2023년 6월에 출간된 proteomics tutorial
3. Data Analaysis: Peptide Identification
the raw data set produced by a single LS-Ms/Ms run is a large collection of spectra, each with a retention time, m/z values, intensities, and metadata
LC-MS/MS를 통해 만들어진 raw data는 retention time, m/z, intensity, metadata로 이루어진 대용량 파일이다.
이렇게 만들어진 데이터를 MaxQuant, Proteome Discoverer같은 소프트웨어에 넣으면 peptide(또는 protein)과의 일치 score와 identification 정보를 만드는 것이다.
untargeted bottom-up DDA proteomics에서 가장 많이 쓰이는 identification approach는 Database Search이다. (예를 들면 SEQUEST 같은 방법)
they(de novo) have their own disadvantages and are ususally only used for specialized applications in which the peptides in the sample are not encoded by a species' genome, such as antigen presentation profiling or synthetic peptide library analysis
-> de novo 같은 DB를 필요로하지 않는 분석은 genome에 의해 인코딩되지 않은 특수한 분야에만 사용이 된다고 함
Charge Specific Peptide ion(precursors)은 b ion, y ion 이런 것들을 말하는 건가..? -> 잘 모르겠음
3.1 Database Search Algorithm Example: a Simplified Description of SEQUEST
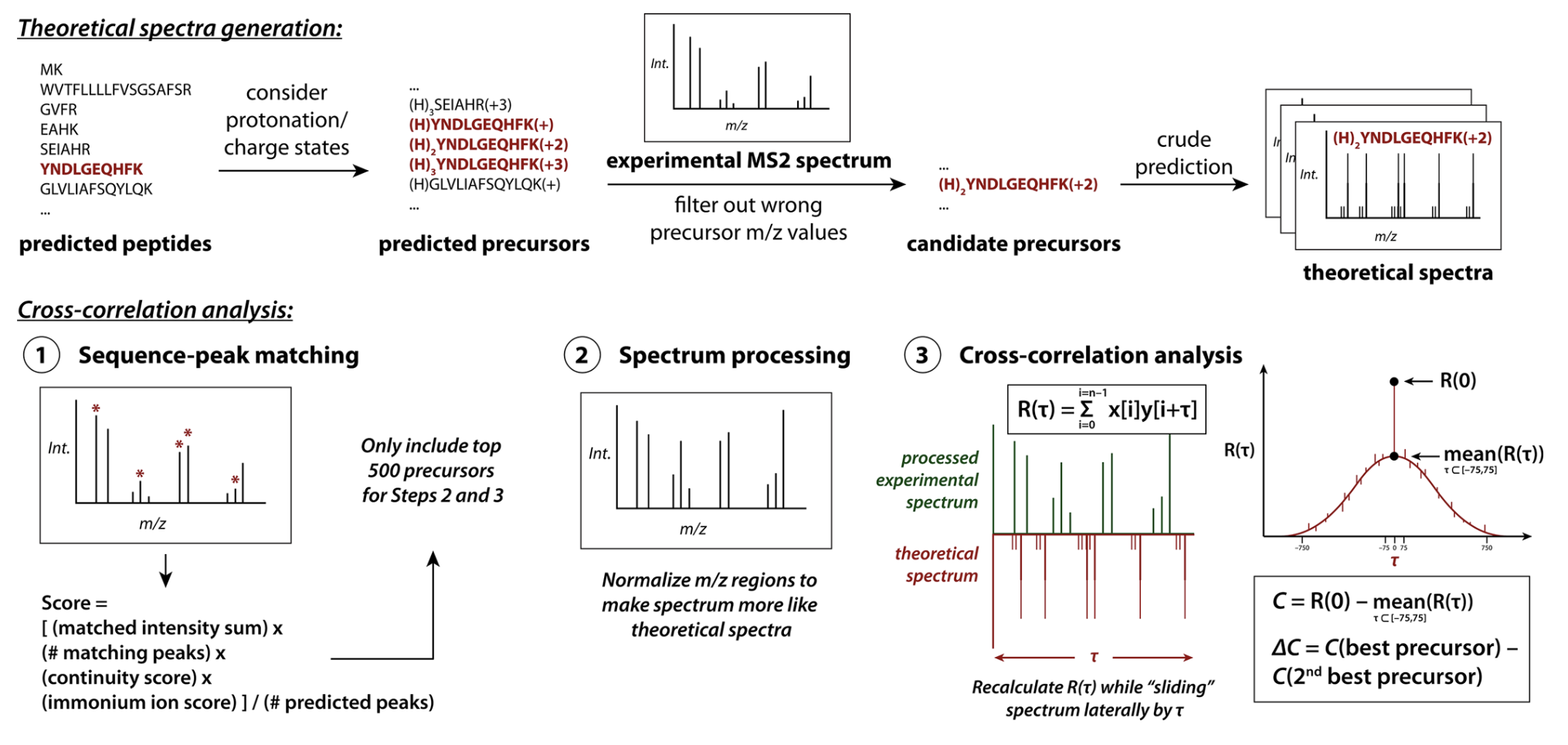
figure 12
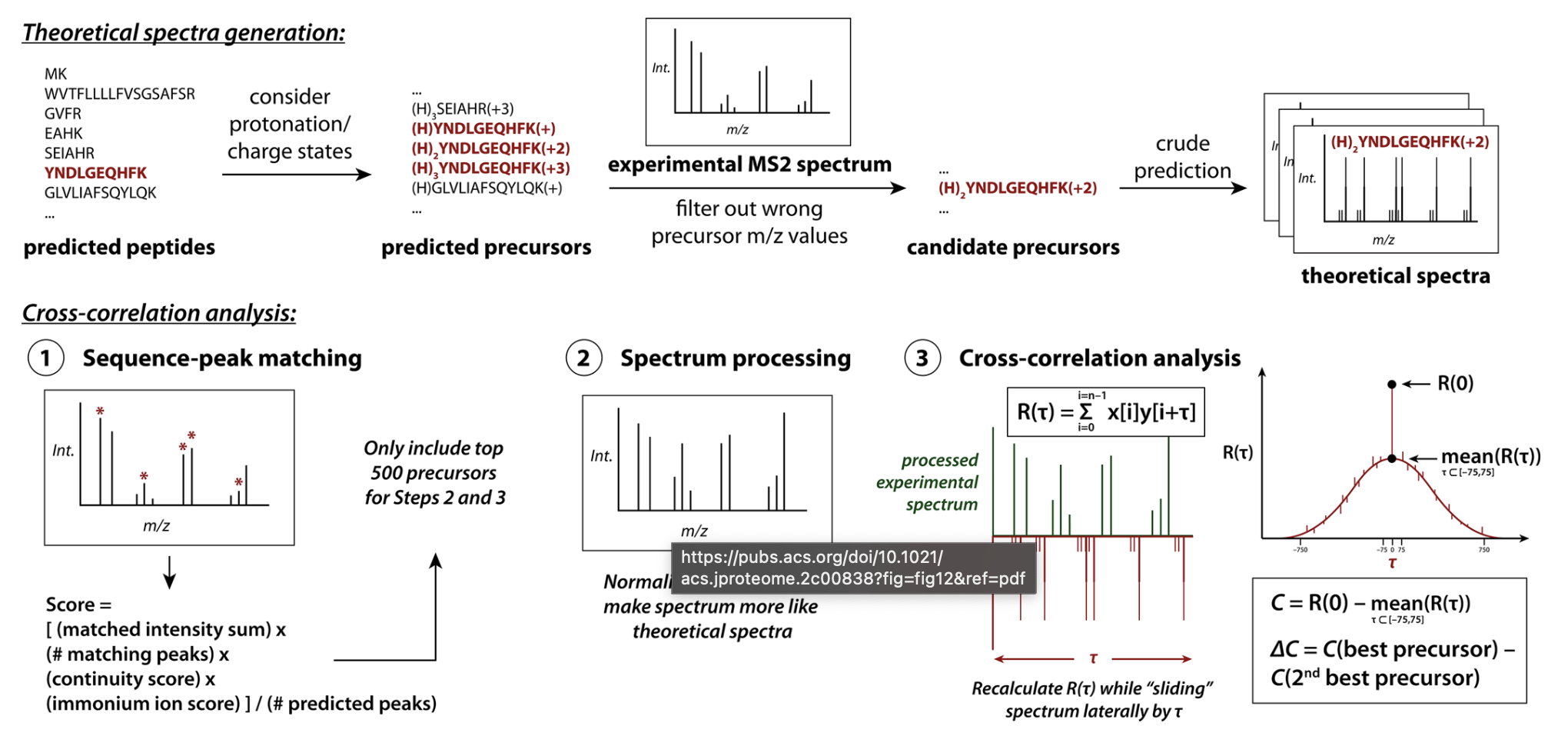
First, the peptides predicted from the reference proteome are filtered so that only precursors(i.e., charge state-specific peptide ions) with m/z values similar to that of the ion isolated for fragmentation are considered, and then theoretical spectra are generated.
-> 실제 스펙트럼 데이터에서 b-ion, y-ion 같은 precursor만 남긴 뒤에(filter out wrong precursor m/z values), DB에서 mass가 일치하는 sequence들을 가져오고 그 sequence들로 이론적인 스펙트럼을 만듦(crude prediction)
Theoretical spectra are quickly filtered by crudely comparing the experimental spectrum to the predicted fragments' m/z calues in a procedure inspired by classical manual spectrum interpretation: the numbers of matching fragments, the MS2 intensities, and other relevant features are combined into a score.
Theoretical spectra generation
- predicted peptides(ex. YNDLGEQHFK)를 protonation과 charge state를 고려하여 predicted precursor(ex. (H3)YNDLGEQHFK(+3))로 만듦
- experimental MS2 spectrum에서 잘못된 precursor m/z value를 걸러낸다.
- 그 실험으로 얻은 MS2 spectrum으로 candidate peptide를 골라낸 뒤에, 걔를 crude prediction을 거쳐서 theoretical spectra를 만듦
Cross-correlation analysis
- Sequence-peak을 매칭하여 스코어 구하기!
Score = [(matched intensity sum)*(#matching peaks) (continuity score) * (immonium ion score) / (#predicted peaks)
이 과정에서 top 500개의 precursor들만 남긴다. - spectrum processing -> m/z region을 normalize하여 더 이론적인 스펙트럼처럼 보이게 함. 즉 precursor peak을 제거하고, spectrum을 같은 크기의 10개의 region으로 나누고, 그 region안에서의 intensity를 normalize함
-> 이렇게 하는 이유는 experimental spectrum을 theoretical spectrum으로 보이게 하기 위함임. (theoretical spectrum을 만들때는 variable fragmentation efficiency가 무시되기 때문임.) -> ㅇ?? - theoretical spectrum과 experimental spectrum의 m/z에 있는 intensity들을 곱해서 correlation을 계산 (R(0))
- tau값을 -75~+75로 이동하면서 R(tau)를 계산하고 최종 XCorr 값은 R(0) - mean(R(tau))
This procedure controls the global false discovery rate(FDR)
Importantly, it is assumed that a random nonpeptide spectrum is equally likely to match a decoy or non-decoy peptide.
Therefore, given ant score threshold, there are an equal number of false target PSMs above the threshold, there are an equal number of false target PSMs above the threshold as decoy PSMs.
-> random한 스펙트럼은 target과 decoy에 같은 분포로 매치가 되기 때문에, 어떤 score threshold를 정해도, 그 threshold를 넘는 매치 중에 같은 수의 target match와 decoy match가 존재를 한다.
The proportion of target PSMs above a score threshold that are false can therefore be estimated as the number of decoy PSMs
This procedure controls the global FDR
the average proportion of accepted PSMs thata are false.
threshold를 정할 때는 델타 C, XCorr, crude sequence-peak match score 등등 어떤 score 값을 써도 되지만, 어떤 스코어를 쓰느냐에 따라 true match를 가려내는 ability가 다름
true peptide를 최대한 많이 찾아내도록 FDR을 control하는 방법으로, 여러 search score들을 linear combination해서 쓰기도 한다.
linear combination(선형 결합)이란, 아래 식처럼 벡터에 스칼라곱을 하여 더한 형태를 의미한다.
또한 detection을 더 잘하기 위해서 PSM의 다른 요소들을 이용하기도 하는데, 예를 들면 precursor mass error(실험으로 얻은 스펙트럼과 라이브러리를 통해 만든 이론적인 스펙트럼의 precursor peak 사이의 차이. 보통 ppm(parts per million) 값으로 1e6을 곱하여 이용 ) 등이 있다.
linear combination에서의 coefficients는 'Percolator'같은 머신러닝 알고리즘을 이용해서 가장 정확한 FDR을 추정할 수 있는 값들을 찾아낸다. (coefficient optimazation)
이런 과정을 통해 찾아낸 이 FDR은 global FDR이고, 각각의 PSM에는 local FDR이라는 것도 있다.
local FDR이란 한 PSM에 대해, 그 PSM과 비슷한 스코어를 가진 PSM들에 중에서 estimated false target match proportion을 의미한다. 이것도 decoy hit의 개수로 estimate 하는 것이다.
4. Peptide Quantification
이 블로그 글에는 없지만 이 튜토리얼 글의 앞부분에 나와있는 내용인데, HPLC는 Mass spectrometer가 돌아가는 중에 계속 기계에다가 peptide를 뿌린다.
한번의 scan cycle이 돌 때, 기계 3번 이하 정도의 횟수를 돈다.
그래서 MS1 peak은 여러 번 관찰이 된다. (전체 run time동안 fragment는 한 번 일어났는데도 불구하고 말이다.)
LFQ
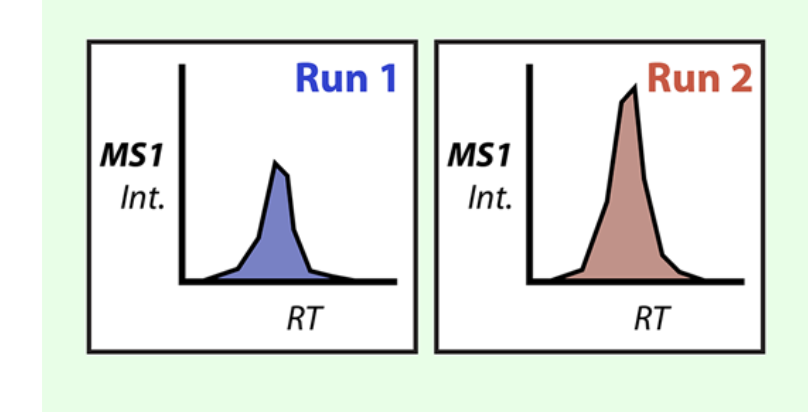
위 그림과 같은 chromatographic peak에서 피크의 height나, area under the curve(AUC)같은 특징들이 peptide의 relative abundance를 계산할 때 쓰인다.
이런 걸 'label free quantification(LFQ)'라고 부른다.
이런 LFQ 방식을 쓰면 한번 mass spectrometor를 run 할 때마다, 하나의 sample만 분석이 가능하다.
SILAC
stable isotope labeling with amino acid in cell culture를 줄여서 SILAC이라고 부른다.
이게 뭐하는 거냐면 아까 위에서. 말한 LFQ 같은 방식은 한번 돌릴 때 하나의 sample만 분석을 할 수가 있어서 throughput이 떨어진다.
그래서 한번에 2-3개 정도를 돌릴 수 있게, sample에다가 reagent를 이용해서 라벨링을 하는 것이다.
biological system is utilized to label the whole proteome
TMT
TMT는

유익한 글이었습니다.