인프런 김영한 님의 스프링 입문 - 코드로 배우는 스프링 부트, 웹, MVC, DB 접근 기술 강의를 보고 정리한 내용입니다.
웹 개발은 크게 3가지 방식으로 볼 수 있다.
- 정적 컨텐츠 (파일을 그대로 웹 브라우저에 전달)
- MVC와 템플릿 엔진 (서버에서 변형을 해서 전달)
- API (json 전달, 서버끼리 통신, …)
1. 정적 컨텐츠
- 스프링 부트는 정적 컨텐츠 기능을 자동으로 제공한다.
- 원하는 html을 추가하면 그대로 view로 출력된다.
정적 컨텐츠란 ?
- Spring.io 링크
- 스프링 부트는 기본적으로
/static(/public,/resources,/META-INF/resources) 경로로부터 정적 콘텐츠 기능을 제공한다. - Spring MVC의
ResourceHttpRequestHandler를 사용하여 정적 리소스를 처리하고,ebMvcConfigurer를 추가해addResourceHandlers메서드를 오버라이드하여 동작을 수정할 수 있다. - 독립 실행형 web application에서는 기본 서블릿이 활성화되어, 스프링이 요청을 처리하지 않을 경우
ServletContext의 루트에서 콘텐츠를 제공하지만, 대부분의 경우 스프링이DispatcherServlet을 통해 모든 요청을 처리한다. - 기본적으로 정적 리소스는
/**경로에 매핑되고,properties에spring.mvc.static-path-pattern속성을 사용해 경로를 지정할 수 있다.spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/resources/** properties에spring.resources.static-locations속성을 사용해 정적 리소스 위치를 커스터마이징할 수 있다.
동작 환경 그림
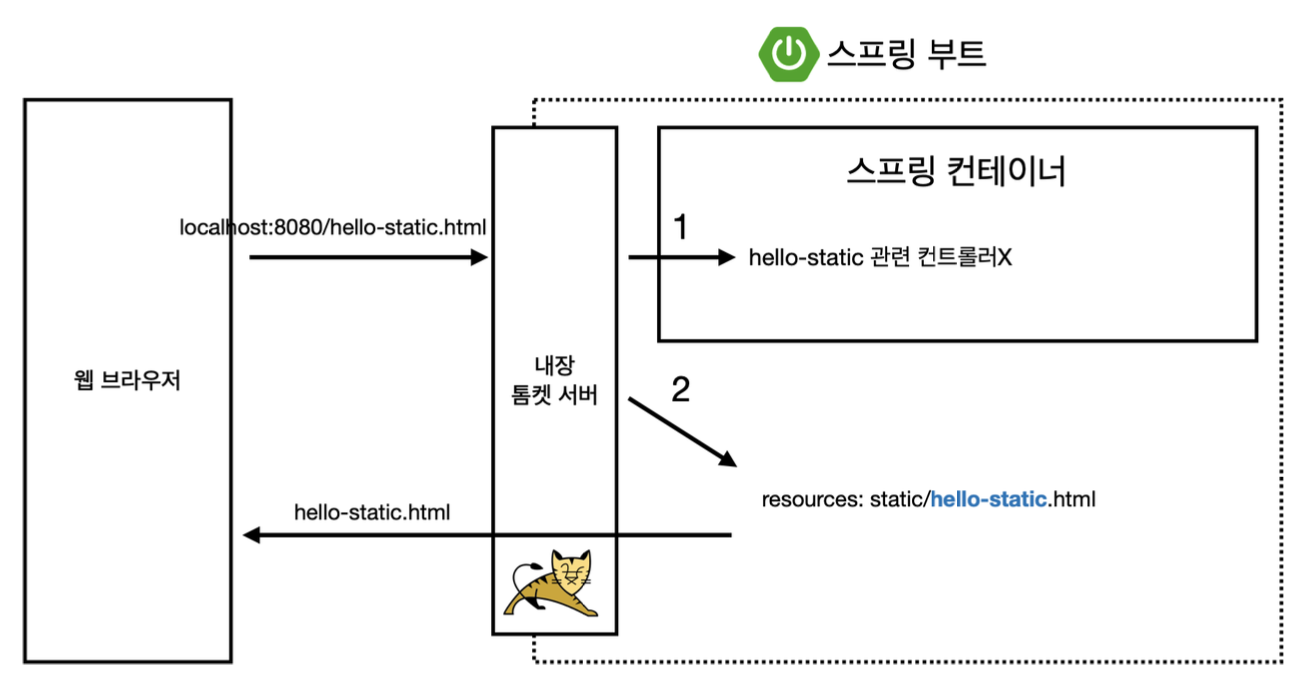
- 웹 브라우저에서 localhost:8080/hello-static.html 요청
- 톰캣 서버가 이 요청을 받아 스프링 컨테이너로 전달
- 스프링 컨테이너는 해당 요청에 대한 컨트롤러가 있는지 먼저 확인
- 없을 경우, 스프링 부트가
resources/static경로에서hello-static.html파일을 찾음 - 파일이 존재하면 해당 정적 컨텐츠 반환
2. MVC와 템플릿 엔진
MVC: Model, View, Controller
- View: 화면을 그리는데 모든 역량을 집중
- Controller, Model: 비즈니스 로직, 내부적 처리에 집중
동작 환경 그림
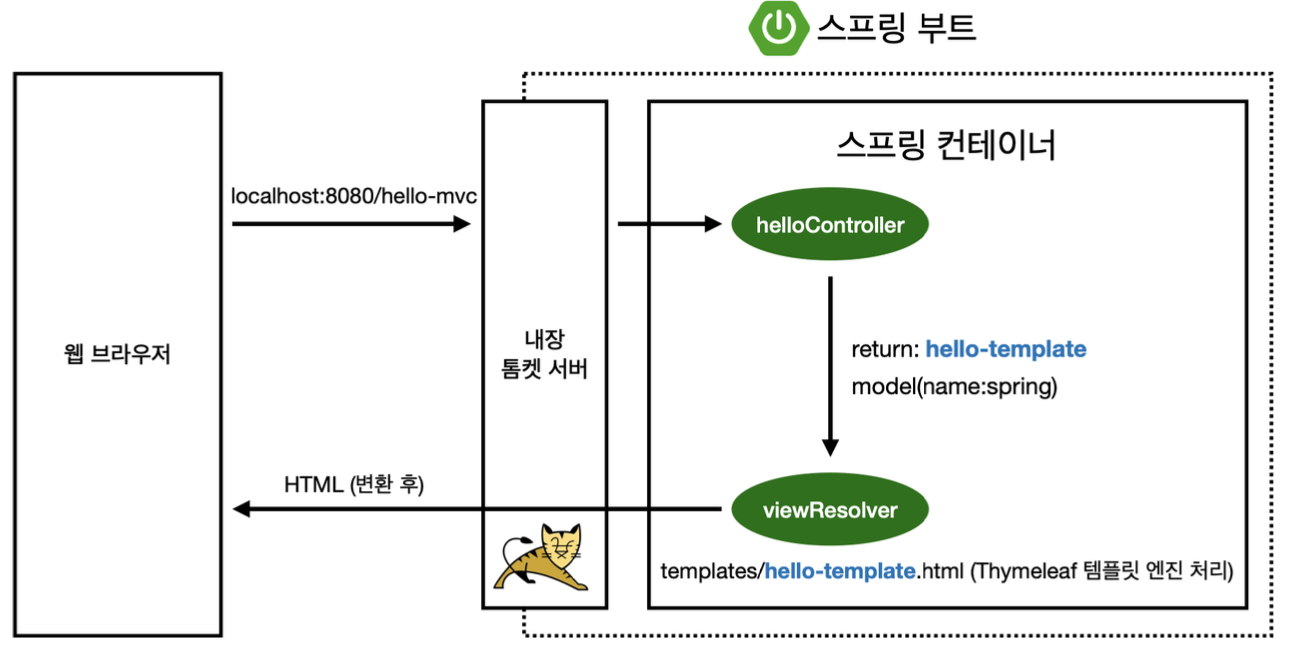
- 웹 브라우저에서 http://localhost:8080/hello-mvc?name=spring 요청
- 톰캣 서버가 이 요청을 받아 스프링 컨테이너로 전달
- 스프링 컨테이너는 해당 요청에 대한 컨트롤러가 있는지 확인 후 해당 요청에 대한 메서드 호출
- 내부 메서드 실행
@RequestParam값이 있는지 확인(required = true가 기본값이라)- 없을 경우,
MissingServletRequestParameterException반환 Model에RequestParam으로 받은 값 추가 후 반환
ViewResolver(뷰를 찾아주고 템플릿 엔진 연결) 스프링 부트가resources/tempaltes경로에서 return의 StringName(ViewName) 파일을 찾음- Thymeleaf 템플릿 엔진에게 처리 요청
- Thymeleaf 템플릿 엔진이 렌더링 후 변환된 HTML을 웹 브라우저에 반환
3. API
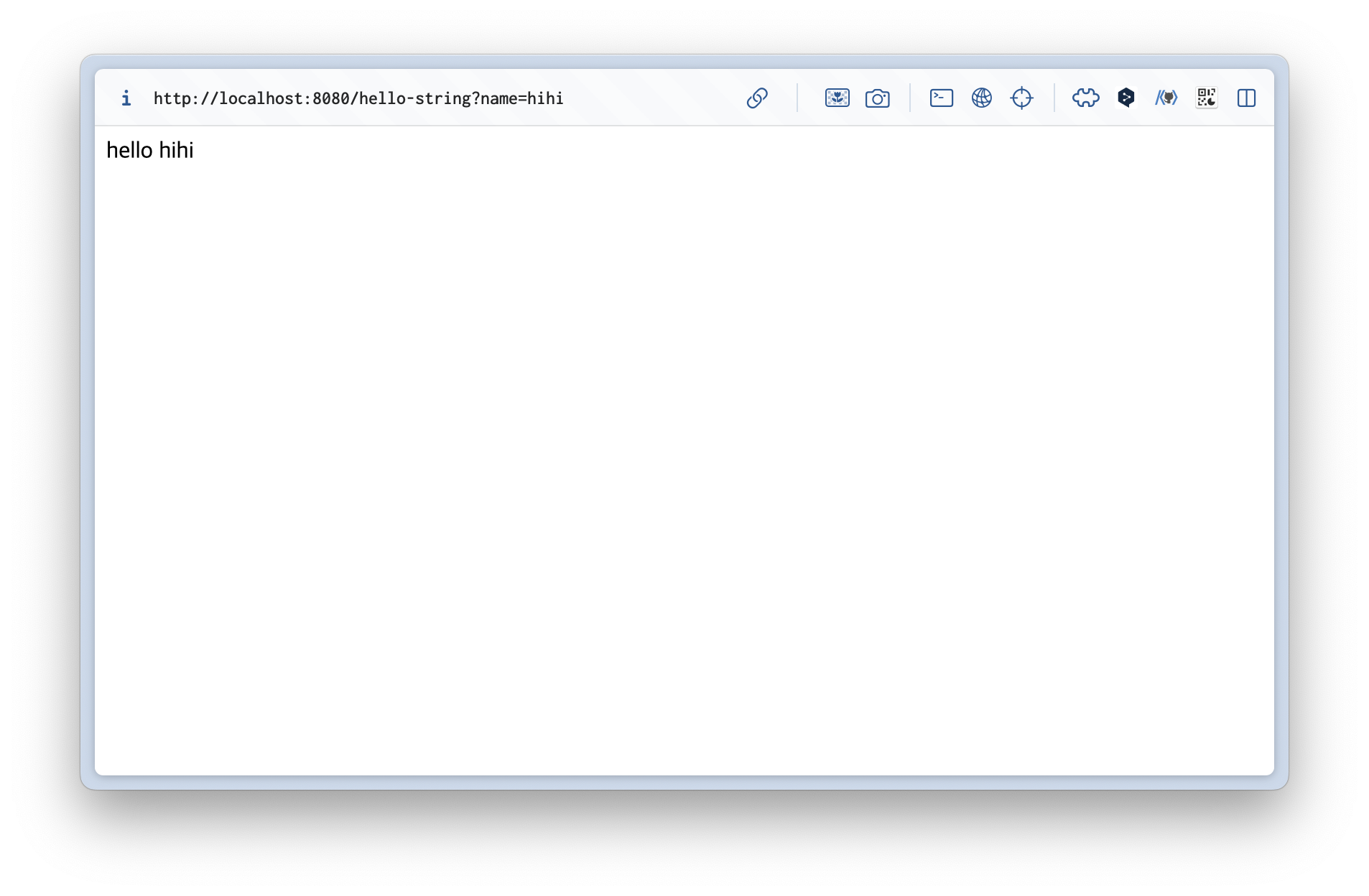
@ResponseBody 문자 반환
@GetMapping("hello-string")
@ResponseBody // http body에 데이터를 직접 넣겠다
public String helloString(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
return "hello " + name;
}@ResponseBody를 사용하면ViewResolver를 사용하지 않음- 대신에 HTTP의 body에 문자 내용을 직접 반환(HTML body tag를 말하는 것이 아님)
- 실행 결과
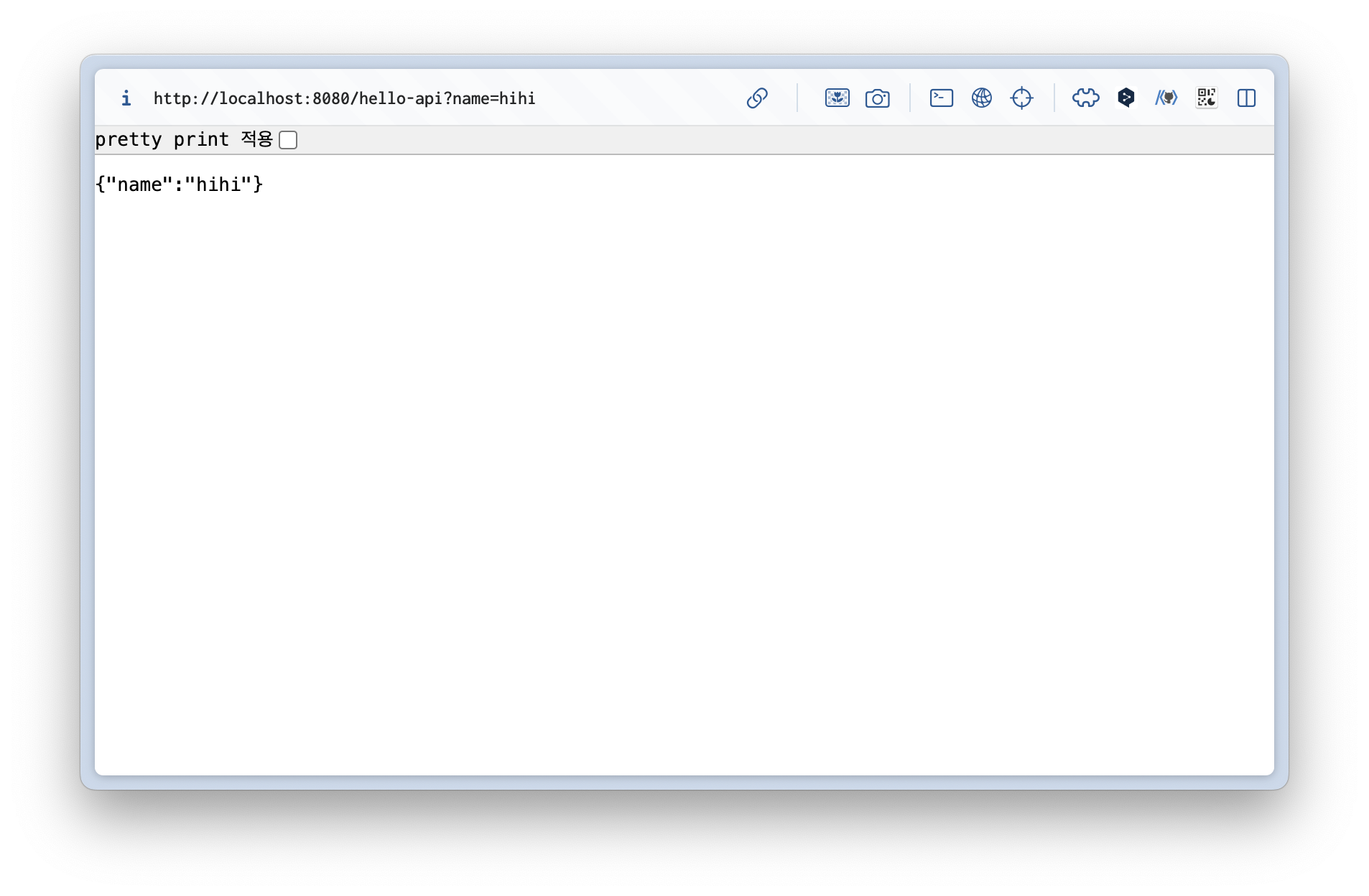
@ResponseBody 객체 반환
@GetMapping("hello-api")
@ResponseBody
public Hello helloApi(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
Hello hello = new Hello();
hello.setName(name);
return hello;
}
static class Hello {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}@ResponseBody를 사용하고, 객체를 반환하면 객체가 JSON으로 변환됨- 실행 결과
동작 환경 그림
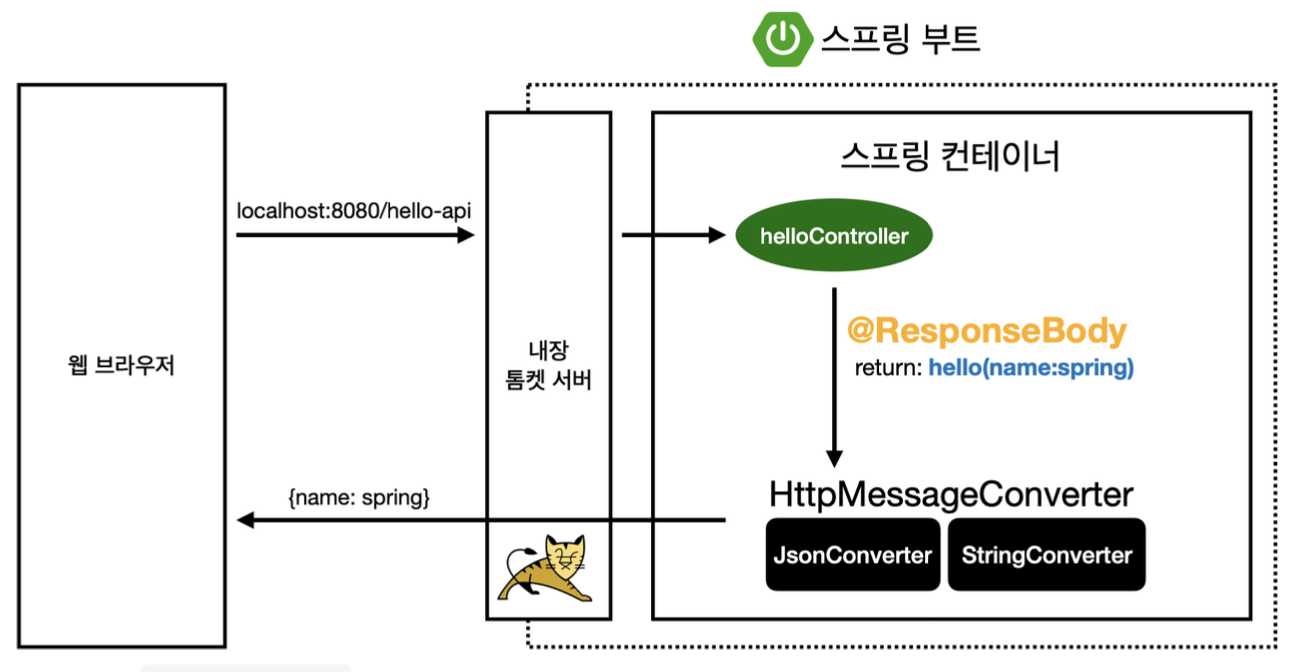
- 웹 브라우저에서 http://localhost:8080/hello-api?name=spring 요청
- 톰캣 서버가 이 요청을 받아 스프링 컨테이너로 전달
- 스프링 컨테이너는 해당 요청에 대한 컨트롤러가 있는지 확인 후 해당 요청에 대한 메서드 호출
@ResponseBodyAnnotation을 확인HttpMessageConverter가 작동- 문자일 경우,
StringConverter(StringHttpMessageConverter)가 return String Value 그대로 - 객체일 경우,
JsonConverter(MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter)가 객체를 json 형식의 데이터로 만듬
- 문자일 경우,
- HTTP Body로 반환
@ResponseBody를 사용- HTTP의 BODY에 문자 내용을 직접 반환
viewResolver대신에HttpMessageConverter가 동작- 기본 문자처리:
StringHttpMessageConverter - 기본 객체처리:
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter - byte 처리 등등 기타 여러 HttpMessageConverter가 기본으로 등록되어 있음
💡 Jackson: 범용적으로 사용되는 객체 → json 스타일 변환 라이브러리
