
IPv6 Addressing and Subnetting
The first 64-bits of any IPv6 address is the network ID,
and the second 64-bits of any IPv6 address is the host ID.
FF00::
Is used for multicast.
Multicast is a way of addressing groups of hosts all at once.
FE80::
Used for link-local unicast.
Link-local unicast addresses allow for local network segment communications and are configured based upon a host's MAC address.
The link-local address are used by an IPv6 hosts to receive their network configuration, which is a lot like how DHCP works.
IPv6 Headers
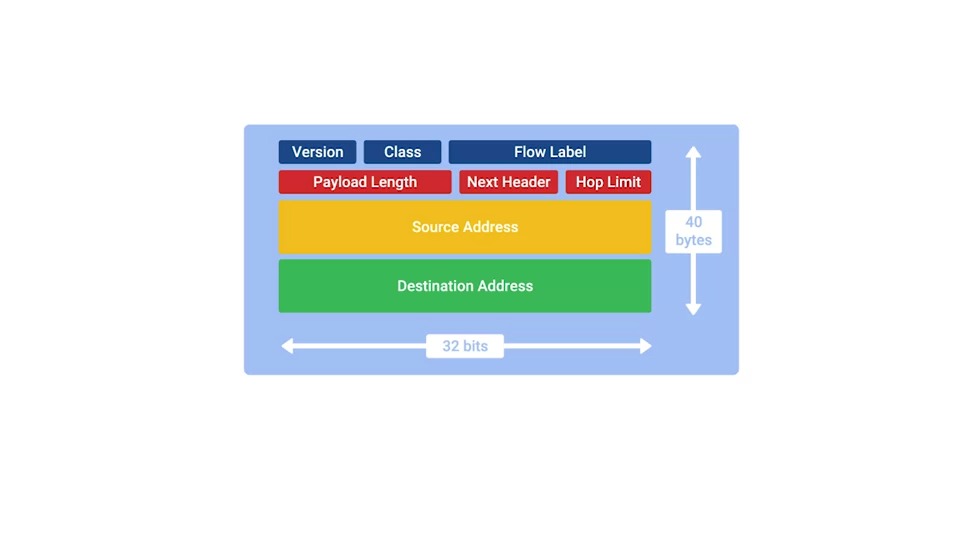
Version field
A 4-bit field that defines what version of IP is in use.
Traffic class field
An 8-bit field that defines the type of traffic contained within the IP datagram, and allows for different classes of traffic to receive different priorities.
Flow label field
A 20-bit field that's used in conjunction with the traffic class field for routers to make decisions about the quality of service level for a specific datagram.
Payload length field
A 16-bit field that defines how long the data payload section of the datagram is
Next header field
A unique concept to IPv6, and needs a little extra explanation.
Hop limit field
An 8-bit field that's identical in purpose to the TTL field in an IPv4 header.
IPv6 and IPv4 Harmony
Any IPv6 address that begins with 80 zeros, and is then followed by 16 ones is understood to be part of the IPv4 mapped address space.
IPv6 tunnels
IPv6 tunnels take incoming IPv6 traffic and encapsulate it within traditional IPv4 datagrams.
IPv6 tunnel broker
Companies that provide IPv6 tunnelnig endpoints for you, so you don't have to introduce additional equipment to your network.
