이 글은 시간 정보를 반영하는 지식그래프(temporal KGs)를 활용해서 다단계(multi-hop) 추론을 Agents 기반으로 수행하는 내용을 다룬 OpenAI Codebook을 리뷰한다. 텍스트에서 시간정보를 비롯한 객체와 관계를 추출해서 property graph를 구축하고, 이를 활용해서 어떻게 다단계 추론을 하는지에 대해서 다룬다. 특히, MVP 정도의 코드와 Appendix에서는 실제 프로덕션 환경에서 고려해야 할 점들도 설명해서 실제 도메인 환경에 적용할 수 있는 가능성도 있어보인다.
🧩 Temporal Knowledge Graphs
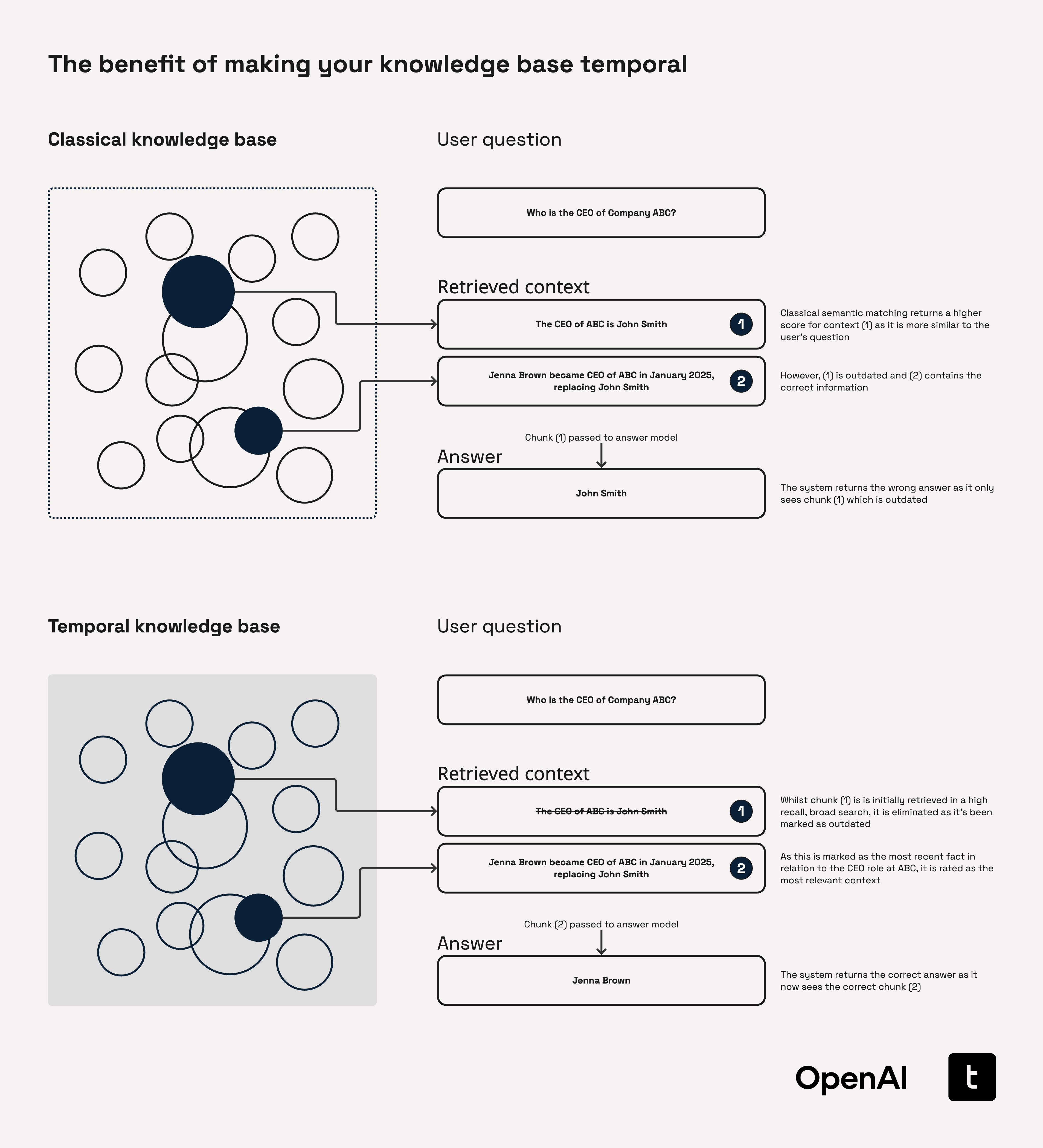
기존의 지식그래프는 정적인 정보를 표현하여 실시간 데이터를 반영하지 못한다. 실시간 정보를 반영하지 않는 데이터에서 발생할 수 있는 문제는 예를 들어, 금융서비스 분야에서 'FY-22 지침이 발표되었을 당시 소배업체 ZZ의 CFO는 누구인가?'와 같은 질의에서 특정 시기의 CFO를 명확하게 찾기 어렵거나 '2023년 2월 이후 YY은행에 대한 무디스의 장기 등급은 어떻게 변했는가?'에 대해 과거와 현재의 등급을 혼동한 답변을 생성할 가능성이 있다.
반면, 지속적으로 업데이트되는 정보를 실시간으로 갱신하고 최신 상태로 유지하는 'Temporal KGs'의 경우, 변경 사항을 추적하거나 타임라인 생성, 시간 기반 검색과 분석 등 더욱 풍부한 검색을 수행할 수 있다.
🧩 Temporal Agents
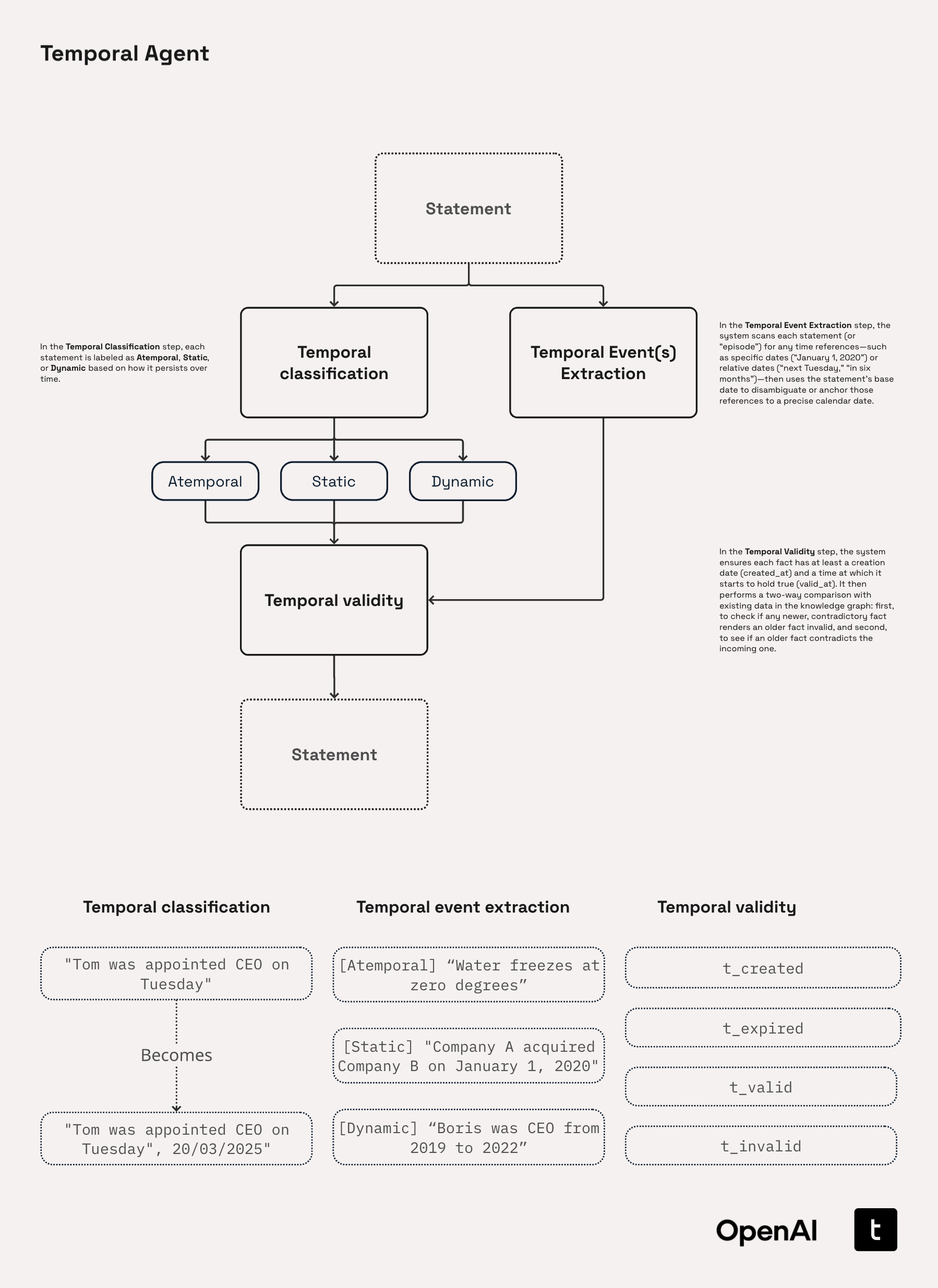
Agents는 temporal KGs를 활용해서 추론 과정을 계획하고, 반복적인 순회를 통해 종속적으로 잠재적인 연결관계를 탐색한다. Temporal Agents는 다음 3단계 파이프라인을 통해서 명령문을 처리한다.
- Temporal Classification: 시간적 요소의 유형을 'Atemporal', 'Static', 'Dynamic' 셋 중 하나로 분류하는 단계이다. Atemporal는 절대 변하지 않는 진리(e.g. 진공 상태에서 빛의 속도는 ≈3×10⁸ m s⁻¹이다)를 의미하고 Static은 특정 시점에만 유효하고 이후에 변경되지 않는 것(e.g. YY는 2014년 10월 23일에 XX회사의 CEO였다)을, Dynamic은 계속 변하는 정보(e.g. YY는 XX회사의 CEO이다)를 의미한다.
- Temporal Event Extraction: 상대적이거나(next friday) 절대적인(January 1, 2020)시간 정보를 식별하고, 규칙적인 형식(e.g. YYYY-MM-DD)으로 변환하는 단계이다. 예를 들어, 월만 아는 경우는 해당 월의 1일로 날짜를 임의로 설정하는 등의 규칙을 설정할 수 있다.
- Temporal Validity Check: 식별된 시간 정보에 't_created', 't_expired', 't_valid', 't_invalid', 등의 태그를 부여한다. 't_invalid'는 새로운 시간 정보가 들어왔을 때, 과거의 항목에 부여하고,
invalidated_by라는 관계로 표현한다.
위 이미지에서 하단에 Temporal classification과 Temporal event extraction의 예시 부분은 잘못 표기된 것 같다. 두 작업의 결과가 바뀌어야 설명과 일치한다.
또한 Temporal Agents를 구축할 어떤 OpenAI 모델을 선택해야 하는지에 대해서도 설명하고 있는데, 시스템을 구축할 때는 일반적으로 큰 모델로 시작한 뒤 나주에 최적화하고 줄이는 방법을 선택하는 것을 제안한다. 따라서 이 Codebook이 작성될 당시에는 GPT-4.1로 시작해서 GPT-4.1-mini, GPT-4.1-nano로 교체해서 테스트 해볼 수 있다.
🧩 Practice
1️⃣ Building Temporal Agents Pipeline
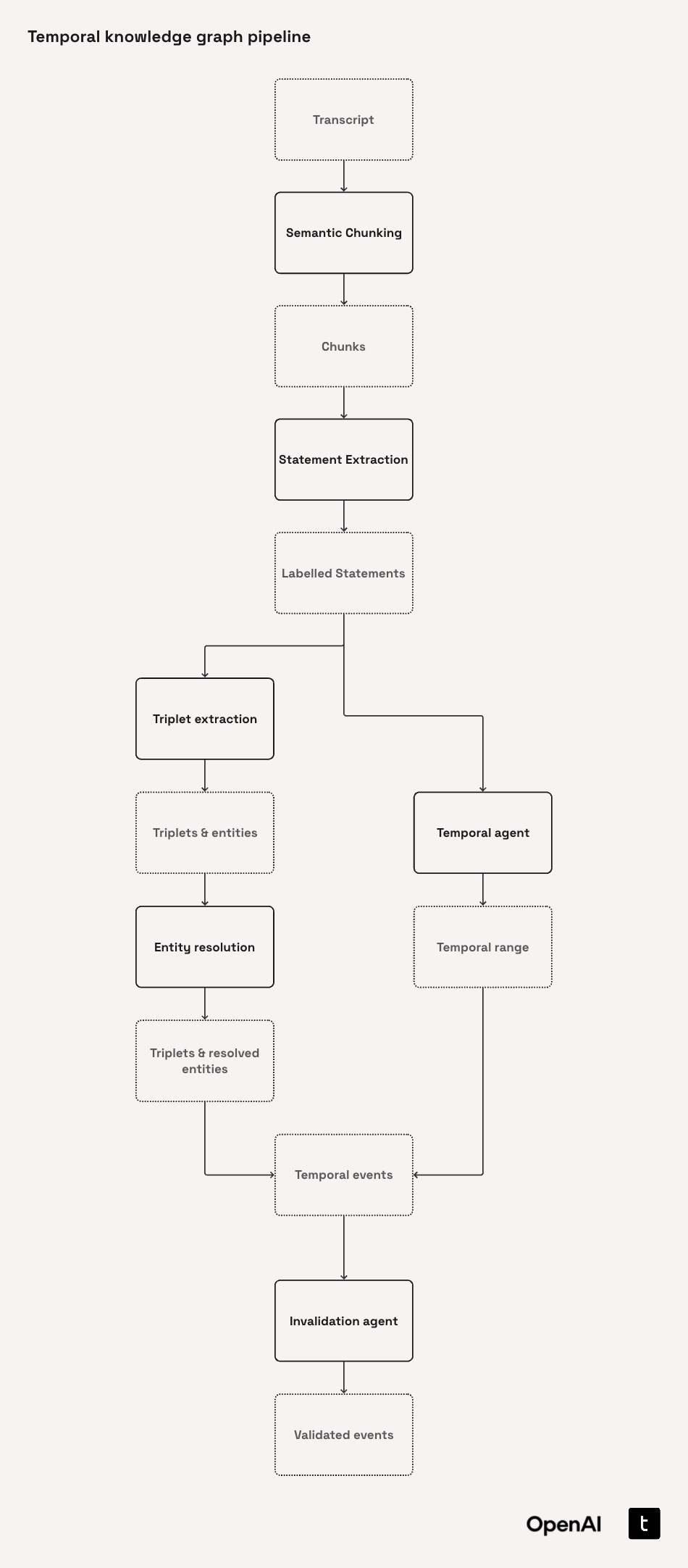
Temporal Agents pipeline은 다음과 같은 순서로 구축된다.
이 실습의 대부분은 텍스트에서 엔티티와 관계를 뽑아서 지식그래프를 생성하는 내용으로 구성되고, 시간 표현에 초점을 맞춘다는 특징이 있다. 이때의 지식그래프는 LPG(Labeled Property Graph) 형식이다. 즉, 기존에 구축된 지식그래프를 갖고 있다면, 추론 부분을 참고해서 활용만 하면 된다는 의미이다. 필자는 노동집약적으로 구축한(ㅋㅋ) RDF 기반의 그래프의 활용 측면에 관심이 있기 때문에 구축 과정은 간단하게만 이해하고 넘어가고자 한다.
1. Load transcripts
예시로 사용하는 데이터는 huggingface의 Earnings Calls Dataset으로, 금융기관의 실적발표 컨퍼런스 콜 녹취록이다. date, company, transcript 컬럼으로 구성되며, 실습에서는 범위를 AMD와 Nvidia라는 두 회사로 제한한다.
실습용 데이터베이스는 SQLite를 사용한다.
2. Creating a Semantic Chunker
Semantic Chunker는 transcript를 의미적인 청크 단위로 분리한다. 즉, 데이터의 한 행은 Transcript가 되고, 이 안의 정보를 Chunk로 분리한다고 이해하면 된다.Chunker 함수는 다음 두 핵심 매서드를 갖는다.
(1) find_quarter: 정규식을 사용해서 'Q1 2023', '2Q FY24' 같은 시간 정보(회계 분기 표현)를 추출해서 quarter필드에 저장한다.
(2) generate_transcripts_and_chunks: 우선, 각 행을 Transcript 객체로 만들고 text, company, date, quarter, chunks 등을 저장할 수 있도록 한다. 이후 OpenAI의 text-emvedding-3-small 모델과 chonkie 라이브러리를 사용해서 의미적 청크 단위로 분리하고, Transcripts 객체의 chunks 필드에 리스트 형태로 저장한다.
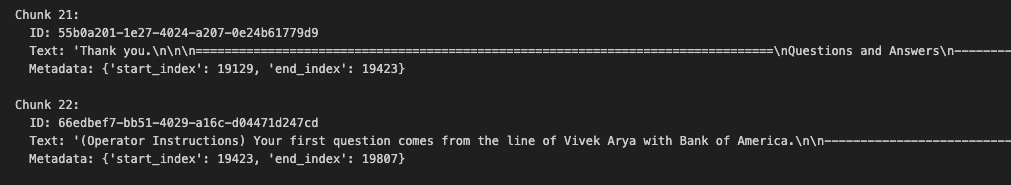
이 단계를 거치면 위와 같이 개별 청크는 unique한 ID를 갖고 metadata에서 start_index와 end_index로 원본 transcript에서의 위치를 표현한다.
3. Laying the Foundations for our Temporal Agent
LLM이 시간 정보를 추출하기 전, 일관된 시간 label체계를 정의하는 단계이다. 예를 들어, 'Our new product will launch next quarter'라는 문장에서 미래 시점을 예측하는 문장인지, 팩트 정보인지를 분리할 필요가 있으며, 위에서 살펴봤던 Static, Dynamic, Atemporal의 명확한 정의와 few-shot 예시를 주고 있다.
4. Statement Extraction
(1) Temporal Types: 시간적 표현을 Atemporal, Static, Dynamic 세 타입으로 분류
(2) Statement Types: Fact(검증 가능한 주장을 뒷받침하는 진술), Opinion(화자의 신념, 판단에 따른 주관적인 진술), Prediction(잠재적인 미래 사건이나 결과를 예측, 가정하는 진술)으로 분류
위와 같은 분류와 분류의 정의를 모두 프롬프트에 넣고, LLM을 기반으로 의미단위를 추출하고 라벨링을 수행한다. 우선 한 문장에서 atomic statement를 추출하는데, 예를 들어 2개 이상의 사실 정보가 담긴 경우, 이를 두 개의 문장 단위로 분리한다는 것이다.
한편, 프롬프트의 재사용성과 pipeline 자동화를 위해서 Junja 템플릿을 사용해서 기본 프롬프트 구조는 유지하면서 내용만 교체하는 방식을 적용했다고 한다.
5. Temporal Range Extraction
추출하는 시간적 표현이 정해진 datetime 형식에 맞도록 설정해주고, 유효성을 검사한다. 코드를 보면 추출을 위한 프롬프트(date_extraction_prompt)를 확인할 수 있다.
6. Creating our Triplets
추출한 엔티티를 triple 형식으로 표현할 때 사용할 관계(edge에 표현할 relationships)와 속성(node와 relationship의 predicate) 정의한다. 이 관계와 속성은 데이터의 특성에 따라 적절한 정의가 필요하다.
PREDICATE_DEFINITIONS = {
"IS_A": "Denotes a class-or-type relationship between two entities (e.g., 'Model Y IS_A electric-SUV'). Includes 'is' and 'was'.",
"HAS_A": "Denotes a part-whole relationship between two entities (e.g., 'Model Y HAS_A electric-engine'). Includes 'has' and 'had'.",
"LOCATED_IN": "Specifies geographic or organisational containment or proximity (e.g., headquarters LOCATED_IN Berlin).",
"HOLDS_ROLE": "Connects a person to a formal office or title within an organisation (CEO, Chair, Director, etc.).",
"PRODUCES": "Indicates that an entity manufactures, builds, or creates a product, service, or infrastructure (includes scale-ups and component inclusion).",
"SELLS": "Marks a commercial seller-to-customer relationship for a product or service (markets, distributes, sells).",
"LAUNCHED": "Captures the official first release, shipment, or public start of a product, service, or initiative.",
"DEVELOPED": "Shows design, R&D, or innovation origin of a technology, product, or capability. Includes 'researched' or 'created'.",
"ADOPTED_BY": "Indicates that a technology or product has been taken up, deployed, or implemented by another entity.",
"INVESTS_IN": "Represents the flow of capital or resources from one entity into another (equity, funding rounds, strategic investment).",
"COLLABORATES_WITH": "Generic partnership, alliance, joint venture, or licensing relationship between entities.",
"SUPPLIES": "Captures vendor–client supply-chain links or dependencies (provides to, sources from).",
"HAS_REVENUE": "Associates an entity with a revenue amount or metric—actual, reported, or projected.",
"INCREASED": "Expresses an upward change in a metric (revenue, market share, output) relative to a prior period or baseline.",
"DECREASED": "Expresses a downward change in a metric relative to a prior period or baseline.",
"RESULTED_IN": "Captures a causal relationship where one event or factor leads to a specific outcome (positive or negative).",
"TARGETS": "Denotes a strategic objective, market segment, or customer group that an entity seeks to reach.",
"PART_OF": "Expresses hierarchical membership or subset relationships (division, subsidiary, managed by, belongs to).",
"DISCONTINUED": "Indicates official end-of-life, shutdown, or termination of a product, service, or relationship.",
"SECURED": "Marks the successful acquisition of funding, contracts, assets, or rights by an entity.",
}7. Temporal Event
TemporalEvent는 이 에이전트가 추출한 모든 핵심 정보를 하나의 데이터 구조로 묶어서 표현한 객체이다. 객체에서 표현한 필드는 다음과 같다.
- id: 사건의 고유 식별자
- chunk_id: 어떤 텍스트 청크(문단, 문장 등)에서 나온 사건인지
- statement: 원문에서 추출된 핵심 문장 (RawStatement)
- embedding: 사건을 벡터로 표현 (유사도 계산용)
- triplets: (주어-동사-목적어) 구조의 UUID 리스트
- valid_at / invalid_at: 사건이 유효해진 시점 / 만료된 시점
- temporal_type: 사건의 시간적 특성 (예: STATIC, DYNAMIC 등)
- statement_type: 사건의 성격 (예: fact, prediction, claim 등)
- created_at / expired_at: 시스템 생성 및 만료 처리 시
- invalidated_by: 해당 사건을 무효화시킨 다른 사건의 ID
8. Defining out Temporal Agent
이제 위에서 정의한 Chunking, Statement 추출, Label 부여, entity추출, triplet 생성 등의 과정을 실제로 수행하는 단계이다(코드 실행 순서대로 설명한다고 이해하면 됨). 실행 결과로 all_event(모든 TemporalEvent 객체 리스트), all_triplets(추출된 모두 s-p-o 관계), all_entities(문장 내에 등장한 모든 엔티티)를 얻게 된다.
9. Entity Resolution
ER은 동일한 객체를 인식해서 중복을 제거하는 단계이다. 우선 RapidFuzz를 사용해서 유사한 형태의 텍스트 기반으로 엔티티들을 클러스터링하고, 해당 클러스터의 대표값(medoid)를 선택한다. 이후 약어 등을 고려하여 최종적으로 공통 객체를 정의한다.
10. Invalidation agent
이 작업은 시간적 논리를 적용해서 새로운 시간 정보가 들어왔을 때, 이전 정보를 무효화(invalidate)하게 만드는 검증 프로세스이다. 프롬프팅을 통한 LLM을 활용해서 진행하는데, 외부 지식을 사용하지 않고 주어진 관계 정보들만 기반으로 case1이 case2에 의해 무효화되는지를 판단하게 만든다.
최종적으로 생성한 데이터를 파이썬의 networkx 라이브러리를 사용해서 그래프를 생성하면 위와 같은 형태를 확인할 수 있다. 실제 프로덕션 환경에서는 Neo4j와 같은 그래프 데이터베이스를 사용하면 된다.
2️⃣ Building Multi-Step Retrieval System Over a KGs
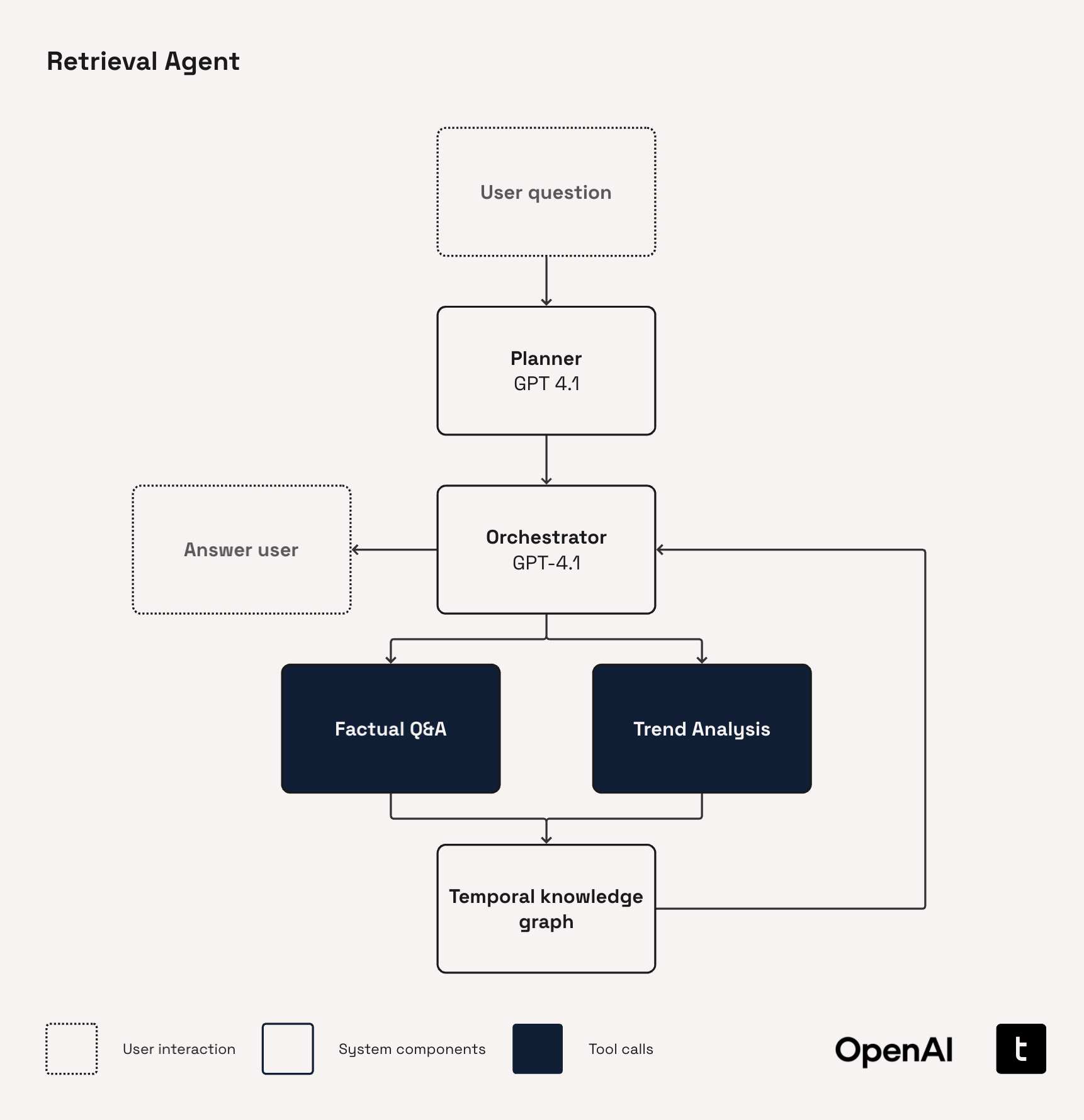
이제 구축한 지식그래프를 활용해서 단순히 질의에 적합한 참조데이터를 쿼리하는 방식이 아닌, 다단계 추론 검색을 수행한다. Retrievel Agent는 위와 같은 플로우로 구성되는데, 우선 Planner는 사용자의 질문을 제안된 그래프 연산의 작원 시퀀스로 분해한다. 이후 Orchestrator를 통해 실행되는데, 지식그래프에서 정보를 검색하거나 필요한 도구를 호출하고, 적절한 답변을 생성할때까지 이 과정을 반복적으로 수행한다.
- Planner
Task-orientated planner는 하위 에이전트 블록이 수행하는 작업을 간략하게 설명하고, 목표가 확정적이거나 작업이 누락되거나 중복되는 위험이 있을 때 선호되는 방법이다.
Hypothesis-orientated planner는 시스템이 사용자의 질문에 응답하여 확인, 거부, 혹은 개선할 수 있는 일련의 가설을 구성한다. 각 단계는 검증 가능한 주장을 나타내며, 선택적으로 조치를 제공하기도 한다. 새로운 정보가 해결책의 범위를 크게 바꿀 수 있는 개방형 연구에 적합한 방식이다.
아래 코드는 task-oriented 방식의 planner의 프롬프트이다.
async def initial_planner(user_question: str) -> str:
"""Return an initial plan for answering the user's question."""
initial_planner_system_prompt = (
"You work for the leading financial firm, ABC Incorporated, one of the largest financial firms in the world. "
"Due to your long and esteemed tenure at the firm, various equity research teams will often come to you "
"for guidance on research tasks they are performing. Your expertise is particularly strong in the area of "
"ABC Incorporated's proprietary knowledge base of earnings call transcripts. This contains details that have been "
"extracted from the earnings call transcripts of various companies with labelling for when these statements are, or "
"were, valid. You are an expert at providing instructions to teams on how to use this knowledge graph to answer "
"their research queries. \n"
"The teams will have access to the following tools to help them retrieve information from the knowledge graph: \n"
"1. `factual_qa`: Queries the knowledge graph for time-bounded factual relationships involving a given entity and predicate. \n"
"2. `trend_analysis`: Wraps the factual_qa tool with a specialised agent to perform in-depth trend analysis \n"
"It shoudld also be noted that the trend_analysis tool can accept multiple predicate arguments as a list. \n "
"You may recommend that multiple calls are made to the tools with different e.g., predicates if this is useful. \n "
"Your recommendation should explain to the team how to retrieve the information from the database through these "
"tools only. "
)
initial_planner_user_prompt = (
"Your top equity research team has came to you with a research question they are trying to find the answer to. "
"You should use your deep financial expertise to succinctly detail a step-by-step plan for retrieving "
"this information from the the company's knowledge base of earnings call transcripts extracts. "
"You should produce a concise set of individual research tasks required to thoroughly address the team's query. "
"These tasks should cover all of the key points of the team's research task without overcomplicating it. \n\n"
"The question the team has is: \n\n"
f"{user_question} \n\n"
"Return your answer under a heading 'Research tasks' with no filler language, only the plan."
)
input_messages = [
{"role":"system", "content": initial_planner_system_prompt},
{"role":"user", "content": initial_planner_user_prompt}
]
initial_plan = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=input_messages
)
return initial_plan.output_textOrchastrator가 호출할 수 있는 함수들을 정의하고, 사용하는 과정을 'Function Calling'이라고 한다. 사용하는 함수들은 기존에 OpenAI나 LangChain 등에서 사전에 정의해둔 함수(이미지 생성, 웹 검색 등)를 사용할 수도 있고 사용자가 직접 정의할 수도 있다.
.
.
.
지금까지 다룬 예시는 프로토타입이고, 실제 프로덕션 환경에서 활용하기 위해 추가적으로 고려해야 하는 사항들은 Appendix에서 더 다룬다고 한다. 간단하게 살펴보면, 동일한 이벤트를 참조하는 중복되는 이벤트를 식별하거나 병합하는 작업, 모호한 날짜 표현을 더욱 구체적으로 명시하는 규칙 등을 설정하여 더 정교한 시간 기반 검색을 할 수 있다. 또한 위에서 언급했듯, Neo4j와 같은 데이터베이스 기반으로 쿼리를 통한 retrievel process를 구축할 수 있다.
한편, 다단계 추론에 대해서는 여전히 모호함이 있다. Planner를 통해서 단계적으로 추론 과정을 설정하고, function calling을 통해서 각 단계별로 필요한 함수를 호출해서 반복적으로 수행하는 건 기존의 Agents의 특성인데, 지식그래프의 노드와 관계 사이를 반복적, 확장적으로 탐색하는 방법에 대한 명확한 방법이 궁금했다.
