Spring AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)
1. AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)란?
관점 지향 프로그래밍 : 어떤 로직을 핵심적인 관점과 부가적인 관점으로 나누고 각각을 모듈화
- 핵심 관점 : 핵심 로직
- 부가적인 관점 : 핵심 로직을 실행하기 위한 부가적인 작업(DB연결, 로깅, 파일 입출력 등)
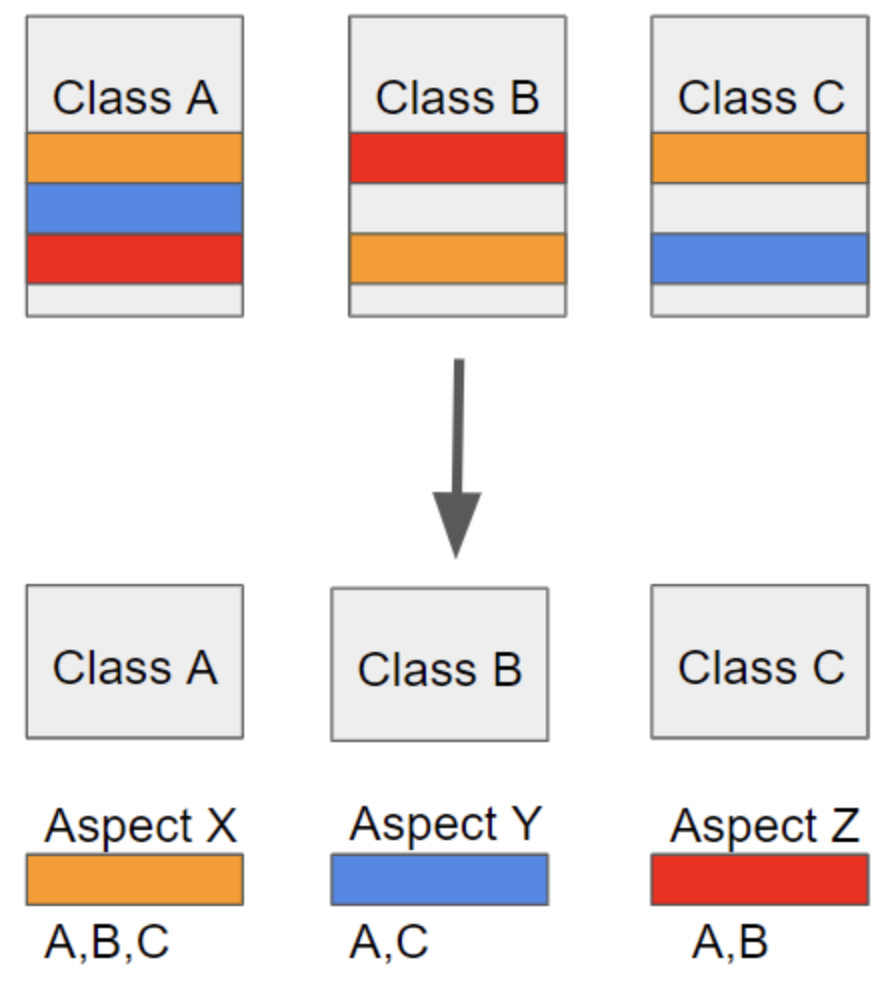
흩어진 관심사(Crosscutting Concerns) : 다른 부분에서 계속 반복해서 쓰는 코드들
-> Aspect로 모듈화하고 핵심적인 비즈니스 로직에서 분리하여 재사용
2. AOP 관련 annotation
1. pointcut
: Aspect를 어디에 적용할 것인지 정의
1-1. execution(접근제어자 / 반환형 / 패키지를 포함한 클래스 경로 / 파라미터)
@Pointcut("execution(public void get*())")
public형의 반환값이 없는 get으로 시작하는 모든 메소드중 파라미터가 존재하지 않는 메소드들에게 적용
// * : 모든 값
//.. : 0개 이상 모든 값
@Pointcut("execution(* *(..))")
모든 접근제어자와 반환형
어떠한 경로의 클래스든 모두 적용
.. : 파라미터가 몇개가 존재하던지 상관없이 실행
@Pointcut("execution(* com.java.example.study())")
com.java.example class의 study() 메소드가 호출될 때 실행
@Pointcut("execution( com.java...*())")
.. : 해당 패키지를 포함한 모든 하위 패키지에 적용
1-2. within(class 경로)
: 패키지 내의 모든 메소드에 적용할 때 사용
@Pointcut("within(com.java.example.*)")
com.java.example 하위의 모든 클래스의 모든 메소드에 적용
1-3. bean(bean id)
: 해당 bean id를 가지고 있는 bean의 모든 메소드에 적용
@Pointcut(bean(example))
example이라는 bean id를 가진 bean의 모든 메소드에 적용
2. Advice
: 언제 핵심 로직에 반영할 것인지를 결정
@Advice("pointcut")
pointcut : 어떤 메소드가 실행될 때
advice : 언제 공통 코드를 실행 -> 메소드 전/후/...
2-1. before
: 메소드 실행 전
@Before("execution(* com.java.example.study())")
2-2. after
: 메소드 실행 후
@After("execution(* com.java.example.study())")
pointcut 지시자 미리 설정
@Pointcut("execution(* com.java.example.study())")
private void pointcut() {}
//
@Before("pointcut()")
@After("pointcut()")
2-3. AfterReturning
: 반환된 후
@AfterReturning(value = "pointcut()", returning = "returnValue")
returning 속성을 통해 메소드의 반환값 확인 가능
2-4. AfterThrowing
: 예외가 던져지는 시점
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointcut()", throwing = "exception")
throwing 속성을 통해 메소드의 exception 내용 확인 및 사용 가능
2-5. Around
: 메소드가 호출되는 전 과정
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogAspect.class);
@Around("execution(* com.java.example.study())")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 메소드를 실행
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
stopWatch.stop();
logger.info(stopWatch.prettyPrint());
return proceed; // 결과 리턴
}
}
@Aspect : class가 부가기능 class임을 알려주는 annotation
@Component : spring bean으로 등록(Spring bean에만 aop를 적용 가능)
ProceedingJoinPoint interface
- getSignature() : 호출되는 메서드에 대한 정보를 구한다
- getTarget() : 대상 객체를 구한다
- getArgs() : 파라미터의 목록을 구한다
- proceed() : 타겟 메소드 실행
3. annotation 기반 AOP
1. 기능을 추가하고자 하는 메소드에 annotation 붙임
@LogExecutionTime
public void exampleMethod() {
...
}2. annotation 정의
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LogExecutionTime {
}@Target(ElementType.METHOD) : annotation을 메소드에 사용
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) : annotation이 runtime까지 유지
3. Aspect class 작성
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogAspect.class);
@Around("@annotation(LogExecutionTime)")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 메소드를 실행
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
stopWatch.stop();
logger.info(stopWatch.prettyPrint());
return proceed; // 결과 리턴
}
}4. Proxy pattern
비즈니스 로직의 중간에 소스코드를 삽입하는 방식
- Source Code -> ByteCode
: 소스코드가 바이트코드가 되는 시점에 코드 injection - ByteCode -> Class Load
: ByteCode가 메모리로 올라갈 때 injection - Proxy Pattern
Spring은 AOP를 구현하기 위해 3.Proxy Pattern을 사용한다
Proxy Pattern의 구조와 Flow
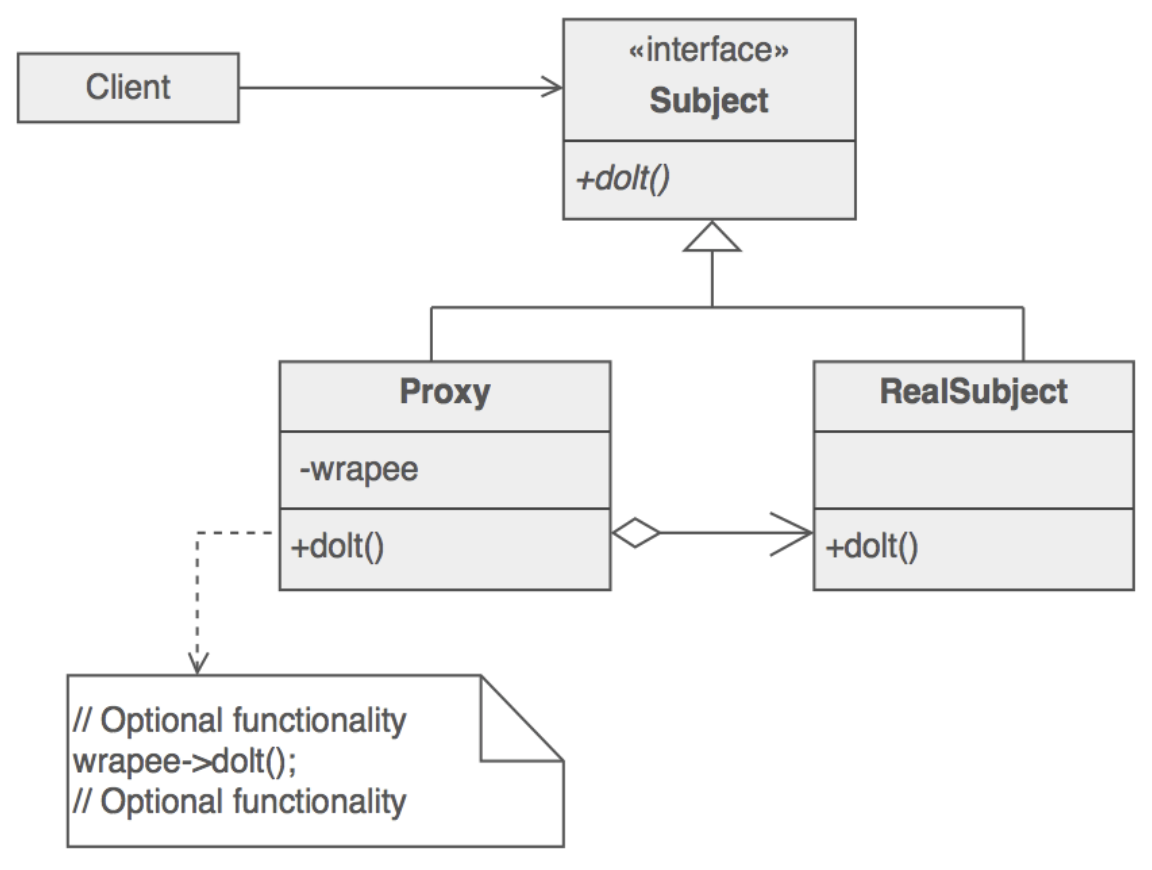
- Client가 해당 함수를 직접 호출하는 대신 Proxy 호출
- Proxy class에서 실제 class 호출
- Client에게 반환
@Service
public class TestEventService implements EventService {
@override
public void createEvent() {
System.out.println("create event");
}
@override
public void publishEvent() {
System.out.println("create event");
}
}@Primary
@Service
public class ProxyTestEventService implements EventService {
@Autowired
TestEventService testEventService;
@override
public void createEvent() {
long begin = system.currentTimeMillis();
testEventService.createEvent();
system.out.println(system.currentTimeMillis()-begin);
}
@override
public void publishEvent() {
long begin = system.currentTimeMillis();
testEventService.createEvent();
system.out.println(system.currentTimeMillis()-begin);
}
}@Primary : 우선순위 선정
-> client가 EventService를 통해 메서드를 호출하면 proxy 객체가 호출
@Service : 해당 클래스를 루트 컨테이너에 bean 객체로 생성
Spring AOP Proxy Pattern
- JDK Dynamic Proxy
- CGlib Proxy
