 [백준] 12850 : 본대 산책2 - 분할정복, 행렬, 행렬제곱
[백준] 12850 : 본대 산책2 - 분할정복, 행렬, 행렬제곱
출처 : 배열에서 이동 acmicpc.net/problem/1981
| 시간 제한 | 메모리 제한 |
|---|---|
| 1초 | 256 MB |
문제
n×n짜리의 배열이 하나 있다. 이 배열의 (1, 1)에서 (n, n)까지 이동하려고 한다. 이동할 때는 상, 하, 좌, 우의 네 인접한 칸으로만 이동할 수 있다.
이와 같이 이동하다 보면, 배열에서 몇 개의 수를 거쳐서 이동하게 된다. 이동하기 위해 거쳐 간 수들 중 최댓값과 최솟값의 차이가 가장 작아지는 경우를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 n(2 ≤ n ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 다음 n개의 줄에는 배열이 주어진다. 배열의 각 수는 0보다 크거나 같고, 200보다 작거나 같은 정수이다.
출력
첫째 줄에 (최대 - 최소)가 가장 작아질 때의 그 값을 출력한다.
예제
입력 :
5
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 8 |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| 8 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
출력:
2
해설
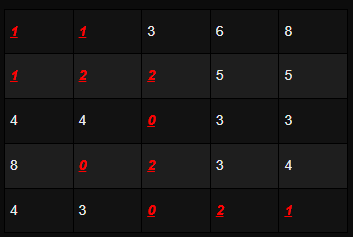
아이디어
출발점(1,1) 부터 도착점 (n,n) 까지 이동하면서, 거쳐간 수의 최대 최소 차가 최소가 되게해야한다.
최솟값을 구해야하므로 나올 수 있는 경우의 수 중에 최대최소 차가 가장 작은것부터 탐색한다.
우선, 출발점과 도착점은 반드시 지나야하므로, 초기 최대최소로 설정해준다.
M(max) : 1, m(min) : 1
출발점부터 현재 최대 최소로 탐색 가능한만큼 완전 탐색한다.
M : 1, m : 1

현재 최대 최소로는 도착점까지 도달하지 못했다.
다음으로 생기는 경우의수는 다음과 같다
M : 3, m : 1, dif(difference) : 2 (new)
M : 2, m : 1, dif : 1 (new)
M : 4, m : 1, dif : 3 (new)
이 중 최대최소 차가 가장 적은 두번쨰 경우로 탐색을 시작한다.
M : 2, m : 1

다음 가능한 경우의 수를 탐색한다
M : 3, m : 1, dif : 2
M : 4, m : 1, dif : 3
M : 5, m : 1, dif : 4 (new)
M : 2, m : 0, dif : 2 (new)
차가 제일 적은 첫번째 경우 탐색
M : 3, m : 1, dif : 2
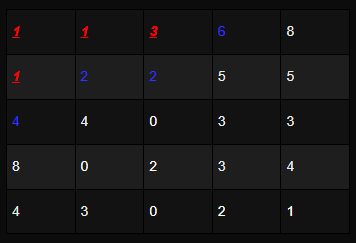
다음 경우의 수
M : 4, m : 1, dif : 3
M : 5, m : 1, dif : 4
M : 2, m : 0, dif : 2
M : 6, m : 1, dif : 5 (new)
차가 제일 적은 세번째 경우 탐색
M : 2, m : 0, dif : 2
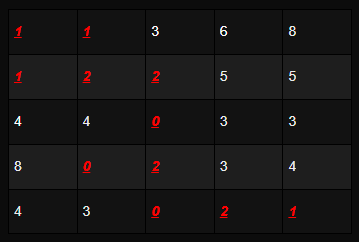
이때,도착지까지 도달했으므로 답은 2가 된다.
좌표와, 최대최소는 쌍으로 되어있으므로 두 정수의 쌍을 표현할 P 클래스를 구현한다. 추후 HashSet으로 방문 체크를 할거라 싱글턴 기법으로 구현해 같은 점에대한 해쉬코드를 같게 해준다.
private static class P{
public final int x, y;
private P(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
private static P[][] ps;
static {
ps = new P[201][201];
}
public static P get(int x, int y){
if (ps[x][y] == null){
return ps[x][y] = new P(x, y);
}
return ps[x][y];
}
}경우의수들은 항상 최대최소 차가 가장 적은값을 뽑아야하므로 우선순위 큐로 구현한다.
PriorityQueue<P> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1.y - o1.x, o2.y - o2.x));중복된 최대최소를 경우의수로 생각 할 필요 없으므로 중복체크를 할 HashSet을 구현한다.
HashSet<P> visit = new HashSet<>();최대 최소 쌍을 골랐을때 출발점으로부터 탐색 할 메소드를 구현한다. 이때 탐색하며 새로 가능한 점을 Set 자료구조로 반환하고, 도착지까지 도착할 경우 null을 반환한다.
private static HashSet<Integer> find(P minmax){
int min = minmax.x;
int max = minmax.y;
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[N][N];
ArrayDeque<P> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addLast(P.get(0,0));
visit[0][0] = true;
while (!deque.isEmpty()){
P p = deque.pollFirst();
if (p.x == N-1 && p.y == N-1)
return null;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = p.x + dx[i];
int y = p.y + dy[i];
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= N || y >= N) continue;
if (visit[x][y]) continue;
if (min <= map[x][y] && map[x][y] <= max){
visit[x][y] = true;
deque.addLast(P.get(x,y));
}
else {
set.add(map[x][y]);
}
}
}
return set;
}출발점과 도착점으로 초기 최대 최소쌍을 설정해준다.
P init = P.get(Math.min(map[0][0], map[N-1][N-1]), Math.max(map[0][0], map[N-1][N-1]));순차적으로 너비 우선 탐색을 할 코드를 구현한다.
HashSet<P> visit = new HashSet<>();
queue.add(init);
visit.add(init);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
P p = queue.poll();
HashSet<Integer> next = find(p);
if (next == null){
System.out.println(p.y - p.x);
break;
}
for (Integer i : next) {
if (i > p.y){
P nextp = P.get(p.x, i);
if (visit.contains(nextp)) continue;
queue.add(nextp);
visit.add(nextp);
}
else if (i < p.x){
P nextp = P.get(i, p.y);
if (visit.contains(nextp)) continue;
queue.add(nextp);
visit.add(nextp);
}
}
}최악의 경우 100x100개의 쌍이 만들어지고
그래프의 정점이 최대 100x100이므로
O(N^4logN) 100,000,000 x log100(=6.x) 으로 표현되지만, 모든 쌍이 그래프의 모든 점을 탐색하지 않으니 시간안에 들어 올 것 같다.
공간 복잡도는 가능한 쌍의 수와 같아 최대 100x100의 두개의 int쌍이 생겨 공간복잡도는 넉넉하다.
| 시간 복잡도 | 공간 복잡도 |
|---|---|
| O(N^4logN) | 100x100x8Byte + a |
코드
github에서 코드 보기 : https://github.com/LuizyHub/CodingTestStudy/blob/master/src/Baek1981.java

import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static final int[] dx = {-1, 0, 0, 1};
public static final int[] dy = {0, 1, -1, 0};
private static class P{
public final int x, y;
private P(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
private static P[][] ps;
static {
ps = new P[201][201];
}
public static P get(int x, int y){
if (ps[x][y] == null){
return ps[x][y] = new P(x, y);
}
return ps[x][y];
}
}
private static int N;
private static int[][] map;
private static HashSet<Integer> find(P minmax){
int min = minmax.x;
int max = minmax.y;
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[N][N];
ArrayDeque<P> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addLast(P.get(0,0));
visit[0][0] = true;
while (!deque.isEmpty()){
P p = deque.pollFirst();
if (p.x == N-1 && p.y == N-1)
return null;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = p.x + dx[i];
int y = p.y + dy[i];
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= N || y >= N) continue;
if (visit[x][y]) continue;
if (min <= map[x][y] && map[x][y] <= max){
visit[x][y] = true;
deque.addLast(P.get(x,y));
}
else {
set.add(map[x][y]);
}
}
}
return set;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new int[N][N];
StringTokenizer st;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
P init = P.get(Math.min(map[0][0], map[N-1][N-1]), Math.max(map[0][0], map[N-1][N-1]));
PriorityQueue<P> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1.y - o1.x, o2.y - o2.x));
HashSet<P> visit = new HashSet<>();
queue.add(init);
visit.add(init);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
P p = queue.poll();
HashSet<Integer> next = find(p);
if (next == null){
System.out.println(p.y - p.x);
break;
}
for (Integer i : next) {
if (i > p.y){
P nextp = P.get(p.x, i);
if (visit.contains(nextp)) continue;
queue.add(nextp);
visit.add(nextp);
}
else if (i < p.x){
P nextp = P.get(i, p.y);
if (visit.contains(nextp)) continue;
queue.add(nextp);
visit.add(nextp);
}
}
}
}
}결론
지난번 아기상어 문제처럼 우선순위 큐를 이용한 너비우선 탐색을 진행하였다.
개선할 점으로는 매번 새로운 탐색을 진행하므로 이전 상황을 메모해두면 이전 상황부터 탐색을 진행해, 탐색 부분에서 속도를 줄일 수 있을 것 같다. 맵 사이즈가 최대 100x100이기 때문에 이 문제에서는 문제가 되지는 않았다.
대부분 사람들은 주어지는 숫자가 200이하 자연수인점을 이용해서 이분탐색(투 포인터)를 이용해 최소 해를 찾았다. 주어지는 수의 범위가 컸다면 내가 풀었던 방식으로 풀어야 할 것같다.

