개요
Pintos Project: Threads의 두 번째 요구사항은 "Priority Scheduling"을 구현하는 것입니다.
Priority
pintos 스레드(thread)에는 우선순위(priority)가 존재합니다. 우선순위가 높을수록 스케줄러에게 먼저 선택 받게 되며, lock, semaphore 같은 리소스도 먼저 획득하게 됩니다.
Priority Inversion
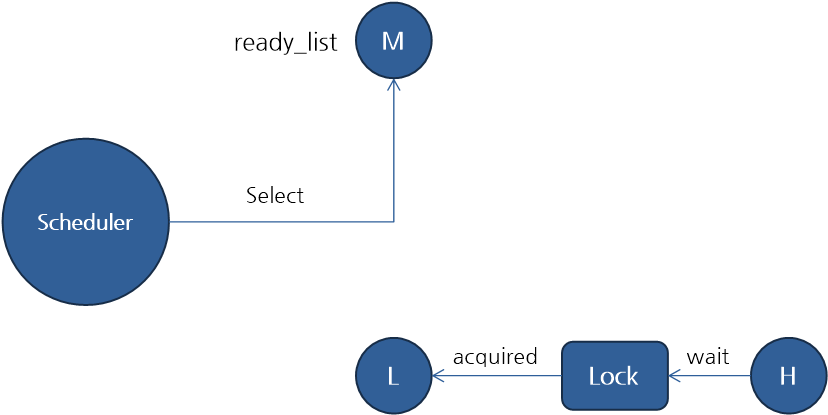
우선순위가 H(High), M(Medium), L(Low)인 스레드가 있을 때, L 스레드가 lock을 획득하고, H 스레드는 L 스레드가 획득한 lock을 대기하고 있는 상황에서, M 스레드가 ready_list에 있으면 L 스레드는 실행 기회를 획득할 수 없습니다. 왜냐하면 M 스레드의 우선순위가 L 스레드보다 더 높기 때문에, 스케줄러는 M 스레드에게 실행 기회를 먼저 주기 때문입니다. 따라서 H 스레드는 M 스레드보다 우선순위가 높은데도 불구하고 더 나중에 실행되게 되는데 이러한 현상을 "Priority Inversion"이라고 합니다.
Priority Donation
이 문제를 해결하려면 H 스레드가 lock을 점유하고 있는 L 스레드에게 자신의 우선 순위를 빌려줘서 먼저 실행할 수 있게 하는 것입니다. 이 방식을 "Priority Donation"이라고 합니다.
Nested Donation
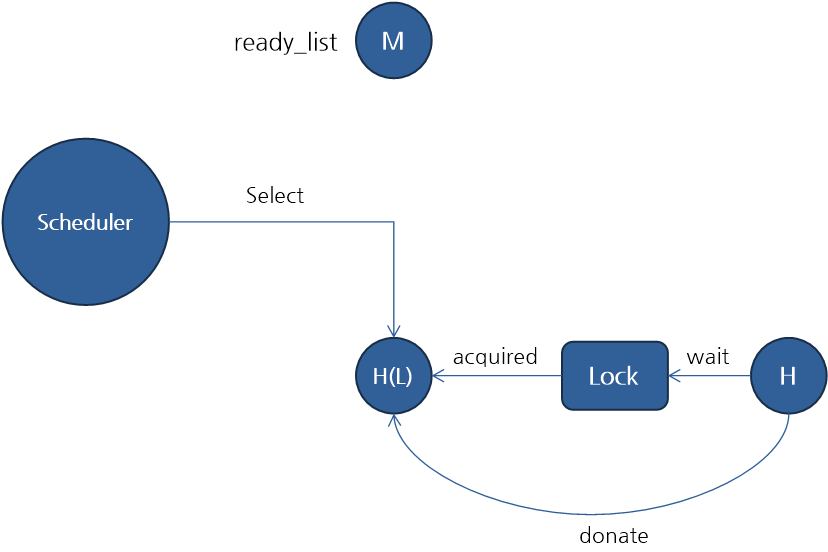
H 우선순위를 가진 스레드(H 스레드)가 M 우선순위를 가진 스레드(M 스레드)가 획득한 lock을 기다리고 있고, M 스레드가 L 우선순위를 가진 스레드(L 스레드)가 획득한 lock을 기다리고 있다면, H 스레드가 기부한 우선순위를 M 스레드가 L 스레드에게 다시 기부한다면 L 스레드가 먼저 작업을 완료해서 lock을 풀 수 있습니다. 이렇게 기부 받은 우선 순위를 다시 전파하는 것을 "Nested Donation"이라고 합니다.
Before
After

구현
Priority Donation
/* thread.h */
struct thread
{
...
int captured_priority
struct thread *donated_to;
struct list donation_list;
struct list_elem donation_elem;
...
}Priority Donation을 구현하기 위해서 4개의 변수를 thread 구조체에 추가합니다.
- captured_priority: thread의 원래 우선순위를 저장합니다. 우선순위를 기부 받았다가, 기부가 끝나면 이 변수에 저장된 값으로 우선순위를 설정합니다.
- donated_to: thread에게 우선순위를 기부 받고 있는 스레드를 가리킵니다. 이 변수는 nested donation 기능을 구현할 때 사용합니다.
- donation_list: thread에게 기부 중인 스레드를 관리하는 리스트입니다. donation_elem으로 요소를 연결합니다.
/* thread.c */
void
thread_donate_priority (struct thread *to)
{
struct thread *from = thread_current ();
ASSERT (to->priority < from->priority);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
donate_priority (to, from->priority, 0);
list_push_back (&to->donation_list, &from->donation_elem);
from->donated_to = to;
list_sort (&ready_list, thread_priority_greater, NULL);
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
thread_donate_priority 함수는 "from" 스레드(thread)가 파라미터로 전달된 "to" 스레드에게 자신의 우선순위를 기부합니다. 이때, 인터럽트(interrupt)를 비활성화하여 경쟁 상태에 빠지지 않도록 합니다. 우선순위를 기부한 후에는 "to" 스레드의 "donation_list"에 기부한 스레드를 등록하고, "from" 스레드의 "donated_to" 변수가 "to" 스레드를 가리키도록 설정합니다.
기부가 완료되면 ready_list를 정렬합니다. (우선 순위 기부를 통해서 ready_list 안에 있는 스레드의 우선 순위가 바뀌었을 수도 있기 때문에 정렬 통해 다시 가장 높은 우선 순위가 리스트 앞에 오도록 합니다.)
/* thread.c */
static void
donate_priority (struct thread *t, int priority, int level)
{
if (level < PRI_DONATION_MAX)
{
t->priority = priority;
if (t->donated_to != NULL)
donate_priority (t->donated_to, priority, level + 1);
}
}donate_priority 함수는 스레드에게 기부 받은 우선순위를 설정하는 함수입니다. 이때, 이미 스레드가 자신의 우선순위를 기부 중이었다면 기부 받은 우선순위를 기부 중인 스레드에게 전파를 합니다.
Priority Donation 적용
priority donation 기능은 구현했으니 이제 적용할 차례입니다.
lock
/* synch.c */
void
lock_acquire (struct lock *lock)
{
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (!lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (!sema_try_down (&lock->semaphore))
{
struct thread *t = lock->holder;
if (thread_get_priority () > t->priority)
thread_donate_priority (t);
sema_down (&lock->semaphore);
}
lock->holder = thread_current ();
}락(lock)을 획득할 때는 현재 락을 점유 중인 스레드보다 더 우선순위가 높다면 우선순위를 기부합니다.
/* synch.c */
void
lock_release (struct lock *lock)
{
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
struct thread *cur = thread_current ();
for (struct list_elem *waiter = list_begin (&lock->semaphore.waiters);
waiter != list_end (&lock->semaphore.waiters);
waiter = list_next (waiter))
{
struct thread *t = list_entry (waiter, struct thread, elem);
for (struct list_elem *donor = list_begin (&cur->donation_list);
donor != list_end (&cur->donation_list);
donor = list_next (donor))
{
if (t == list_entry (donor, struct thread, donation_elem))
{
list_remove (donor);
break;
}
}
}
if (!list_empty (&cur->donation_list))
cur->priority = list_entry (list_max (&cur->donation_list, thread_priority_less, NULL),
struct thread, donation_elem)->priority;
else
cur->priority = cur->captured_priority;
lock->holder = NULL;
sema_up (&lock->semaphore);
}락(lock)을 해제할 때는 락을 기다리고 있는 스레드 중에 우선순위를 기부했던 스레드가 있다면 기부 목록에서 제거합니다.
그리고 기부 목록에 요소가 있다면 가장 높은 우선 순위를 찾아서 스레드의 우선순위를 그 값으로 설정합니다. 기부 목록이 비어있다면, 원래 우선순위로 복구합니다.
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
struct thread *awoke_thread = thread_current ();
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters))
{
struct list_elem *elem = list_max (&sema->waiters, thread_priority_less, NULL);
list_remove (elem);
awoke_thread = list_entry (elem, struct thread, elem);
thread_unblock (awoke_thread);
}
sema->value++;
intr_set_level (old_level);
if (!intr_context () && thread_current ()->priority < awoke_thread->priority)
thread_yield ();
}pintos에서 락(lock)은 세마포어(semaphore)로 구현되어 있습니다. 따라서 실제로 스레드가 락을 대기하기 위해 블록(block)되거나, 다시 준비(ready)상태로 설정되는 동작은 세마포어 관련 함수에 구현되어 있습니다. 그래서 sema_up 함수에서 리소스를 대기 중인 스레드를 깨우게 되는데 이때 우선순위가 가장 높은 스레드를 찾아서 깨웁니다. 그리고 그 스레드가 현재 스레드보다 우선순위가 높으면 실행을 양보합니다.
condtion
/* synch.c */
struct semaphore_elem
{
struct list_elem elem;
struct semaphore semaphore;
struct thread *holder;
};
static bool
semaphore_elem_greater (const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
struct semaphore_elem *x = list_entry (a, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct semaphore_elem *y = list_entry (b, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
return x->holder->priority > y->holder->priority;
}
void
cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock)
{
struct semaphore_elem waiter;
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
waiter.holder = thread_current ();
sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0);
list_insert_ordered (&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem, semaphore_elem_greater, NULL);
lock_release (lock);
sema_down (&waiter.semaphore);
lock_acquire (lock);
}condtion 변수에도 스레드의 우선순위를 반영할 수 있게 condtion 대기 목록에 스레드를 우선순위가 높은 순으로 추가합니다.
Priority Scheduling
/* thread.c */
void
thread_unblock (struct thread *t)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (is_thread (t));
old_level = intr_disable ();
ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED);
list_insert_ordered (&ready_list, &t->elem, thread_priority_greater, NULL);
t->status = THREAD_READY;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
void thread_yield (void)
{
struct thread *cur = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (cur != idle_thread)
list_insert_ordered (&ready_list, &cur->elem, thread_priority_greater, NULL);
cur->status = THREAD_READY;
schedule ();
intr_set_level (old_level);
}priority scheduling을 위해서 ready_list에 스레드를 넣을 때 우선순위가 높은 순서대로 넣도록 합니다.
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority)
{
enum intr_level old_level = intr_disable ();
struct thread *t = thread_current ();
if (list_empty (&t->donation_list))
t->priority = new_priority;
t->captured_priority = new_priority;
if (!list_empty (&ready_list))
{
struct thread *preemptible = list_entry (list_front (&ready_list), struct thread, elem);
if (preemptible->priority > t->priority)
thread_yield ();
}
intr_set_level (old_level);
}스레드의 우선순위를 변경하게 될 경우, 먼저 스레드의 우선순위가 기부를 받아서 설정되었는지 확인합니다. 만약 기부를 받고 있는 상태라면 우선순위를 바로 변경하는 것이 아니라 captured_priority에 저장하고 나중에 적용합니다. 그리고 우선순위가 변경되었다면, 변경된 우선순위가 대기 목록에 있는 스레드의 우선순위보다 낮아진다면 바로 실행을 양보합니다.
Github
- link: https://github.com/chahoseong/pintos
- branch: project/threads
Reference
https://thierrysans.me/CSCC69/projects/WWW/pintos_2.html#SEC26