머리 자름!
일요일이니까.. 스타벅스에서 C 연습해보기
링크드리스트를 가급적 인터넷 검색 없이 구현해 보기 도전!
C로 싱글 링크드 리스트 구현
규칙
- 가급적 인터넷, GPT 도움 없이 구현한다.
- 검색은 전체 코드가 아닌 C문법에만 한정한다.
필요 기능 정리
- 노드 구조체
- 노드의 값
- 다음 노드 포인터
- 메서드
- 노드 생성
- 리스트에 노드 추가
- 리스트에서 노드 삭제
- 리스트에서 노드 검색
- 리스트에서 노드 업데이드
- 전체 노드 리스트 시각화
- 변수
- 리스트의 시작 노드를 담는 헤드 변수
구현 중 문법 정리
리눅스 파일 생성
touch linked_list.c
echo "안녕하세요, 리눅스 파일 생성 예시입니다." > 파일이름.txt
typedef
구조체를 선언할 시점에서는 자기를 참조하는 멤버를 생성할 때는
typedef로 지정한 별칭을 쓸 수 없다.
/* 이건 불가한 코드 */
typedef struct Node
{
int val;
node_t *next_ptr;
} node_t;
/* 이렇게 멤버는 struct로 하고 typdedef 이후에 쓸 수 있음.*/
typedef struct Node
{
int val;
struct Node *next_ptr;
} node_t;노드 구조체 정의
typedef struct Node
{
int val;
struct Node *next;
} node_t;노드 생성
node_t *create_node(int val)
{
node_t *new_node = (node_t *)malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if (new_node == NULL)
{
printf("메모리 할당에 실패했습니다.\n");
return NULL;
}
new_node->val = val;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}노드 추가
생성된 노드를 리스트의 맨 뒤에 추가한다!
리스트에는 최소한 1개의 노드가 있어야 추가할 수 있다.
void append_node(node_t *head, node_t *node)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return;
}
node_t *current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
if (current->next == NULL)
{
current->next = node;
return;
}
current = current->next;
}
return;
}노드 찾는 함수
node_t *find_node(node_t *head, int val)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("리스트가 비어있습니다.\n");
return NULL;
}
node_t *current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
if (current->val == val)
{
printf("%d를 찾았습니다.\n", val);
return current;
}
current = current->next;
}
printf("%d를 찾지 못했습니다.\n", val);
return NULL;
}노드 업데이트 함수
void update_node(node_t *head, int old_val, int new_val)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("리스트에 노드가 없습니다.\n");
return;
}
node_t *node = find_node(head, old_val);
if (node)
{
node->val = new_val;
}
return;
}노드 삭제 함수
void delete_node(node_t *head, int val)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("리스트에 노드가 없습니다.\n");
return;
}
node_t *current = head;
while (current->next != NULL)
{
if (current->next->val == val)
{
node_t *deleted_node = current->next;
current->next = current->next->next;
free(deleted_node);
printf("%d를 삭제했습니다.\n", val);
return;
}
current = current->next;
}
return;
}전체 리스트를 프린트하는 함수
void print_list(node_t *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("리스트에 노드가 없습니다.\n");
return;
}
node_t *current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
printf("%d -> ", current->val);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}싱글 연결 리스트에 테일 포인터 변수를 생성하는 게 의미있을까?
단방향에서는 딱히 의미 없음!
필요한 경우인지 검토 후 생성할 수는 있음.
main()
int main()
{
/* 리스트 초기화 */
node_t *head = init();
/* 노드 추가 */
append_node(head, create_node(1));
append_node(head, create_node(2));
append_node(head, create_node(3));
/* 리스트 출력 */
print_list(head);
/* 노드 검색 */
find_node(head, 2);
find_node(head, 4);
/* 노드 값 변경 */
update_node(head, 3, 4);
/* 리스트 출력 */
print_list(head);
/* 노드 검색 */
find_node(head, 4);
/* 노드 삭제 */
delete_node(head, 4);
/* 리스트 출력 */
print_list(head);
return 0;
}
이중포인터로 헤드값 바꾸는게 어려워서 우선 항상 리스트에 더미 노드를 추가해서 헤드는 변동할 필요 없이 처리함.
우선 1차로 이렇게 구현해보고, 이제 리스트가 비어있는 경우와 헤드를 바꾸는 경우도 구현해보기!
이중 포인터 활용한 코드
GPT 구현
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
} node_t;
node_t *createNode(int data)
{
node_t *newNode = (node_t *)malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if (newNode == NULL)
{
printf("메모리 할당 오류\n");
exit(1);
}
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertNode(node_t **head, int data)
{
node_t *newNode = createNode(data);
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
void deleteNode(node_t **head, int data)
{
node_t *current = *head;
node_t *prev = NULL;
while (current != NULL && current->data != data)
{
prev = current;
current = current->next;
}
if (current == NULL)
{
printf("%d를 찾을 수 없습니다.\n", data);
return;
}
if (prev == NULL) /* 삭제할 노드가 헤드인 경우 헤드 위치를 옮긴다. */
{
*head = current->next;
}
else /* 그외의 경우에는 직전 노드의 다음 포인터를 삭제 노드의 다음 노드로 변경한다. */
{
prev->next = current->next;
}
free(current);
}
void printList(node_t *head)
{
node_t *current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
printf("%d -> ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int main()
{
node_t *head = NULL;
insertNode(&head, 1);
insertNode(&head, 2);
insertNode(&head, 3);
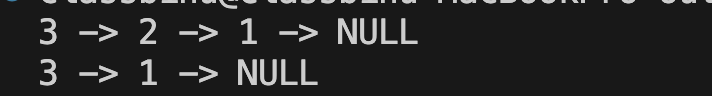
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 2);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
이중 포인터 조금 감은 잡히는데 응용은 아직 못하겠음!
조금 더 고민해보기
