Order Statistics
- The ith order statistic in a set of n elements is the ith smallest element
- The minimum is thus the 1st order statistic
- The maximum is the nth order statistic
- The median is
- the (n+1)/2 order statistic, if n is odd
- lower median i=n/2, upper median i=(n/2)+1, if n is even
Finding Min and Max Simultaneously
- Input : n numbers
- Output : min and max
- n-1 comparisons for min, n-1 comparisons for max : total 2n-2 comparisons
- Can we do better?
- Don’t compare each element to min and max separately, but process elements in pairs - compare the elements of a pair to each other.
- Then compare the larger element to the current max so far, and compare the smaller element to the current min so far
- Only 3 comparisons for every 2 elements
- For initial min and max :
- If n is even, compare the first two elements and set the larger to max and the smaller to min. Then process the rest in pairs.
: 1 initial comparison and 3(n-2)/2 more comparisons = 3n/2 – 2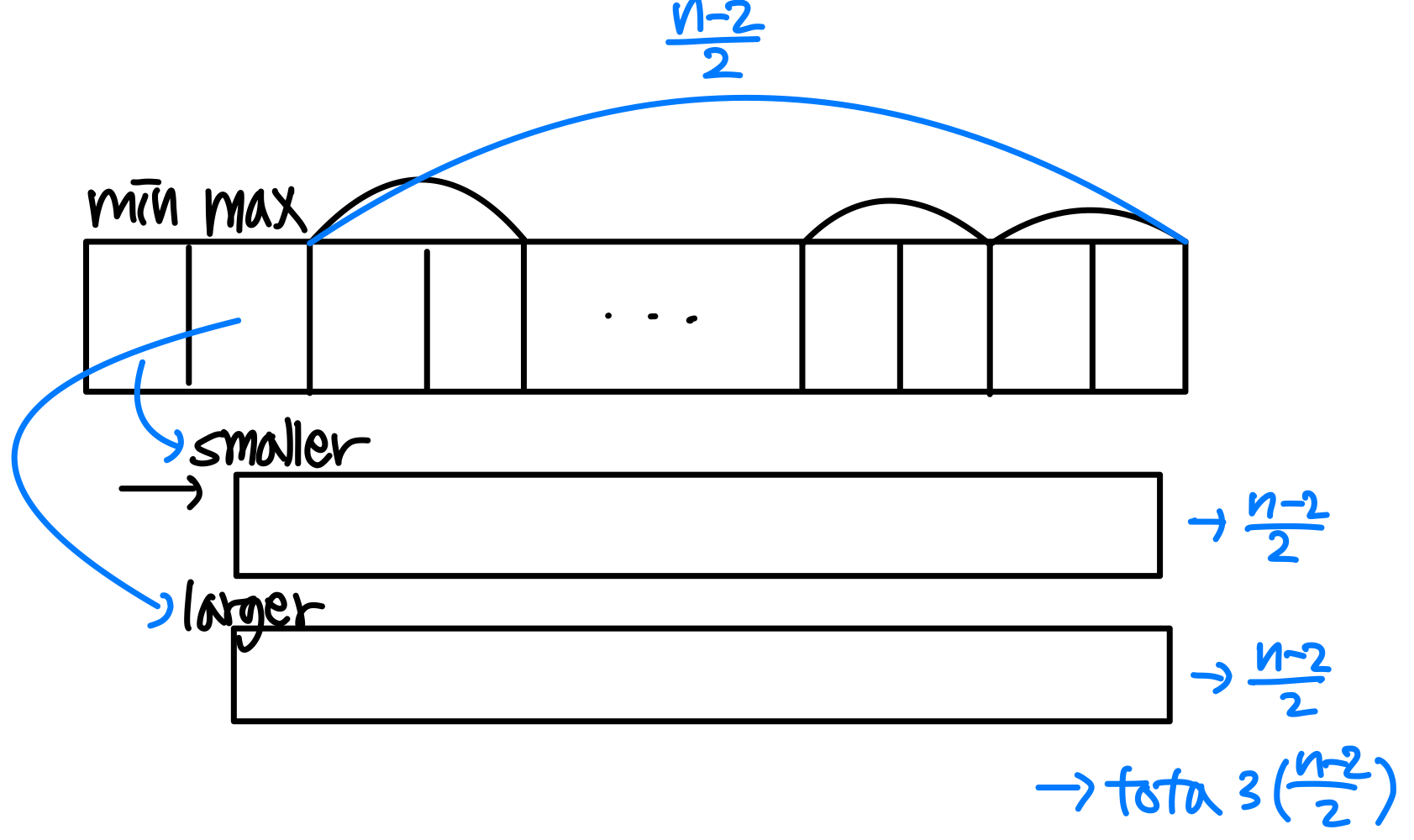
- If n is odd, set both min and max to the first element. Then process the rest in pairs.
: If n is odd, 3(n-1)/2 comparisons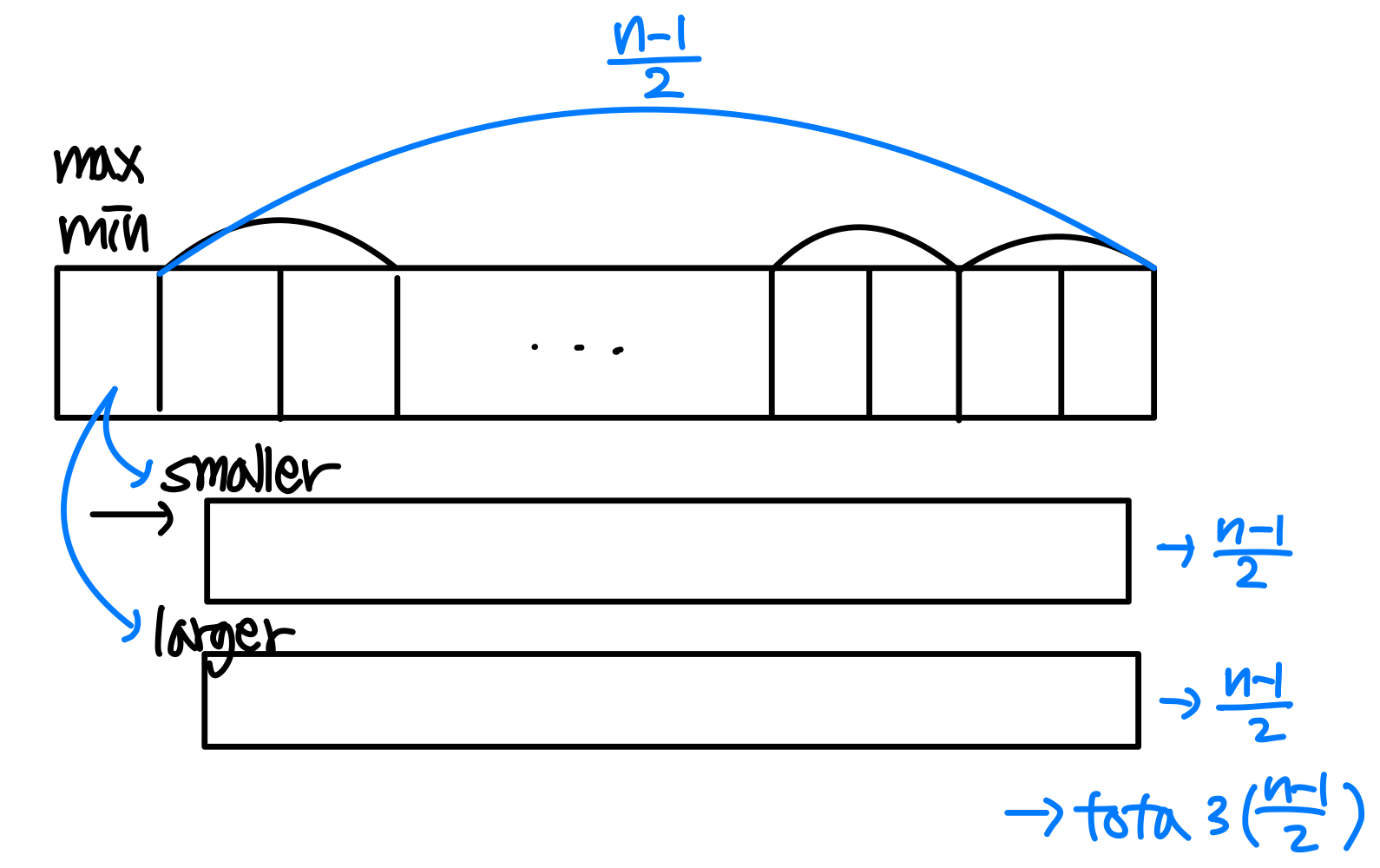
- If n is even, compare the first two elements and set the larger to max and the smaller to min. Then process the rest in pairs.
The Selection Problem
- A more interesting problem is selection: finding the ith smallest element of a set
- Input: A set A of n (distinct) elements and a number i, with 1 ≤ i ≤ n.
- Output: The element x in A that is larger than exactly i-1 other elements of A → ith element

- We will study two algorithms:
- A practical(실용적인) randomized algorithm with Θ(n) expected(avg) running time
- A cool algorithm of theoretical interest only with Θ(n) worst-case running time
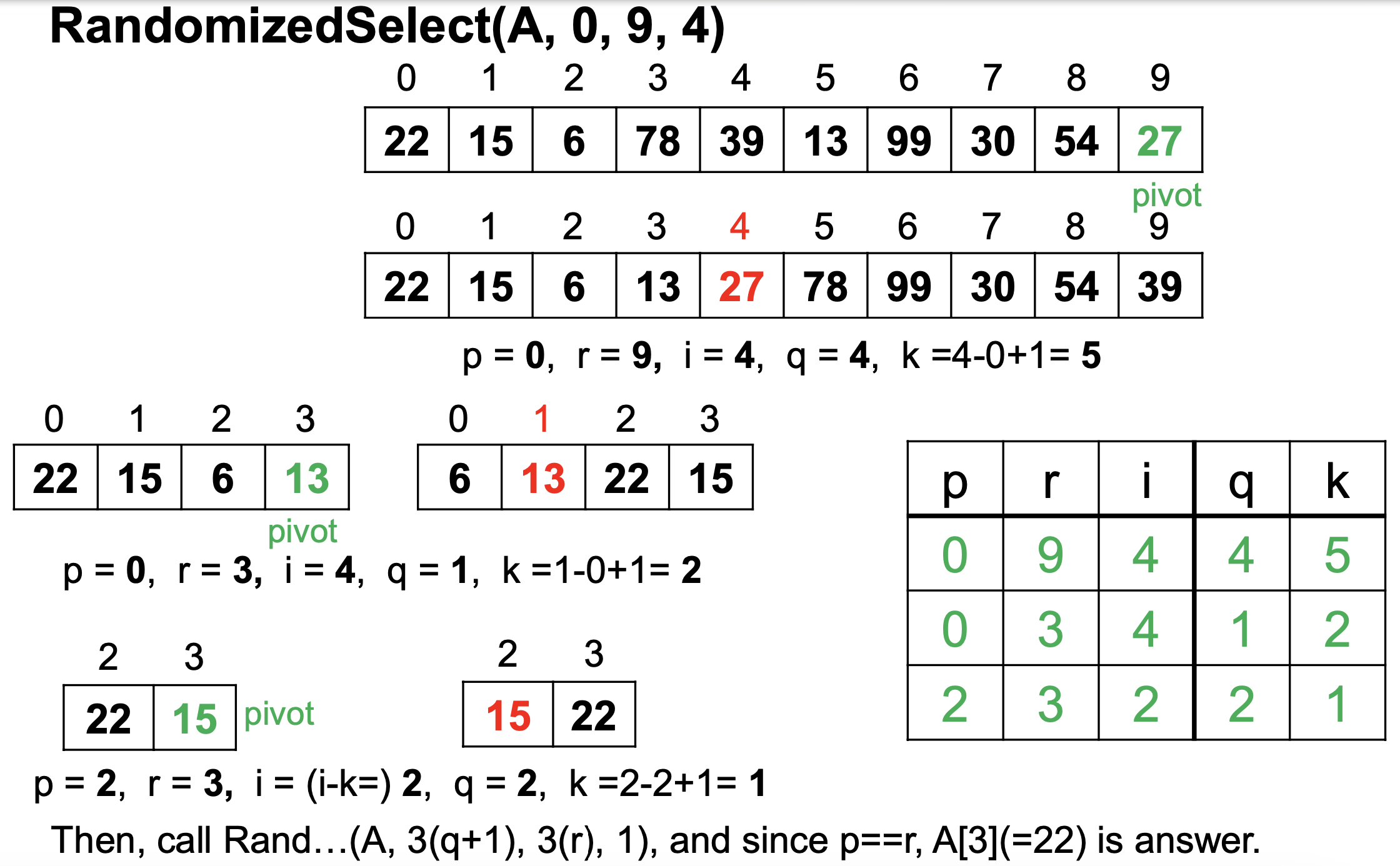
Randomized Selection
- Key idea: use partition() from quicksort
- But, only need to examine one subarray
- This saving shows up in running time: Θ(n) → 양쪽 다 필요 x
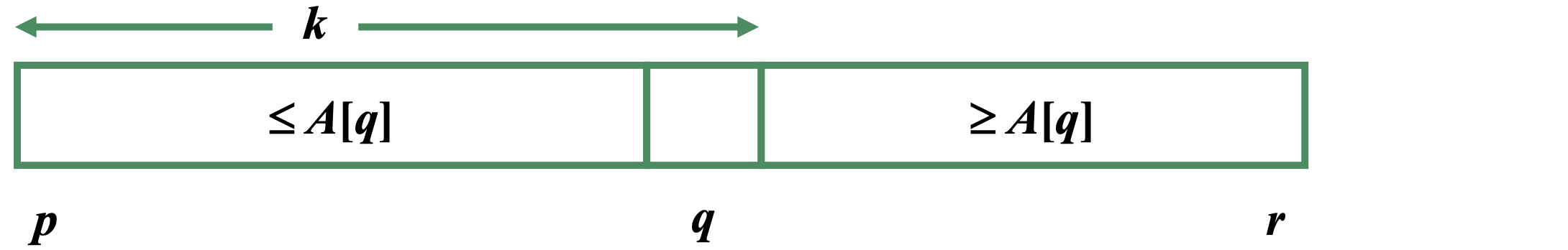
- Partition the array A[p..r] into two (possibly empty) subarrays A[p..q-1] and A[q+1..r]
- If i=k, return A[q]
- If i < k, find ith in the subarray A[p..q-1]
- If i > k, find (i-k)th smallest element in the subarray A[q+1..r]
Example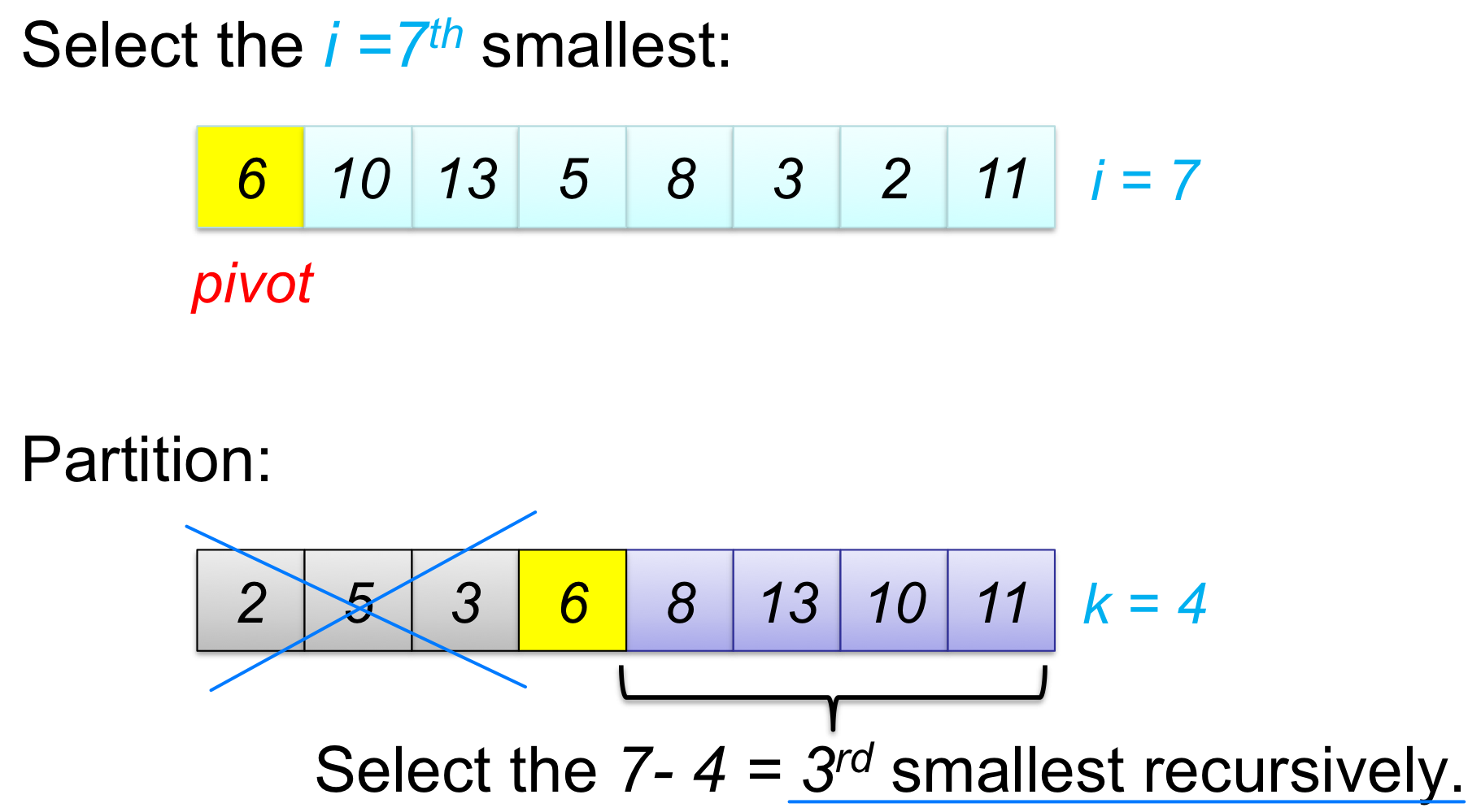
Code
Intuition for analysis
- ( All our analyses today assume that all elements are distinct )

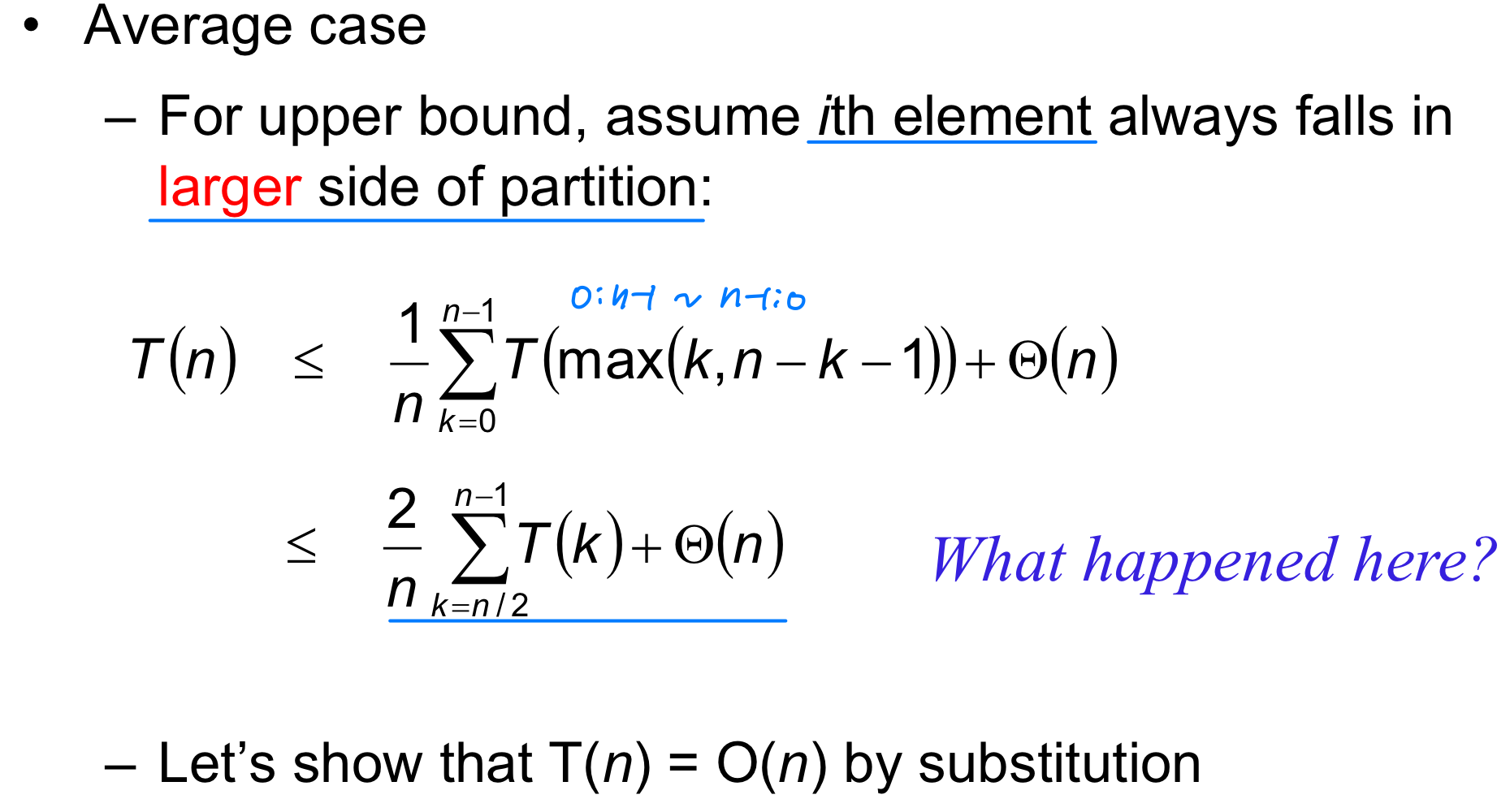
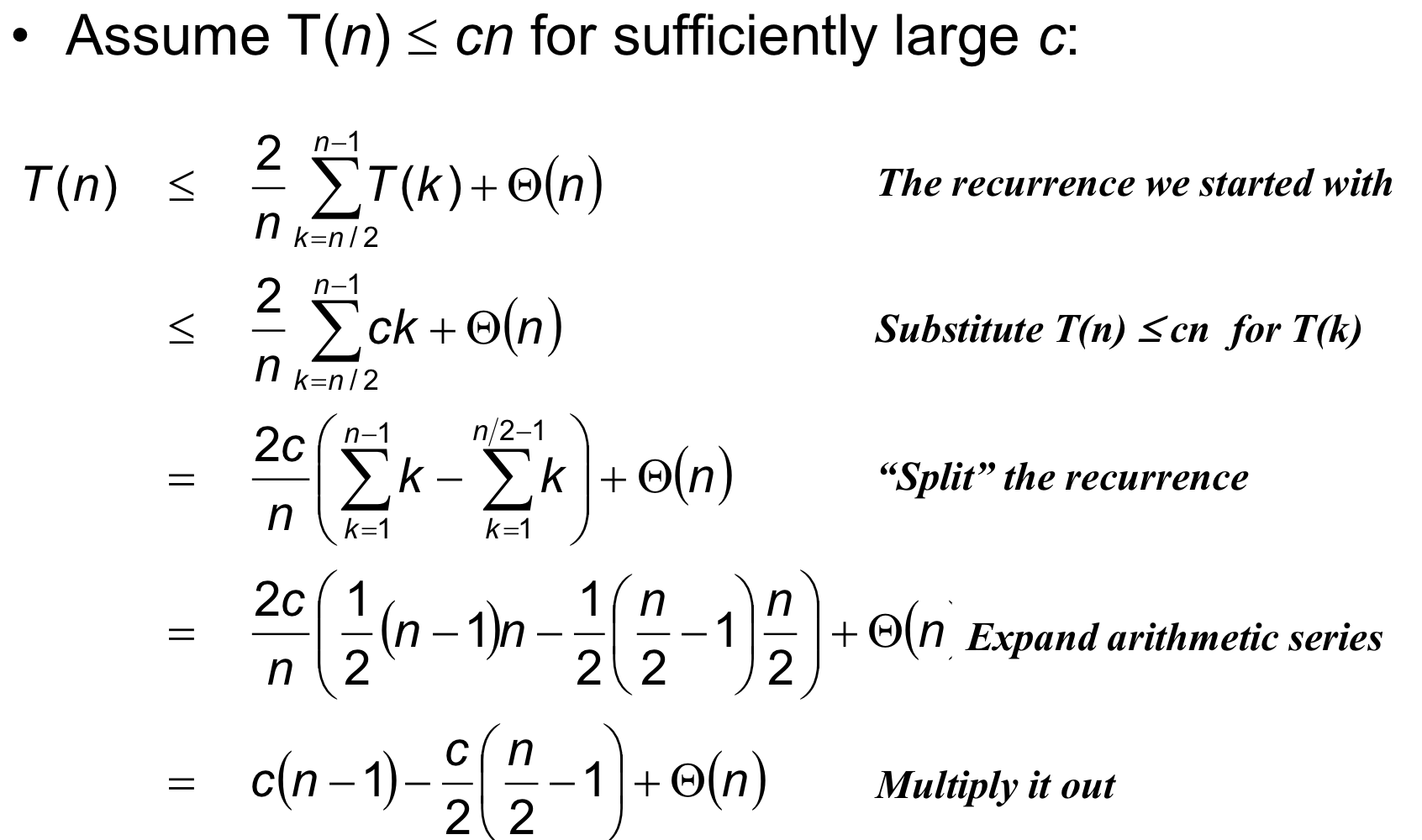

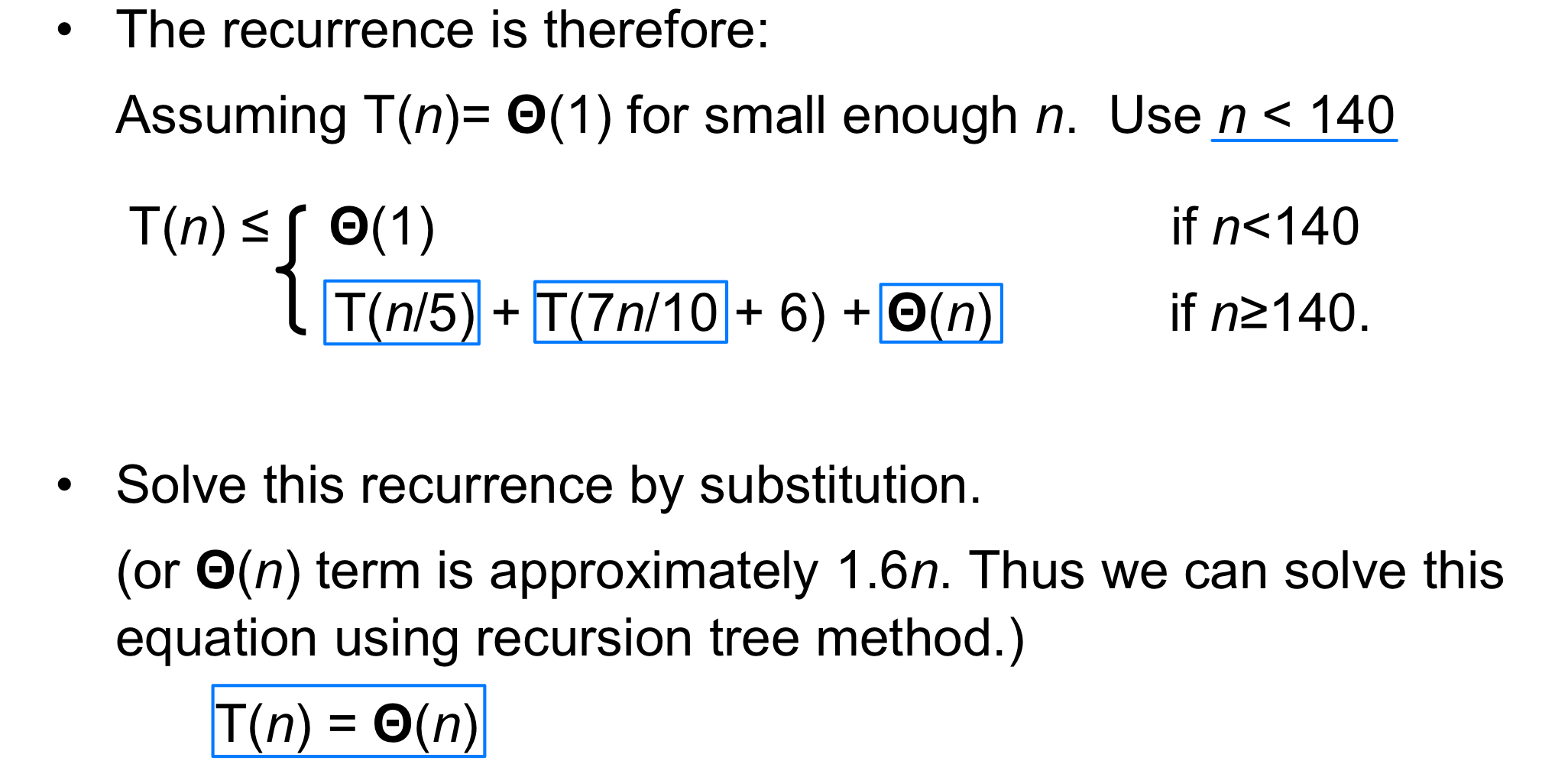
Worst-case Linear-Time Selection
- Randomized algorithm works well in practice.
But in worst case its time complexity is O(n) - What follows is a worst-case linear time algorithm, really of theoretical interest only
- Basic idea:
- Generate a good partitioning element
- Call this element x
Pesudo-code
Initially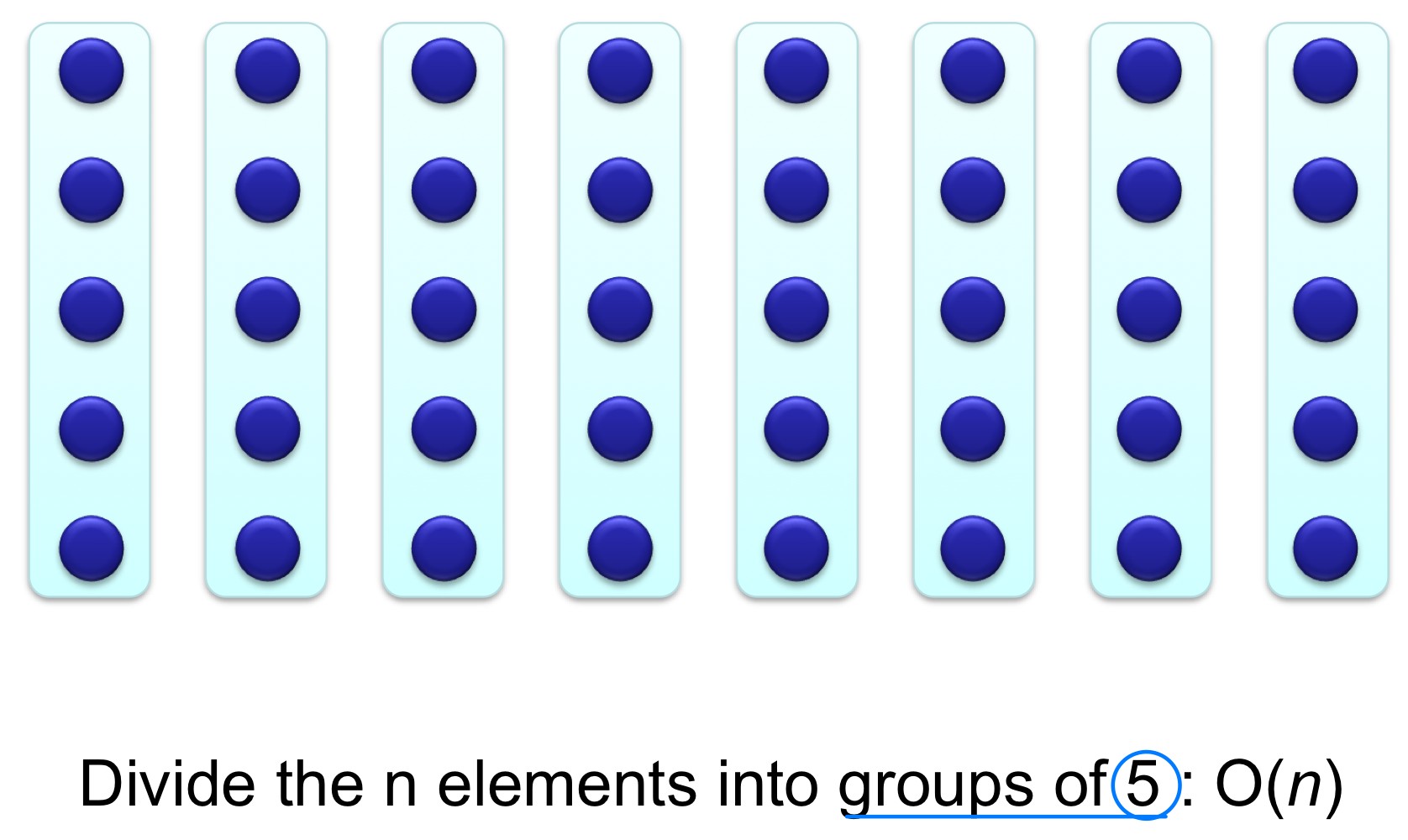
Step 2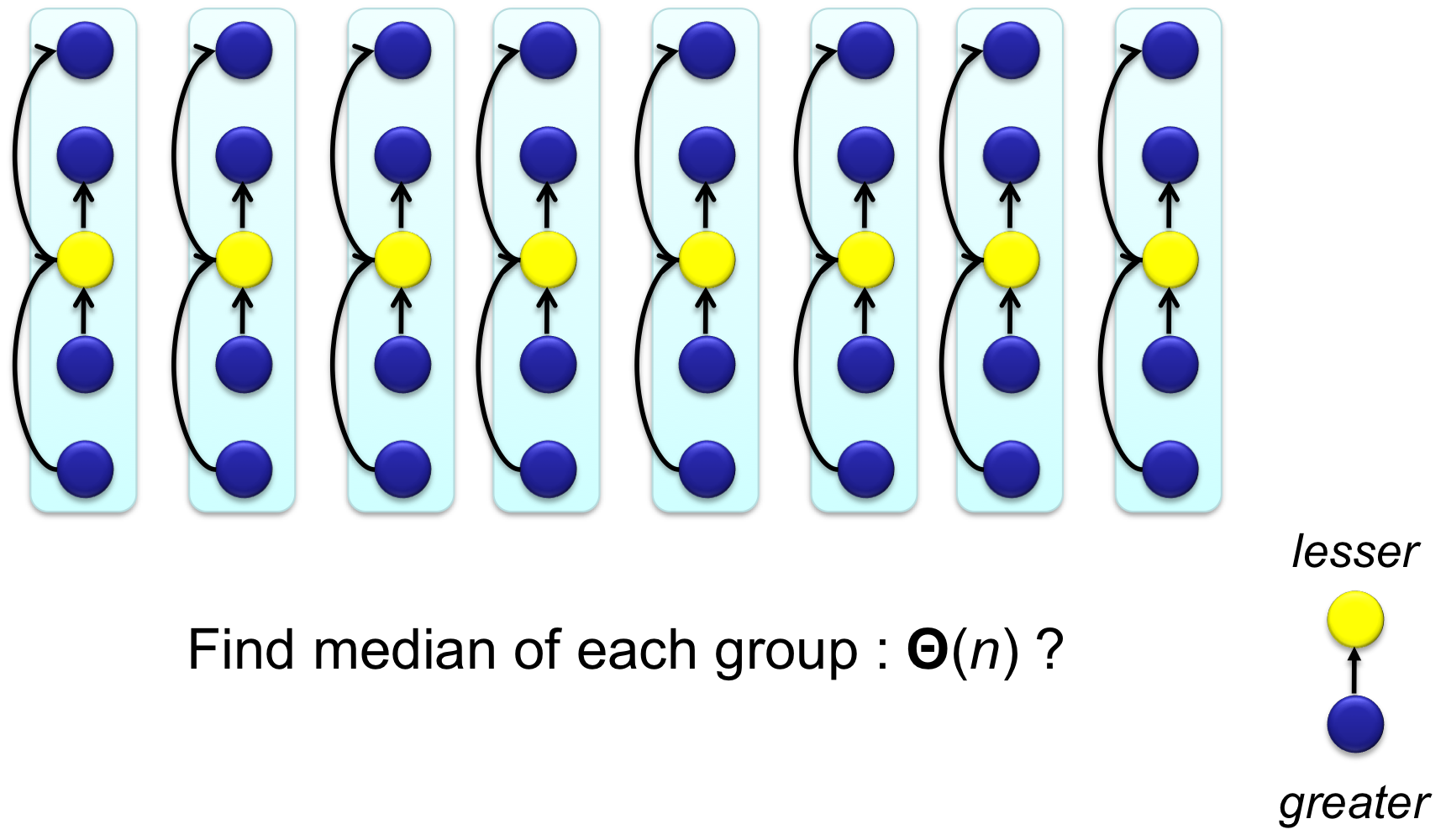
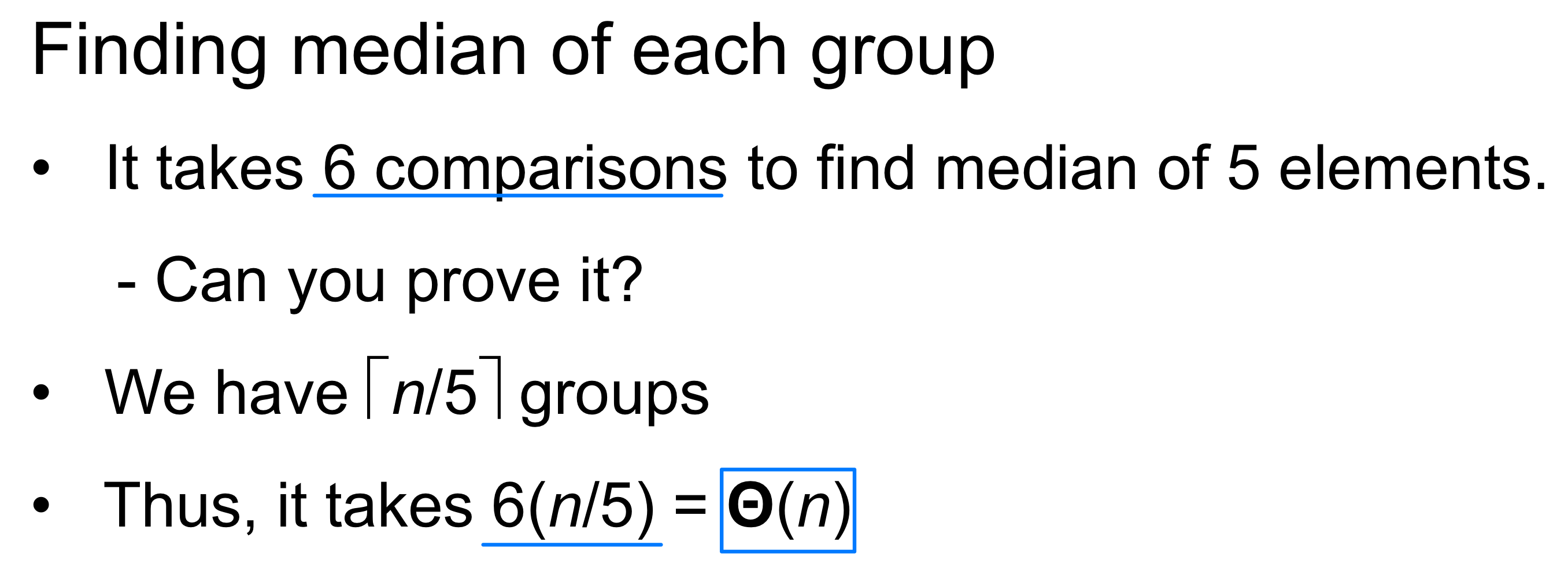
Step 3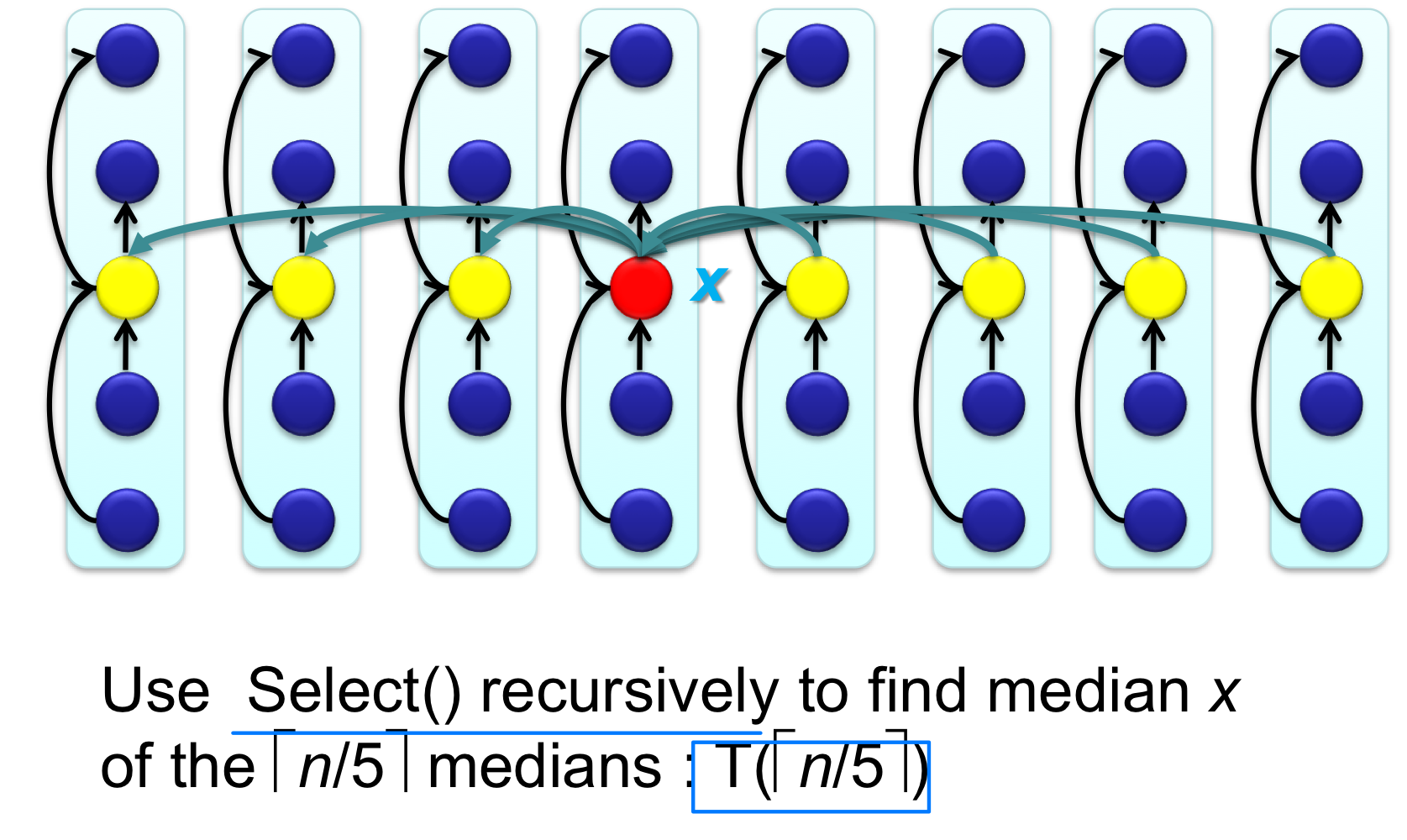
Around the pivot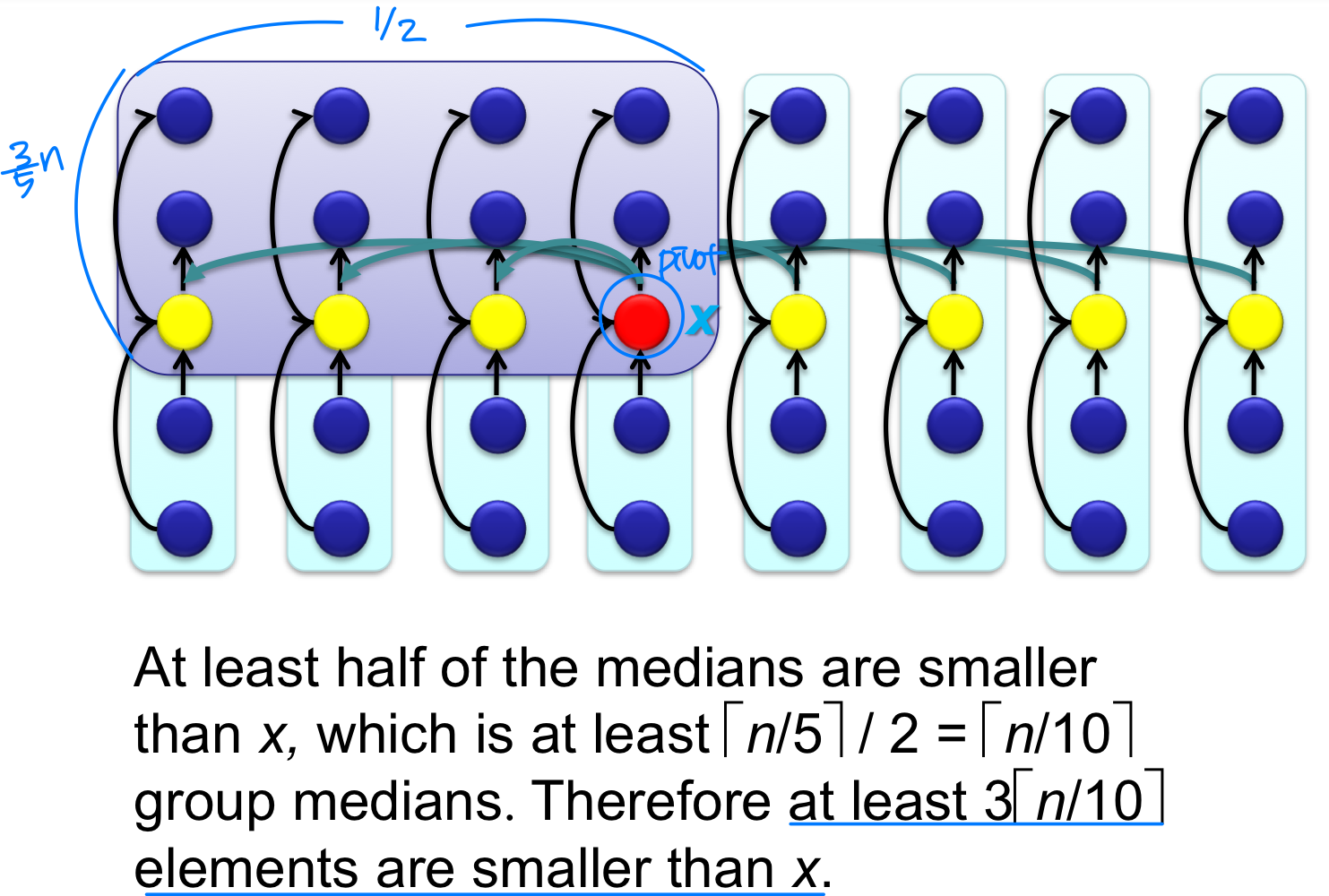
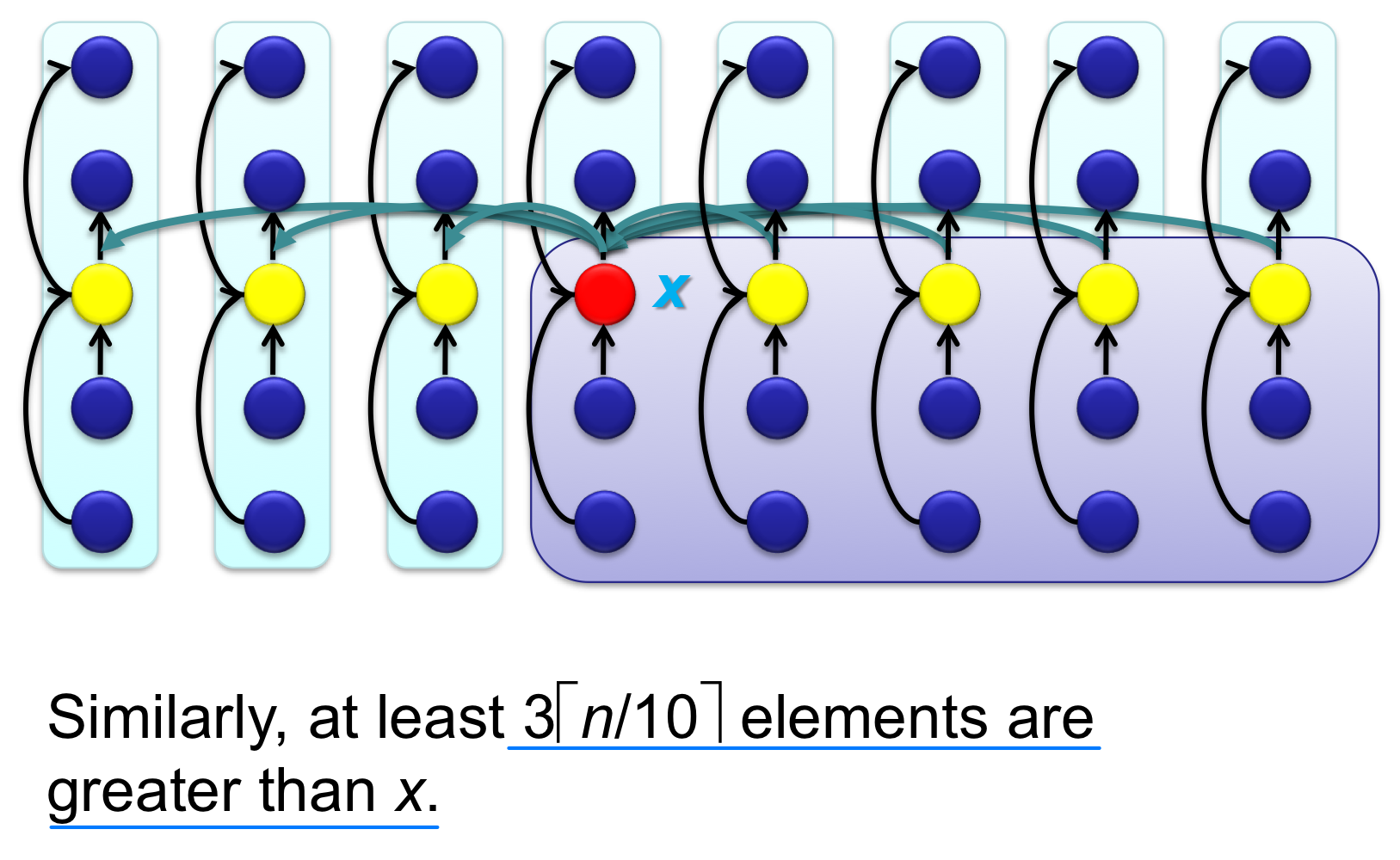

Analysis
Exercise in Class
1. 

2. What is the minimum number of comparisons that is needed to find median of 5 elements
A. 6
HGU 전산전자공학부 용환기 교수님의 23-1 알고리듬 분석 수업을 듣고 작성한 포스트이며, 첨부한 모든 사진은 교수님 수업 PPT의 사진 원본에 필기를 한 수정본입니다.

