External Data Bus
A row of wires that interconnect the parts of computer.
Registers
Store data that our CPU works with.
Memory Controller Chip
The bridge between the CPU and the RAM.
Address Bus
connects CPU to MCC
Cache
fatster than RAM.
L1 : the smallest and fastest
L2
L3
Clock wire
Keeps CPU's operation in sync.
Clock Speed
The maximum number of clock cycle that it can handle in a certain time period.
Overclocking
Increases the rate of your CPU clock cycles in order to perform more tasks.
CPU
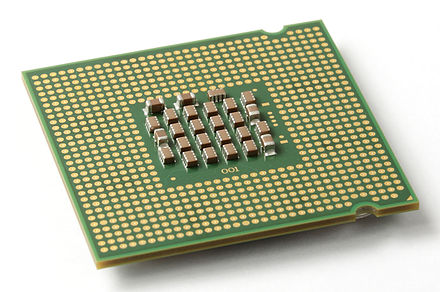
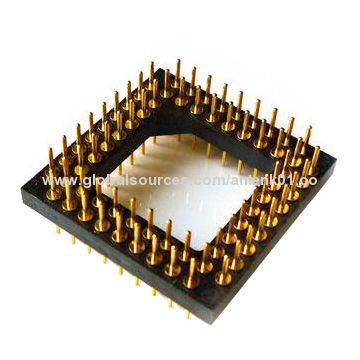
Two major types of CPU sockets
-
Land Grid Away(LGA)
-
Pin Grid Away(PGA)
RAM
Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM)
The one most commonly found in computers.
Where a one or zero is sent to DRAM,
it source each bit in a microscopic capacitor.
Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM)
This type of RAM is synchronized to our system's clock speed allowing quicker processing of data.
Double Data Rate SDRAM ( DDR SDRAM )
Faster than both
Motherboard
Chipset
Decides how components talk to each other on our machine.
Chipset is made of two chips.
- Northbridge : interconnects stuff like RAM and video cards.
- Southbridge : maintains out IO or input/output controllers.
Peripherals
External devices we connect to our computer, like a mouse, keyboard , nad moniot.
Expansion slots
Give us the ability to increase the functionality of our computer.
The standard of expansion slot today is PCE express or
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express.
Form Factor
The amount of stuff we can put in it and the amount of space we'll have.
The most common form factor of motherboard is ATX
which stands for Advanced Technology eXtended.
Storage
Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
Uses a spinning platter a mechanical arm to read and write information.
Solid State Drives (SSD)
Doesn't have a moving parts.
The information is stored on microchips and data travels a lot faster than HDDs.
Interfaces that hard drives use to connect to our system.
- Serial ATA : Uses one cable for data transfer.
- NVM Express (NVMe) : Instead of using a cable to connect your drive to your machine, the drive was added as an expansion slot.
Power Supplies
Types of electricity
- Direct Current(DC) : flows in one direction.
- Alternating Current(AC) : changes directions constantly.
Our computers use DC voltage, so we have to have a way to convert the AC voltage from our power company to something we can use.
- Volatge : 전압 (push)
- Amperage (AMP) : the amount of electriciry coming out.
- Wattage : the amount of volts and amps that a device needs. (pull)
Mobile Devices
System on a Chip (SoC)
Packs the CPU, RAM, and sometimes even the storage onto a single chip.
Batteries and Charging Systems
Charge Cycle
One full charge and discharge of a battery.
Peripherals
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
The most popular connections for out gadgets.
USB 2.0 : Transfer speeds of 480 Mb/s (megabits)
USB 3.0 : Transfer speeds of 5 Gb/s (gigabits)
* USB 3.1 : Transfer speeds of 10 Gb/s (gigabits)
