onSheet()란?
선언 하기
특정 조건을 만족하면 뷰를 모달 형식으로 띄워주는 코드입니다. 그 특정 조건은 바인딩으로 연결한 Bool 변수가 true가 될 때입니다. 보통 아래의 코드처럼 초기값이 false인 @State 변수를 선언해두고 버튼 등을 활용해서 해당 변수를 true로 바꿔줍니다.
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
//1️⃣ @State로 Bool값을 선언
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false
var body: some View {
Button {
shouldShowModal = true //2️⃣ 버튼을 누르면 true가 되도록
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
}
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal) {
ModalView()
}
//3️⃣ sheet안에 binding으로 전달하고 띄울 View를 정의한다.
}
}.sheet()를 어디에 붙여야 할까?
✅ 꼭 버튼에 붙일 필요는 없고 버튼을 포함한 상위 View에 붙여도 됩니다. (많이 하는 방법)
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false
var body: some View {
VStack { //👉 Button을 감싸는 VStack
Button {
shouldShowModal = true
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
}
EmptyView()
}
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal) {
ModalView()
}
}
}🤷♂️ 약간 이상한 코드이기는 합니다만 심지어 버튼 내부에 붙여도 되긴 됩니다.
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
shouldShowModal = true
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal) {
ModalView()
}
}
EmptyView()
}
}
}🚫 하지만 병렬로 연결된 독립적인 View에 붙이면 작동이 안됩니다.
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
shouldShowModal = true
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
}
EmptyView()
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal) {
ModalView()
}
}
}
}그렇다면 Binding으로 Modal에 shouldShowModal을 전달하면 Modal을 dismiss할 수 있을까요?
🙆♂️ 결론은 가능합니다!

import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
shouldShowModal = true
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
}
}
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal) {
ModalView(shouldShowModal: $shouldShowModal) //👉 binding 변수를 전달
}
}
}
struct ModalView: View {
@Binding var shouldShowModal: Bool
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
shouldShowModal = false //👉 binding 변수를 false로
} label: {
Text("Close Modal")
}
}
}
}👍 하지만 더 많이 사용하는 방법은 아래와 같습니다.
위 처럼 binding 변수로 전달해도 되지만 단지 뷰를 dismiss하기 위해서만 사용하는 변수를 굳이 하위 뷰에 전달할 필요는 없습니다. 하위 뷰가 스스로 할 수 있는 것을 굳이 상위 뷰에 의존할 필요는 없죠. 아래처럼 presentationMode를 활용하는 방법이 더 좋습니다.
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
shouldShowModal = true
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
}
}
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal) {
ModalView()
}
}
}
struct ModalView: View {
@Environment(\.presentationMode) var mode
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
mode.wrappedValue.dismiss()
} label: {
Text("Close Modal")
}
}
}
}🔬didSet과 willSet으로 실험 해보기
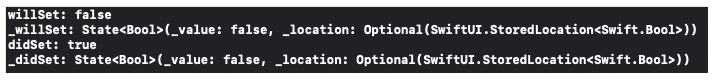
아래 콘솔에 출력된 내용은 모달을 띄울 때와 dismiss하는 동작을 마치고 나서 출력된 내용입니다. 즉 모달을 띄울 때는 true가 되기는 하지만 _를 붙여서 내부 값을 찍어보면 항상 false를 유지하고 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
또한 모달을 dismiss 한다고 해서 false로 변하는 것도 아니라는 것도 볼 수 있습니다.
즉 내부적으로는 항상 초기값를 유지하고 있다가 true가 되는 코드를 만날때만 모달을 띄워주는 역할을 하는 코드입니다.
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false {
didSet {
print("didSet: \(shouldShowModal)")
print("_didSet: \(_shouldShowModal)")
}
willSet {
print("willSet: \(shouldShowModal)")
print("_willSet: \(_shouldShowModal)")
}
}
그런 만약 초기값이 true라면?
예상한 대로 앱을 실행하자마자 모달이 뜨는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = true
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
shouldShowModal = true
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
}
}
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal) {
ModalView()
}
}
}
onDismiss로 모달이 dismiss될 때 수행할 동작 정의하기
.sheet()에는 하나의 인자를 더 추가할 수 있는데요. 바로 onDismiss입니다. 여기에 sheet로 띄운 모달이 dismiss될 때 수행할 동작을 정의할 수 있습니다. 전달하는 타입은 () → Void입니다.
struct ContentView: View {
@State var shouldShowModal: Bool = false
@State var count = 0 //👉 변수를 하나 선언
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button {
shouldShowModal = true
} label: {
Text("Show Modal")
}
Text("Modal Dismiss count: \(count)") //👉 해당 변수를 보여주는 Text
}
.sheet(isPresented: $shouldShowModal, onDismiss: { count += 1 }) {
ModalView()
}
//👉 modal이 dismiss될 때마다 count를 1씩 늘려줌.
}
}
