문제
아주 옛날 옛적 로마 사람들은 로마 숫자를 사용하여 숫자를 나타내었다.
- 그들은 1 을 I (Capital i)로 쓰고 5 를 V, 10 을 X, 50 을 L, 100 을 C, 500 을 D, 1000 을 M 으로 나타낸다. 즉, 2 는 II 로 나타내고, 3 은 III 로 나타낸다.
- 하지만 4 를 쓰기엔 IIII 네 번을 써야 해서 너무 귀찮기도 하고 몇 개가 있는지 세려면 눈이 아파서 로마인들은 4 를 IV 라고 나타내기로 하였다. (IV = 5 - 1 = 4) 즉, 같은 문자를 4 번 이상 반복하지 않는 방식을 쓰기로 하였다. 이 방식을 계속 적용해 9 는 IX 로 나타내고 40 은 XL 90 을 XC 400 은 CD 900 은 CM 으로 나타낸다.
자, 이제 숫자가 아라비아 숫자나 로마 숫자가 무작위로 주어진다. 이때, 로마 숫자가 주어지면 아라비아 숫자를 구하고, 아라비아 숫자가 주어지면 로마 숫자를 구하여라. (우리가 자주 쓰는 숫자(0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)를 아라비아 숫자라고 한다.)
입력
입력의 첫 줄에는 테스트 케이스의 개수 T 가 주어진다.
그 다음 줄부터 T 줄에 걸쳐서 아라비아 숫자나 로마 숫자가 무작위로 주어진다. 이 숫자들의 범위는 모두 1 이상 3999 이하이다.
출력
각 테스트 케이스에 대해서 로마 숫자가 주어지면 그 숫자에 해당하는 아라비아 숫자를 출력하고, 아라비아 숫자가 주어지면 그 숫자에 해당하는 로마 숫자를 출력하여라.
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/13273
풀이
아라비아 숫자를 로마숫자로변환할때는 미리 만들어놓은 문자열 배열을 인덱스로 접근할 수 있도록 만들어놓으면 편하다.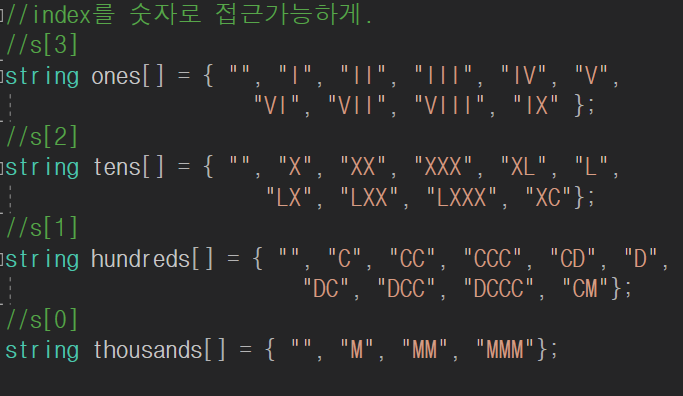
이렇게 0~9의 숫자가 대응된다. (0의경우는 표기를 아예 안함.)
반대로 아라비아숫자로 변환시는 로마숫자의 맨앞부터
위에서만든 문자열배열을 이용해서 9부터 1까지 역순의 인덱스로 접근하면 된다.
이때 string 의 find함수로 시작위치를 찾아서 비교하였다.
또, 아라비아숫자 '0'을 표기 하기위해 9~1중에서 못찾은 경우 맨앞자리에 0이 안붙도록 고려하여 숫자 '0'을 붙여주면 된다.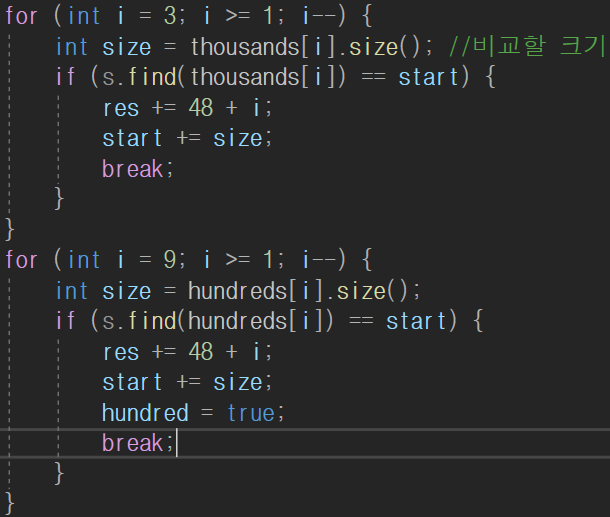 9부터 1까지 역순으로 find함수를 사용중이다.
9부터 1까지 역순으로 find함수를 사용중이다.
 숫자 0 을 붙여주는 부분
숫자 0 을 붙여주는 부분

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using std::vector; using std::stack; using std::queue;
using std::deque; using std::string; using std::pair;
using std::sort;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef pair<ll, int> pli;
typedef pair<int, ll> pil;
typedef pair<int, char> pic;
typedef pair<char, int> pci;
//index를 숫자로 접근가능하게.
//s[3]
string ones[] = { "", "I", "II", "III", "IV", "V",
"VI", "VII", "VIII", "IX" };
//s[2]
string tens[] = { "", "X", "XX", "XXX", "XL", "L",
"LX", "LXX", "LXXX", "XC"};
//s[1]
string hundreds[] = { "", "C", "CC", "CCC", "CD", "D",
"DC", "DCC", "DCCC", "CM"};
//s[0]
string thousands[] = { "", "M", "MM", "MMM"};
int t;
void init();
void func();
void roma(string s);
void arabia(string s);
void init() {
scanf("%d", &t);
}
void func() {
char input[50];
while (t--) {
scanf("%s", &input);
string s(input);
if (49 <= input[0] && input[0] <= 57) //아라비아 숫자인가
roma(s);
else
arabia(s);
}
}
//아라비아숫자를 로마숫자로
void roma(string s) {
string res;
if (s.size() == 1) {
res = res.append(ones[s[0] - '0']);
}
else if (s.size() == 2) {
res = res.append(tens[s[0] - '0']);
res = res.append(ones[s[1] - '0']);
}
else if (s.size() == 3) {
res = res.append(hundreds[s[0] - '0']);
res = res.append(tens[s[1] - '0']);
res = res.append(ones[s[2] - '0']);
}
else {
res = res.append(thousands[s[0] - '0']);
res = res.append(hundreds[s[1] - '0']);
res = res.append(tens[s[2] - '0']);
res = res.append(ones[s[3] - '0']);
}
printf("%s\n", res.c_str());
}
//로마숫자를 아라비아 숫자로
void arabia(string s) {
string res;
int start = 0;
bool hundred = false;
bool ten = false;
bool one = false;
for (int i = 3; i >= 1; i--) {
int size = thousands[i].size(); //비교할 크기
if (s.find(thousands[i]) == start) {
res += 48 + i;
start += size;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 9; i >= 1; i--) {
int size = hundreds[i].size();
if (s.find(hundreds[i]) == start) {
res += 48 + i;
start += size;
hundred = true;
break;
}
}
//백의자릿수가 0일때, 하지만 맨앞자리에 0이 오지않도록.
if (!hundred && res.size() != 0) res += '0';
for (int i = 9; i >= 1; i--) {
int size = tens[i].size();
if (s.find(tens[i]) == start) {
res += 48 + i;
start += size;
ten = true;
break;
}
}
if (!ten && res.size() != 0) res += '0';
for (int i = 9; i >= 1; i--) {
int size = ones[i].size();
if (s.find(ones[i]) == start) {
res += 48 + i;
start += size;
one = true;
break;
}
}
if (!one && res.size() != 0) res += '0';
printf("%s\n", res.c_str());
}
int main(void) {
init();
func();
return 0;
}