python
yield로 permutaions, combinations 구현하기
itertools를 사용하다 보니 순열, 조합 관련 알고리즘을 직접 구현할 수 있는 능력의 필요성을 느꼈습니다.
itertools의 permutations, combinations를 공부하면서 알게된 yield를 활용해보기로 했습니다.
재귀형태를 뛰고있어서 어떻게 generate()의 결과값을 permutation()밖으로 끄집어낼지 찾아보다가 yield from 을 알게되어 활용했습니다.
import time
def permutation(arr, r):
arr = sorted(arr)
used = [False for _ in range(len(arr))]
def generate(chosen):
if len(chosen) == r:
time.sleep(1)
yield chosen
for i in range(len(arr)):
if not used[i]:
used[i] = True
chosen.append(arr[i])
yield from generate(chosen)
used[i] = False
chosen.pop()
yield from generate([])
def combination(arr, r):
arr = sorted(arr)
def generate(chosen, start):
if len(chosen) == r:
time.sleep(1)
yield chosen
for i in range(start, len(arr)):
if arr[i] not in chosen:
chosen.append(arr[i])
yield from generate(chosen, i+1)
chosen.pop()
yield from generate([], 0)
test = ['A','B','C']
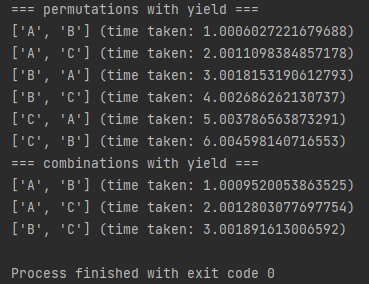
print('=== permutations with yield ===')
start = time.time()
for p in permutation(test, 2):
print('{} (time taken: {})'.format(p, time.time() - start))
print('=== combinations with yield ===')
start = time.time()
for c in combination(test, 2):
print('{} (time taken: {})'.format(c, time.time() - start))
실행결과
baekjoon
외판원 순환2
N = int(input())
cost = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(N)]
def find(visited, now):
if (visited << N) | now in dp:
return dp[(visited << N) | now]
if visited == (1 << N) - 1:
return cost[now][0] if cost[now][0] > 0 else 10 ** 9
tmp = 10 ** 8
for i in range(1, N):
if not visited & (1 << i) and cost[now][i]:
tmp = min(tmp, find(visited | (1 << i), i) + cost[now][i])
dp[visited << N | now] = tmp
return tmp
# key: visited << N | now, value: cost
dp = {}
# visited: bit로 표현된 방문한 도시 ex) 0b1000 4개 중 첫번째 도시만 방문함
print(find(1, 0))정말 예술적인 코드를 발견해서 조금 수정해서 적용해봤다.
연산자 끼워넣기
def f(result, idx, a, b, c, d):
global N, nums, maximum, minimum
if idx == N:
if result > maximum:
maximum = result
if result < minimum:
minimum = result
if a:
f(result + nums[idx], idx+1, a-1, b, c, d)
if b:
f(result - nums[idx], idx+1, a, b-1, c, d)
if c:
f(result * nums[idx], idx+1, a, b, c-1, d)
if d:
f(int(result / nums[idx]), idx+1, a, b, c, d-1)
N = int(input())
nums = [*map(int, input().split(' '))]
a, b, c, d = map(int, input().split(' '))
maximum = -10**9
minimum = 10**9
f(nums[0], 1, a, b, c, d)
print(f'{maximum}\n{minimum}')
이것도 놀라워서 원본코드를 참고해서 조금 수정해봤다.
