문제 요약
예제
4
1 4 3 2
4
1 2 4
2 3 3
3 4 2
1 4 10[1, 4, 3, 2]의 배열이 주어졌다.
이 배열의 조작 방법은 총 4가지가 있다.
1. 1번과 2번 요소를 바꿈 (비용: 4)
2. 2번과 3번 요소를 바꿈 (비용: 3)
3. 3번과 4번 요소를 바꿈 (비용: 2)
4. 1번과 4번 요소를 바꿈 (비용: 10)
이 조작만을 이용해서 최저 비용으로 [1, 2, 3, 4]의 오름차순(비내림차순) 배열을 만들어야 한다.
위 예제의 경우는 다음과 같이 만들 수 있다.
[1, 4, 3, 2]→ 3번 조작 →[1, 4, 2, 3]비용 : 2[1, 4, 2, 3]→ 2번 조작 →[1, 2, 4, 3]비용 : 5[1, 2, 4, 3]→ 3번 조작 →[1, 2, 3, 4]비용 : 7
즉 정답은 7이 된다.
풀이
다익스트라를 이용해서 풀 수 있다.
이 때 각 배열의 상태가 하나의 노드가 된다.
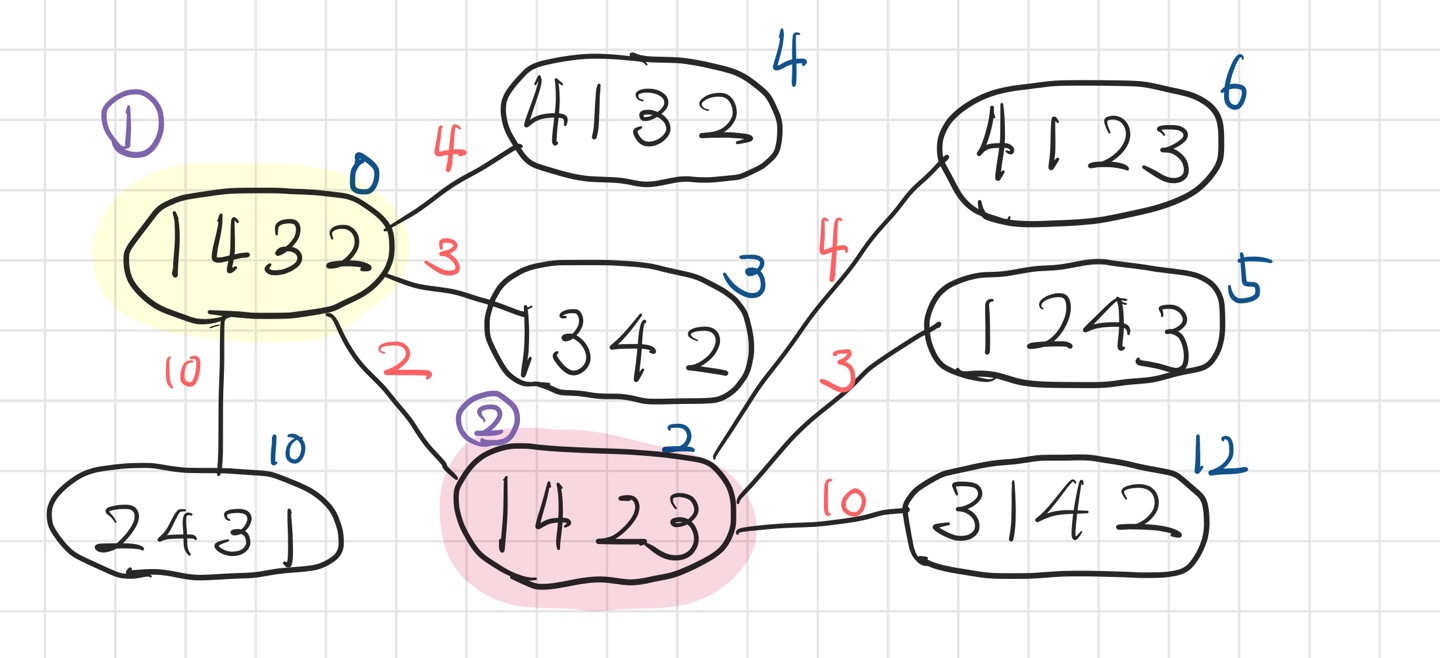
[1, 4, 3, 2]라는 배열이 하나의 노드가 되고,
조작의 종류에 따라 그래프를 생성하면서 다익스트라 탐색을 진행한다.
최초 배열인 [1, 4, 3, 2] 부터 시작해서 조작 종류 4가지를 모두 수행하면
[2, 4, 3, 1][1, 4, 2, 3][1, 3, 4, 2][4, 1, 3, 2]
그림과 같이 4가지의 노드가 생성된다.
이중 다익스트라 알고리즘에 따라 비용이 가장 낮은 [1, 4, 2, 3] 배열 노드를 선택하여 다시 조작 종류만큼 탐색한다.
[1, 4, 2, 3] 에서 3. 3번과 4번 요소를 바꿈 (비용: 2)조작을 수행하면[1, 4, 3, 2]가 되는데
이는 이미 비용 0으로 생성된 노드가 있으므로 탐색하지 않는다.
이렇게 모든 탐색을 수행하면 기존 다익스트라 알고리즘과 동일한 그래프인,
시작 배열 [1, 4, 3, 2] 부터 다른 노드로 가는 최소 비용으로 이루어진 그래프를 얻는다.
만약 그래프에 [1, 2, 3, 4]에 해당하는 노드가 있다면 그 노드의 비용을 출력하면 된다.
없으면 목표 노드에 도달 할 수 없음을 의미하므로 -1을 출력하면 된다.
코드
설명
배열을 정수로 바꾸기
def arr2num(arr):
digit = 1
num = 0
for a in arr:
num += a * digit
digit *= 10
return num이번에는 딕셔너리를 이용해 노드를 저장할 것이다. 그런데 딕셔너리의 키는 immutable(변경할 수 없는)객체여야 하므로 리스트 상태로 저장할 수 없다.
지금 생각하면 tuple로 저장하는 방법이 있어을 것 같은데, 메모리 사용도 고려해서 배열을 정수로 바꾸어주는 함수를 만들었다.
[1, 3, 2, 4]는 4231로 뒤집은 정수를 반환하는 함수이다.
불편하다면 함수를 조금 고쳐 1324를 반환하도록 해도 상관 없을 것 같다.
Node 클래스 만들기
class Node:
def __init__(self, arr, cost):
self.arr = arr # 노드의 배열
self.visited = False # 해당 노드를 탐색 완료했는지 여부
self.cost = cost # 현재 이 노드에 도달하기 위한 최저 비용최근에 Trie 자료구조를 배웠을 때 클래스를 이용하던 것이 생각나 노드를 클래스로 구현해보았다.
각각의 Node 인스턴스는 딕셔너리에 value로 저장된다.
다익스트라 알고리즘 구현
def solution(arr, manipulates):
graph = dict()
graph[arr] = Node(arr, 0)
hq = [] # 다익스트라를 위한 우선순위 큐
heapq.heappush(hq, (graph[arr].cost, arr))
while hq:
cost, arr = heapq.heappop(hq)
node = graph[arr]
if node.visited:
continue
for l, r, c in manipulates:
temp = arr.copy()
next_cost = cost + c
temp[l], temp[r] = temp[r], temp[l]
if graph.get(temp) is None:
graph[temp] = Node(temp, next_cost)
heapq.heappush(hq, (next_cost, temp))
continue
if next_cost < graph[temp].cost:
graph[temp].cost = next_cost
heapq.heappush(hq, (next_cost, temp))
node.visited = True
return graph최소힙을 이용한 우선순위 큐로 다익스트라를 구현하였다.
다익스트라에 대해 알고 있을 것이라 생각해서 자세한 서명은 스킵한다.
한가지 독특한 점은 노드를 새로 생성하면서 그래프를 탐색해야 하므로
dict.get() 메서드를 이용해 생성되지 않은 노드인지를 확인해 새로 생성하는 과정이 추가되었다.
정답 출력
# 비내림차순 배열
target = list(sorted(arr))
target_num = arr2num(target)
graph = solution(arr, manipulates)
print(graph[target_num].cost if graph.get(target_num) else -1)목표인 비내림차순 배열을 생성한 뒤
solution 함수에서 탐색이 완료된 그래프를 받아와 비내림차순 배열에 도달할 수 있는지를 확인한다.
도달 가능하다면 비용을, 아니면 -1을 출력한다.
전체 코드
import sys, heapq
input = sys.stdin.readline
class Node:
def __init__(self, arr, cost):
self.arr = arr
self.visited = False
self.cost = cost
# 배열로부터 딕셔너리 키로 사용될 정수 생성 (배열을 뒤집은 정수형태)
def solution(arr, manipulates):
graph = dict()
graph[arr] = Node(arr, 0)
hq = [] # 다익스트라를 위한 우선순위 큐
heapq.heappush(hq, (graph[arr].cost, arr))
while hq:
cost, arr = heapq.heappop(hq)
node = graph[arr]
if node.visited:
continue
for l, r, c in manipulates:
temp = arr.copy()
next_cost = cost + c
temp[l], temp[r] = temp[r], temp[l]
if graph.get(temp) is None:
graph[temp] = Node(temp, next_cost)
heapq.heappush(hq, (next_cost, temp))
continue
if next_cost < graph[temp].cost:
graph[temp].cost = next_cost
heapq.heappush(hq, (next_cost, temp))
node.visited = True
return graph
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = int(input())
arr = list(map(int, input().split()))
arr.insert(0, 0) # 1부터 시작하므로 안쓰는 0번 인덱스에 최소값 0 삽입
M = int(input())
manipulates = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(M)]
# 비내림차순 배열
target = list(sorted(arr))
graph = solution(arr, manipulates)
print(graph[target].cost if graph.get(target) else -1)시간은 Python3에서 716ms를 기록했다.
코멘트
배열 하나가 통채로 노드가 되어 다익스트라로 푼다는 접근법을 상상도 못했다.
앞으로 유한개의 조작 조건과 이에 대한 비용이 주어진다면
이런식으로 그래프를 만들어 푸는 방법을 생각해 봐야할 것 같다.

