Target Marketing: Select and Enter a Market
• In our modern, complex society, it is a mistake to assume everyone’s needs are the same. // 현대적이고 복잡한 사회에서 모든 사람의 요구가 동일하다고 가정하는 것은 실수임.
• Market fragmentation occurs when diverse interests and backgrounds of individuals create greater diversity in needs and wants. // 시장 세분화는 개인의 다양한 관심사와 배경이 욕구와 욕구의 다양성을 더 크게 만들 때 발생
-Technological and cultural advances have fueled growing fragmentation of markets. / /기술적, 문화적 발전으로 시장의 분열이 증가
-Consider the choice you made as a consumer of higher education …
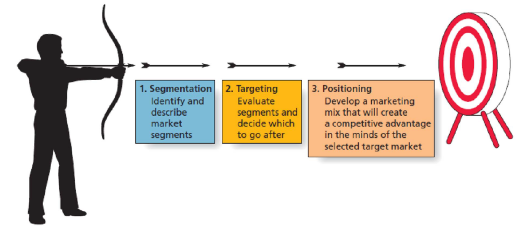
Step 1: Segmentation
• Segmentation is the process of dividing a larger market into smaller pieces based on meaningful, shared characteristics. //세분화는 의미 있고 공유 된 특성에 따라 큰 시장을 작은 조각으로 나누는 과정
-Useful in both consumer and B2B contexts // 소비자 및 B2B 컨텍스트 모두에게 유용
-Many different dimensions, or segmentation variables, that marketers can utilize // 마케터가 활용할 수있는 다양한 차원 또는 세분화 변수
Segmenting Consumer Markets
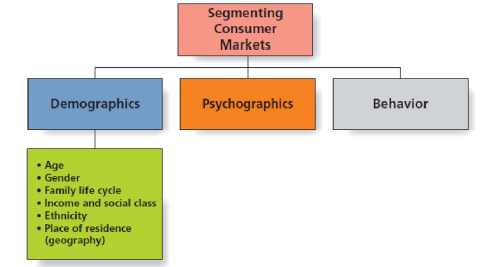
Segmenting by Demographics: Age and Generational Marketing // 인구 통계별 세분화 : 연령 및 세대 별 마케팅
• Children
• Teens and Tweens
• Generation Z
-Born after 1994
• Generation Y (=“Millennials” or the “Baby Boomlet”)
-aka Millennials or Echo Boomers
-Born between 1979 and 1994
• Generation X (born between 1965 and 1978)
-Has entrepreneurial reputation, views home as an expression of individuality //기업가 적 명성을 가지고 있으며 가정을 개성의 표현으로 간주
• Baby-boomers (born between 1946 and 1964)
-Key segment due to their size and earnings, willing to invest money, time, and energy to maintain youthful image //규모와 수입으로 인한 핵심 부문, 젊은 이미지를 유지하기 위해 돈, 시간 및 에너지를 기꺼이 투자
• Mature consumers
-Focus on lifestyle factors, such as mobility //mobility 같은 라이프 스타일 요소에 집중
Segmenting by Demographics: Gender
• Many products appeal to one sex or the other
-Metrosexual: A straight, urban male who is keenly interested in fashion, home design, gourmet cooking, and personal care. // 메트로 섹슈얼 : 패션, 홈 디자인, 미식 요리 및 개인 관리에 관심이있는 이성애자 도시 남성.
Segmenting by Demographics: Family Life Cycle
• Family needs and expenditures change over time. //가족의 필요와 지출은 시간이 지남에 따라 변화
-As families move through stages, different product categories ascend or descend in importance. // 가족이 단계별로 이동함에 따라 다양한 제품 범주의 중요성이 높아지거나 낮아짐
-Even if importance is constant, needs within category may change (e.g., furniture). // 중요도가 일정하더라도 카테고리 내 욕구 (예 : 가구)는 변경 될 수 있음
Segmenting by Demographics: Income and Social Class
• Income (소득)
-Strongly connected to buying power
• Social Class (사회적 계층)
-Upper class, middle class and lower class
-Many consumers buy according to an image they’d like to portray, not their actual level. // 많은 소비자가 실제 수준이 아닌 묘사하고 싶은 이미지에 따라 구매
-For instance, “easy credit” may lead consumers to buy cars and homes they can’t truly afford. // 예를 들어, "쉬운 신용"은 소비자가 진정으로 감당할 수없는 자동차와 주택을 구매하도록 유도함.
Segmenting by Demographics: Ethnicity
• U.S. ethnic and cultural diversity is increasing. //미국의 인종 및 문화적 다양성이 증가중
-African Americans, Hispanic Americans and Asian Americans are
largest groups and growing.
-Content marketing establishes thought leadership with specific groups. // 콘텐츠 마케팅은 특정 그룹과의 사고 리더십을 확립
-Managers practice cultural diversity. // 관리자는 문화적 다양성을 실천
Segmenting by Demographics: Place of Residence
• Geodemography 지리학
-Combines demographics with geography //인구 통계 + 지리
-PRIZM provides detailed segment profiles by zip code based on geodemography and lifestyle. // PRIZM은 지리 및 라이프 스타일에 따라 우편 번호별로 상세한 세그먼트 프로필을 제공
• Geotargeting 지역 타겟팅
-Geographically customized web advertising that feeds local ads to users. // 사용자에게 지역 광고를 제공하는 맞춤형 웹 광고
-Underscores much paid search advertising on Google and other search engines. // Google 및 기타 검색 엔진에서 많은 유료 검색 광고를 강조
Segmenting by Psychographics
• Uses psychological, sociological, and anthropological factors to categorize customers. // 심리적, 사회 학적, 인류 학적 요인을 사용하여 고객을 분류
-Shared “AIOs”
-Best known system is VALS
-Psychographics: The use of psychological, sociological, and anthropological factors to construct market segments // 시장 세그먼트를 구성하기 위한 심리적, 사회 학적, 인류학적 요인들 사용
Segmenting by Behavior
• Categorizes consumers based upon how they act toward, feel about, or use a product // 제품에 대한 행동, 느낌 또는 사용 방식에 따라 소비자를 분류
-User status
-80/20 rule
-Long tail concept
-Usage occasions
Segmenting B2B Markets
• Segmentation also useful for B2B firms!
-Helps B2B companies understand needs and characteristics of potential customers // B2B 기업이 잠재 고객의 요구 사항과 특성을 이해하도록 지원
• Firms can be categorized based on: // 기업은 다음을 기준으로 분류
-Organizational demographics // 조직의 인구 통계
-Production technologies used // 사용 된 생산 기술
-User status // 유저 현황
Segmentation, Not Stereotyping
• The idea of segmenting is to identify groups of customers with similar needs. // 세분화의 아이디어는 유사한 요구를 가진 고객 그룹을 식별하는 것
-Allows marketing to be more efficient and more effective // 마케팅이 더 효율적이고 효과적일 수 있음.
• There are many ways by which marketers may segment consumer and business markets. //마케터가 소비자 및 비즈니스 시장을 세분화하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있음
Step 2: Targeting
• The next step is targeting, in which marketers evaluate each potential segment and decide upon which groups of customers they will invest marketing resources. // 타겟팅 = 마케팅 담당자가 각 잠재 세그먼트를 평가하고 마케팅 리소스에 투자 할 고객 그룹을 결정
-Selected groups are known as target markets // 선택된 그룹은 목표 시장으로 알려져있음
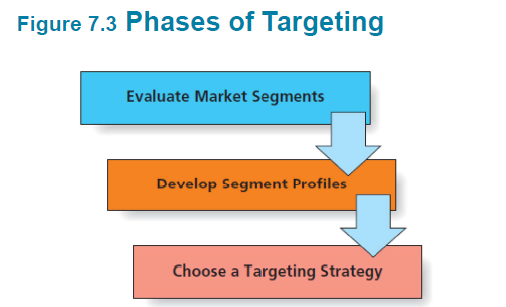
Phase 1: Evaluation of Market Segments // 시장 세그먼트 평가
• A viable market segment should: 실행 가능한 시장 부문?
-have members with similar wants and needs that are different from those in other segments. // 다른 부문과는 다른 유사한 욕구와 욕구를 가진 회원이 있음
-be measureable in size and purchasing power. // 크기와 구매력이 측정 가능해야 함.
-be large enough to be profitable. // 수익성이 있을만큼 충분히 커야함.
-be reachable by marketing communications. // 마케팅 커뮤니케이션을 통해 도달 가능
-have needs the marketer can address.
Phase 2: Develop Segment Profiles
• After segments are identified, marketers should develop profiles or descriptions of the typical customers within a segment. // 세그먼트를 식별 한 후 마케팅 담당자는 세그먼트 내에서 일반적인 고객에 대한 프로필이나 설명을 개발해야 함.
-Segment profiles might include demographic, location, lifestyle and product-usage characteristics. // 세그먼트 프로필에는 인구 통계, 위치, 라이프 스타일 및 제품 사용 특성이 포함될 수 있음
Phase 3: Choosing a Targeting Strategy
• The final phase in targeting is to choose a target strategy to follow. A fundamental decision must be made as to whether the firm will pursue a single large segment or focus on
meeting the needs of multiple, smaller markets. // 타겟팅의 마지막 단계는 따라야 할 목표 전략을 선택하는 것입니다. 회사가 하나의 큰 세그먼트를 추구할지 아니면 집중할지에 대한 근본적인 결정을 내려야합니다.
여러 소규모 시장의 요구를 충족합니다.
Customized Targeting Strategy
• Customized marketing strategy
-Tailoring specific products to individual customers // 특정 제품을 개별 고객에게 맞춤
-Common in personal and professional services, and in industrial marketing // 개인 및 전문 서비스, 산업 마케팅에서 일반적
-Mass customization is the extreme case, which involves modifying a basic product to meet the needs and tastes of an individual consumer. // 대량 맞춤화는 개인 소비자의 요구와 취향에 맞게 기본 제품을 수정하는 극단적 경우
Ethical/Sustainable Decisions in the Real World // 현실 세계에서의 윤리적 / 지속 가능한 결정
(example)
• Candy companies have received scrutiny for advertising directly to children. 사탕 회사는 어린이에게 직접 광고하는 것에 대한 조사를 받음
• A large number of candy companies have announced that they will no longer advertise directly to children.// 많은 사탕 회사에서 더 이상 어린이에게 직접 광고하지 않겠다고 발표
-Should candy companies be allowed to advertise directly to children?
Step 3: Positioning
- Positioning is the process by which marketers develop a marketing strategy to influence how a particular market segment perceives a good or service in comparison to the competition. // 포지셔닝은 마케팅 담당자가 특정 시장 부문이 경쟁과 비교하여 상품 또는 서비스를 인식하는 방식에 영향을 미치는 마케팅 전략을 개발하는 프로세스
Positioning Statement
• An expression of a product’s positioning that is internally developed and maintained in order to support the development of marketing communication that articulates the specific value offered by a product
// 제품이 제공하는 특정 가치를 명확하게 표현하는 마케팅 커뮤니케이션 개발을 지원하기 위해 내부적으로 개발 및 유지되는 제품의 포지셔닝 표현
Modifying Positioning Strategies
• Repositioning establishes a new position in response to market changes. // 리포지셔닝은 시장 변화에 대응하여 새로운 위치를 설정
-Commonly used to change the brand image // 일반적으로 브랜드 이미지 변경에 사용
-Repositioning can breathe life into “retro” brands. // 리포지셔닝은 "레트로"브랜드에 생명을 불어 넣을 수 있음.
Bringing a Product to Life: Brand Personality
• Positioning strategies often try to create a brand personality. // 포지셔닝 전략은 종종 브랜드 개성을 만들려고함.
-A distinctive image that captures a brand’s character and benefits. // 브랜드의 특성과 혜택을 포착하는 독특한 이미지.
• Brand anthropomorphism // 브랜드 의인화
-Assigning human characteristics and qualities to a brand // 인간의 특성과 자질을 브랜드에 부여
-Pillsbury Doughboy is an example
Perceptual Map (지각도)
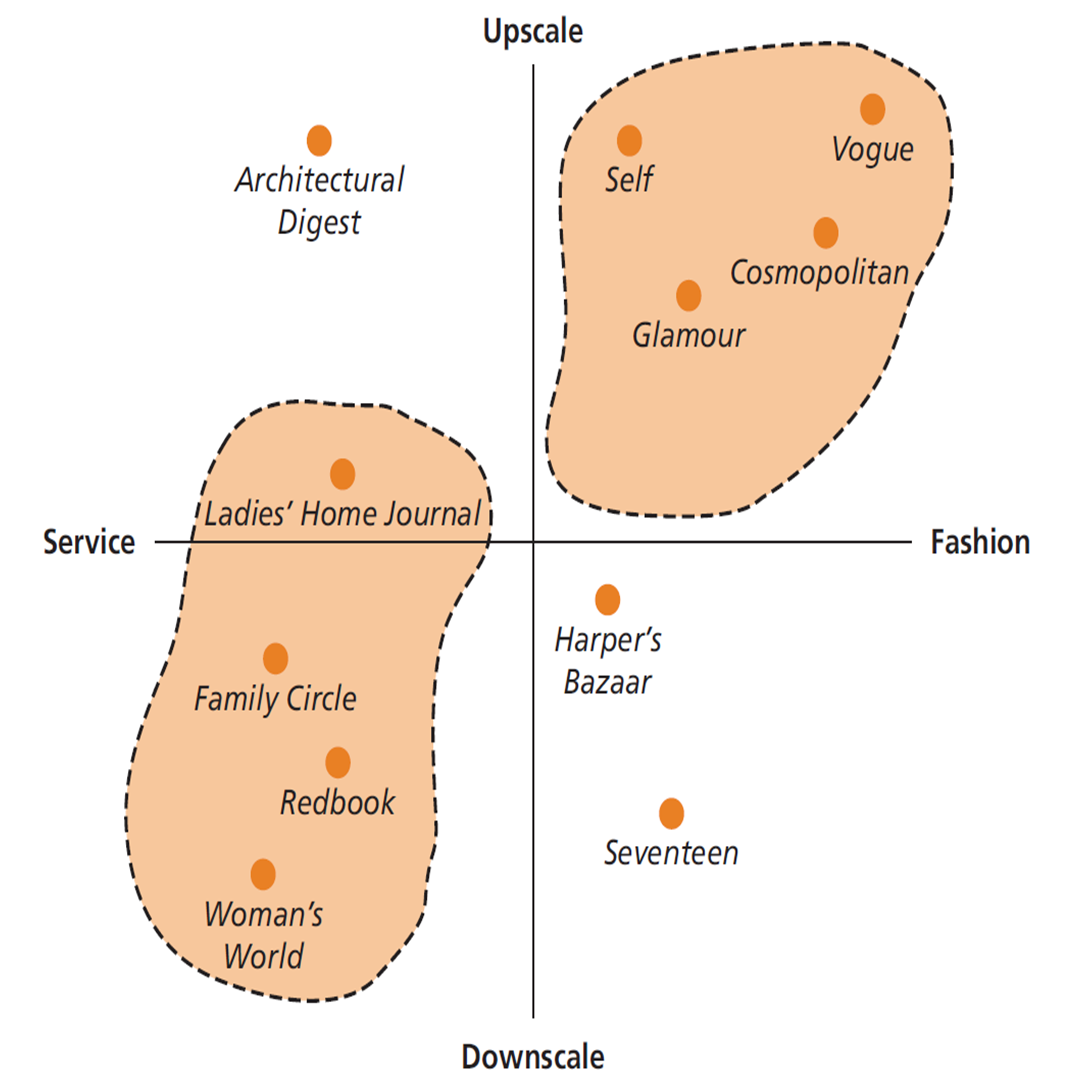
- NOTES:
• Recall that one way of positioning a brand is by means of creating a superior brand image. This implies that part of the marketer’s job is to create a brand personality that consumers will prefer over competing products // 브랜드를 포지셔닝하는 한 가지 방법은 우수한 브랜드 이미지를 만드는 것임을 상기하십시오. 이는 마케팅 담당자의 업무 중 일부가 소비자가 경쟁 제품보다 선호 할 브랜드 개성을 창출하는 것임을 의미합니다
Positioned for Success
- Successful brand positioning should align clearly with the company’s competitive advantage(s). // 성공적인 브랜드 포지셔닝은 회사의 경쟁 우위와 명확하게 일치해야함
-In turn, marketing mix elements should support a distinctive brand image and value proposition for the target market. // 마케팅 믹스 요소는 타겟 시장에 대한 고유한 브랜드 이미지와 가치 제안을 지원해야함
