DI
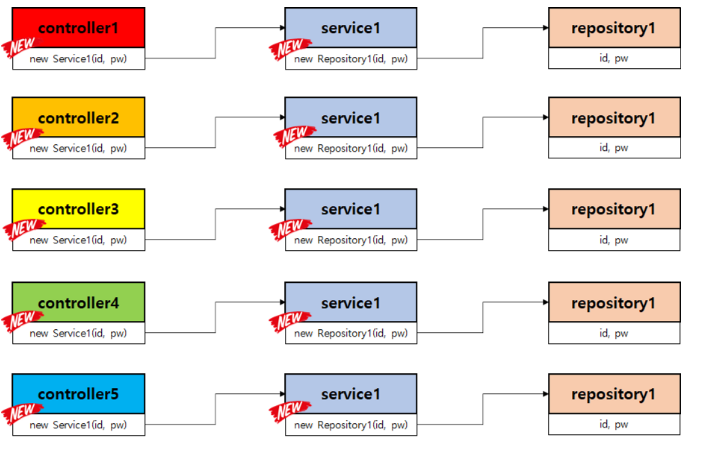
- 강한 결합 : Controller가 필요한 service 만들어쓰고, servce가 필요한 repository 만들어 쓰고. 강한 결합일 시 아래쪽에서 하나만 바뀌면 그걸 쓰는 모든 객체들을 다 바꿔야 한다.
컨트롤러가 서비스를, 서비스가 리포짓터리를 제어.
싱글톤 패턴
: 강한 결합을 해결하려면 객체 생성은 딱 1번만하고 생성된 객체를 모든 곳에서 재사용하면된다.
Class Service1 {
private final Repository1 repitory1;
// repository1 객체 사용
public Service1(Repository1 repository1) {
//this.repository1 = new Repository1(); < 이렇게 하지않고
this.repository1 = repository1;
}
}
// 객체 생성
Service1 service1 = new Service1(repository1);- new를 쓰지 않고 생성이 된 repository1의 객체를 파라미터로 받아와서 private final 변수에 넣어주는 식으로 사용. DI. 의존성 주입.
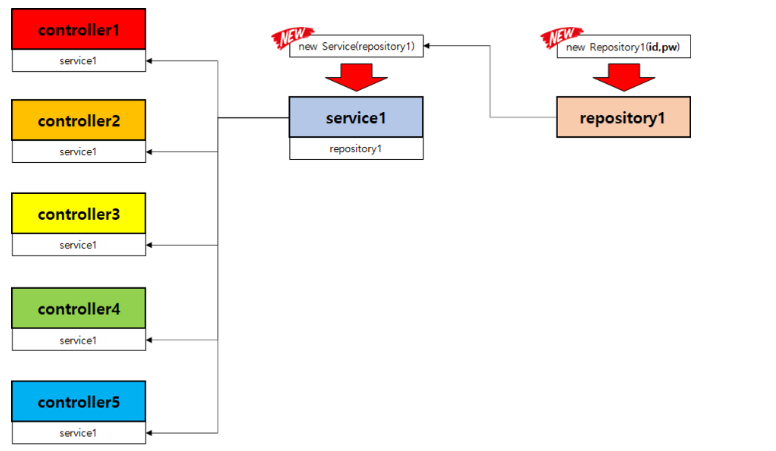
느슨한 결합
: 미리 만들어놓은 repository를 service가 그대로 쓰고, 미리 만든 service도 controller가 재사용하면 결합이 느슨해지고 제어의 방향이 바뀐다.
리포짓토리가 서비스를, 서비스가 컨트롤러를 제어.
IoC(제어의 역전)
: 일반적으로는 사용자가 자신이 필요한 객체를 생성해서 사용하지만,
용도에 맞게 이미 만들어진 객체를 필요에 따라 가져다가 사용.
기존의 컨트롤러->서비스->레포 쪽으로 가던 제어가 반대 방향으로 바뀌었다.
IoC 컨테이너
: DI를 사용하려면 우선 객체 생성이 되어 있어야 한다. 스프링 프레임워크는 필요한 객체를 생성하여 관리하는 역할을 대신해준다.
-
스프링 Ioc 컨테이너 :
빈을 모아둔 통 -
빈(bean): 스프링이 관리하는 객체
빈 등록 방법
-
@Component : 클래스를 선언할 때 위에 @Component 애너테이션 설정.
그러면 스프링 서버가 해당 클래스로 객체를 하나 생성하고 그걸 IoC 컨테이너에 빈으로 저장한다.
@SpringBootApplication의 위치와 그 하위 패키지들의 경우에만 설정이 된다. -
@Bean : 개발자가 직접 객체를 생성해 빈으로 등록 요청.
BeanConfiguration 클래스를 만들고 @Configuration를 달고 내가 등록하려는 함수 위에 @Bean을 설정하면 된다.
package com.sparta.myselectshop.config;
import com.sparta.myselectshop.repository.ProductRepository;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfiguration {
@Bean
public ProductRepository productRepository() {
String dbUrl = "jdbc:h2:mem:db";
String username = "sa";
String password = "";
return new ProductRepository(dbUrl, username, password);
}
}빈 사용 방법
- @Autowired
멤버변수 선언 위에 @Autowired를 달면 스프링에 의해 DI가 된다.
@Component
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
// ...
}변수를 private final로 만들고 생성자 위에 @Autowired를 달아도 스프링에 의해 DI가 된다.
@Component
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
@Autowired
public ProductService(ProductRepository productRepository) {
this.productRepository = productRepository;
}
// ...
}-
IoC컨테이너에 의해 관리되는 클래스 내에서만 쓸 수있다.
-
Spring 4.3부터 생성자 선언이 1개일때는 생략이 가능하다.
-
Lombok의 @RequiredArgsConstructor를 사용하면 멤버 변수에 private final만 붙이면 생성자를 만들고 @Autowired를 하는 과정을 생략 가능하다.
- ApplicationContext : 아래의 방법으로도 가능하다. (잘 쓰진 않는 느낌)
@Component
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
@Autowired
public ProductService(ApplicationContext context) {
// 1.'빈' 이름으로 가져오기
ProductRepository productRepository = (ProductRepository) context.getBean("productRepository");
// 2.'빈' 클래스 형식으로 가져오기
// ProductRepository productRepository = context.getBean(ProductRepository.class);
this.productRepository = productRepository;
}
// ...
}Spring 3계층 어노테이션
-
스프링 3계층 @는 모두 @Component
(@Controller, @RestController, @Service, @Repository) -
JpaRepository<"@Entity 클래스", "@Id 의 데이터 타입">를 상속(extends)받는 interface 로 선언하면 Spring Data JPA에 의해 자동으로 @Repository가 추가된다.
Spring Framework
-
Enterprise applications 개발 편의성 제공. 기업용 어플리케이션
-
스프링은 결국 기업용 애플리케이션의 요구사항 해결에 초점을 맞춘 프레임워크
- 신뢰성이 중요
- 서버의 안정성 유지 중요
- 데이터 관리가 중요
막대한 양의 데이터 관리, 여러 사용자가 동시 접속 시 데이터 일관성
- 스프링은 개발자들이 기업의 요구사항 즉, @Service에만 집중할 수 있도록
반복되고 실수가 많은 @Controller와 @Repository쪽을 대신 해준다.
@Scheduled
- @SpringBootApplication 이 있는 class 에 @EnableScheduling 추가!
@Slf4j
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class Scheduler {
private final NaverApiService naverApiService;
private final ProductService productService;
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
// 초, 분, 시, 일, 월, 주 순서
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 1 * * *")
public void updatePrice() throws InterruptedException {
log.info("가격 업데이트 실행");
List<Product> productList = productRepository.findAll();
for (Product product : productList) {
// 1초에 한 상품 씩 조회합니다 (NAVER 제한)
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
String title = product.getTitle();
List<ItemDto> itemDtoList = naverApiService.searchItems(title);
ItemDto itemDto = itemDtoList.get(0);
// i 번째 관심 상품 정보를 업데이트합니다.
Long id = product.getId();
productService.updateBySearch(id, itemDto);
}
}
}