ER MODEL
Conceptual Data Model
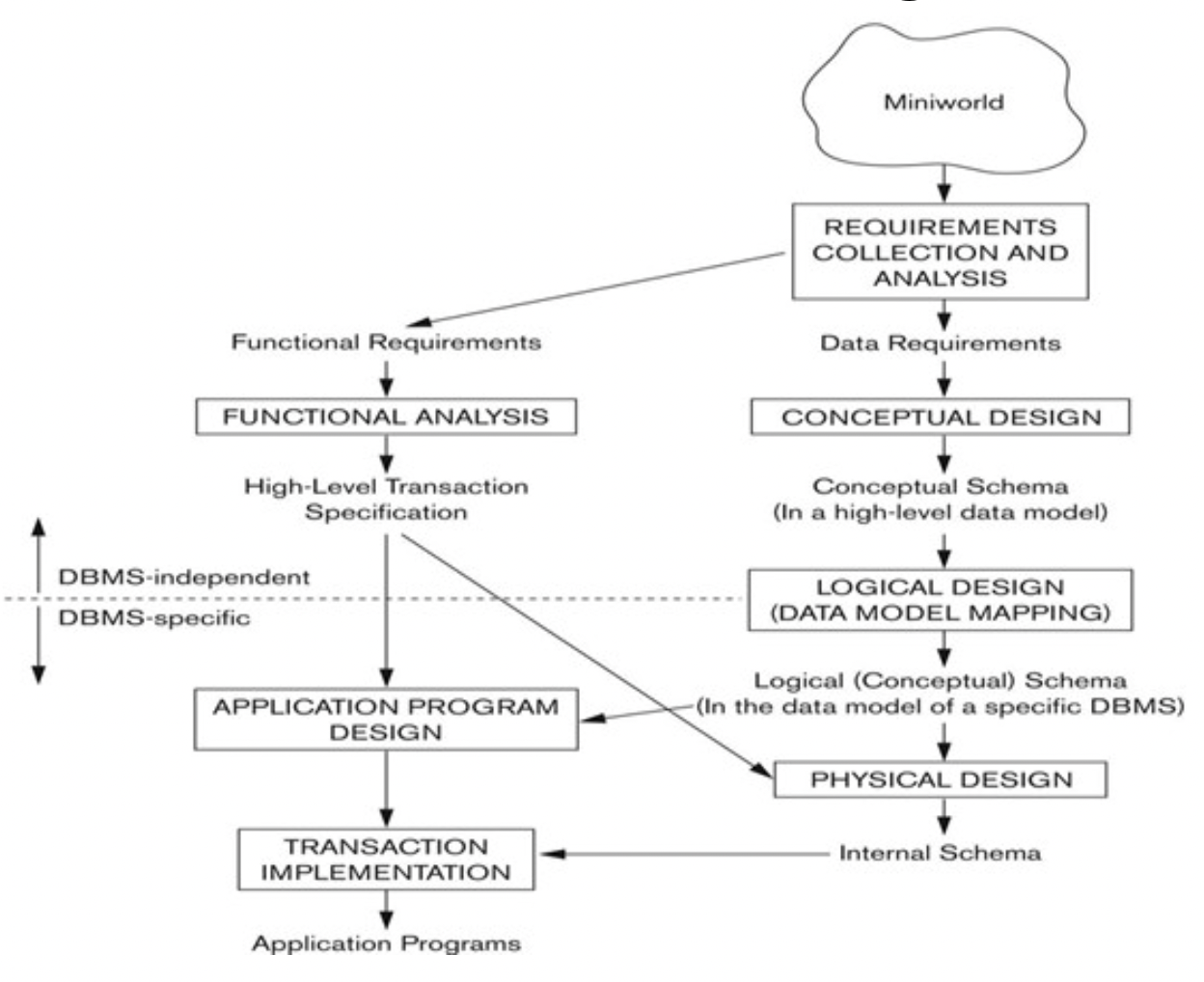
Overview of Database Design Process
Database application
Includes two main activities: applications design & database design
Application design
- DB에 접근하는 programs and interfaces에 초점
Database design
- Conceptual=> DB application의 conceptual schema를 디자인하기 위함 (external)
- Logical
- Physical (internal)
A Simplified Overview of Database Design Process
STEPS
- Requirements collection and analysis (DB 설계)
- Functional/Data requirements
- Conceptual design
- Conceptual schema
- Logical design(or data model mapping)
- Logical schema
- DBMS마다의 DDL을 사용하기에 DBMS마다 달라짐
- Physical design
- Internal schema: internal storage structures, file organizations, indexes, access paths, and parameters for database files
ENTITY TYPES, ENTITY SETS, ATTRIBUTES, AND KEYS
Concepts: Entites & Attributes
- Entity-Relationship (ER) model는 data를 "Entites", "Relationships", "Attributes"로 표현
Entity(s)
- ER model의 기본 concept
- DB에 표현되는 구체적인 things 또는 objects 의미
Attribute(s)
- entity를 구체적으로 기술하기 위한 특성
- entity는 해당 attributes에 대한 특정 값을 가진다.
- 각 attribute는 value set(or data type)를 가진다.
- E.g. integer, string, date, enumerated type...
Types of Attributes(1/3)
Simple(atomic)
- 각 entity는 attribute에 대한 single atomic value(원자값)을 가진다.
- E.g. SSN, Sex
Composite (합성)
- attribute는 몇 개의 components로 결합될 수 있다.
- E.g., Address(Apt#, Room#, Street, City, State, ZipCode, Country), or Name(FirstName, LastName)
- Composition은 "composite"한 몇몇 components와 계층구조를 이룰 수도 있다.
Multi-valued (다중 값)
- entity는 해당 attribute에 대해 여러 개의 values를 가질 수도 있다.
- E.g. Car entity의 "Color" attribute (차가 여러 색을 가질 수도 있음), STUDENT entity의 "PreviousDegrees" attribute (이전 학위는 석사, 학사일 수 있음)
- 위와 같은 multi-valued attributes는 ER에서 {Color}, {PreviousDegrees}로 표현
Types of Attributes(2/3)
- Composite & Multi-valued attributes는 극히 드물게 임의적인 수준의 레벨로 중첩될 수 있다. 아래의 예시로 이해할 수 있을 것
- E.g {PreviousDegrees(College, Year, Degree, Field)}
- {}: Multi-valued, (): Composite
Types of Attributes(3/3)
Stored attributes vs. Derived attributes
- Stored attribute: value가 저장된 attribute
- Derived attribute: 이미 저장된 attribute로부터 값이 파생될 수 있는 attribute
- Birth_data vs. Age -> 생년월일을 알면 Age를 도출할 수 있음
- Number_of_employees of a DEPARTMENT entity -> 해당 DEPARTMENT에 속한 EMPLOYEE의 수를 세면 도출할 수 있음
Complex attributes
- Composite attributes & Multi-valued attributes의 Mixed attributes
- Address_phone
{Address_phone({Phone(Area_code, Phone_number)}, Address(Street_address(Number, Street, Apartment_number), City, State, Zip))} - Q: How many composite attributes in the above complex attribute, Address_phone?
Phone, Address, Street_address
- Address_phone
Entity Types and Entity Sets
Entity type (intension)
- 기본 attributes가 동일한 entities의 type (like schema)
- ER digrams에서는 rectangle box에 표현
- E.g. EMPLOYEE, COMPANY
Entity set (extension)
- DB에 존재하고 있는 특정 entity type의 특정 시점에서의 all entites의 collection (like state)
- E.g. EMPLOYEE: e1, e2, ...

Key Attributes of an Entity Type
Key attribute (키 속성)
- 유일한 식별자이고, entity당 one or more key attribute를 가질 수 있다.
- 각 entity가 unique한 값을 가져야 하고, uniquely identified될 수 있도록 하는 entity type의 attribute
- E.g. SSN of EMPLOYEE, Student_number of STUDENT
Value Sets (Domains) of Attributes
- 각 simple attribute는 value set (or domain of values) 와 관련있다.
- Domain가 다르면 해당 attribute로 저장되지 않는다.
- Date는 MM-DD-YYYY 형식을 포함하는 값이어야 한다.
- value set은 각 entity에 대한 attribute에 연관된 values of set을 지정
- Value sets는 대부분의 programming languages에서의 data types과 비슷
Notation and Example for Entity & Attribute in Entity-Relationship (ER) Diagrams

INITIAL CONCEPTUAL DESIGN OF A DATABASE
Requirements (1/2)
- Company는 (multiple) DEPARTMENTs로 구성되어 있다.
- 각 department는 unique name, unique number를 가지고, department를 관리하는 특정 employee도 가진다.
- department는 PROJECTs를 관리한다.
- 각 project는 unique name, unique number, single location 정보를 가진다.
Requirements (2/2)
- 각 EMPLOYEE는 아래의 attributes를 가진다:
- name, Social Security Number(SSN: 주민번호), address, salary, sex, and birth date
- 각 employee는 한 개의 department에 works for하지만, 몇몇 개의 projects에 works on할 수도 있다.
- 각 employee는 여러 명의 DEPENDENTs(부양가족)을 가질 수 있다.
- 각 dependent는 first name, sex, birth date, and employee에 대한 relationship 정보를 가진다.
Initial Conceptual Design of Entity Types for the COMPANY Database Schema
- 앞서 언급한 requirements에 기반하여 아래 4개의 initial entity types를 정의할 수 있다.
- DEPARTMENT
- Name(key), Number(key), Locations(Multivalued), Manager, and Manager_start_date attribute를 가짐
- PROJECT
- Name(key), Number(key), Location, Controlling_department attribute를 가짐
- EMPLOYEE
- Name(composite), Ssn(key), Address(simple), Salary, Birth_date, Department, and Supervisor attribute를 가짐
- DEPENDENT
- Employee(composite), Dependent_name(key), Sex(simple), Birth_date, and Relationship(to the employee)
아래는 4개의 Entity types에 대한 Design이다.

RELATIONSHIP TYPES, RELATIONSHIP SETS, ROLES, AND STRUCTURAL CONSTRAINTS
Relationships, Relationship Types, Relationship Sets, Instances, Degree of a Relationship Type
A relationship (관계)
- 두 개 또는 그 이상의 distinct한 entities들이 구체적인 의미로 relate되어 있는 것
- Ex1) EMPLOYEE 홍길동 works on the SpaceX PROJECT.
- Ex2) EMPLOYEE 안철수 works for the H&R DEPARTMENT.
A relationshipe type R (관계 유형)
- n entity types로부터의 entities간의 associations의 type
- relationship type의 degree: 관계에 참여하는 (distinct) entity types의 수
- WORKS_ON and WORKS_FOR의 Degree?
- ex) Unary(1) (for self), Binary (2) (involving two), Tertiary (about three), ...
- WORKS_ON and WORKS_FOR의 Degree?
n entity types간의 relationship set R (관계 집합)
- relationship instances 의 set에 대해,
- 각 는 n개의 개별 entities에 연관되고,
- 에 있는 각 entity 는 set의 멤버이다. ()
Degree of a Relationship Type

Relationship Type vs. Relationship Set

Role Name
- 관계에서 가지는 역할(관계의 의미)로, 참여한 Entity에 부여됨
- 모든 참여 entity types가 distinct한 경우, 필요하지 않다. (entity type name = role name) -> 하나에만 참여하는 경우
- 하지만 하나의 entity type이 하나 이상의 relationship type에 다른 역할들로 참여하는 경우에는 role name의 명시가 필요해진다.
Recursive Relationship (or Self-Referencing Relationships)

- 참여하는 두 entity는 서로 다른 역할을 하는 동일한 entity type
- 1)EMPLOYEE와 2)EMPLOYEE 간의 SUPERVISION relationships
1): supervisor or boss의 역할
2): worker or subordinate의 역할 - 위 그림에서 1은 supervisor role을 의미하고, 2는 supervisee role을 의미
Structural Constraints on Binary Relationship Types (이진 관계 유형의 구조적 제약조건)
Scenarios
- "모든 employee는 정확하게 1개의 department에만 work for해야 한다."
- "몇 명의 employee는 그들의 department를 관리한다."
1) Cardinality ratio (of a binary relationship)
- entity가 참여하는 relationship instances의 최대 숫자를 명시 e.g., 1:1, 1:N, N:1, M:N
- 1:N

- 1:N
Relationship Instances of the MANAGES 1:1 Relationship between EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT

Relationship Instances of the WORKS_ON M:N Relationship between EMPLOYEE and PROJECT

Relationship Instances of the WORKS_FOR 1:N Relationship between DEPARTMENT and EMPLOYEE

- employee는 1개의 department에만 works_for하지만, department입장에서는 1개의 department에 N개의 employee가 works_for할 수 있음
2) Participation constraint (on each participating entity type)
- 어떤 relation type에 대해 어떤 entity가 존재하기 위해서는, 또 다른 entity와 (전체적 또는 부분적으로) 관계되어야 한다.
- 참여할 수 있는 relationship instances의 최소 숫자 (cardinality ratio는 최대 숫자)
- "Every employee must work for ad department."
- employee entities의 total set에 있는 모든 entity는 WORKS_FOR를 통해 department에 관계되어야 함.
- "Every employee doesn't have to manage a department."
- employee entities 중 몇 명만 MANAGE를 통해 몇 개의 department에 관계되어야 함.
- Total participation (Called existence dependency)
- entity들의 instance가 모두 참여
- ER diagram에서 double line으로 표현
- Partial participation (by default)
- entity들의 instance 중 일부가 참여
- ER diagram에서 single line으로 표현
Attributes of Relationship Types
-
entity types와 비슷하게 relation types 또한 relationship attributes를 가질 수 있다.
- "How many hours per week (HoursPerWeek) Rachel work on the ECM project?"
- "When (Start_date) did Chandler start managing his department?"
-
대부분의 relationship attributes는 M:N relationships에서 사용된다.
-
1:N relationships에서, relationship attributes는 relationship에서 N-side에 있는 entity type으로 이동할 수 있다.
- e.g., WORKS_FOR 관계에서, Emp_start_date는 EMPLOYEE entity로 이동 가능
Q_? 1:1에서는 가능할까 ?
- 어느쪽으로든 가능하다.
WEAK ENTITY TYPES
- 이전까지는 Strong entity types에 대해서 배웠고, 여기서 다룰 weak entity type은 쉽게 말해 다른 entity가 존재해야 존재할 수 있는 entity type이라고 할 수 있다.
Concept
Weak Entity Types
: 자기 자신을 위한 key attribute를 가지지 않는 entity type
- child (or subordinate) entity type이라고도 불린다. (C.f. 앞에서 다룬 entity type은 regular (or strong) entity types)
Weak entity type entities
- 자기 자체로 존재가 불가능
- 또다른 entity type or parent(dominant, identifying, or owner) entity type의 특정 entities와 관계됨으로써 식별이 가능하다.
Q?
Weak entity type은 해당 entity type을 식별하는 relationship에 대해서 항상 partial vs. total participation 중 어떤 participation을 가질까 ?
- owner entity 없이는 식별할 수 없기에 total participation을 가진다.
Concept and Notation in ER
Weak entity type entities
- 아래의 combination으로 식별될 수 있다. (Weak key + Strong key)
- weak entity type의 partial key
- 같은 owner entity에 관계되어 있는 weak entities를 uniquely하게 식별할 수 있는 attribute를 사용
- 식별하는 relationship type에 관계된 parent entity
- 일반적으로, parent's id를 사용
- weak entity type의 partial key
- Notation in a ER diagram

REFINING THE ER DESIGN FOR THE COMPANY DATABASE
Recall the Initial Design of the Four Entity Types

Identifying Relationshiops between Entity Types
- Requirements를 통해 만들어낸 Binary relationships
- WORKS_FOR: EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
- MANAGES: EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
- CONTROLS: DEPARTMENT and PROJECT
- WORKS_ON: EMPLOYEE and PROJECT
- SUPERVISION: EMPLOYEE (as supervisor) and EMPLOYEE (as supervisee) -> Unary relationships가 아닌 이유 ?
- DEPENDENTS_OF: EMPLOYEE and DEPENDENT
Discussion of Relationship Types
- relationships에 참여하고 있는 동일 entity types 간 하나 이상의 relationship types가 존재할 수 있다.
- 서로 다른 의미 부여가 필요 (적절한 role name 부여 ?)
- C.f. MANAGES and WORKS_FOR (EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT 간 별개의 relationship types)
Additional Discussion on Relationship Structural Constraints
- Relationship type R에 참여하는 entity type E의 participation에 대한 constraints
- 각 entity e in E가 최소 min, 최대 max 만큼 relationship instances in R에 참여한다면, (min, max)로 명시
- Default (no Constraint): min = 0 (partial participation), max = n (no limit)
- Examples
- MANAGES relationship에서,
DEPARTMENT의 participation은 (1,1)
EMPLOYEE의 participation은 (0,1)- WORKS_FOR relationship에서,
EMPLOYEE의 participation은 (1,1)
DEPARTMENT의 participation은 (0,n)
- WORKS_FOR relationship에서,
- MANAGES relationship에서,
Notation for Relationships in ER Diagrams

Examples of Relationships in ER Diagrams

A Refined ER Schema for the COMPANY Database
Using the notation of cardinality ratio

Using the notation of (min, max) + role names

