alarm-timer
alarm-timer 프로젝트는 busy-waiting 상태에 있는 timer_sleep()함수를 개선해주는 프로젝트이다.
초기 timer_sleep()함수
void
timer_sleep (int64_t ticks) {
int64_t start = timer_ticks ();
ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_ON);
while (timer_elapsed (start) < ticks)
thread_yield ();
}timer_sleep()의 매개변수는 스레드를 얼마나 잠재울 것이냐는 의미로 tick을 받는다.
thread_yield ()함수에 대해 설명해주자면, 현재 실행중인 스레드를 ready_list의 맨 마지막에 넣어주고 ready_list의 맨 앞의 스레드를 깨워서 실행해주는 함수다.
timer_elapsed (start)함수는 start를 인자로 넣어주면 전체 시간에서 start만큼을 빼주기 때문에 timer_sleep()을 하고 시간이 얼마나 지났는지를 반환해준다.
결국 이 코드는 반복문을 돌면서 tick이 timer_elapsed (start)를 넘을때까지 ready_list에 스레드를 넣어주고 빼고를 해야하기 때문에 busy-waiting 현상이 일어난다.
개선한 timer_sleep()함수
void
timer_sleep (int64_t ticks) {
int64_t start = timer_ticks ();
ASSERT (intr_get_level () == INTR_ON);
if (timer_elapsed (start) < ticks)
thread_sleep (start + ticks);
}busy-waiting 현상이 일어난다는 것은 반목적으로 계속 확인해준다는 말이다. 따라서 반복문을 조건문으로 바꾸어주었고 thread_sleep라는 함수를 만들어 인자로 깨어날 시간을 넘겨주면 thread_sleep 함수는 sleep_list를 만들어서 sleep_list에 잠재울(현재) 스레드를 넣어주는 역할을 해준다.
추가한 thread_sleep()함수
void
thread_sleep (int64_t wakeup_tick) { //스레드를 재워주는 함수
struct thread *curr = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
if (curr == idle_thread) //현재 스레드가 아이들 스레드면 그냥 리턴
return;
old_level = intr_disable (); //슬립하는 도중에 인터럽트가 발생하면 안됨
curr->wakeup_tick = wakeup_tick; //스레드가 깨어날 시각을 매개변수값으로 설정.
list_insert_ordered(&sleep_list, &curr->elem, wakeup_tick_less_and_high_priority_first, NULL); //깨어날 시간 기준으로 정렬해주고 같다면 우선순위 기준으로 정렬
do_schedule(THREAD_BLOCKED); //현재 스레드의 상태를 block로 만들고 다음 스레드 실행
intr_set_level (old_level);
}지금까지는 스레드를 잠재울 경우에 대해 말해보았다. 스레드를 재웠으면 깨우는 부분도 있을 것이다.
그 부분이 timer_interrupt()함수라고 생각했다. 그 이유는 timer_interrupt함수가 스레드의 tick을 올려주는 부분이기 때문이다. 그래서 tick이 일정tick 이상 올라갔다면 sleep_list에 재웠던 스레드를 깨워두면된다.
초기 timer_interrupt() 함수
static void
timer_interrupt (struct intr_frame *args UNUSED) {
ticks++;
thread_tick ();
}개선한 timer_interrupt() 함수
static void
timer_interrupt (struct intr_frame *args UNUSED) {
ticks++;
thread_tick();
if(thread_can_wakeup(ticks))
thread_wakeup(ticks);
}timer_interrupt함수를 부를때마다 현재 tick이 일정량 이상 올라가면 sleep_list에서 스레드를 깨워주는 thread_wakeup()함수를 실행해 주었다. thread_can_wakeup()함수는 인자로 현재 tick값을 받고 그 tick값이 sleep_list의 맨 처음 스레드의 일어날시간을 넘어섰다면 true를 반환해준다. 맨 앞의 sleep_list의 맨 앞 값만 봐주는 이유는 sleep_list에 삽입해줄때 일어날시간을 기준으로 오름차순으로 삽입해 주었기 때문에 가능했다.
bool
thread_can_wakeup (int64_t curr_tick) {
if(list_empty(&sleep_list))
return false;
struct thread *first_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&sleep_list),struct thread, elem);
return curr_tick >= first_thread->wakeup_tick;
}추가한 thread_wakeup() 함수
void
thread_wakeup(int64_t cur_tick) {
if (list_empty(&sleep_list))
return;
struct thread *wakeup_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&sleep_list), struct thread, elem);
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable (); //깨우는 도중에 인터럽트가 발생하면 안됨
//sleep_list에 있는 스레드중에 깨어날 시간이 현재 시간보다 작은 스레드들을 깨워줌
while (wakeup_thread->wakeup_tick <= cur_tick && !list_empty(&sleep_list)) {
wakeup_thread->status = THREAD_READY; //깨울 스레드의 상태를 레디상태로 바꿔주고
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, list_pop_front (&sleep_list), high_priority_first, NULL); //레디 리스트에 넣는다.
wakeup_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&sleep_list), struct thread, elem);
}
intr_set_level (old_level);
}thread_wakeup함수는 매개변수로 현재 tick을 받는다. 그리고 sleep_list를 순회하면서 현재tick보다 작은 깨어날 시간을 가진 스레드를 ready_list로 넣어준다. 여기서 주의할 점은 sleep_list에서 빼서 ready_list에 넣는 순서다. 만약 위 코드대로 안하고 먼저 ready_list에 넣어준다면 ready_list와 sleep_list가 꼬일것이다.
틀린 thread_wakeup() 코드
★삭제와 삽입의 순서가 중요★
void thread_wakeup(int64_t cur_tick) {
if(list_empty(&sleep_list))
return;
struct thread *wakeup_first_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&sleep_list), struct thread, elem);
if(wakeup_first_thread->wakeup_tick <= cur_tick){
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
wakeup_first_thread->status = THREAD_READY;
list_push_back (&ready_list, &wakeup_first_thread->elem);
list_pop_front(&sleep_list);
intr_set_level (old_level);
printf("<thread wakeup>\n");
printf("wakeup_first_thread->wakeup_tick : %d\n",wakeup_first_thread->wakeup_tick);
printf("cur_tick : %d\n",cur_tick);
}
}삽입 후 삭제시에 문제점!
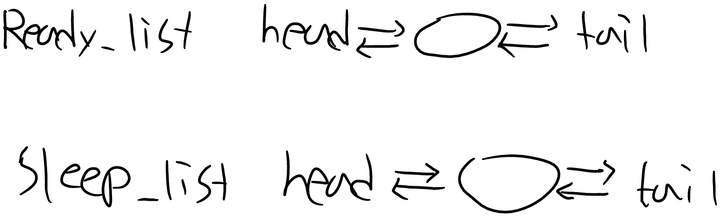
아래 그림처럼 삽입을 먼저 하게되면 삭제시에 ready_list에 삽입한 스레드도 같이 삭제될 것이다.

결국 ready_list에 삽입한 스레드도 삭제된다.