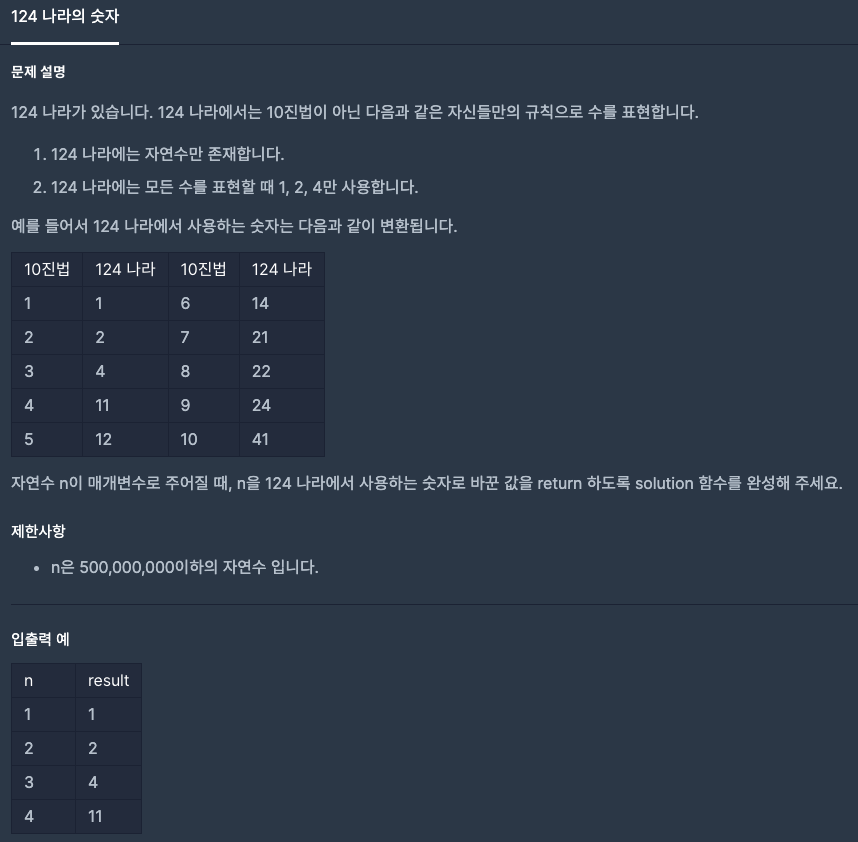
124 나라의 숫자
1. Problem
2. Others' Solution
- 첫 번째 방법 (규칙을 이용 참고)
- 3으로 나누어 떨어지면 4를 추가하고 n-1
- 3으로 나누어 떨어지지 않으면 그대로 3진법 적용
def solution(n):
answer = ''
while n:
if n % 3:
answer += str(n % 3)
n //= 3
else:
answer += "4"
n = n//3 - 1
return answer[::-1]- 두 번째 방법 (진법의 원리를 이용)
- 3진법은
0,1,23개의 숫자를 순서대로 싸이클을 돌리며 수를 표현하는 방법이며 2 이상이 되면 올림수를 만들며 수를 표현함 (10진법은 0~9 까지의 10개의 숫자를 순서대로 싸이클 돌리며 9 이상이되면 올림수를 만들어 10으로 시작) - 10진수를 3진법으로 나타낼 때, 소인수분해 과정에서 나타나는 나머지는
0,1,2이므로0,1,2로 표현한다고 생각할 수 있지만, 다르게 생각한다면 싸이클을 돌릴 수 에서 0번 째, 1번 째, 2번째 수를 나타낸다고 생각도 가능 - 즉, 만약 3진법을
0,1,2가 아닌7,8,93개의 숫자를 사용하여 표현한다고하면,7(0) -> 8(1) -> 9(2) -> 87(3) -> 88(4)-> 89(5)이런식으로 표현할 수도 있음 - 문제에서 요구하는 것은 3진법의 원리에서
0,1,2가 아닌1,2,4의 수를 사용하는 것이고, 0이 나타나는 순간은 0 그 자체거나 표현할 수 있는 수의 싸이클을 넘어 갈때 (예들 들면 3진법에서 3 = 10)이므로, 이를 없애기 위해 -1을 수행하고 표현할 수 있는 수를 1씩 증가시키면됨 (3진법에서 10-1 = 2 이지만 2가 3을 표현해야되기 때문에 0,1,2 가 아닌 1,2,3 에 맞추면됨)
def solution(n):
answer = ''
while n > 0:
n -= 1
answer = '124'[n%3] + answer
n //= 3
return answer
또는
def solution(n):
if n<=3:
return '124'[n-1]
else:
q, r = divmod(n-1, 3)
return solution(q) + '124'[r]
3. Learned
- 진법을 표현하는 방법에 대해 새로운 시각으로 접근하게 됨
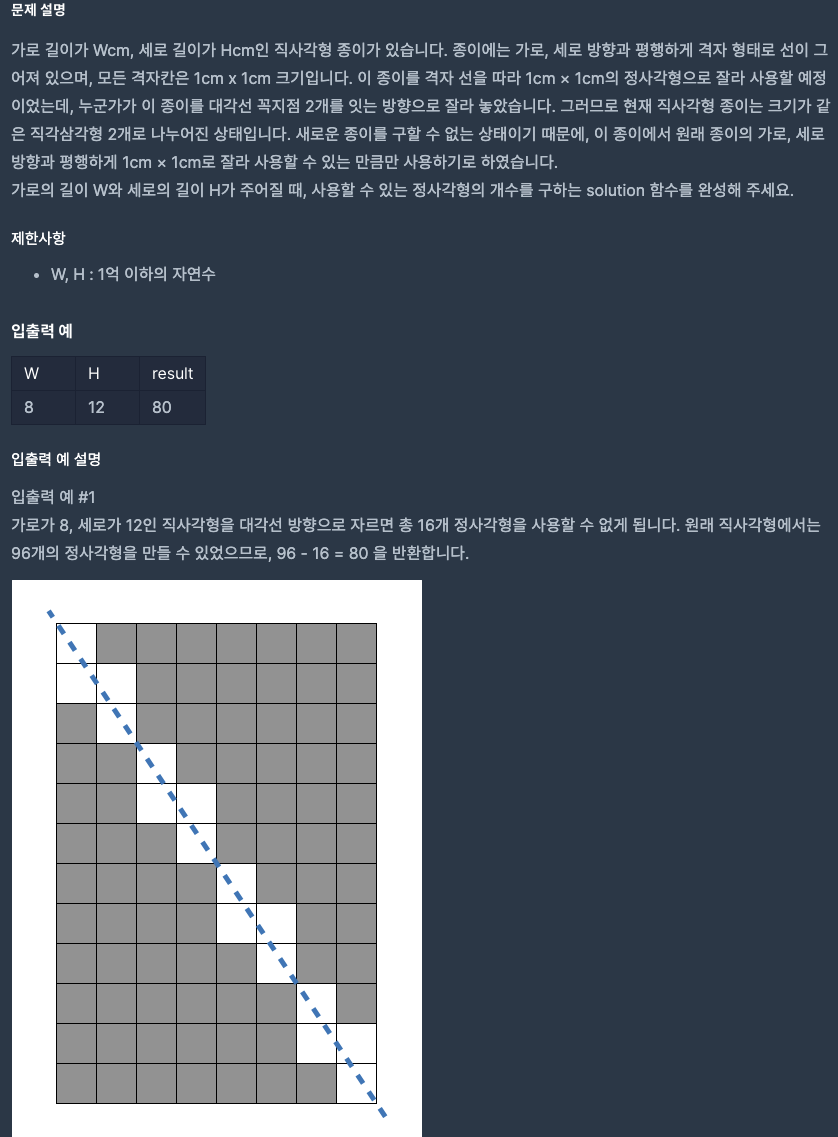
멀쩡한 사각형
1. Problem
2. My Solution
- 1x1 부터 3x6 까지 직접 그려보며 규칙을 찾아봄
- 발견한 규칙은 아래와 같지만 3x6 을 잘못 그려서 규칙은 애초에 잘못된 거였음
# 4가지의 경우
# 1. w = 1 또는 h = 1 인 경우 0개 반환
# 2. w = h 인경우 w개 만큼 빠짐
# 3. w = 홀수 또는 h = 홀수 인 경우 w + h - 1 개 만큼 빠짐 (3x6 규칙 에러)
# 4. w = h = 짝수인 경우 (큰 것을 작은거로 나눈 몫 x 작은 거) 만큼 빠짐
import math
def solution(w,h):
if w == 1 or h == 1:
return 0
if w == h:
return w*h-w
if w % 2 == 1 or h % 2 == 1:
return w*h-(w+h-1)
else:
return w*h - (math.ceil(max(w,h) / min(w,h)) * min(w,h))
3. Others' Solution
- 최대공약수를 이용한 풀이법 (참고)
1. 대각선을 지나가므로 가로의 길이만큼 가로로 직사각형을 자르고, 세로의 길이만큼 세로로 직사각형을 자름
2. 여기서 중복되는 직사각형을 빼면 됨 w+h-(중복되는 직사각형 수)
3. 중복되는 직사각형의 수 = 최대 공약수 - 위에서 3번 경우 -> 최대 공약수가 1 일 때
- 위에서 4번 경우 -> 최대 공약수가 1 이상일 때
import math
def solution(w,h):
return w*h - (w+h-math.gcd(w,h))
4. Learned
- 규칙을 찾아 식을 세우기 위해선 하나씩 구해본 결과값이 정확해야함, 3x6 일 때를 제대로 구했으면 아마 한 단계 더 나아가서 규칙을 새로 정의했을 것 같음
- 문제에서 주어지는 것들을 최대한 이용하자. 2개의 수가 주어지면 두 수의 관계를 정의할 수 있는 모든 관계를 생각해보기 (최대공약수, 최소공배수 등등)
기능개발
1. Problem

2. My Solution
- 개발 완료 여부에 상관없이 배포 순서가 고정되어 있으므로 스택에 역순으로 PUSH 한다음에 pop 을 수행하면 배포 순서대로 배포가 이루어짐
def solution(progresses, speeds):
answer = []
tasks = []
for task in range(len(progresses)-1,-1,-1):
tasks.append([task,progresses[task]])
for day in range(1,101):
completed_cnt = 0
if not tasks:
break
# 하루가 지나서 진도가 늘어남
for i in range(len(tasks)):
tasks[i][1] += speeds[tasks[i][0]]
while tasks:
if tasks[-1][1] >= 100:
tasks.pop()
completed_cnt += 1
else:
break
if completed_cnt >= 1:
answer.append(completed_cnt)
return answer
3. Learned
- 고정된 순서대로 작업이 이루어져야 될 때는 스택을 이용해보자
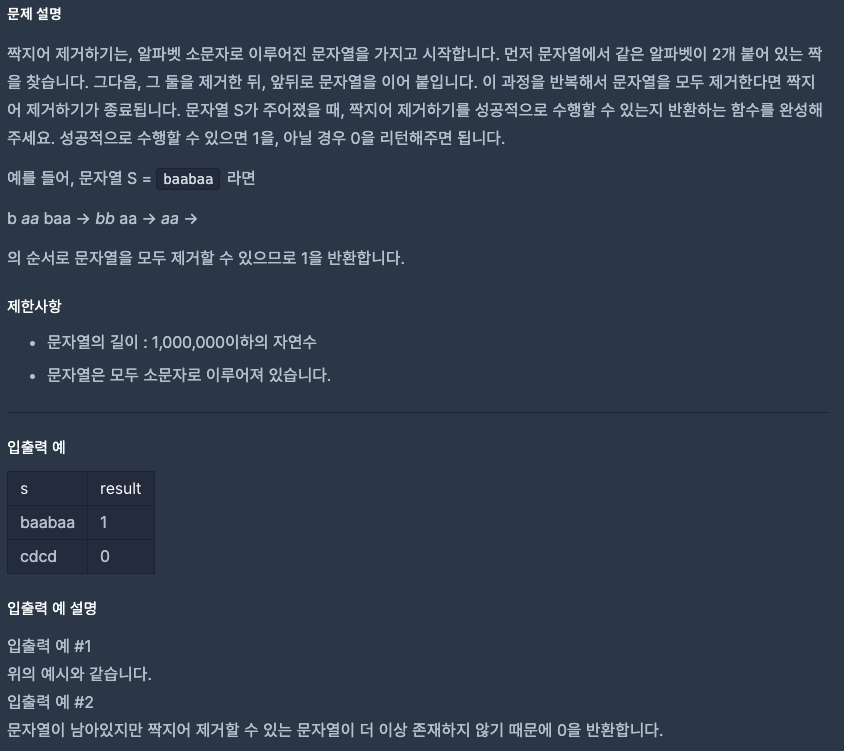
짝지어 제거하기
1. Problem
2. My Solution
- 짝을 괄호라고 생각하고 괄호 문제 해결처럼 스택 자료구조를 이용함
def solution(s):
answer = 0
stack = []
for alphabet in s:
if not stack:
stack.append(alphabet)
elif stack[-1] == alphabet:
stack.pop()
else:
stack.append(alphabet)
return 0 if stack else 1
3. Learned
- 특정 원소를 순서에 맞게 제거 해야한다면 스택을 생각해보자
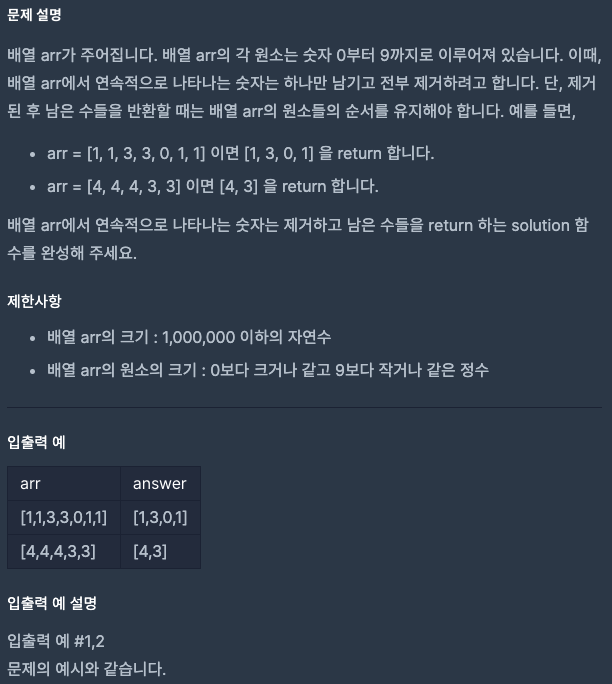
같은 숫자는 싫어
1. Problem
2. My Solution
- 바로 직전에 등장하는 원소를 pre_num 으로 계속 가지고있음
def solution(arr):
answer = [arr[0]]
pre_num = arr[0]
for num in arr[1:]:
if num != pre_num:
answer.append(num)
pre_num = num
return answer
3. Others' Solution
- arr[-1:]를 이용하면 자료형이 null([]) 이여도 에러를 발생시키지 않고 맨 뒤에 있는 원소에 접근
answer[-1:]의 반환값은 리스트이기 때문에 비교할 num 또한 리스트로 변환해야함
def solution(arr):
answer = []
for num in arr:
if [num] != answer[-1:]:
answer.append(num)
return answer
4. Learned
- 만약 문제가 순서를 유지하면서 중복을 제거하는 문제였다면 OrderedDict 자료형 (순서를 유지한 Dict) 이용하면됨
from collections import OrderedDict
list(OrderedDict.fromkeys(arr))더 맵게
1. Problem
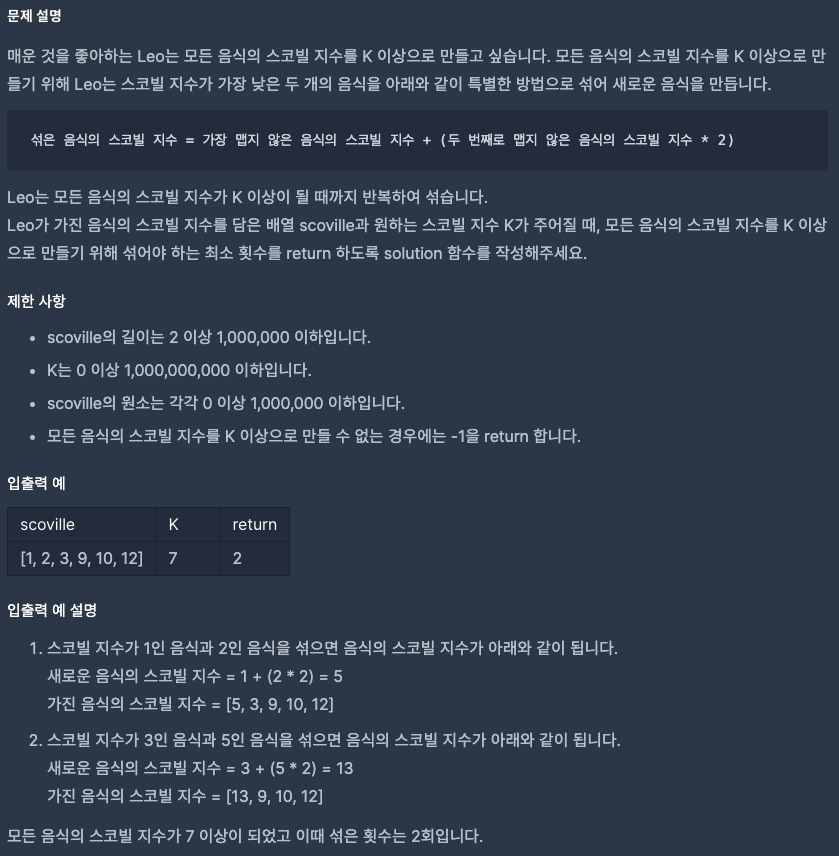
2. My Solution
- 문제 해결 원리
1. 정렬
2. 제일 작은 것이 K 보다 크면 return
3. 가장 작은 것과 2번 쨰로 작은 것을 pop()하여 섞은 다음 push()
4. 1~3 반복
5. 더 이상 섞을 게 없어 1개만 남을 때, 해당 음식의 scoville 이 K 보다 작으면 return -1- 입력 n 의 크기는 1,000,000 이기 때문에
1,3과정에서 시간초과가 발생할 가능성이 높음. deque은 sort 기능이 없기 때문에 heapq 모듈을 사용하여 최소힙(우선순위 큐)로 문제를 해결
3. Learned