Linked List
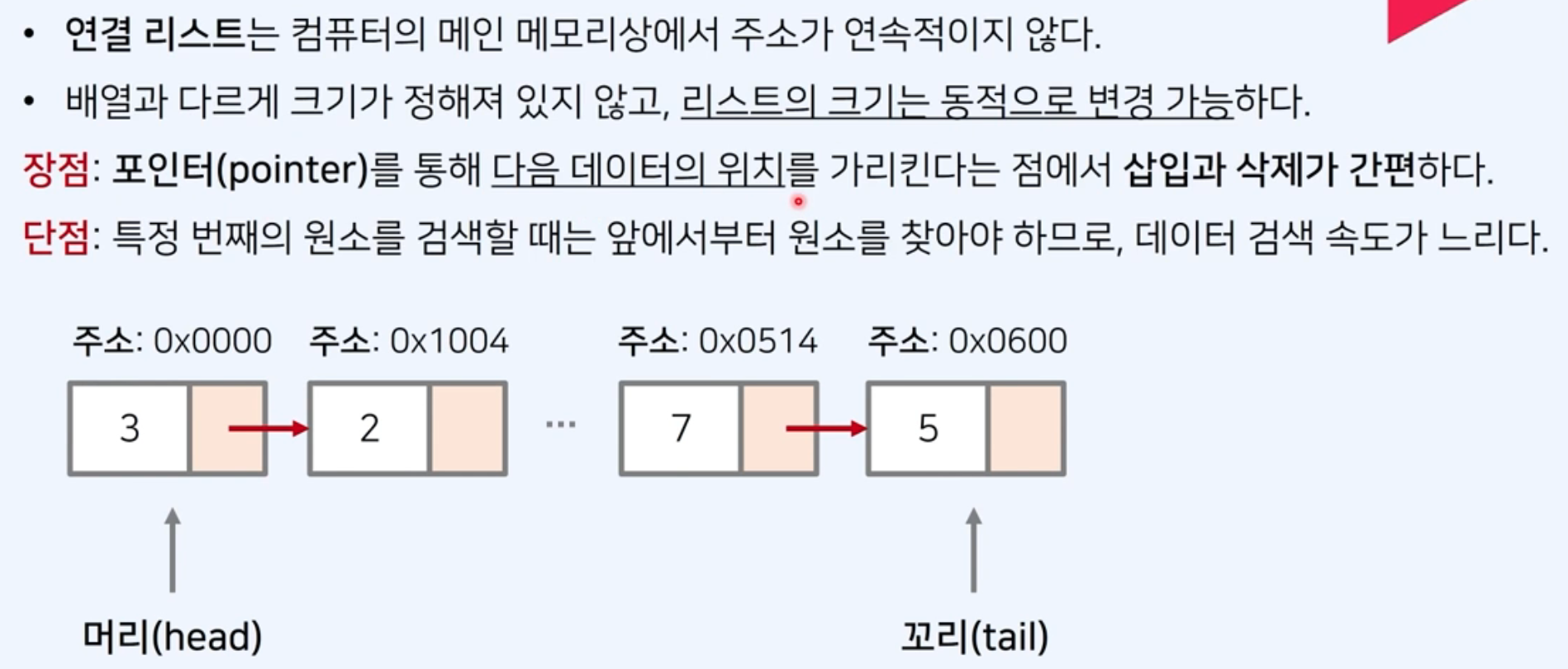
링크드 리스트(Linked List)는 여러 개의 노드(Node)로 구성되어 있으며, 각 노드는 두 부분으로 이루어져 있습니다: 하나는 데이터를 저장하는 부분이고, 다른 하나는 다음 노드를 가리키는 참조(Reference) 부분입니다.
링크드 리스트를 이해하기 쉬운 예로, 기차를 생각해보세요. 기차는 여러 개의 칸으로 이루어져 있습니다. 링크드 리스트의 각 노드는 기차의 한 칸과 같습니다. 각 칸에는 승객들이 타고 있으며(데이터), 칸과 칸 사이에 연결장치(참조)가 있어서 다음 칸을 연결하고 있습니다.
링크드 리스트에는 두 가지 주요한 유형이 있습니다:
- 단일 연결 리스트(Singly Linked List): 각 노드가 다음 노드만 가리키는 경우입니다. 이는 한 방향으로만 이동이 가능하며, 마지막 노드는 null 참조를 가집니다.
- 양방향 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List): 각 노드가 이전 노드와 다음 노드를 모두 가리키는 경우입니다. 이 구조는 양 방향으로 이동이 가능하여, 이전 노드와 다음 노드에 대한 참조를 모두 포함합니다.
장점:
- 동적 크기: 링크드 리스트는 노드의 개수에 따라 크기가 자동으로 조절됩니다. 따라서 공간이 필요할 때마다 노드를 추가하거나 불필요한 노드를 삭제할 수 있습니다.
- 삽입 및 삭제 용이성: 링크드 리스트에서는 노드의 참조만 변경하면 쉽게 삽입과 삭제가 가능합니다. 배열과 비교하면, 빠르게 추가와 삭제가 가능한 장점이 있습니다.
단점:
- 무작위 접근 불가: 링크드 리스트는 순차적으로 노드를 탐색해야 하므로, 특정 인덱스에 빠르게 접근할 수 없습니다. 이러한 특징 때문에 링크드 리스트는 검색 속도가 느릴 수 있습니다.
- 메모리 오버헤드: 각 노드는 데이터 외에 참조 정보도 저장해야 하므로, 배열보다 메모리 사용이 비효율적일 수 있습니다.
- 메모리 오버헤드(Memory Overhead) 는 어떤 프로세스나 데이터 구조에서 필요한 데이터를 저장하는 데 사용되는 메모리 이외의 추가적인 메모리 사용량을 의미합니다. 이는 특정 작업이나 데이터 구조를 구현하고 관리하는 데 필요한 부가적인 메모리 공간을 나타냅니다. 링크드 리스트에서 메모리 오버헤드는 주로 노드의 참조 정보에 의해 발생합니다. 링크드 리스트의 각 노드는 데이터 외에도 다음 노드를 가리키는 참조 정보를 저장해야 합니다. 양방향 연결 리스트의 경우, 각 노드는 이전 노드를 가리키는 참조 정보도 저장해야 하므로, 메모리 오버헤드가 더 커질 수 있습니다. 이러한 메모리 오버헤드는 배열과 같은 자료구조와 비교했을 때 링크드 리스트의 단점 중 하나로 간주됩니다. 배열의 경우, 데이터를 저장하기 위한 연속된 메모리 공간만 필요하기 때문에 메모리 사용이 보다 효율적입니다. 하지만, 링크드 리스트의 동적 크기 조절과 삽입 및 삭제의 용이성 등의 장점이 있으므로, 상황에 따라 적절한 자료구조를 선택해야 합니다. 메모리 오버헤드를 줄이려면, 다음과 같은 방법을 고려할 수 있습니다:
- 필요한 경우에만 링크드 리스트를 사용하고, 그렇지 않으면 메모리 효율적인 자료구조를 선택하세요.
- 링크드 리스트의 사용이 필수적인 경우, 노드를 추가하거나 삭제할 때 메모리를 효율적으로 관리하여 메모리 누수를 최소화하세요.
- 양방향 연결 리스트 대신 단방향 연결 리스트를 사용하여 참조 정보의 메모리 사용량을 줄일 수 있습니다. 단, 이 경우 양방향 이동이 불가능하다는 점을 고려해야 합니다.
- 메모리 오버헤드(Memory Overhead) 는 어떤 프로세스나 데이터 구조에서 필요한 데이터를 저장하는 데 사용되는 메모리 이외의 추가적인 메모리 사용량을 의미합니다. 이는 특정 작업이나 데이터 구조를 구현하고 관리하는 데 필요한 부가적인 메모리 공간을 나타냅니다. 링크드 리스트에서 메모리 오버헤드는 주로 노드의 참조 정보에 의해 발생합니다. 링크드 리스트의 각 노드는 데이터 외에도 다음 노드를 가리키는 참조 정보를 저장해야 합니다. 양방향 연결 리스트의 경우, 각 노드는 이전 노드를 가리키는 참조 정보도 저장해야 하므로, 메모리 오버헤드가 더 커질 수 있습니다. 이러한 메모리 오버헤드는 배열과 같은 자료구조와 비교했을 때 링크드 리스트의 단점 중 하나로 간주됩니다. 배열의 경우, 데이터를 저장하기 위한 연속된 메모리 공간만 필요하기 때문에 메모리 사용이 보다 효율적입니다. 하지만, 링크드 리스트의 동적 크기 조절과 삽입 및 삭제의 용이성 등의 장점이 있으므로, 상황에 따라 적절한 자료구조를 선택해야 합니다. 메모리 오버헤드를 줄이려면, 다음과 같은 방법을 고려할 수 있습니다:
적합한 상황:
- 노드의 삽입과 삭제가 빈번한 경우: 링크드 리스트는 노드를 추가하거나 삭제할 때 다른 요소의 이동이 필요하지 않으므로, 이러한 작업이 빈번한 경우에 적합합니다.
- 데이터 크기가 불확실한 경우: 데이터 크기가 미리 알려져 있지 않거나, 동적으로 변경될 가능성이 있는 경우에도 링크드 리스트가 유용합니다.
부적합한 상황:
- 무작위 접근이 필요한 경우: 배열이나 다른 자료구조가 무작위 접근에서 더 빠르고 효율적이므로, 이러한 작업이 필요한 경우 링크드 리스트는 부적합합니다.
- 메모리 사용량이 중요한 경우: 메모리 사용량이 크게 문제되지 않는 경우가 아니라면, 메모리 오버헤드를 고려해야 합니다.
주의사항:
- 메모리 누수: 링크드 리스트에서 노드를 삭제할 때, 참조를 제대로 처리(메모리 해제)하지 않으면 메모리 누수가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 순환 참조: 단순 연결 리스트가 아닌 경우, 잘못된 참조로 인해 순환 참조가 발생
코드 구현
Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
if self.head == None:
self.head = Node(data)
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
node.next = Node(data)
def delete(self, data):
print('삭제대상:', data)
# 헤드가 비어있을 경우의 방어코드
if self.head == None:
print('링크드 리스트가 비어있습니다.')
return
else:
if self.head.data == data: # 헤드의 데이터가 삭제 대상인 경우
temp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
del temp
else: # 삭제 대상이 중간에 위치하거나 마지막일 경우 아래의 코드로 처리 가능
node = self.head
while node.next:
print('다음노드:', node.next, '삭제대상:', data)
if node.next.data == data:
temp = node.next
node.next = node.next.next
del temp
print(data, ' 삭제성공')
return
else: # 삭제 대상이 아니라면 다음 노드로..
node = node.next
def print(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(node.data)
node = node.next
def search_node(self, data):
node = self.head
while node:
if node.data == data:
return node
else:
node = node.next
linkedList = LinkedList()
for data in range(1, 10):
linkedList.append(data)
linkedList.print()
linkedList.delete(5)
linkedList.print()더블 링크드 리스트
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, prev=None, next=None):
self.data = data
self.prev = prev
self.next = next
class DoubleLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def append(self, data):
if self.head == None:
self.head = Node(data)
self.tail = self.head
else:
node = self.head
while node.next:
node = node.next
newNode = Node(data)
node.next = newNode
newNode.prev = node
self.tail = newNode
def search_from_head(self, data):
node = self.head
while node:
if node.data == data:
return node
else:
node = node.next
return false
def search_from_tail(self, data):
node = self.tail
while node:
if node.data == data:
return node
else:
node = node.prev
return false
def append_before(self, data, beforeNodeData):
node = self.tail
while node.data != beforeNodeData:
node = node.prev
if node == None:
return False
newNode = Node(data)
beforeNode = node.prev
beforeNode.next = newNode
newNode.prev = beforeNode
newNode.next = node
return True
def append_after(self, data, afterNodeData):
node = self.head
while node.data != afterNodeData:
node = node.next
if node == None:
return False
afterNode = node.next
newNode = Node(data)
afterNode.prev = newNode
newNode.prev = node
newNode.next = afterNode
node.next = newNode
return True
def delete(self, data):
print('삭제대상:', data)
# 헤드가 비어있을 경우의 방어코드
if self.head == None:
return false
else:
if self.head.data == data: # 헤드의 데이터가 삭제 대상인 경우
temp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
del temp
else: # 삭제 대상이 중간에 위치하거나 마지막일 경우 아래의 코드로 처리 가능
node = self.head
while node.next:
if node.next.data == data:
targetNode = node.next
node.next = node.next.next
del targetNode
return
else: # 삭제 대상이 아니라면 다음 노드로..
node = node.next
def print(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(node.data)
node = node.next
def search_node(self, data):
node = self.head
while node:
if node.data == data:
return node
else:
node = node.next
doubleLinkedList = DoubleLinkedList()
for data in range(1, 10):
doubleLinkedList.append(data)
doubleLinkedList.print()
doubleLinkedList.delete(5)
doubleLinkedList.print()
doubleLinkedList.append_before(6.5, 7)
doubleLinkedList.print()
doubleLinkedList.append_after(3.5, 3)
doubleLinkedList.print()JS
단일 링크드 리스트
// 노드 클래스 정의
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// 링크드 리스트 클래스 정의
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// 리스트가 비어있는지 확인하는 메소드
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
// 리스트에 노드를 추가하는 메소드
add(data) {
const node = new Node(data);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
// 리스트가 비어있을 경우
this.head = newNode; // head와 tail이 새 노드를 가리킴
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// 리스트에 노드가 있는 경우
this.tail.next = newNode; // 현재 tail 노드가 새 노드를 가리키도록 함
this.tail = newNode; // tail을 새 노드로 업데이트
}
this.size++; // 노드 개수 증가
}
// 리스트에서 데이터를 삭제하는 메소드
remove(data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("List is empty");
}
if (this.head.data === data) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.size === 1) {
this.tail = null;
}
this.size--;
return;
}
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode = null;
while (currentNode !== null) {
if (currentNode.data === data) {
// 마지막 요소일 경우
if (currentNode.next === null) {
this.tail = previousNode;
}
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode = null;
this.size--;
return;
}
// 해당하지 않는다면
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
throw new Error("Data not found in the list");
}
// 리스트에서 데이터를 찾는 메소드
find(data) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode !== null) {
if (currentNode.data === data) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
throw new Error("Data not found in the list");
}
// 리스트의 모든 노드를 출력하는 메소드
print() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = "";
while (currentNode !== null) {
result += currentNode.data + (currentNode.next ? " -> " : "");
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
}
// 링크드 리스트 인스턴스 생성
function assert(condition, message) {
if (condition) {
console.log("✅ " + message);
} else {
console.log("❌ " + message);
}
}
const linkedList = new LinkedList();
console.log("Add=======================");
linkedList.add(10);
linkedList.add(20);
linkedList.add(30);
linkedList.add(40);
const result1 = linkedList.print();
assert(result1 === "10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40", "Adding elements to the list");
// 중복 데이터 추가 테스트
linkedList.add(30);
const afterAddDuplicate = linkedList.print();
assert(
afterAddDuplicate === "10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 -> 30",
"Adding duplicate data"
);
// 리스트의 첫 번째 노드 찾기 테스트
try {
const firstNode = linkedList.find(30);
assert(firstNode.data === 30, "Finding the first node in the list");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
// 리스트의 마지막 노드 찾기 테스트
try {
linkedList.find(50);
console.log("❌ Finding non-existing node");
} catch (error) {
assert(
error.message === "Data not found in the list",
"Finding non-existing node"
);
}
// 리스트에 단일 노드가 있는 경우 데이터 삭제 테스트
const singleNodeList = new LinkedList();
singleNodeList.add(100);
try {
singleNodeList.remove(100);
const afterRemoveSingleNode = singleNodeList.print();
assert(afterRemoveSingleNode === "", "Removing the single node in the list");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
// 리스트 크기 확인 테스트
const sizeTestList = new LinkedList();
sizeTestList.add(1);
sizeTestList.add(2);
sizeTestList.add(3);
assert(sizeTestList.size === 3, "Checking the size of the list");
try {
linkedList.remove(20);
const afterRemove20 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove20 === "10 -> 30 -> 40 -> 30", "Removing element 20");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
try {
linkedList.remove(10);
const afterRemove10 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove10 === "30 -> 40 -> 30", "Removing element 10");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
try {
linkedList.remove(40);
const afterRemove40 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove40 === "30 -> 30", "Removing tail element");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
const isNotEmpty = linkedList.isEmpty();
assert(!isNotEmpty, "Checking if list is not empty");
try {
linkedList.remove(30);
const afterRemove30 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove30 === "30", "Removing head element");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
const result4 = linkedList.print();
assert(result4 === "30", "Printing list Checking if list is not empty");
try {
linkedList.remove(30);
const afterRemove30 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove30 === "", "Removing last element");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
const result5 = linkedList.print();
assert(result5 === "", "Printing list after removing last element");
const isEmpty2 = linkedList.isEmpty();
assert(isEmpty2, "Checking if list is empty");양방향(더블) 링크드 리스트
// Node class definition
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
// DoublyLinkedList class definition
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// Add data to the list
add(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// Remove data from the list
remove(data) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Empty");
}
if (this.head.data === data) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.head !== null) {
this.head.prev = null;
} else {
// When there's no element left in the list
this.tail = null;
}
this.size--;
return;
}
let currentNode = this.head.next;
while (currentNode !== null) {
if (currentNode.data === data) {
if (this.tail.data === data) {
this.tail = currentNode.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
currentNode.prev.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next.prev = currentNode.prev;
}
this.size--;
return;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
throw new Error("Data not found in the list");
}
// Find a node with the given data in the list
find(data) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode !== null) {
if (currentNode.data === data) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
throw new Error("Data not found in the list");
}
// Find a node with the given data in the list, starting from the tail
reverseFind(data) {
let currentNode = this.tail;
while (currentNode !== null) {
if (currentNode.data === data) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
throw new Error("Data not found in the list");
}
// Print the list in the forward direction
print() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let result = "";
while (currentNode !== null) {
result += currentNode.data + (currentNode.next ? " <-> " : "");
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return result;
}
// Print the list in the reverse direction
reversePrint() {
let currentNode = this.tail;
let result = "";
while (currentNode !== null) {
result += currentNode.data + (currentNode.prev ? " <-> " : "");
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return result;
}
// Check if the list is empty
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
}
// 링크드 리스트 인스턴스 생성
function assert(condition, message) {
if (condition) {
console.log("✅ " + message);
} else {
console.log("❌ " + message);
}
}
const linkedList = new DoublyLinkedList();
console.log("Add=======================");
linkedList.add(10);
linkedList.add(20);
linkedList.add(30);
linkedList.add(40);
const result1 = linkedList.print();
assert(result1 === "10 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> 40", "Adding elements to the list");
// 중복 데이터 추가 테스트
linkedList.add(30);
const afterAddDuplicate = linkedList.print();
assert(
afterAddDuplicate === "10 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> 40 <-> 30",
"Adding duplicate data"
);
// 리스트의 첫 번째 노드 찾기 테스트
try {
const firstNode = linkedList.find(30);
assert(firstNode.data === 30, "Finding the first node in the list");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
try {
const firstNode = linkedList.reverseFind(30);
assert(firstNode.data === 30, "Reverse finding the first node in the list");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
// 리스트의 마지막 노드 찾기 테스트
try {
linkedList.find(50);
console.log("❌ Finding non-existing node");
} catch (error) {
assert(
error.message === "Data not found in the list",
"Finding non-existing node"
);
}
// 리스트에 단일 노드가 있는 경우 데이터 삭제 테스트
const singleNodeList = new DoublyLinkedList();
singleNodeList.add(100);
console.log(singleNodeList);
try {
singleNodeList.remove(100);
console.log(singleNodeList);
const afterRemoveSingleNode = singleNodeList.print();
assert(afterRemoveSingleNode === "", "Removing the single node in the list");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
// 리스트 크기 확인 테스트
const sizeTestList = new DoublyLinkedList();
sizeTestList.add(1);
sizeTestList.add(2);
sizeTestList.add(3);
assert(sizeTestList.size === 3, "Checking the size of the list");
try {
linkedList.remove(20);
console.log(linkedList);
const afterRemove20 = linkedList.print();
console.log(afterRemove20);
assert(afterRemove20 === "10 <-> 30 <-> 40 <-> 30", "Removing element 20");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
const reversed = linkedList.reversePrint();
console.log(reversed);
try {
linkedList.remove(10);
const afterRemove10 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove10 === "30 <-> 40 <-> 30", "Removing element 10");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
try {
linkedList.remove(40);
const afterRemove40 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove40 === "30 <-> 30", "Removing tail element");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
const isNotEmpty = linkedList.isEmpty();
assert(!isNotEmpty, "Checking if list is not empty");
try {
linkedList.remove(30);
const afterRemove30 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove30 === "30", "Removing head element");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
const result4 = linkedList.print();
assert(result4 === "30", "Printing list Checking if list is not empty");
try {
linkedList.remove(30);
const afterRemove30 = linkedList.print();
assert(afterRemove30 === "", "Removing last element");
} catch (error) {
console.log("❌ " + error.message);
}
const result5 = linkedList.print();
assert(result5 === "", "Printing list after removing last element");
const isEmpty2 = linkedList.isEmpty();
assert(isEmpty2, "Checking if list is empty");재귀 함수를 이용한 단일 링크드 리스트
// 단일 링크드 리스트 노드 클래스 정의
class ListNode {
data;
next;
constructor(data) {
this.data = data; // 노드에 저장할 데이터
this.next = null; // 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터
}
}
// 단일 링크드 리스트 클래스 정의
class LinkedList {
head;
size;
constructor() {
this.head = null; // 리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 가리킴
this.size = 0; // 리스트의 노드 개수
}
// 재귀 함수를 사용하여 노드를 추가하는 메소드
add(data, currentNode = this.head) {
if (!this.head) {
// 리스트가 비어있을 경우
this.head = new ListNode(data);
} else if (!currentNode.next) {
// 다음 노드가 없는 경우
currentNode.next = new ListNode(data);
} else {
this.add(data, currentNode.next); // 다음 노드로 이동
}
this.size++; // 노드 개수 증가
}
// 재귀 함수를 사용하여 노드를 삭제하는 메소드
remove(data, currentNode = this.head, prevNode = null) {
if (!currentNode) {
// 현재 노드가 없는 경우
return;
}
if (currentNode.data === data) {
// 삭제할 데이터를 찾았을 경우
if (prevNode) {
// 이전 노드가 있는 경우
prevNode.next = currentNode.next;
} else {
// 삭제할 노드가 head인 경우
this.head = currentNode.next;
}
this.size--; // 노드 개수 감소
} else {
// 다음 노드로 이동하며 재귀 호출
this.remove(data, currentNode.next, currentNode);
}
}
// 재귀 함수를 사용하여 리스트에서 데이터를 찾는 메소드
find(data, currentNode = this.head) {
if (!currentNode) {
// 현재 노드가 없는 경우
return null;
}
if (currentNode.data === data) {
// 찾고자 하는 데이터를 가진 노드를 찾았을 경우
return currentNode; // 해당 노드를 반환
}
// 다음 노드로 이동하며 재귀 호출
return this.find(data, currentNode.next);
}
// 재귀 함수를 사용하여 리스트의 모든 노드를 출력하는 메소드
print(currentNode = this.head, result = "") {
if (!currentNode) {
// 현재 노드가 없는 경우
console.log(result); // 결과 문자열 출력
return;
}
result += currentNode.data + (currentNode.next ? " -> " : ""); // 현재 노드의 데이터를 결과 문자열에 추가
this.print(currentNode.next, result); // 다음 노드로 이동하며 재귀 호출
}
}
// 테스트 코드
const linkedList = new LinkedList();
// 데이터 추가 테스트
linkedList.add(10);
linkedList.add(20);
linkedList.add(30);
linkedList.add(40);
// 리스트 출력: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40
linkedList.print();
// 데이터 검색 테스트
console.log(linkedList.find(20)); // ListNode { data: 20, next: ListNode { data: 30, ... } }
console.log(linkedList.find(50)); // null
// 데이터 삭제 테스트
linkedList.remove(20);
linkedList.remove(10);
// 리스트 출력: 30 -> 40
linkedList.print();
// 데이터 삭제 테스트 (tail)
linkedList.remove(40);
// 리스트 출력: 30
linkedList.print();
// 데이터 삭제 테스트 (head)
linkedList.remove(30);
// 리스트 출력: (빈 리스트)
linkedList.print();