지난 시간 복습
CarRace
package com.tech.gt006.race;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
class RaceThreadx extends Thread{
RaceFrame frame;
int x,y,w,h;
public RaceThreadx(RaceFrame frame, int x, int y, int w, int h) {
this.frame=frame;
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.w=w;
this.h=h;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("쓰레드 동작");
Random r=new Random();
Dimension d=frame.getSize();
int widthLast=(int)(d.getWidth()-(2*x))+30;
for (; x < widthLast; x+=20) {
frame.repaint();
try {
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(1000)+30); // 슬립 시간이 각각 다름
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
frame.repaint();
}
}
class RaceFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
RaceThreadx thread1;
RaceThreadx thread2;
RaceThreadx thread3;
RaceThreadx thread4;
RaceThreadx thread5;
// 버튼준비
JButton startButton=new JButton("시작");
JButton clearButton=new JButton("초기화");
Dimension d;
int i[]= {0,0,0,0,0}; // 등수 매기는 용도
boolean re1=true,re2=true,re3=true,re4=true,re5=true;
private Image img,img1,img2,img3,img4;
public RaceFrame() {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// 버튼에 수신자 부착
startButton.addActionListener(this);
clearButton.addActionListener(this);
JPanel p=new JPanel();
p.add(startButton);
p.add(clearButton);
add(p,"North");
// 쓰레드 객체 생성
thread1=new RaceThreadx(this,50,150,38,36);
thread2=new RaceThreadx(this,50,200,38,36);
thread3=new RaceThreadx(this,50,250,38,36);
thread4=new RaceThreadx(this,50,300,38,36);
thread5=new RaceThreadx(this,50,350,38,36);
img=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getImage("2car.png");
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics g) {
super.paint(g);
System.out.println("painting");
// 등수 판정
for (int k = 0; k < i.length; ++k) {
if (thread1.x >= 750 && i[k] == 0 && re1) {
i[k] = 1;
re1 = false;
} else if (thread2.x >= 750 && i[k] == 0 && re2) {
i[k] = 2;
re2 = false;
} else if (thread3.x >= 750 && i[k] == 0 && re3) {
i[k] = 3;
re3 = false;
} else if (thread4.x >= 750 && i[k] == 0 && re4) {
i[k] = 4;
re4 = false;
} else if (thread5.x >= 750 && i[k] == 0 && re5) {
i[k] = 5;
re5 = false;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(i));
// 등수 출력
if (i[0] > 0) g.drawString("1등: " + i[0] + "번자동차", 260, 350);
if (i[1] > 0) g.drawString("2등: " + i[1] + "번자동차", 260, 370);
if (i[2] > 0) g.drawString("3등: " + i[2] + "번자동차", 260, 390);
if (i[3] > 0) g.drawString("4등: " + i[3] + "번자동차", 260, 410);
if (i[4] > 0) g.drawString("5등: " + i[4] + "번자동차", 260, 430);
g.drawLine(750, 0, 750, 400); // finish line
g.drawImage(img, thread1.x, thread1.y, thread1.w, thread1.h, this);
g.drawImage(img, thread2.x, thread2.y, thread2.w, thread2.h, this);
g.drawImage(img, thread3.x, thread3.y, thread3.w, thread3.h, this);
g.drawImage(img, thread4.x, thread4.y, thread4.w, thread4.h, this);
g.drawImage(img, thread5.x, thread5.y, thread5.w, thread5.h, this);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(e.getSource()==startButton) {
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread4.start();
thread5.start();
}else if(e.getSource()==clearButton) {
thread1=new RaceThreadx(this,50,150,38,36);
thread2=new RaceThreadx(this,50,200,38,36);
thread3=new RaceThreadx(this,50,250,38,36);
thread4=new RaceThreadx(this,50,300,38,36);
thread5=new RaceThreadx(this,50,350,38,36);
for (int k = 0; k < i.length; k++) {
i[k]=0;
}
re1=true;
re2=true;
re3=true;
re4=true;
re5=true;
repaint();
}
}
}
public class CarRace {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RaceFrame frame=new RaceFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(850,500);
frame.setLocation(300,100);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}결과
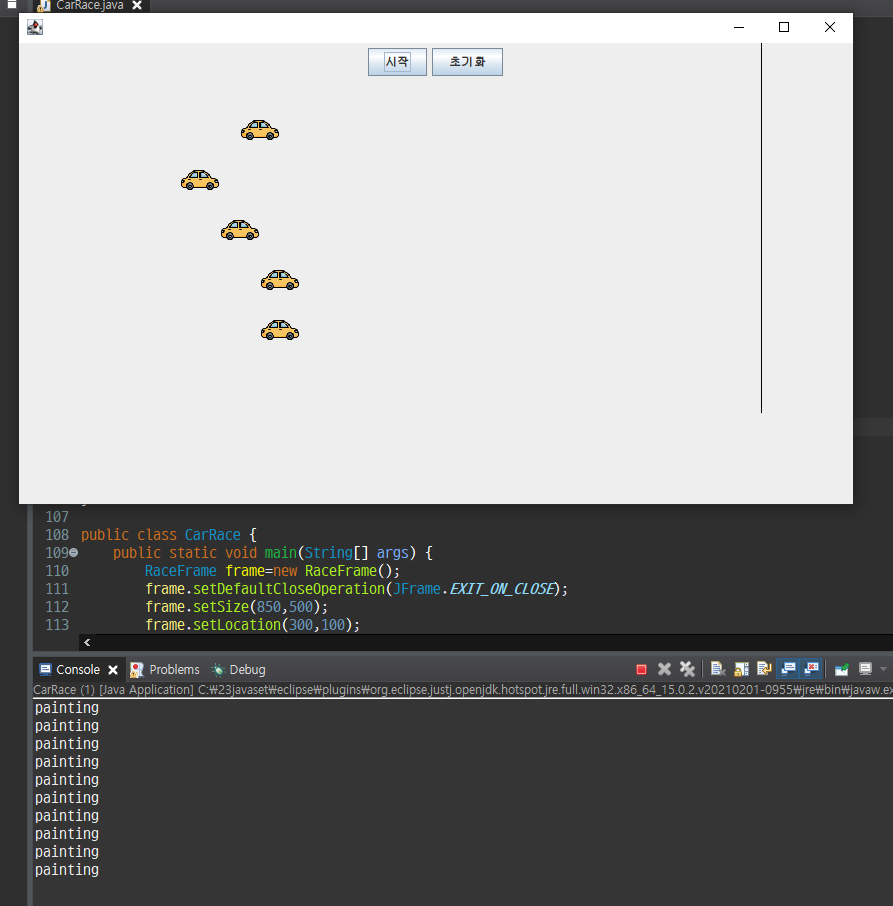
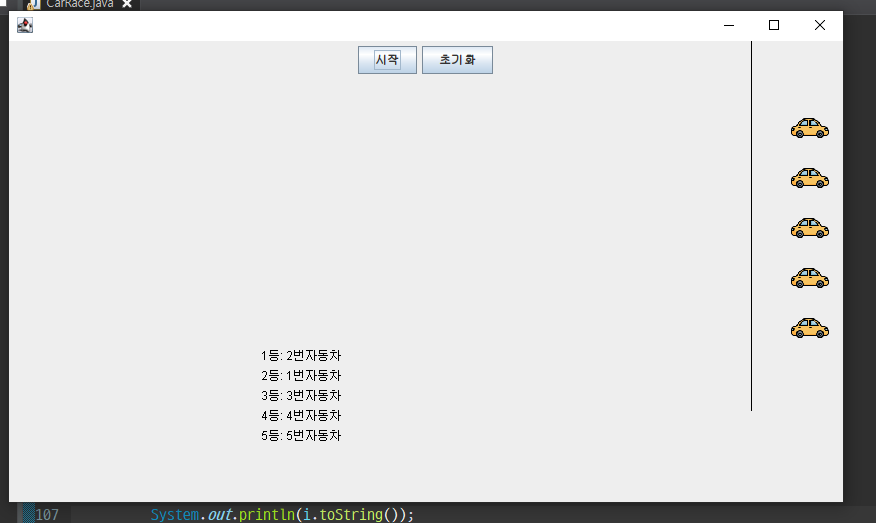
현재는 Thread를 stop시키는 명령 없이 초기화를 시킨 것이기 때문에
아직 초기화 버튼의 역할은 차 이미지를 처음 위치로 옮기는 것만 하고, thread를 멈추는 역할은 아니다.
제네릭 (Generic)
Generic(제네릭) 이란 결정되지 않은 타입을 파라미터로 처리하고 실제 사용할 때 파라미터를 구체적인 타입으로 대체시키는 기능
public class Box <T> {
public T content;
}\ 는 T가 타입 파라미터임을 뜻하는 기호, 타입이 필요한 자리에 T를 사용할 수 있음을 알려주는 역할을 함.
만약 T를 String 으로 대체하고 싶다면
Box<String> box = new Box<String>();
box.content = "안녕하세요";
String content = box.content;여기서 꼭 T 를 쓰는게 아니라 A~Z 까지 아무거나 써도 된다.
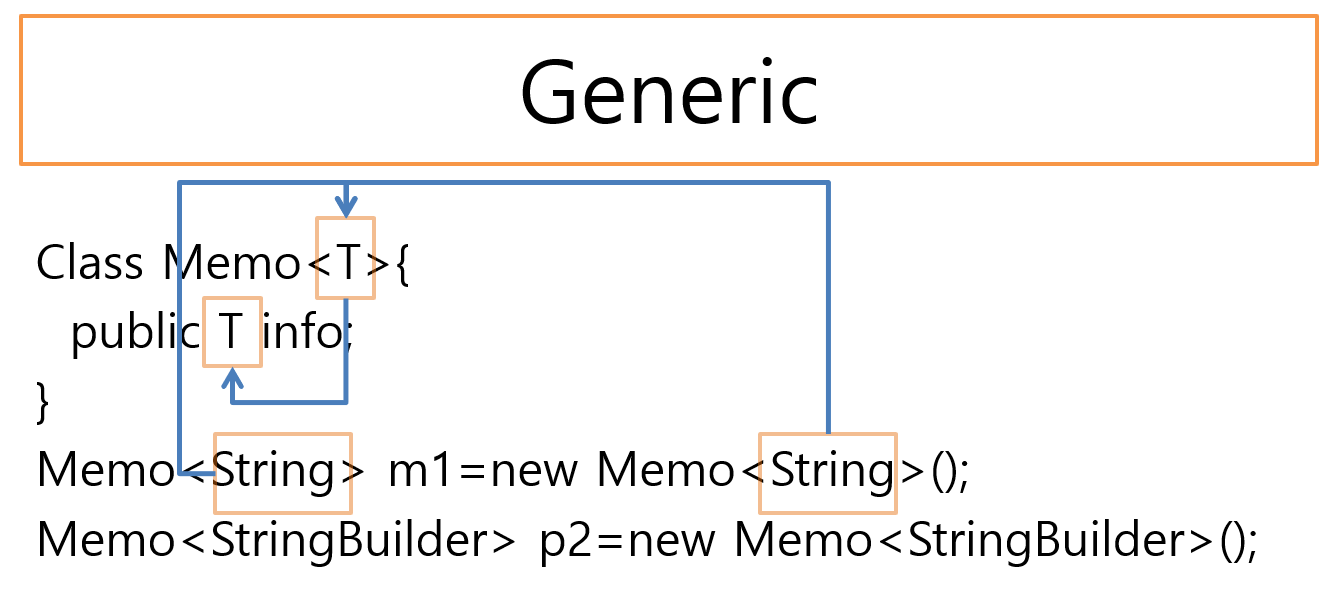
즉, 1 개의 class를 타입을 지정하지 않고 정의한 후, 차후에 1개 가지고 여러 타입을 지정해서 쓸 수 있으므로 효율적이다.
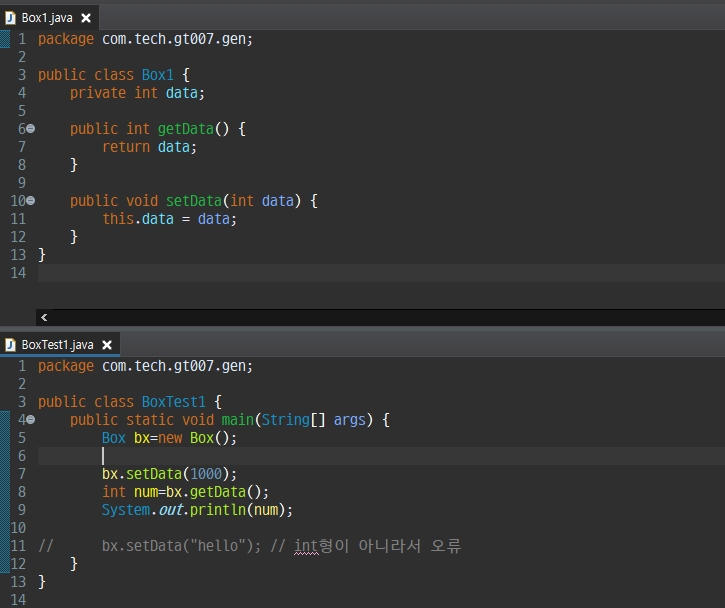
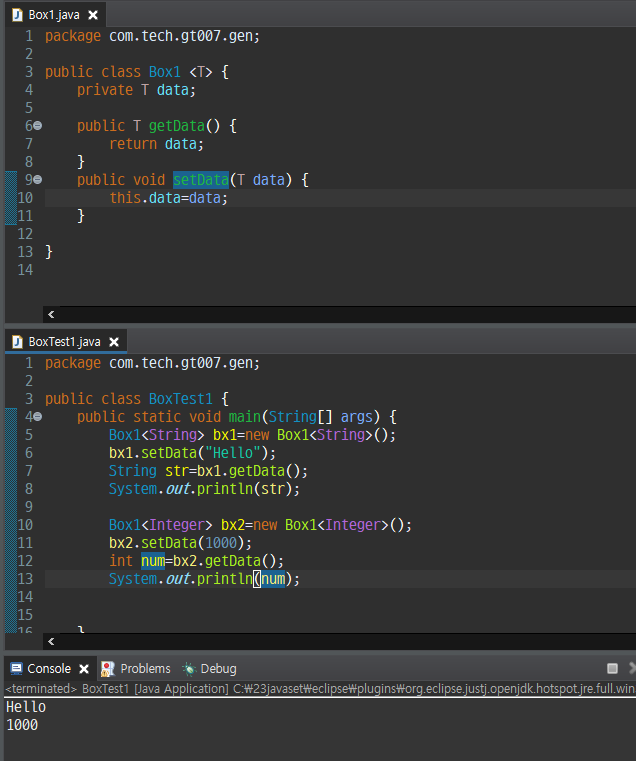
제네릭 활용
문자에 주로 사용되는 의미
T : type
E : element
K : key
V : value
N : number
package com.tech.gt007.gen;
import java.util.Arrays;
class GenericMethod{
public static <T> T getLast(T[] a) {
return a[a.length-1];
}
}
public class GenericMethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] language=new String[3];
language[0]="C#";
language[1]="C++";
language[2]="JAVA";
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(language));
String last=GenericMethod.getLast(language);
System.out.println(last);
Integer[] nums=new Integer[3];
nums[0]=100;
nums[1]=200;
nums[2]=300;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
Integer lastnum=GenericMethod.getLast(nums);
System.out.println(lastnum);
}
}결과
[C#, C++, JAVA]
JAVA
[100, 200, 300]
300package com.tech.gt007.gen;
import java.util.Arrays;
class GenSwapMethod{
public static <T> void swap(T[] a,int i,int j) {
T tmp=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=tmp;
}
}
public class GenSwapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] fruits= {"apple","banana","orange"};
GenSwapMethod.swap(fruits, 0, 2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(fruits));
}
}결과
[orange, banana, apple]package com.tech.gt007.gen;
class OrderVal<K,V>{
private K key;
private V value;
public OrderVal(K key,V value) {
this.key=key;
this.value=value;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
}
public class OrderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OrderVal<String,Integer> pi=new OrderVal("mykey",10000);
System.out.println(pi.getKey()+","+pi.getValue());
OrderVal<String,String> ps=new OrderVal("mykey","50000");
System.out.println(ps.getKey()+","+ps.getValue());
}
}결과
mykey,10000
mykey,50000와일드카드 타입 파라미터
제네릭 타입을 매개값이나 리턴 타입으로 사용할 때 타입 파라미터로 ?(와일드카드) 를 사용할 수 있다. ? 는 범위에 있는 모든 타입으로 대체할 수 있다는 표시.
제한된 타입 파라미터
경우에 따라서는 타입 파라미터를 대체하는 구체적인 타입을 제한할 필요가 있다.
ex) 상한이 있는 / 하한이 있는 경우
package com.tech.gt007.gen;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
// 상한이 있는 제너릭
public class GenericTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// List<Object> li=Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5);
List<Integer> li=Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5);
// List<Double> li=Arrays.asList(1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5);
System.out.println("sum : "+sumOfList(li));
}
private static double sumOfList(List<? extends Number> list) {
double s=0.0;
for (Object n : list) {
s+=Double.parseDouble(n.toString());
}
return s;
}
}결과
sum : 15.0상한을 Number 로 정해버린 제네릭