SpaCy는 python과 cython으로 작성된 자연어 처리(NLP) 오픈 소스 라이브러리로, 자연어 처리 작업을 위한 다양한 도구 및 모델을 제공한다. Spacy는 다국어 지원이 가능하며, 품사 태깅/구문 분석/개체명 인식/워드 임베딩 등을 수행할 수 있다.
Build Custom dataset with SpaCy NER Annotation Tool
사실 당장 개체명 인식 커스텀 데이터셋을 만들어보라고 하면 좀 막막할 거 같은데.. (내가 그래서) spaCy에서 커스텀 데이터셋 어노테이션 툴을 지원하고 있다.
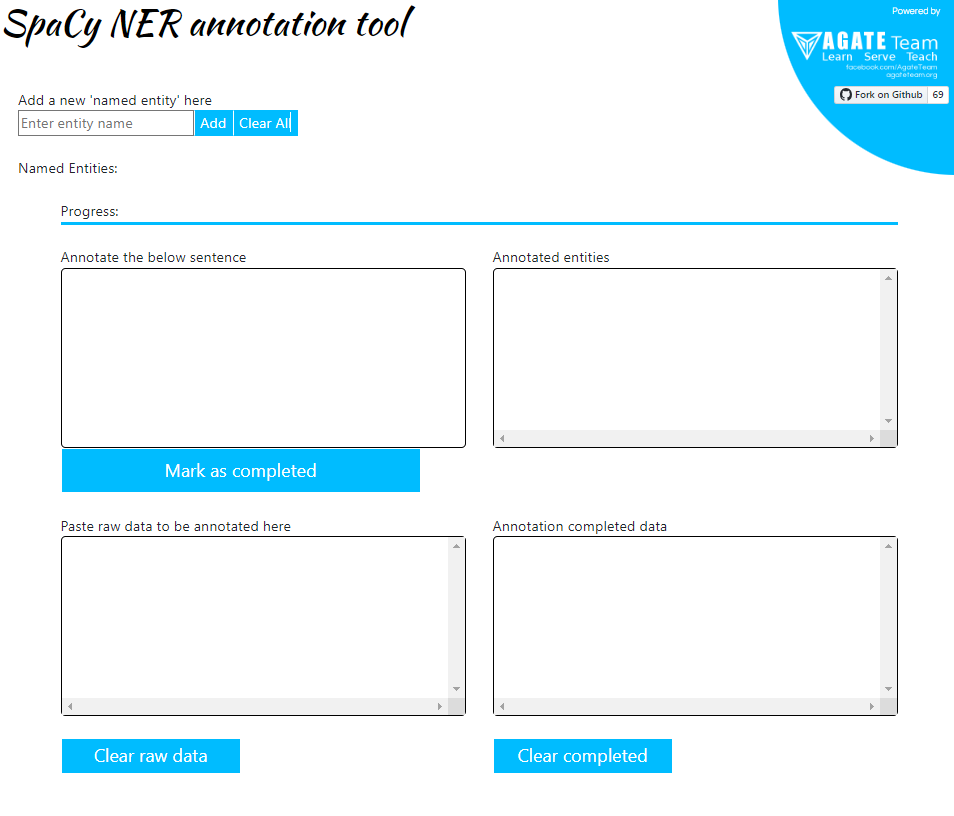
사용 방법
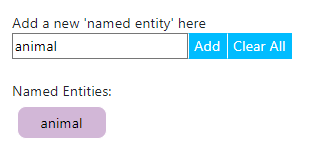
- 커스텀으로 추가하고자 하는 named entity를 입력하고 Add한다. 예시로 “animal”이라는 entity를 입력해 보았다.
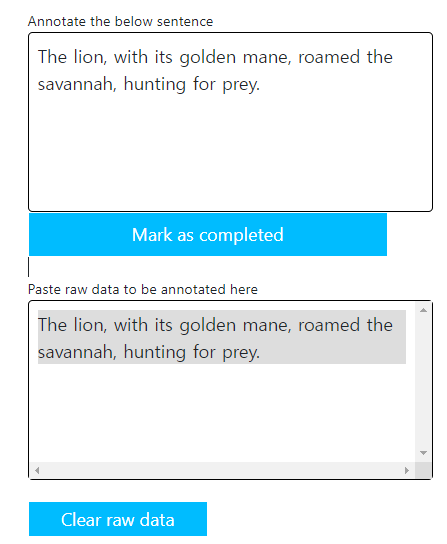
- annotation을 수행할 sentence를 입력한다. 왼쪽 하단 “Paste raw data ~ “이 부분에 sentence를 넣으면, 왼쪽 상단에 자동으로 복붙이 될 것이다.
- 왼쪽 상단에서 annotation 마킹을 진행한다. 마킹하고자 하는 entity를 드래그(그러니까 나의 경우는 lion이 드래그 대상이 된다.)하고 new Named Entity에 추가했던 animal을 클릭한다.
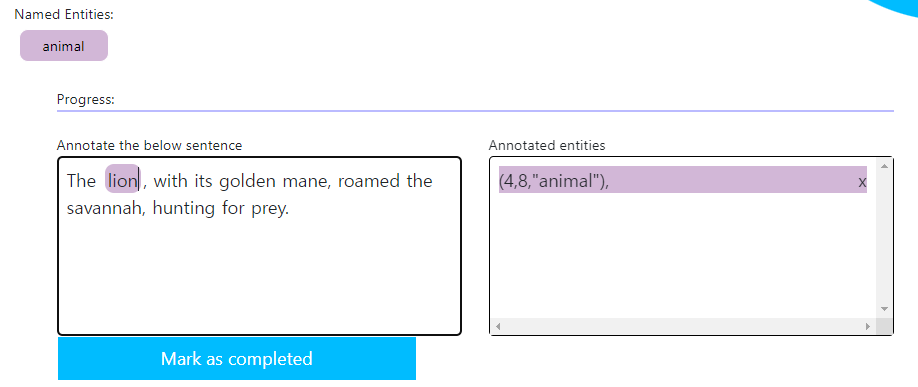
그러면 위 그림처럼 오른쪽 상단 Annotated entities에 (, , Named Entity) 이렇게 어노테이션이 되었을 것이다. 여기서 , 는 내가 어노테이션한 글자의 위치이다. (글자의 인덱스라고 보면 됨. 문장 시작 부분을 0부터 시작해서, 띄어쓰기, 특문 등 포함하여 +1씩)
그러니까
lion을 예로 들어 보면은, T(0)h(1)e(2) (3)l(4)i(5)o(6)n(7) (8)이니까 lion의 위치는 4, 5, 6, 7까지. 마킹은 (4, 8)이므로 마지막 위치는 포함하지 않으니 실질적으로 [-1]인걸로 보면 되겠다.만약 마킹이 여러 개라면, 같은 방법으로 어노테이션 하면 된다. 다음 그림을 보자.
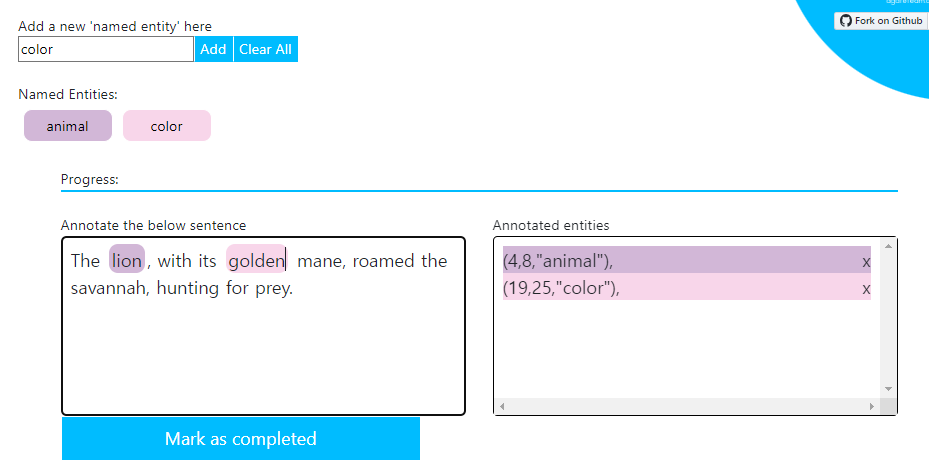
예시를 위해 임의로
color를 new named entity로 추가했다.golden을 드래그한 후 Named Entities의color를 클릭하면 오른쪽 annotated entities에 새로운 entity로 추가되는 것을 볼 수 있다.마킹이 끝났다면
Mark as completed를 클릭. 다음과 같이 Annotation completed data를 얻을 수 있다.

이런 식으로 반복해서 어노테이션 데이터들을 충분히 모아보자.
Train custom dataset with SpaCy
들어가기 전에, 우선 spaCy가 깔려있지 않다면 pip install로 설치해주자. 아마 별 문제 없이 설치될 것이다. spaCy에서는 다국어를 지원하지만, 여기서는 영어를 쓸 것이기 때문에..
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")영어 기반 사전학습 모델인 en_core_web_sm 을 불러오자. 여기서 에러가 난다면, 터미널에서 en_core_web_sm을 설치해주면 된다.
$ python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm 그리고 위에서 만들었던 커스텀 데이터셋을 train, dev set으로 나누어서 불러오자.
나는 귀찮아서(…) 몇개 안 만들었지만.. 원활한 학습을 위한다면 the more, the better인거 아시조? 유남쌩?
train = [("In the quiet of the night, the hoot of an owl echoed through the woods.",{"entities":[(42,45,"animal")]}),
("Startled by the sudden movement, the deer sprinted through the forest.",{"entities":[(37,41,"animal")]}),
("The lion, with its golden mane, roamed the savannah, hunting for prey.",{"entities":[(4,8,"animal")]}),
("A playful puppy chased its tail in circles, full of boundless energy.",{"entities":[(10,15,"animal")]}),
("At the zoo, children giggled as they watched the monkeys swing from branch to branch.",{"entities":[(49,56,"animal")]}),
("Hidden in the tall grass, the tiger patiently stalked its unsuspecting victim.",{"entities":[(30,35,"animal")]}),
("Beneath the clear waters, colorful fish darted among the coral reefs.",{"entities":[(35,39,"animal")]}),
("The graceful swan glided across the calm surface of the pond, leaving a trail of ripples.",{"entities":[(13,17,"animal")]}),
("With a flap of its mighty wings, the eagle soared high above the mountain peaks.",{"entities":[(37,42,"animal")]}),
("Farmers relied on their trusty horses to plow the fields and transport goods.",{"entities":[(31,37,"animal")]}),
("Deep in the burrow, the rabbit nestled with its newborn kits.",{"entities":[(24,30,"animal")]}),
("In the distance, a herd of wild horses galloped freely across the open plains.",{"entities":[(32,38,"animal")]}),
("A curious squirrel scampered up the tree, its fluffy tail twitching with excitement.",{"entities":[(10,18,"animal")]}),
("With a gentle nudge, the mother giraffe encouraged her calf to take its first steps.",{"entities":[(32,39,"animal")]}),
("In the tropical rainforest, colorful parrots filled the canopy with their vibrant plumage and calls.",{"entities":[(37,44,"animal")]}),]
dev = [("The scientific expedition aimed to study the behavior of elusive dolphins in their natural habitat.",{"entities":[(65,73,"animal")]}),
("Surrounded by a cloud of dust, the bull charged at the matador in the center of the arena.",{"entities":[(35,39,"animal")]}),
("The wounded bird was tenderly nursed back to health by a kind-hearted animal lover.",{"entities":[(12,16,"animal")]}),
("The roar of the waterfall masked the sounds of frogs croaking in the nearby pond.",{"entities":[(47,52,"animal")]}),
("A curious cat batted at a dangling string, its whiskers twitching with curiosity.",{"entities":[(10,13,"animal")]}),]자, 이 데이터를 이제 spaCy에서 학습하기 위해 .spacy format으로 변환해줄 거다.
from spacy.tokens import DocBin
db = DocBin()
for text, annotations in train:
doc = nlp(text)
ents = []
for start, end, label in annotations:
span = doc.char_span(start, end, label=label)
ents.append(span)
doc.ents = ents
db.add(doc)
db.to_disk("./train.spacy")
db = DocBin()
for text, annotations in dev:
doc = nlp(text)
ents = []
for start, end, label in annotations:
span = doc.char_span(start, end, label=label)
ents.append(span)
doc.ents = ents
db.add(doc)
db.to_disk("./train.spacy")위 코드는 DocBin을 활용해서 train, dev를 각각 .spacy 폼으로 변환하는 코드이다. spaCy 공식 도큐먼테이션을 그대로 참고했다.
그리고 이 코드를 실행해서 2개의 spacy 파일(train.spacy, dev.pacy)을 얻었다면, 학습을 위한 config 파일을 만들어야 할 차례다.
spaCy Documentation의 Quickstart에서 이 config 만드는 방법을 설명해주고 있다.
링크를 접속해서, Quckstart 부분을 보면은 이렇게나 친절하게 config 파일 만들어줘버림.
해당사항 체크체크 해서 base_config.cfg 만들고 복사 붙여넣기 하거나 오른쪽 아래 저장 버튼 눌러서 그대로 가져가서 써먹어도 된다.
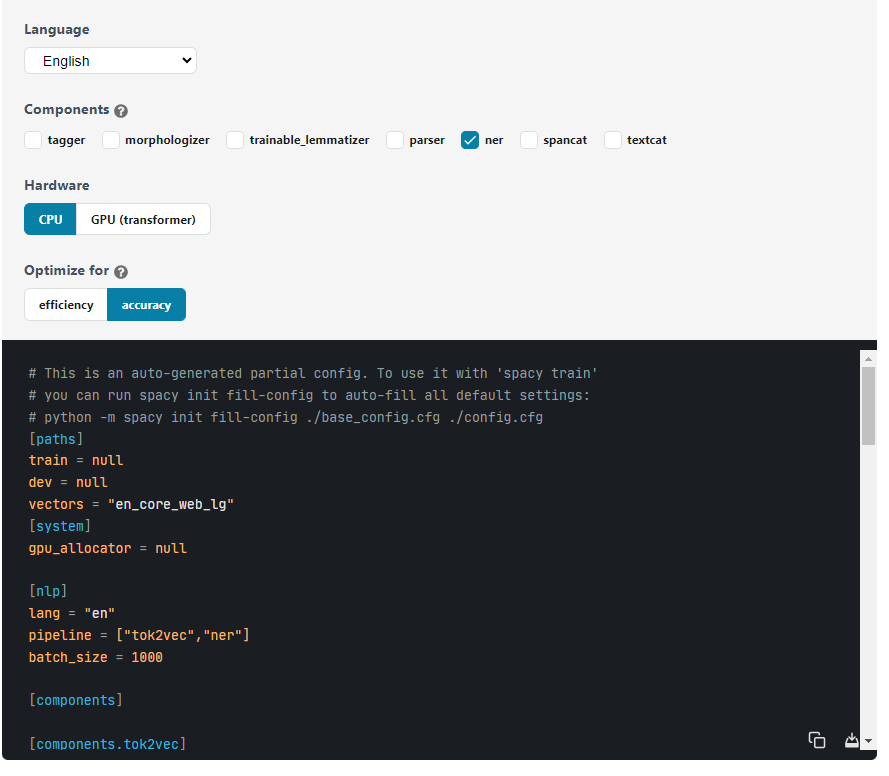
GPU를 사용할 경우, spacy-transformers를 추가 설치해야 한다. ($ pip install spacy-transformers)
참고로 그림에서 [paths] 부분의 train, dev = null 값은 내 train, dev 파일 경로로 직접 수정해줘야 한다.
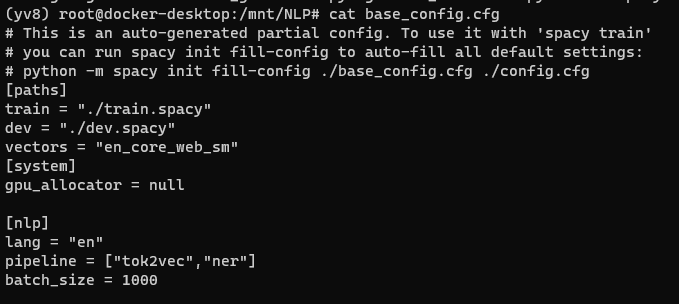
이렇게 base config 파일이 만들어졌으면, 다음 명령어를 실행한다
$ python -m spacy init fill-config base_config.cfg config.cfg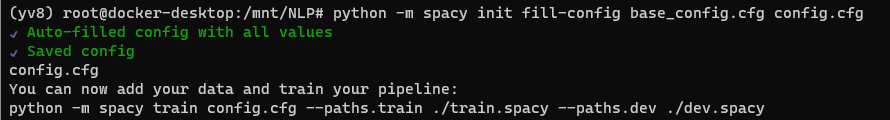
실행하면 config.cfg 파일이 추가로 생길건데, 제대로 만들어졌으면 터미널에 위와 같은 메시지가 떴을 것이다.
그러면 학습 준비가 다 된건데, 학습을 시작하려면 다음 명령어를 실행한다.
$ python -m spacy train config.cfg --output ./output --paths.train ./train.spacy --paths.dev ./dev.spacy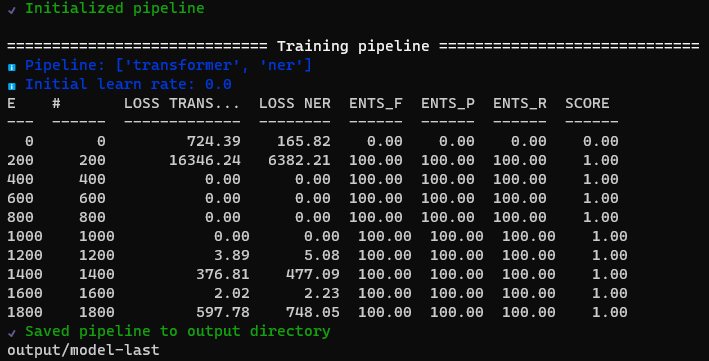
학습이 완료되면 model-last, model-best에 파일이 생성된다.
Test custom NER model
그러면 학습이 잘 됐는지 확인해 볼 차례다.
import spacy
nlp1 = spacy.load(r"./output/model-best")
doc = nlp1("Choonsik is a cat living with Ryan.") # input sample text
print(doc)
for entity in doc.ents :
print(f"{entity.text}({entity.label_})")
학습 모델을 불러와서 다음 테스트 문장을 실행해보면, "😸"을 "animal"로 잘 찾는 것을 볼 수 있다! 이 방법을 응용해서, 더 다양한 named entity들을 학습 시켜 보면 유용할 것 같다.