[백준] 12850 : 본대 산책2 - 분할정복, 행렬, 행렬제곱
출처 : 본대 산책2 acmicpc.net/problem/12850
| 시간 제한 | 메모리 제한 |
|---|---|
| 1초 | 512 MB |
문제
숭실 대학교 정보 과학관은 유배를 당해서 캠퍼스의 길 건너편에 있다. 그래서 컴퓨터 학부 학생들은 캠퍼스를 ‘본대’ 라고 부르고 정보 과학관을 ‘정보대’ 라고 부른다. 준영이 또한 컴퓨터 학부 소속 학생이라서 정보 과학관에 박혀있으며 항상 꽃 이 활짝 핀 본 대를 선망한다. 어느 날 준영이는 본 대를 산책하기로 결심하였다. 숭실 대학교 캠퍼스 지도는 아래와 같다.
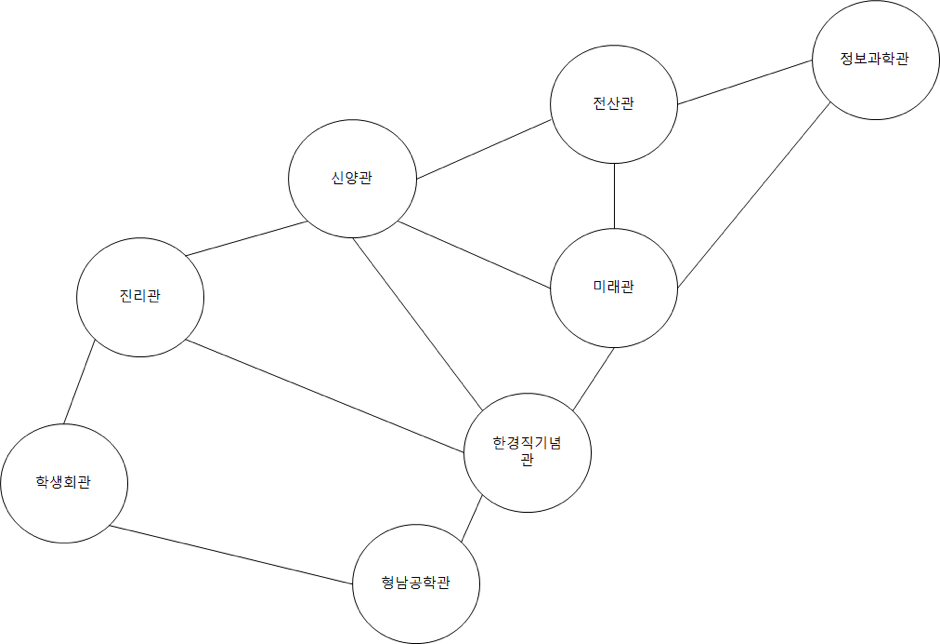
(편의 상 문제에서는 위 건물만 등장한다고 가정하자)
한 건물에서 바로 인접한 다른 건물로 이동 하는 데 1분이 걸린다. 준영이는 산책 도중에 한번도 길이나 건물에 멈춰서 머무르지 않는다. 준영이는 할 일이 많아서 딱 D분만 산책을 할 것이다. (산책을 시작 한 지 D분 일 때, 정보 과학관에 도착해야 한다.) 이때 가능한 경로의 경우의 수를 구해주자.
입력
D 가 주어진다 (1 ≤ D ≤ 1,000,000,000)
출력
가능한 경로의 수를 1,000,000,007로 나눈 나머지를 출력한다.
아이디어
그림을 그래프처럼 생각하며, 건물들을 각각 노드로 만들었다.
/*
js - jb
| \ |
sa - ml
| \ |
jl - hk
| |
hs - hn
0 - 1
| \ |
2 - 3
| \ |
4 - 5
| |
6 - 7
*/
N번 이동했을때 각 건물에 도착하는 경우의수는,
N-1번 건물에 연결된 건물에 도착하는 수의 합이다.
Buildings[N][node.num] = Buildings[N-1][node.connected1] + Buildings[N-1][node.connecter2} ... ;
따라서 내가 만든대로면, N번째의 1번 노드에 도착하는 경우의수를 계산하면된다.
- Bottom Up방식
바텀 업 방식으로 차례대로 구하면 총 N번의 반복문을 돌게 될것이다. 공간복잡도는 직전 값과 현재 값만 필요하므로 거의 안들것으로 예상된다.
최대 1억이라는 값이 들어와 O(1억) 을 1초로 계산했을때 시간제한에 걸림을 알 수 있다.시간 복잡도 공간 복잡도 O(N) 거의 안듦
-
행렬곱을 이용한 거듭제곱 분할정복
반복문 방식을 보다싶이 같은 연산이 N번 반복됨을 알 수 있다. 이는, 특정 행렬에 같은 행렬을 N번 곱하는 연산으로 표현 가능다.int[] ansMatrix = {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0}; int[][] matrix = { //0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 {0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0},//0 {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0},//1 {1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0},//2 {1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0},//3 {0,0,1,0,0,1,1,0},//4 {0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1},//5 {0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},//6 {0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0},//7 };ansMatrix는 처음 움직임을 표현한 배열이다. 시작점에서 연결된 지점으로 한칸씩 이동한것을 표현했으며, 이 행렬에 matrix를 계속 곱해준다면, 반복문에서 했던 연산이 반복됨을 알 수 있다.
따라서 matrix의 2의n제곱의 제곱값을 미리 구해 거듭제곱을 분할정복하면 O(logN)이라는 시간복잡도로 값을 구할 수 있다.
예를들어보자. matrix의 1,2,4,8,16...2^31제곱값을 구해놓는다.
100제곱값은 64제곱 32제곱 4제곱의 곱으로,
2050은 2048제곱 2제곱의 곱으로 분할해서 미리 계산한 값을 이용해 목표값을 표현 할 수 있다.
공간복잡도 또한 256MB임에 충분함을 알 수 있다.시간 복잡도 공간 복잡도 O(logN) 4Byte*8*8*31 + a
코드
Bottom Up방식
백준에서 코드 보기 : http://boj.kr/9447a952e18d44878b0e250942f9af39
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
private static int N;
private static final int MOD = 1_000_000_007;
private static int[][] buidings = new int[2][8];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int current = 0;
int pre = 1;
buidings[current][0] = 1;
buidings[current][3] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
current = (current+1)%2;
pre = (pre+1)%2;
buidings[current][0] = ((buidings[pre][1] + buidings[pre][2])%MOD + buidings[pre][3])%MOD;
buidings[current][1] = (buidings[pre][0] + buidings[pre][3])%MOD;
buidings[current][2] = (((buidings[pre][0] + buidings[pre][3])%MOD + buidings[pre][4])%MOD + buidings[pre][5])%MOD;
buidings[current][3] = (((buidings[pre][0] + buidings[pre][1])%MOD + buidings[pre][2])%MOD + buidings[pre][5])%MOD;
buidings[current][4] = ((buidings[pre][2] + buidings[pre][5])%MOD + buidings[pre][6])%MOD;
buidings[current][5] = (((buidings[pre][2] + buidings[pre][3])%MOD + buidings[pre][4])%MOD + buidings[pre][7])%MOD;
buidings[current][6] = (buidings[pre][4] + buidings[pre][7])%MOD;
buidings[current][7] = (buidings[pre][5] + buidings[pre][6])%MOD;
}
System.out.println(buidings[current][1]);
}
}
/*
js - jb
| \ |
sa - ml
| \ |
jl - hk
| |
hs - hn
0 - 1
| \ |
2 - 3
| \ |
4 - 5
| |
6 - 7
*/
행렬곱을 이용한 거듭제곱 분할정복
백준에서 코드 보기 : http://boj.kr/c4d99cd262bb4b9584ce5d3e5b2bd36d
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
private static int N;
private static final int MOD = 1_000_000_007;
private static int[] ansMatrix = {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0};
private static long[][][] binaryMatrix = new long[32][8][8];
private static int[][] matrix = {
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
{0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0},//0
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0},//1
{1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0},//2
{1,1,1,0,0,1,0,0},//3
{0,0,1,0,0,1,1,0},//4
{0,0,1,1,1,0,0,1},//5
{0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},//6
{0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0},//7
};기본 값 세팅
private static void initMatrix(){
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
binaryMatrix[0][i][j] = matrix[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < 32; i++) {
binaryMatrix[i] = mutiplyMatrix(binaryMatrix[i-1], binaryMatrix[i-1]);
}
}
private static long[][] mutiplyMatrix(long[][] a, long[][] b){
long[][] ans = new long[8][8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
ans[i][j] += a[i][k]*b[k][j];
ans[i][j]%=MOD;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private static int[] mutiplyMatrix(int[] a, long[][] b){
int[] ans = new int[a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b[i].length; j++) {
ans[i] += a[j]*b[i][j];
ans[i] %= MOD;
}
}
return ans;
}행렬곱 연산을 위한 매소드 정의와, matrix 2의n제곱꼴의 값을 미리 구해주는 함수
private static void solution(int count){
String s = Integer.toBinaryString(count);
int size = s.length();
long[][] toMultiply = new long[8][8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
toMultiply[i][i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '1'){
toMultiply = mutiplyMatrix(toMultiply,binaryMatrix[size-i-1]);
}
}
ansMatrix = mutiplyMatrix(ansMatrix, toMultiply);
System.out.println(ansMatrix[1]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
initMatrix();
solution(N-1);
}
}
결론
처음에는 Bottom Up방식 말고는 가장 빠른 방법이 없다고 생각했다. 직접 구현해보며 규칙성을 찾으려고도 해봤으나, 찾기는 힘들었고 그러다 떠오른방식은 선형대수학에서 배웠던 행렬식의 제곱을 쉽게 구하는 방법이 떠올랐다.

출처 : STEM CookBook, 기초 선형대수학(2판)
책의 일부분을 발췌해왔다. 이와같이 직교 대각화 행렬을 구할 수 있다면 이 문제는 O(1)만에 문제를 해결할 수 있었겠지만, 실제 풀이를 보았듯이 이 행렬은 이러한 연산이 불가능 했다. 행렬이 대각화가 되지 않아서, 결국에는 거듭제곱의 분할정복으로 문제를 풀게 되었다.
또, 자연스럽게 사용하고있었지만 이진수를 다루기에는 비트연산도 훌륭한 방법이지만, Integer.toBinaryString이라는 매소드로 문자열로 다루는것도 좋은 방법인거같다. 시험장이라면 이 방법이 편하기때문에 이 방법을 선택할것이다.
이 문제는 행렬 거듭제곱에 관한 문제였지만, 큰 거듭제곱을 연습하기 좋은 문제가 있어 첨부해본다.

