풀이
- 비트마스크 알고리즘을 이용해 풀어보자
n x m 배열을 조각으로 나누는 경우의 수를 비트마스크로 표현할 수 있다.
조각 합 구하기
백준 문제로 예시를 들어보자
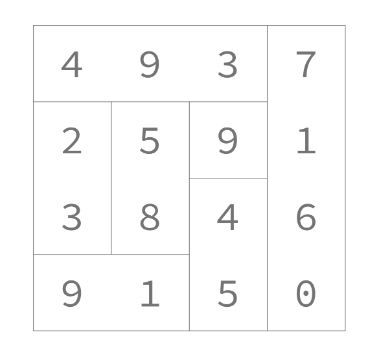
여기서 세로크기가 1인 조각을 1, 가로크기가 1인 조각을 0이라 하면 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.
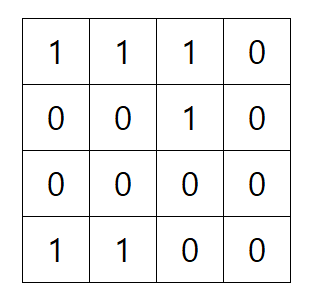
원래 숫자가 담긴 배열을 paper, 0과 1로 변환된 배열을 bit라고 할 때
# 행방향 탐색
for i in range(N):
rowsum = 0
for j in range(M):
if bit[i][j]:
rowsum = rowsum*10 + paper[i][j]
else:
total += rowsum
rowsum = 0
total += rowsum왼쪽위 가장 첫번째 조각
493을 예로 들어보자
1.bit[0][0]은 1이므로rowsum = 4
2.bit[0][1]은 1이므로rowsum = 40 + 9 = 49
3.bit[0][2]은 1이므로rowsum = 490 + 3 = 493
4.bit[0][3]은 0이므로total = 0 + 493,rowsum = 0
5.for j반복문이 끝났으므로total = 493 + 0 = 493
이런식으로 해당 조각의 합을 구할 수 있게 된다.
열 방향의 경우 i와 j 순서를 거꾸로 하여 반복문을 돌며서 colsum을 구해주면 된다.
# 열방향 탐색
for j in range(M):
colsum = 0
for i in range(N):
idx = (i*M) + j
if not bit[i][j]:
colsum = colsum*10 + paper[i][j]
else:
total += colsum
colsum = 0
total += colsum오른쪽 가장위 조각
7160을 예로 들어보자
1.bit[0][3]은 0이므로colsum = 7
2.bit[1][3]은 0이므로colsum = 70 + 1 = 71
3.bit[2][3]은 0이므로colsum = 710 + 6 = 7166
4.bit[3][3]은 0이므로colsum = 7160 + 0 = 7160
5.for i반복문이 끝났으므로total = total + 7160
비트마스크 활용
이제 조각을 나눌 수 있는 모든 경우를 확인하면서 최대값을 찾아야한다.
여기서 0과 1로된 배열 대신 비트마스크를 이용하는 것이 핵심이다.

비트 :
0011 0000 0100 0111=12359
그 외에 다음과 같은 예시가 있다.
모든 조각을 세로로 나누는 경우 :
0000 0000 0000 0000= 0
모든 조각을 가로로 나누는 경우 :
1111 1111 1111 1111=2^16 - 1
즉 n x m 배열이 주어졌을 때, 2^(n*m) -1 까지 반복문을 돌면 조각을 나누는 모든 경우의 수를 확인할 수 있게 된다.
코드
if __name__ == "__main__":
N, M = map(int, input().split())
paper = [list(map(int, input().rstrip())) for _ in range(N)]
answer = -1
for case in range(1 << (N*M)):
total = 0
# 행방향 탐색
for i in range(N):
rowsum = 0
for j in range(M):
idx = (i*M) + j
if case & (1 << idx):
rowsum = rowsum*10 + paper[i][j]
else:
total += rowsum
rowsum = 0
total += rowsum
# 열방향 탐색
for j in range(M):
colsum = 0
for i in range(N):
idx = (i*M) + j
if not (case & (1 << idx)):
colsum = colsum*10 + paper[i][j]
else:
total += colsum
colsum = 0
total += colsum
answer = max(answer, total)
print(answer)
그 외의 풀이방법
사실 위의 방법처럼 0부터 2^(m*n)까지 일일히 반복문을 돌면 시간이 오래걸린다.
왜냐하면 2 x 2 배열에서 1010과 0101은 동일한 조각을 나타내는데, 이러한 중복이 모두 포함되기 때문이다.
때문에 굳이 비트마스크를 활용할 것이 아니라면 DFS 비슷한 것을 이용하는 방법도 있다.
코드
- 정리되지 않은 코드라 조금 더럽습니다!!
def find_start():
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if chk[i][j] == 0:
return (i, j)
return 0
def get_piece(x, y, temp, total, axis):
global answer
chk[x][y] = 1
temp = f'{temp}{paper[x][y]}'
if (axis == 'row' or axis == 'both') and 0 <= x+1 < N and chk[x+1][y]==0:
get_piece(x+1, y, temp, total, 'row')
if (axis == 'column' or axis == 'both') and 0 <= y+1 < M and chk[x][y+1]==0:
get_piece(x, y+1, temp, total, 'column')
next_start = find_start()
if next_start:
xx, yy = next_start
get_piece(xx, yy, '', total+int(temp), 'both')
else:
answer = max(answer, total+int(temp))
chk[x][y] = 0
if __name__ == "__main__":
N, M = map(int, input().split())
paper = [list(map(str, input().rstrip())) for _ in range(N)]
chk = [[0] * M for _ in range(N)]
answer = -1
get_piece(0, 0, '', 0, 'both')
print(answer)비트마스크를 활용한 코드는 876ms, 위의 방법은 284ms의 시간이 나온다.

