)-dddd-dddd 형식을 따른다.
- Ex2) Dates는 year, month, date에 대해 yyyy-mm-dd, or dd/mm/yyyy 등 여러 형식을 가진다.
attribute name
: relation에서 domain을 알려주는 역할을 한다.
- attribute에 해당하는 data elements의 의미를 해석하는데 사용된다. 따라서 구체적인 attribute name을 지정해야 한다.
- E.g., domain Date는 "Invoice-date" or "Payment-date"와 같은 서로 다른 의미를 정의하는데 사용될 수 있다.
Relational Model Concepts: "Formal" Definitions - State
relation state
: 해당 attributes의 domain의 Cartesian product의 부분집합, 쉽게 말해서, attribute들의 domain을 만족하는 모든 value들의 집합은 relation에 저장 가능하고 이를 relation state라고 한다.
Catersian Product ?
all possible combinations of values
- 각 domain은 attribute로 저장할 수 있는 모든 가능한 값들을 포함하고 있다.
- Ex1) "Cust-name" attribute:
dom(Cust-name): varchar(30) -> 최대 길이가 30(byte)까지 가능한 문자열 - Ex2) "Cust-id" attribute:
dom(Cust-id): int -> 4-byte 정수
- Ex1) "Cust-name" attribute:
Relational Model Concepts: "Formal" Definitions - Summary
- Given a relation
- -> state 의미
- : relation의 schema
- : relation의 name
- : relation의 attributes
- : relation 의 특정 state
- 에 존재하는 tuples의 set
- , 는 n-tuple
- , 각 는 의 element
- 아래에서 다루겠지만, tuple의 순서는 중요하지 않지만, attribute의 순서는 중요하다.
Relational Model Concepts: Formal Definitions - Example
relation
: 가능한 모든 combinations은
relation state
: relation state
or
Example
- 인 경우, 이는 가능한 relation state 중 하나이고, 은 4개의 2-tuple을 가진다. (attribute가 2개이므로 2-tuple)
Relational Model Concepts
Definition Summary
RELATIONAL MODEL CONSTRAINTS AND RELATIONAL DATABASE SCHEMAS

"Characteristics" of Relations
Ordering of tuples in a relation:
- tuples는 정렬의 대상이 아니다.
- tuple ordering은 relation definition의 부분이 아니다. relation은 logical/abstract level에서 facts를 표현하려고 하기 때문이다.
- 따라서 tuples의 순서가 바뀌더라도 같은 정보를 의미한다.
Ordering of attributes in a relation schema
- 의 attributes -> tuple or 에서 attribute의 순서는 지켜져야 한다.
- relation의 definition에 의해, n-tuple은 n values의 정렬된 list 형태이다. (relation의 정의에 ordering이 포함되므로, 순서는 무조건 지켜져야 한다.)
- C.f. 하지만 더 general한 definition에서는 no order가 존재하기도 하는데, 이는 각각의 attributes가 name과 value의 pair로서 값을 가진다.

-위의 두 tuple은 identical한데, 이는 relation의 정의에 ordering이 포함되지 않기 때문이다. - 또한 이러한 tuples는 name과 value가 함께 존재하기 때문에 "self-describing"이라고 한다.
- C.f. 하지만 더 general한 definition에서는 no order가 존재하기도 하는데, 이는 각각의 attributes가 name과 value의 pair로서 값을 가진다.
Values in a tuple:
모든 values는 atomic해야 한다.
- Composite & multi-valued attributes는 받아들여지지 않는다.
- 나중에 나올 개념인 first normal form assumption에 기반을 둔 flat relational model이라고 칭한다.
- Composite attributes => simple attributes, Multi-valued attributes => separate relations로 ER model mapping된다.

각 tuple의 value는 해당 column에 해당하는 attribute의 domain
으로부터 나와야한다.
가 의 relation state 의 tuple인 경우
- 각 는 로부터 나온 값이어야 한다.
NULL values in certain tuples
- 아래의 값을 표현하기 위해 사용
- Unknown (아직 모르는 경우)
- Not available (아직 해당 정보가 없는 경우)
- Inapplicable (적용이 되지 않는 경우, ex) 성별에 따라 신체검사 항목이 다르다. 어떤 경우는 적용하지 않을 수 있다.)
- E.g., '김아무개' -> 'Gender'(Unknown에 해당), 'Fax_Number'(Not available에 해당), 'State'(Inapplicable에 해당)
Notation:
- : relation 의 attribute name (e.g., STUDENT.Name)
- 특정 relation 안에서 모든 attribute의 이름은 달라야 한다.
- tuple t의 component values는 or 로 표기
- tuple t의 attribute 의 값인 를 의미
- : attributes 의 값을 포함하고 있는 t의 subtuple을 의미한다.
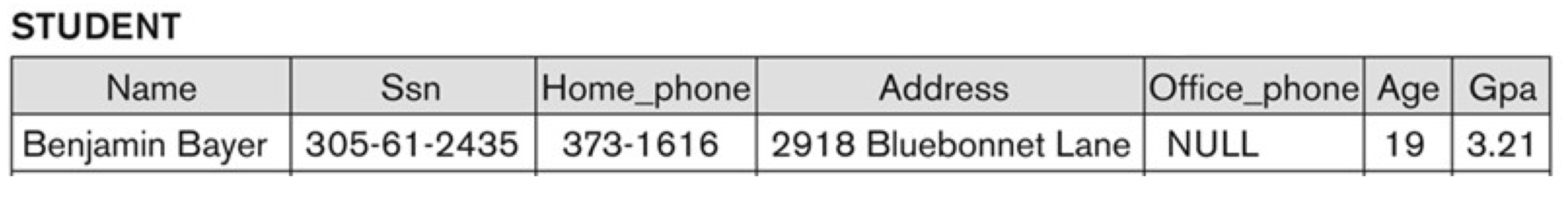
- t[Name] = Benjamin Bayer, t[Ssn, Gpa, Age] = <305-61-2435, 3.21, 19>
RELATIONAL MODEL COSTRAINTS AND RELATIONAL DATABASE SCHEMAS
Constraints (제약조건)
- DB의 일관성, 무결성을 유지하기 위해 사용되는 조건으로 DB에 저장되는 값들에 대한 filter와 비슷한 역할을 수행한다.
- i) 어떤 값들이 허용되는지, ii) 어떤 값들이 DB에 들어올 수 없는지를 결정
- 3 main categories
- 1: Inherent or implicit constraints
- data model 자체에 기반을 둠
E.g., relation model은 어떤 attribute도 값들이 list형태로 들어오는 것을 허용하지 않는다. ({1,2,3,4,5,6}의 list를 value로 저장하지 않는다. atomic한 형태로 분해해서 전달해야 한다.)
- data model 자체에 기반을 둠
- 2: Schema-based or explicit constraints
- data model schema에 직접적으로 표현: e.g., unique constraint C.f., total/participation or min/max cardinality ratio in ER Model
- 3: Application-based or semantic constraints (or business rules)
- application programs에서 제약해야하는 조건으로, data model에서는 기술할 수 없다.
- E.g., if age > 65 and hours > 40, then total wages must be doubled. (Data model 자체에서는 표현을 할 수 없기에 application 내에서 처리해야 한다)
- application programs에서 제약해야하는 조건으로, data model에서는 기술할 수 없다.
- 1: Inherent or implicit constraints
Category 2: Relational Integrity Constraints
integrity: 흠, 결함이 없음, 즉 정확한 data를 가지고 있음을 의미
Constraints는 모든 유효한 relation states에서 예외 없이 지켜져야 하는 conditions이다.
- Main types of constraints in the relational data model:
1) Key constraints (키 제약조건): Unique constraints (유일 제약조건)
- key attribute를 가지는 tuple들은 절대로 중복될 수 없다. (key value의 중복 불가)
2) Entity integrity constraints (개체 무결성 제약조건)
- Primary key value는 NULL 불가
3) Referential integrity constraints (참조 무결성 제약조건)
- foreign key는 참조하는 relation의 primary key를 참조해야 한다. 그리고 참조하는 tuple이 존재해야 한다 (FK가 참조하는 PK와 상관없는 값을 가지면 안된다.) - 추가적으로, domain constraint (도메인 제약조건)
- tuple의 모든 value는 해당 attribute의 domain으로부터 나온 값이어야 한다.
- attribute가 허용한다면, NULL값 또한 가능하다.
C2-1) Key Constraints
- definition에 의거해, relation안의 모든 tuple들은 distinct해야 한다.
- relation이 tuple들의 "set"이기 때문. (same element가 없다는 의미)
- relation 의 Superkey (한 relation 내에 있는 속성들의 집합으로 구성된 key)
- 의 attributes의 subset인 SK는 아래의 조건을 따라야 한다:
- uniqueness property: 어떠한 유효한 relation state 에 있는 2개의 tuple도 동일한 SK 값을 가질 수 없다. (쉽게 말해 적어도 이 SK에 대해서는 2개 이상의 tuple도 중복되어서는 안된다.)
- 에 있는 distinct한 tuple 에 대해,
- uniqueness property: 어떠한 유효한 relation state 에 있는 2개의 tuple도 동일한 SK 값을 가질 수 없다. (쉽게 말해 적어도 이 SK에 대해서는 2개 이상의 tuple도 중복되어서는 안된다.)
- 의 attributes의 subset인 SK는 아래의 조건을 따라야 한다:
- relatoin 의 Key
- "minimal" superkey
- 즉, key가 superkey K일때, K에서 어떤 attribute를 제거하면 더이상 superkey가 되지 않는다. => 해당 relation의 tuple들을 유일하게 식별하지 못하게 됨
- 이해를 돕기 위한 link
- superkey만으로 다른 모든 tuples를 구분할 수 있지만, superkey를 구성하는 어떤 attribute는 다른 tuple과 중복된 값을 가질 수도 있다. 하지만 key의 경우는 그럴 수 없다 ?
[Q] Is a superkey a key?
- 틀렸다. superkey에 unique하지 않은 attribute가 포함되어 있을 수도 있다.
Example: Consider the CAR relation schema
- CAR (State, Reg#, VIN, Make, Model, Year)
- [Q] CAR has two superkeys. what are they?
- SKey1 = {State, Reg#} -> {AZ, 6280}
- SKey2 = {VIN} -> {VW12345}
- [Q] Is {VIN, Make} a key, a superkey, or both?
- [Q] Is {State, Reg#} a key, a superkey, or both?
In general:
- 어떠한 key든 superkey가 된다. (하지만 그 반대는 불가능)
- key를 포함하고 있는 attributes의 어떤 set이든 superkey가 된다.
- 모든 tuple들을 유일하게 식별할 수 있게 해줌 (key), 다른 추가적인 attribute가 있다해도 이미 존재하는 attribute set과 같은 값을 갖지 않는다 (따라서 superkey)
- minimal superkey 또한 key이다.
- relation schema는 여러 개의 key를 가질 수 있고, 이 key들을 candidate key( or secondary key)라고 한다. 그리고 이 중 임의로 하나를 선택해 (또는 attribute의 size가 가장 작은 하나를 선택해) primary key라고 한다.
KEY attribute + Attribute => Superkey
Ex) CAR (State, Reg#, VIN, Make, Model, Year)
- VIN: primary key attribute로 선택하는데, 이유는 SK1은 2개의 attribute를 갖고, SK2는 1개의 attribute로 구성되어 있기 때문
- primary key attribute가 아닌 다른 candidate keys는 unique keys로 기술된다.
primary key value는 아래 경우에서 사용된다:
- relation에서 각 tuple을 unique하게 식별하는 경우 (tuple identity 제공)
- 한 tuple에서 다른 tuple을 참조하는 경우; referencing relation에서 foreign key로 표현
General rule about key:
- candidate key 중 attributes의 수가 가장 작은 것을 primary key로 선택 (항상 그렇지 않을 수도 있다.)
Relational Database Schema
relational database schema란 무엇인가 ?
- 동일한 database에 있는 relation schemas S의 set
- S: 전체 database schema의 name
- S = 이고, Integrity Constraints(ICs)의 set
- IC: database의 일관성과 무결성을 보존하기 위해 지켜져야 하는 제약조건
- Key, Not-Null, domain, and two other types
- IC: database의 일관성과 무결성을 보존하기 위해 지켜져야 하는 제약조건
- 는 database S에 있는 relation schema 각각의 이름이다.
A Refined ER Schema for the COMPANY Database

Schema Diagram for the COMPANY Relational Database Schema

Relational Database State
S의 relational database state DB의 정의
- relation states의 set, 는 아래를 만족
- 각 는 의 state
- relation state는 IC에 명시된 integrity constraints를 만족한다.
- relational database state는 relational database snapshot (or instance)라고도 한다. (하지만 instance라는 용어는 single tuples에도 적용되기에, 사용하지 않도록 한다)
- snapshot을 찍는 것처럼 특정 시점의 상태를 보여주기 때문에 이와 같이 칭함
- constraints를 만족하지 않는 database state는 invalid하다고 한다.
Populated Database State
- 각 relation은 현재 relation state에 있는 여러 개의 tuple들을 가질 것이다.
- relational database state는 모든 개별 relation states의 합집합이다.
- database가 변경되면 (i.e., tuple이 수정, 삽입, 삭제되는 경우), 새로운 state가 생성된다.
- relational database를 변경시키는 기본 operations:
- INSERT: relation에 새로운 tuple 생성
- DELETE: relation에 있는 기존 tuple을 삭제
- MODIFY or UPDATE: 기존 tuple의 attribute를 변경
A Possible DB State for COMPANY


C2-2) Entity Integrity Constraint
개체 무결성 제약조건
database schema에 존재하는 각 relation schema R의 primary key attributes인 PK는 어떠한 tuple에서도 NULL 값을 가질 수 없다.
-> 유일성을 잃어버리지 않기 위해서
- primary key value는 NULL 값이 될 수 없다.
- for any tuple in
- PK가 여러 attributes를 포함하는 경우, 그 중 어느 하나도 NULL이 되어선 안됨
- primary key values는 개별 tuple을 식별하기 위해 사용하는데, 이 값이 NULL이 되면 어느 tuple들을 distinct하게 식별할 지 알 수 없음
- non-PK attribute에 대해서는 NULL 값이 할당될 수도 있음
Referential Integrity Constraint (1/3)
참조 무결성 제약조건
두 relations가 관련된 제약조건 (다른 2개의 constraint는 1개의 relation에 해당)
- 두 relations에 있는 tuples간의 일관성을 유지하기 위해 사용된다.
- E.g. Dno of EMPLOYEE
모든 EMPLOYEE tuple에 있는 Dno값은 DEPARTMENT relation에 있는 tuple들의 Dnumber값과 매치되어야 한다.
- E.g. Dno of EMPLOYEE
- 2개의 relations에 있는 tuples간의 relationship을 표현하기 위해 사용
- referecing relation: EMPLOYEE
- referenced relation: DEPARTMENT
Referential Integrity Constraint (2/3)
- referencing relation 에 존재하는 tuples은 FK(=foreign key attribute) attribute를 가지고, 이는 referenced relation 의 primary attribute인 PK를 참조한다.
- 이면, 에 있는 tuple은 에 있는 를 참조한다. ( -> referencing, -> referenced)
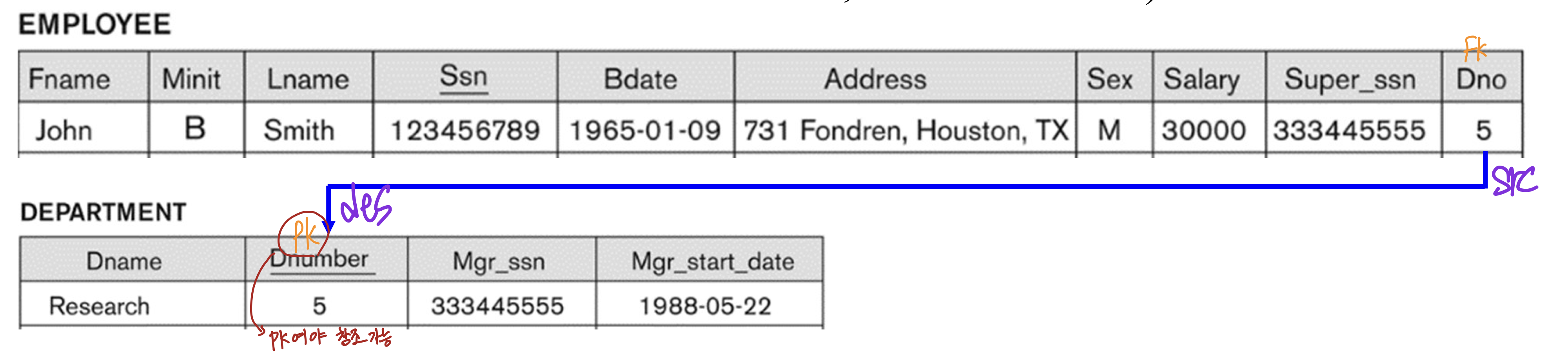
Referential Integrity Constraint (3/3)
- referencing relation 에 있는 foreign key attribute인 FK는, 아래 두 가지 값을 가질 수 있다.
1) : 즉, referenced relation 에 있는 기존의 primary key value (PK에 해당하는 값이 존재해야 함)
2) 또는, NULL - FK가 null인 경우, 에 있는 FK는 PK에 속해서는 안된다.
- PK는 NULL일 수 없다는 Entity integrity constraint를 위반하기 때문이다.
Example: Referential Integrity Constraints for COMPANY

- EMPLOYEE의 Super_ssn은 FK이지만, EMPLOYEE의 PK에 속하지 않기에, null값이 가능하다.
C3) Other Types of Constraints
Semantic Integrity Costraints:
- Application semantics에 기반하여 application programs단에서 기술
- data model 자체에서는 표현할 수 없다.
- Example: "The max number of hours per employee for all projects that one works is limited up to 52 hours per week." -> 어떻게 model에서 이를 구현 ?
- general-purpose constraint specification language를 사용하여 기술할 수 도 있다.
CREATE TRIGGER&CREATE ASSERTION문으로 triggers와 assertions을 생성 가능 (제약조건 생성)
CREATE TABLE문으로 아래의 것들을 정의할 수 있다.- keys(primary key), candidate keys(unique constraint), NOT NULL, entity integrity, foreign keys, referential integrity 등..
UPDATE OPERATIONS AND DEALING WITH CONSTRAINT VIOLATIONS
"Update" Operations on Relations
- (1) INSERT, (2) DELETE, or (3) MODIFY(UPDATE) tuple
- 언제든 이러한 operations가 적용될때, relational DB에서 어떠한 integrity constraints도 위반되어선 안된다.
- 몇 update operations는 그룹으로 묶어서 수행될 수도 있다.
- Updates는 자동적으로 다른 update를 유도할 수도 있다.
- integrity constraints를 유지하기 위해서 필요할 수도 있다.
- E.g., 새로운 employee가 들어오면, employees의 total number는 하나 증가한다.
- integrity violation이 발생하는 경우, 몇 actions가 발생할 수 있다:
1) violation을 발생시키는 operation cancel
- RESTRICT(no action) or REJECT option; 많은 DBMSes가 취하는 방식
2) operation을 수행하고, 사용자에게 violation을 알림
- consistency가 이미 깨져버리므로 대부분의 DBMSes는 사용하지 않는 방식
3) 추가적인 updates를 trigger하여, violation이 고쳐지도록 함
- CASCADE(갱신 전파), SET NULL, or SET DEFAULT option:
referencing으로부터 referenced로
4) user-specified error-correction routine을 실행
Possible Violation Cases for INSERT Operation


- Insert into EMPLOYEE <‘Cecillia’, ‘F’, ‘Kolonsky’, NULL, ‘1960-04-05’, ‘6357 Windy Lane, Katy, TX’, ‘F’, 28000, NULL, 4>
- primary key인 Ssn에 NULL값을 insert하려고 하여, Entity integrity constraint가 위반
- Insert <‘Alicia’, ‘J’, ‘Zelaya’, ‘999887777’, ‘1960-04-05’, ‘6357 Windy Lane, Katy, TX’, ‘F’, 28000, ‘987654321’, 4> into EMPLOYEE
- primary key인 Ssn이 중복되어 Key constraint가 위반
- Insert <‘Cecilia’, ‘F’, ‘Kolonsky’, ‘677678989’, ‘1960-04-05’, ‘6357 Wind, Katy, TX’, F, 28000, ‘987654321’, 7> into EMPLOYEE
- EMPLOYEE의 FK인 Dno에 존재하지 않는 DEPARTMENT의 PK를 insert하려고 하여, referential integrity constraint가 위반
- 또한, domain constraint도 위반될 수 있음
Possible Violation Cases for DELETE Operation

- Delete the WORKS_ON tuple with Essn = ‘999887777’ and Pno = 10
- Delete the EMPLOYEE tuple with Ssn = ‘999887777’
- 2options:
1) 많은 tuples이 해당 tuple을 referencing하고 있기에 operation reject, or
2) 해당 tuple을 삭제하고, WORKS_ON으로 deletion을 전파
- 2options:
- Delete the EMPLOYEE tuple with Ssn = ‘333445555’
- 많은 tuples가 영향을 받을 것
Possible Violation Cases for DELETE Operation: Summary
- DELETE는 referential integrity constraint만 위반할 수 있다.
- 이유는 삭제될 tuple은 foreign key로 database에 있는 다른 tuple을 "참조"하고 있기 때문
1) RESTRICT option: deletion reject
2) CASCADE option: 삭제될 tuple에 대한 삭제를 수행하고, 이를 참조하고 있는 tuple 또한 삭제 (be carefully!)
3) SET NULL or SET DEFAULT option: 해당 tuple을 참조하고 있는 tuple의 FK를 NULL or DEFAULT 값으로 지정
- 이유는 삭제될 tuple은 foreign key로 database에 있는 다른 tuple을 "참조"하고 있기 때문
- foreign key constraint를 위해, 위의 options 중 하나를 선택해 logical database design동안 명시해줘야 한다
- Ex) In SQL,
CREATE TABLE products ( p_id numeric(10) not null, s_id numeric(10) not null, FOREIGN KEY (s_id) REFERENCES supplier(s_id ON DELETE CASCADE );- PRODUCT table의 s_id는 supplier의 s_id를 참조하고, SUPPLIER s_id가 1인 tuple이 있는데, 해당 tuple이 삭제되면 s_id=1을 참조하는 PRODUCT의 tuple 또한 삭제
- Ex) In SQL,
Possible Violation Cases for UPDATE Operation
- Update the salary of the EMPLOYEE tuple with Ssn = ‘999887777’ and 28000
- Update the Dno of the EMPLOYEE tuple with Ssn = ‘999887777’ to 7
- DEPARTMENT relation에 Dnumber가 7인 tuple이 없음 -> referential integrity constraint를 위반
- Update the Ssn of the EMPLOYEE tuple with Ssn = ‘999887777’ to ‘987654321’
- Ssn값이 중복됨 -> Key constraint가 위반
Possible Violation Cases for UPDATE Operation: Summary
- UPDATE는 attribute를 변경하면서 (i) domain constraint(attribute의 값은 반드시 atomic)와 (ii) NOT NULL constraint를 위반할 수도 있다.
- 또다른 constraints 또한 update동안 위반될 수 있다.
- update될 attribute가 Primary key attribute인 경우,
- 한 tuple을 delete하고, 새로운 tuple을 insert하는 것과 비슷하게 동작
- 처리를 위해서는, DELETE operation과 비슷한 options이 필요
- 한 tuple을 delete하고, 새로운 tuple을 insert하는 것과 비슷하게 동작
- update될 attribute가 foreign key attribute인 경우,
- referential integrity constraint가 위반될 가능성이 높다
- 처리를 위해서는, DELETE operation과 비슷한 options이 필요
- referential integrity constraint가 위반될 가능성이 높다
- update될 attribute가 PK와 FK attribute 모두가 아닌 경우,
- domain constraints or NOT NULL constraints만 위반될 수 있다.
- 그냥 reject!
- domain constraints or NOT NULL constraints만 위반될 수 있다.
- update될 attribute가 Primary key attribute인 경우,
Transaction Concept(compared to a query)
- Transaction: atomically하게 수행되어야 할 database operations의 series 포함
- OLTP(Online Transaction Processing) 시스템에서 relational database에 대해 실행되는 많은 commercial applications이 초당 수백 또는 수천에 달하는 속도로 transaction을 실행
