크루스칼 알고리즘
지난번 이 MST 를 찾는 크루스칼 알고리즘을 공부하고, 관련한 백준 문제를 풀었다.
문제
마을에 집들(정점)이 있고 집들 사이에 거리(간선)이 주어지는데,
마을을 두 개의 작은 마을로 분할하려고 한다.
한 작은 마을에는 적어도 한 집이 포함되어야 한다.
각 작은 마을에 속한 집들끼리는 서로 연결되어 있다 (스패닝 트리)
집들 사이의 거리의 합을 최소로 하여서 큰 마을을 두 그룹의 작은 마을로 나누어라.
=> 최소 스패닝 트리
문제는 이런데 잠시 생각해보니
그냥 전체 마을에 대한 최소 스패닝 트리를 만들고 마지막의 V-1 번째 간선을 제외하면 큰 마을이 두 개의 작은 마을로 나뉘는 거 아닐까 라는 생각이 들었다.
그냥 처음부터 간선을 V-2 개만 연결하기로 하고 문제를 풀었다.
풀이 1 - ArrayList 사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return Integer.compare(this.weight, o.weight);
}
}
static int N, M;
static int[] parents;
static List<Edge> list = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for (int m=0; m<M; m++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
list.add(new Edge(a,b,c));
}
Collections.sort(list);
makeSet();
int totalWeight = 0;
int edgeCnt = 0;
while (edgeCnt < N-2) {
Edge e = list.remove(0);
int from = e.from;
int to = e.to;
if (!union(from,to)) continue; // 같은 트리에 속하면 pass
totalWeight += e.weight;
edgeCnt++;
}
System.out.println(totalWeight);
}
static void makeSet() {
parents = new int[N+1];
for (int n=1; n<=N; n++) {
parents[n] = n;
}
}
static int findSet(int a) {
if (a == parents[a]) return a;
return parents[a] = findSet(parents[a]);
}
static boolean union(int a, int b) {
int parentA = findSet(a);
int parentB = findSet(b);
if (parentA == parentB) return false;
else if (parentA < parentB) {
parents[parentB] = parentA;
} else {
parents[parentA] = parentB;
}
return true;
}
}

그런데 시간 초과가 나버렸다.
경로 압축도 잘 했는데 뭐가 문제일까?
N (정점의 수) 은 100_000 이하, M (간선의 수) 은 1_000_000 이하이다.
시간복잡도 :

시간복잡도는 널널하다
그런데 이 방법에서는 ArrayList 를 사용하며 remove(0) 연산을 하면서
계속 원소들을 한 칸씩 앞으로 당기고 있는 것을 깨달았다.
그래서 remove 를 사용하지 않고 for 문으로 바꿔서 지우지 않고 원소를 순회하는 것으로 바꿔봤다.
풀이 1-2 - ArrayList 사용 (remove() 사용하지않고 원소순회)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return Integer.compare(this.weight, o.weight);
}
}
static int N, M;
static int[] parents;
static List<Edge> list = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for (int m=0; m<M; m++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
list.add(new Edge(a,b,c));
}
Collections.sort(list);
makeSet();
int totalWeight = 0;
int edgeCnt = 0;
if (N==2) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
for (Edge e : list) {
int from = e.from;
int to = e.to;
if (!union(from,to)) continue; // 같은 트리에 속하면 pass
totalWeight += e.weight;
if (++edgeCnt == N-2) break;
}
System.out.println(totalWeight);
}
static void makeSet() {
parents = new int[N+1];
for (int n=1; n<=N; n++) {
parents[n] = n;
}
}
static int findSet(int a) {
if (a == parents[a]) return a;
return parents[a] = findSet(parents[a]);
}
static boolean union(int a, int b) {
int parentA = findSet(a);
int parentB = findSet(b);
if (parentA == parentB) return false;
else if (parentA < parentB) {
parents[parentB] = parentA;
} else {
parents[parentA] = parentB;
}
return true;
}
}

성공했다.
사실 이것은 방금 글을 쓰면서 "어? 그냥 remove 안하고 원소 순회하면 되겠네?" 하고 성공한 것이다.
방금까지는 PriorityQueue 로 간선 리스트를 관리하거나, Array 로 관리하는 방법으로 문제를 풀었어서
"ArrayList 로는 안되지만 PQ 와 Array 로는 되구나!" 를 느껴서 글을 적고 있었다.
그래도 지금이라도 깨달았으니 좋다.
아쉬우니 PQ와 Array를 이용한 코드도 첨부하겠다.
풀이 2 - PriorityQueue 사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return Integer.compare(this.weight, o.weight);
}
}
static int N, M;
static int[] parents;
static PriorityQueue<Edge> list = new PriorityQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for (int m=0; m<M; m++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
list.add(new Edge(a,b,c));
}
makeSet();
int totalWeight = 0;
int edgeCnt = 0;
while (edgeCnt < N-2) {
Edge e = list.poll();
int from = e.from;
int to = e.to;
if (!union(from,to)) continue; // 같은 트리에 속하면 pass
totalWeight += e.weight;
edgeCnt++;
}
System.out.println(totalWeight);
}
static void makeSet() {
parents = new int[N+1];
for (int n=1; n<=N; n++) {
parents[n] = n;
}
}
static int findSet(int a) {
if (a == parents[a]) return a;
return parents[a] = findSet(parents[a]);
}
static boolean union(int a, int b) {
int parentA = findSet(a);
int parentB = findSet(b);
if (parentA == parentB) return false;
else if (parentA < parentB) {
parents[parentB] = parentA;
} else {
parents[parentA] = parentB;
}
return true;
}
}
풀이 3 - Array 사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int from;
int to;
int weight;
public Edge(int from, int to, int weight) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return Integer.compare(this.weight, o.weight);
}
}
static int N, M;
static int[] parents;
static Edge[] edgeList;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
edgeList = new Edge[M];
for (int m=0; m<M; m++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
edgeList[m] = new Edge(a,b,c);
}
Arrays.sort(edgeList); // 정렬
makeSet();
int totalWeight = 0;
int edgeCnt = 0;
if (N==2) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
for (Edge e : edgeList) {
int from = e.from;
int to = e.to;
if (!union(from,to)) continue; // 같은 트리에 속하면 pass
totalWeight += e.weight;
if (++edgeCnt == N-2) break;
}
System.out.println(totalWeight);
}
static void makeSet() {
parents = new int[N+1];
for (int n=1; n<=N; n++) {
parents[n] = n;
}
}
static int findSet(int a) {
if (a == parents[a]) return a;
return parents[a] = findSet(parents[a]);
}
static boolean union(int a, int b) {
int parentA = findSet(a);
int parentB = findSet(b);
if (parentA == parentB) return false;
else if (parentA < parentB) {
parents[parentB] = parentA;
} else {
parents[parentA] = parentB;
}
return true;
}
}

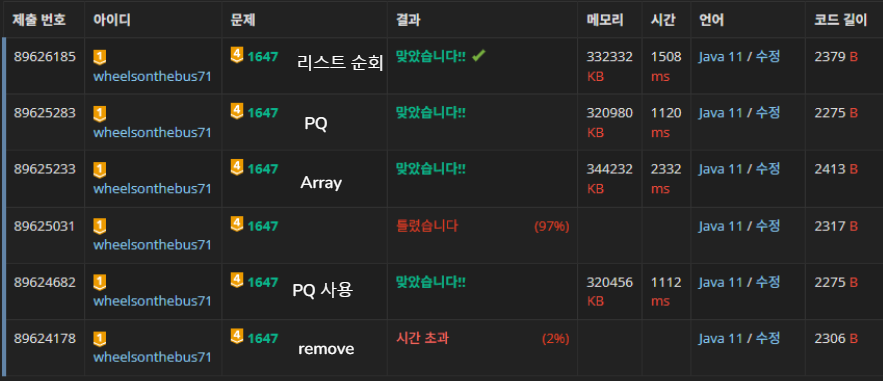
PQ 를 사용하는 것이 가장 시간이 빠르다.
정렬해야할 일이 있으면 PQ를 쓰는 것이 좋겠다.