priority-scheduler
priority-scheduler프로젝트는 우선순위에 따라 실행될 스레드를 관리해주는 코드를 짜는 프로젝트다.
테스트 케이스는 총 12개로 우선순위 스케쥴링을 구현하는데 있어서 필수적인 요소들이 테스트 케이스에 들어갔다. 나는 이 중 priority-condvar을 제외한 나머지 테스트케이스에서 통과했다.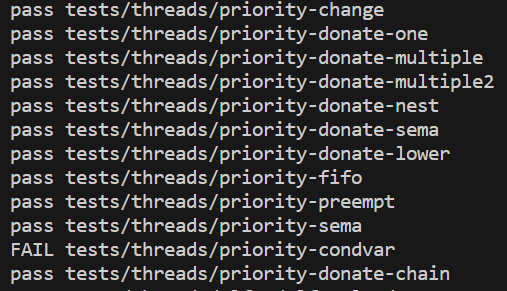
각각 테스트케이스에 대해 설명하자면
priority-change
- 스레드의 우선 순위를 낮추면 더 이상 시스템에서 가장 우선 순위가 높은 스레드가 되지 않도록
스레드가 즉시 산출되는지 확인합니다.
priority-donate-one
- 메인 스레드는 lock을 획득합니다. 그런 다음 lock을 획득하는 것을 차단하는 더 높은 우선 순위의 스레드 두 개를 생성하여 메인 스레드에 우선 순위를 기부하게 합니다. 메인 스레드가 lock을 해제하면 다른 스레드가 우선 순위대로 lock을 획득해야 합니다.
priority-donate-multiple
- 메인 스레드는 잠금 A와 B를 획득한 다음, 더 높은 우선 순위의 두 개의 스레드를 생성합니다. 이 스레드들은 각각 잠금 중 하나를 획득하는 것을 차단하고, 따라서 그 우선 순위를 메인 스레드에 기부합니다. 메인 스레드는 잠금을 차례로 해제하고, 기부된 우선 순위를 포기합니다.
priority-donate-multiple2
- 메인 스레드는 잠금 A와 B를 획득한 다음, 우선 순위가 높은 세 개의 스레드를 생성합니다. 이 중 처음 두 개의 스레드는 잠금 중 하나를 획득하는 것을 차단하여 우선 순위를 메인 스레드에 기부합니다. 메인 스레드는 잠금을 차례로 해제하고 기부된 우선 순위를 포기하여 세 번째 스레드를 실행할 수 있습니다.
이 테스트에서 메인 스레드는 priority-donate-multiple.c와 다른 순서로 잠금을 해제합니다.
priority-donate-nest
- 우선 순위가 낮은 메인 스레드 L은 잠금 A를 획득합니다. 중간 우선 순위 스레드 M은 잠금 B를 획득한 다음 잠금 A를 획득할 때 블록을 생성합니다. 우선 순위가 높은 스레드 H는 잠금 B를 획득할 때 블록을 생성합니다. 따라서 스레드 H는 우선 순위를 M에 할당하고, 이는 다시 스레드 L에 할당합니다.
priority-donate-sema
- 낮은 우선 순위의 스레드 L은 잠금을 획득한 다음, 세마포어 다운을 차단합니다. 중간 우선 순위의 스레드 M은 동일한 세마포어에서 대기하는 것을 차단합니다. 다음, 높은 우선 순위의 스레드 H는 잠금을 획득하려고 시도하고, 우선 순위를 L에게 기부합니다.
다음으로, 메인 스레드가 세마포어 위에 올라가 L을 깨웁니다. 잠금을 해제하고 H를 깨웁니다.
H는 세마포어를 "업"하고, M을 깨웁니다. H가 종료되고 M이 종료되고 L이 종료되며 마지막으로 메인 스레드가 종료됩니다.
priority-donate-lower
- 메인 스레드는 잠금을 획득합니다. 그런 다음 잠금을 획득하는 것을 차단하는 더 높은 우선 순위의 스레드를 생성하여 메인 스레드가 자신의 우선 순위를 메인 스레드에 기부하게 합니다. 메인 스레드는 우선 순위를 낮추려고 시도하는데, 이는 기부가 해제될 때까지 효력이 발생하지 않아야 합니다.
priority-fifo
- 동일한 우선 순위로 여러 스레드를 생성하고 동일한 라운드 로빈 순서로 일관되게 실행되도록 합니다.
priority-preempt
- 우선 순위가 높은 스레드가 실제로 선점하는지 확인합니다.
priority-sema
- 가장 우선순위가 높은 스레드가 세마포어에서 가장 먼저 깨어나는 것을 테스트합니다.
priority-condvar
- cond_signal()이 cond_wait()에서 대기 중인 가장 높은 우선 순위 스레드를 웨이크업하는 테스트를 수행합니다.
priority-donate-chain
- 기본 스레드는 우선 순위를 PRI_MIN으로 설정하고 우선 순위 PRI_MIN + 3, 6, 9, 12, ...로 7개의 스레드(thread 1.7)를 생성합니다. 메인 스레드는 8개의 잠금: 잠금 0.7을 초기화하고 잠금 0을 획득합니다.
thread[i]가 시작되면 먼저 lock[i](i==7.이 아닌 한)을 획득합니다. 이후 thread[i]는 메인 스레드에 의해 유지되는 lock[0]을 제외하고 thread[i-1]에 의해 유지되는 lock[i-1]의 획득을 시도합니다. 잠금이 유지되기 때문에, 메인 스레드가 기부금을 받을 때까지 thread[i-1]는 자신의 우선 순위를 thread[i-1]에 기부합니다.
스레드[1..7]이 생성되어 잠금[0..7]에서 차단된 후, 메인 스레드는 잠금[0]을 해제하고, 스레드[1]의 차단을 해제하고, 이에 의해 선점됩니다. 그런 다음 스레드[1]는 잠금[0] 획득을 완료한 다음 잠금[0]을 해제하고, 잠금[0]을 해제하고, 잠금[1]을 해제하고, 스레드[2]를 차단 해제합니다. 스레드[7]은 최종적으로 잠금[7]과 종료를 획득하고 해제하여 스레드[6], 그리고 스레드[5] 등이 실행되고 마지막으로 메인 스레드가 종료될 때까지 종료되도록 합니다.
또한 인터로퍼 스레드는 우선 순위 p = PRI_MIN + 2, 5, 8, 11, ...에서 생성되며 우선 순위가 p + 1인 해당 스레드가 완료될 때까지 실행되어서는 안 됩니다.
<코드 설명>
thread 구조체
thread 구조체에 맨 처음 우선순위값을 저장할 변수 prev_priority를 추가해주고 스레드가 생성될 때 prev_priority를 초기 인자값으로 받은 우선순위값으로 초기화 해준다.
또 보유한 lock의 주소를 저장할 포인터변수 *wait_on_lock을 추가해주고 자신에게 우선순위를 기부해준 스레드들의 목록을 보기 위해 donors라는 변수를 추개해주었고 자신이 기부한 스레드라면 자신을 기부한 스레드의 donors목록에 넣어주기 위해 donor_elem 변수를 선언해 주었다
struct thread {
/* Owned by thread.c. */
tid_t tid; /* Thread identifier. */
enum thread_status status; /* Thread state. */
char name[16]; /* Name (for debugging purposes). */
int priority; /* Priority. */
int prev_priority; /* donate 되기 전 Priority. */
int64_t wakeup_tick; /* 스레드가 깨어날 시각 (tick) */
void *wait_on_lock; /* 보유한 lock의 주소 */
struct list_elem donor_elem; /* 기부 쓰레드 목록에 들어갈 원소 */
struct list donors; /* 우선순위를 기부한 쓰레드들 */
/* Shared between thread.c and synch.c. */
struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */
thread_create() 함수
새로 생성된 스레드를 먼저 ready_list에 우선순위 기준으로 내림차순으로 넣어주고 (thread_unblock (t)), 우선순위가 지금 실행중인 스레드의 우선순위보다 크다면 thread_yield() 함수로 실행 스레드를 우선순위가 더 큰 값으로 바꿔준다.
tid_t
thread_create (const char *name, int priority,
thread_func *function, void *aux) {
struct thread *t;
tid_t tid;
ASSERT (function != NULL);
/* Allocate thread. */
t = palloc_get_page (PAL_ZERO);
if (t == NULL)
return TID_ERROR;
/* Initialize thread. */
init_thread (t, name, priority);
tid = t->tid = allocate_tid ();
/* Call the kernel_thread if it scheduled.
* Note) rdi is 1st argument, and rsi is 2nd argument. */
t->tf.rip = (uintptr_t) kernel_thread;
t->tf.R.rdi = (uint64_t) function;
t->tf.R.rsi = (uint64_t) aux;
t->tf.ds = SEL_KDSEG;
t->tf.es = SEL_KDSEG;
t->tf.ss = SEL_KDSEG;
t->tf.cs = SEL_KCSEG;
t->tf.eflags = FLAG_IF;
/* Add to run queue. */
thread_unblock (t);
if(thread_current()->priority < priority)
thread_yield();
return tid;
}
thread_set_priority() 함수
현재 실행중인 스레드의 우선순위를 바꿔주는 함수이다. 만약에 바뀐 우선순위가 ready_list에 있는 스레드의 우선순위보다 작을 경우 thread_yield() 해줘야한다.
또 주의할 점은 자신에게 기부한 스레드가 있을 경우 그 스레드는 지금 스레드가 끝나길 기다리고 있는 상태이므로 이 경우에는 현재 스레드를 바꾸지말고 prev_priority만 바꿔줘야 한다.
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority) {
if(list_empty(&thread_current()->donors)) //도너 리스트가 있으면 현재 우선순위를 바꾸면 안됨.
thread_current ()->priority = new_priority;
thread_current ()->prev_priority = new_priority;
if(list_empty(&ready_list))
return;
struct thread *high_priority_readylist_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&ready_list), struct thread, elem);
if (high_priority_readylist_thread->priority > new_priority) {
thread_yield();
}
}lock_acquire() 함수
lock_acquire을 부를 때 두 가지 경우가 있다. 첫 번째는 lock_acquire의 매개변수로 받은 lock을 어떤 스레드가 가지고있는 경우, 그리고 lock을 가지고있는 스레드가 없는 경우, 이렇게 두 가지로 볼 수 있다.
lock을 가지고 있는 스레드가 있는 경우엔 현재 스레드가 lock을 가질 수 없으므로 현재 스레드의 wait_on_lock(lock을 기다리고있다는 의미)을 현재 lock으로 설정해준다.
그리고 원래 락을 지니고 있던 스레드의 원래 우선순위값보다 현재 실행중인 스레드의 우선순위가 더 높다면 그 스레드의 donor리스트에 현재 스레드를 우선순위 기준 내림차순으로 넣어줘야한다. 그리고 lock을 보유한 스레드의 우선순위값을 제일 큰 값으로 재설정해준다. 그 이유는 현재 스레드가 lock을 가지고있는 스레드때문에 실행을 못하기 때문에 lock을 보유한 스레드가 끝난 뒤에 현재 스레드를 실행해야하기 때문이다.
만약 lock을 보유한 스레드도 누군가가 lock을 해제하길 기다리는 스레드일 수도 있다. 그 경우에는 그 스레드가 기다리는 lock의 보유스레드도 최신 우선순위값으로 설정해줘야한다.(nest)
락을 지니고있는 스레드가 없다면 현재 스레드가 기다리는 락이 없다고 해주면 된다.
sema_down()으로 성공적으로 sema의 value값이 내려갔다면 lock의 주인을 현재 스레드로 설정해준다.
void
lock_acquire (struct lock *lock) {
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (!lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if(lock->holder) { //락을 지니고있는 스레드가 있다면
thread_current()->wait_on_lock = lock; //현재 스레드가 기다리고 있는 락을 현재 락으로 설정.
if(lock->holder->prev_priority < thread_current()->priority) { //락을 지니고 있는 스레드의 원래 우선순위가 지금 실행중인 스레드의 우선순위보다 작을 경우
list_insert_ordered(&lock->holder->donors, &thread_current()->donor_elem, high_priority_first_in_donors, NULL); //락이 지니고 있는 스레드의 도너 리스트에 지금 실행중인 스레드를 넣음
if(lock->holder->priority < thread_current()->priority){ //락을 지니고 있는 스레드의 최신 우선순위가 지금 실행중인 스레드의 우선순위보다 클 경우
lock->holder->priority = thread_current()->priority; //락이 지니고 있는 스레드의 우선순위를 지금 스레드의 우선순위로 변경
}
}
//nest
struct lock *connect_lock = (struct lock *)lock->holder->wait_on_lock;
while(connect_lock) {
if(!connect_lock->holder) break;
if(connect_lock->holder->priority < thread_current()->priority) {
connect_lock->holder->priority = thread_current()->priority;
}
connect_lock = (struct lock *)connect_lock->holder->wait_on_lock;
}
}
else //락을 지니고있는 스레드가 없다면
thread_current()->wait_on_lock = NULL;
sema_down (&lock->semaphore);
lock->holder = thread_current ();
}lock_release() 함수
lock_release 함수를 실행한다는 것은 락을 보유한 스레드가 무조건 있다는 의미이다. 따라서 락을 보유한 스레드의 donor 리스트를 돌면서 해당 락을 지닌(우선순위 기부한) 스레드를 삭제해준다. 그리고 donor 리스트가 비었다면 락을 보유한 스레드를 원래 우선순위값으로 바꿔주고 비어있지 않았다면 donor리스트에서 제일 큰 우선순위로 바꿔준다.
lock_acquire할 때와 마찬가지로 lock을 보유한 스레드도 누군가가 lock을 해제하길 기다리는 스레드일 수도 있다. 그 경우에 그 스레드가 기다리는 lock의 보유스레드도 최신 우선순위값으로 설정해줘야한다.(nest)
그리고 lock을 보유한 스레드를 NULL로 만들어주고 sema의 value값을 + 해주면 된다.
여기서 주의할 점은 sema_up() 함수 안에서 기다리고 있는 스레드들중에 맨 앞에 값을 실행시켜주는데, 그 전에 lock_acquire에서 nest로 인해 우선순위값이 변동되었을 수 있기 때문에 정렬을 한뒤에 빼주면 된다.
void
lock_release (struct lock *lock) {
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
int flag = 1;
//release함수에 온다는건 락 홀더가 무조건 있음.
struct thread *lockholer = lock->holder;
//도너 리스트를 돌면서 해당 락을 가지고 있는 리스트를 삭제
struct list_elem *donators = list_begin(&lockholer->donors);
while(donators != list_end(&lockholer->donors)) { //도너리스트의 끝까지 반복
struct thread *free_thread = list_entry(donators, struct thread, donor_elem);
if(lock == free_thread->wait_on_lock) {//인자로 받은 락을 갖고있는 도너들은 모두 삭제해준다.
if(flag){ //첫번째로 나온 도너만 락의 홀더로 지정해준다.
lock->holder = free_thread;
free_thread->wait_on_lock = NULL;
flag = 0;
}
list_remove(donators);
}
donators = donators->next;
}
//락 홀더의 우선순위를 도너리스트중 제일 큰걸로 설정.
//만약 도너리스트가 비었다면 오리지널 우선순위로 설정.
if(list_empty(&lockholer->donors))
lockholer->priority = lockholer->prev_priority;
else
lockholer->priority = list_entry(list_min(&lockholer->donors, high_priority_first, NULL), struct thread, donor_elem)->priority;
//nest
struct lock *connect_lock = (struct lock *)lock->holder->wait_on_lock;
while(connect_lock) {
if(connect_lock->holder && connect_lock->holder->priority == thread_current()->priority) {
connect_lock->holder->priority = list_entry(list_min(&connect_lock->holder, high_priority_first, NULL), struct thread, donor_elem)->priority;
}
connect_lock = (struct lock *)connect_lock->holder->wait_on_lock;
}
lock->holder = NULL;
sema_up (&lock->semaphore);
}※코드 구현시 주의할 점※
list.c 파일 안에 리스트에서 최솟값 혹은 최댓값을 가진 요소를 반환해 주는 함수가 있는데, 함수이름은 list_min과 list_max이다. 하지만 함수 이름대로가 아닌 반대로 반환할 수 있으니 자신이 만든 우선순위 기준과 함수 안에 반환값에 대해 비교해보고 사용하면 된다.
그리고 thread 구조체 안에는 elem과 donor_elem이 있는데, 이 두 변수는 쓰임새가 다르다. 따라서 정렬할 때 기준이 되는 함수도 각각 다르게 사용해줘야 한다.
/* elem을 사용할 때 사용하는 정렬 기준 함수*/
bool
high_priority_first (const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_,
void *aux UNUSED)
{
const struct thread *a = list_entry (a_, struct thread, elem);
const struct thread *b = list_entry (b_, struct thread, elem);
return a->priority > b->priority;
}/* donor_elem을 사용할 때 사용하는 정렬 기준 함수*/
bool
high_priority_first_in_donors (const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_,
void *aux UNUSED)
{
const struct thread *a = list_entry (a_, struct thread, donor_elem);
const struct thread *b = list_entry (b_, struct thread, donor_elem);
return a->priority > b->priority;
}