이전 라이브코딩에서 트라이 자료구조를 구현할 수 있냐는 질문을 받았다. 하지만 자료구조 구현은 예전 학부생때 했던게 전부여서 멘탈이 탈탈 털린 기억이 있다.
오늘은 트라이 자료구조에 대해서 직접 구현해보면서 이전 탈탈 털린 멘탈을 조금이나마 회복해보자.
트라이가 뭘까?
먼저 트라이(Trie)는 "retrieval"에서 나온 이름으로, 접두사트리(Prefix Tree)라고도 불린다. 문자열들을 트리 형태로 저장하여 빠른 탐색을 가능하게하는 자료구조이다.
왜 배열이나 해시맵 대신 트라이를 쓰면 더 효율적일까?
// 일반적인 방법
const words = ["cat", "car", "card", "care", "careful"];
// 단어 검색: O(n × m) - n개 단어를 m 길이만큼 비교
function search(word) {
return words.includes(word);
}
// 접두사로 시작하는 단어 찾기: O(n × m)
function findWithPrefix(prefix) {
return words.filter(word => word.startsWith(prefix));
}위 방식을 사용하면 데이터가 많아질 수록 매우 느려진다. 하지만 트라이를 사용하면
- 검색: O(m)의 시간복잡도로 단어 길이에만 비례한다.
- 접두사 검색 :O(m + k) - m은 접두사 길이, k는 결과 개수
로 탐색을 할 수 있다.
좀 더 자세한 예를들어보자.
배열 방식
// 데이터 예시 (10,000개 단어)
const dictionary = [
"apple", "application", "apply", "computer", "computation",
"compose", "company", "compare", "complete", "complex",
// ... 9,990개 더
];이런 단어를 저장한 배열이 있다고 가정해보고 여기서 "computer"라는 단어를 탐색한다고 생각해보자.
// 배열에서 "computer" 찾기
function searchArray(word) {
for (let i = 0; i < dictionary.length; i++) { // 10,000번 반복 가능
if (dictionary[i] === word) { // 각각 7글자 비교
return true;
}
}
return false;
}최악의 경우 10,000개의 단어를 모두 확인해야하는 상황이 생길 수 있다. 그리고 또 이 단어마다 한글자씩 비교해주기 때문에 computer라는 단어를 찾을때는 8번의 비교가 일어난다.
최악의 경우 80000번의 탐색이 일어난다는 점이다.
트라이방식
// 트라이에서 "computer" 찾기
function searchTrie(word) {
let node = root;
// C → O → M → P → U → T → E → R (8단계만)
for (let char of word) {
node = node.children.get(char);
if (!node) return false;
}
return node.isEndOfWord;
}이렇게 단어 길이만큼 이동하면 되니 총 8번만 탐색하면 된다.
즉 데이터 개수와 무관하게 단어 길이만큼 이동하니 O(m)의 시간복잡도가 소요된다.
그럼 직접 트라이를 구현해보자.
1단계. TrieNode 클래스 만들기
트라이의 각 노드가 어떤 정보를 저장해야하는지 생각해보자.
class TrieNode {
constructor() {
// 자식 노드들 저장 (문자 → TrieNode)
this.children = new Map();
// 이 위치에서 단어가 끝나는지 표시
this.isEnd = false;
}
}각 노드는 "다음에 올 수 있는 문자들"을 모두 저장해야한다. 이 문자열을 노드로 만들어서 children이 저장해주면 된다.
그리고 isEnd라는 변수는 문자열을 탐색할 때 이 문자열이 끝인지 찾는 변수이다.
Root → C → A → R(isEndOfWord: true) → D(isEndOfWord: true)
↑ ↑
CAR 단어 끝 CARD 단어 끝이런식으로 "CAR"를 검색했을 시 R 노드의 isEnd가 true이면 CAR를 찾았다고 할 수 있다.
다음으로 Trie의 기본 구조를 만들어보자.
2. Trie의 기본구조 만들기
이제 위에서 만든 TrieNode들을 관리할 뼈대를 구성하는 단계이다.
class Trie {
constructor() {
// 루트 노드 - 모든 단어의 시작점
this.root = new TrieNode();
}
// 입력 검증 헬퍼 메서드
_validateInput(str) {
return str && typeof str === 'string' && str.length > 0;
}
}루트노드가 필요한 이유는 트라이 역시 트리기반의 자료구조이고, 모든 트리의 시작점에는 루트가 존재한다.
이때 루트노드의 역할은
- 모든 단어의 공통 시작점
- 첫 번째 문자들의 부모역할
- 트라이 전체의 진입노드
로 활용할 수 있다.
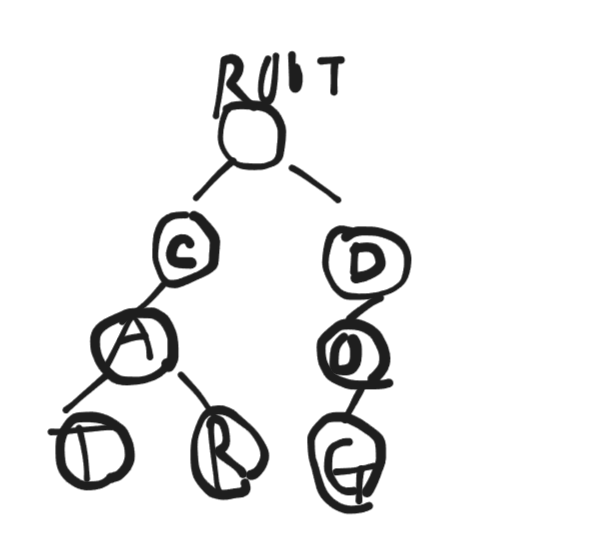
실제로 CAT,CAR,DOG를 넣으면 아래와 같은 트리가 형성된다.
3. insert 메소드 구현하기 (단어삽입)
이제 3단계로 단어를 저장할 insert 메소드를 구현해보자.
insert(word){
// 1. 먼저 단어를 소문자던 대문자던 일관성있게 변경한다.
word = word.toLowerCase();
// 2. 현재 위치의 노드를 root로 설정한다.
let currentNode = this.root;
// 3. 문자들을 탐색한다.
for(let char of word){
// 4. 문자가 존재하지 않으면
if(!currentNode.children.has(char)){
// 4-1. 그 문자를 노드로 만든다.
currentNode.children.set(char, new TrieNode());
}
// 5. 다음 자식 노드로 이동한다.
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
// 6. 단어의 끝을 표시한다.
currentNode.isEnd = true;
}
위 과정을 시각화 해보면
1. Root → C 노드 생성/이동
2. C → A 노드 생성/이동
3. A → R 노드 생성/이동
4. R 노드에서 isEndOfWord = true이렇게 표현할 수 있다.
다음으로 단어를 찾는 search 메소드를 구현해보자.
4. search 메소드 구현하기 (단어찾기)
insert로 단어를 저장했으니, 이제 저장된 단어를 찾는 search를 구현해보자.
검색 기능은 트라이의 핵심이자 매우 자주 사용되는 기능이다.
검색의 아이디어.
트라이에서 단어를 검색한다는건 경로 따라가기 라고 생각하면된다. 그리고 그 경로를 다 따라간뒤 마지막에 도달한 노드가 단어의 끝인지 확인만 해주면 된다.
구현 전략
검색 로직을 두 부분으로 나눠보자.
findNode(): 주어진 문자열의 마지막 노드를 찾는 메서드
search(): 실제 검색 로직을 담당하는 메인 메서드
findNode(word){
let currentNode = this.root;
for(let char of word){
if(!currentNode.children.has(char){
return null // 경로가 없음.
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
return currentNode;
}
이렇게 findNode를 구현했다. 그러면 CARD라는 단어를 찾는 과정을 시각화 해보면
초기 상태: currentNode = root
1단계: 'C' 처리
- root.children.has('c') 확인 → true
- currentNode = root.children.get('c') → C노드로 이동
2단계: 'A' 처리
- C노드.children.has('a') 확인 → true
- currentNode = C노드.children.get('a') → A노드로 이동
3단계: 'R' 처리
- A노드.children.has('r') 확인 → true
- currentNode = A노드.children.get('r') → R노드로 이동
4단계: 'D' 처리
- R노드.children.has('d') 확인 → true
- currentNode = R노드.children.get('d') → D노드로 이동
결과: D노드 반환이렇게 표현할 수 있다. 만약 경로가 없는 경우는
1단계: 'D' 처리
- root.children.has('d') 확인 → false
- return null (즉시 종료)이렇게 null을 반환하게 된다.
search 구현
search가 true를 반환하려면 경로가 우선 존재해야하고, 해당 위치에서 단어가 끝나야한다
이를 함수로 작성하면 아래와 같다.
search(word){
const node = this.findNode(word.toLowerCase());
return node !==null && node.isEnd;
}
5. prefix 접두사 검색 구현하기
접두사 검색은 경로가 하나라도 존재하면 true를 반환하게 만들면된다.
이미 구현했던 findNode함수를 재사용해서 주어진 접두사의 마지막 노드를 찾고, 노드가 존재하면 true를 반환하게 구현하면 끝이다.
search에서는 단어의 끝인지 아닌지도 판별했다면 prefix는 이부분의 조건을 제거한 방식이다.
비교
// search: 두 가지 조건 모두 확인
search(word) {
const node = this._findNode(word.toLowerCase());
return node !== null && node.isEndOfWord; // 두 조건
// ↑ 경로 존재 ↑ 단어 끝 확인
}
// startsWith: 경로 존재만 확인
startsWith(prefix) {
const node = this._findNode(prefix.toLowerCase());
return node !== null; // 한 조건만
// ↑ 경로 존재만 확인
}전체 코드
class TrieNode {
constructor() {
this.children = new Map();
this.isEnd = false;
}
}
class Trie {
constructor() {
// 모든 트라이는 빈 루트 노드를 가지고 있어야 한다.
this.root = new TrieNode();
}
// validation 함수도 추가해줬다.
_validateInput(input) {
if (!input || typeof input !== "string") {
return false;
}
// 영어 알파벳만 허용하는 정규식
return /^[a-zA-Z]+$/.test(input);
}
findNode(word) {
let currentNode = this.root;
for (let i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {
if (!currentNode.children.has(word[i])) {
// 존재하지 않는 단어
return null;
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(word[i]);
}
return currentNode;
}
insert(word) {
if (!this._validateInput(word)) {
throw new Error("Invalid input");
}
// 1. 소문자로 변환한다.
const lowerCaseWord = word.toLowerCase();
// 2. 현재 노드를 루트 노드로 초기화한다.
let currentNode = this.root;
// 3. 소문자로 변환한 단어의 각 문자를 순회한다.
for (let i = 0; i < lowerCaseWord.length; i++) {
const char = lowerCaseWord[i];
// 해당 문자가 현재 노드의 자식 노드에 없으면 새로 추가
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
currentNode.children.set(char, new TrieNode());
}
// 4. 다음 노드로 이동
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
// 단어의 끝에 도달했을 때 해당 노드의 isEnd를 true로 설정
currentNode.isEnd = true;
}
search(word) {
if (!this._validateInput(word)) {
throw new Error("Invalid input");
}
// 1. 노드를 찾는다.
const node = this.findNode(word.toLowerCase());
if (!node) {
console.log("존재 하지 않는 단어", word);
return false;
}
if (node.isEnd) {
console.log("존재하는 단어", word);
return true;
}
return false;
}
isPrefix(prefix) {
if (!this._validateInput(prefix)) {
throw new Error("Invalid input");
}
const node = this.findNode(prefix.toLowerCase());
return node !== null; // null 아니면 무조건 접두사 존재
}
}
실제 문제 풀어보기
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14426 백준의 접두사 찾기라는 문제가 있는데 구현한 트라이를 기반으로 풀어봤다.
const fs = require("fs");
const input = fs.readFileSync(0, "utf8").trim().split("\n");
class TrieNode {
constructor() {
this.children = new Map();
this.isEnd = false;
}
}
class Trie {
constructor() {
this.root = new TrieNode();
}
insert(word) {
let currentNode = this.root;
for (let char of word) {
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
currentNode.children.set(char, new TrieNode());
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
currentNode.isEnd = true;
}
findNode(word) {
let currentNode = this.root;
for (let char of word) {
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
return null;
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
return currentNode;
}
isPrefix(prefix) {
return this.findNode(prefix) !== null;
}
}
const [nm, ...rest] = input;
const [N, M] = nm.split(" ").map(Number);
const S = rest.slice(0, N);
const queries = rest.slice(N);
const trie = new Trie();
for (let word of S) trie.insert(word);
let count = 0;
for (let q of queries) {
if (trie.isPrefix(q)) count++;
}
console.log(count);
이렇게 아까 구현한 prefix함수가 true로 return되면 count를 하는 방식으로 구현했다.
마무리
라이브코딩 때 탈탈 털렸던 트라이 자료구조ㅜ.ㅜ 그리고 최근 면접에서도 자료구조 기반 질문들이 나왔었지만 그때는 꼼꼼하게 대답하지 못했다.
이번에 직접 트라이를 구현하고, 실제 문제를 풀어보면서 다시 기본기를 다지고 자신감을 회복할 수 있었다. 자료구조를 단순히 암기하는 것이 아니라 직접 구현하고 활용해보는 경험이 학습에 많이 도움이 되는것 같다.