File Systems
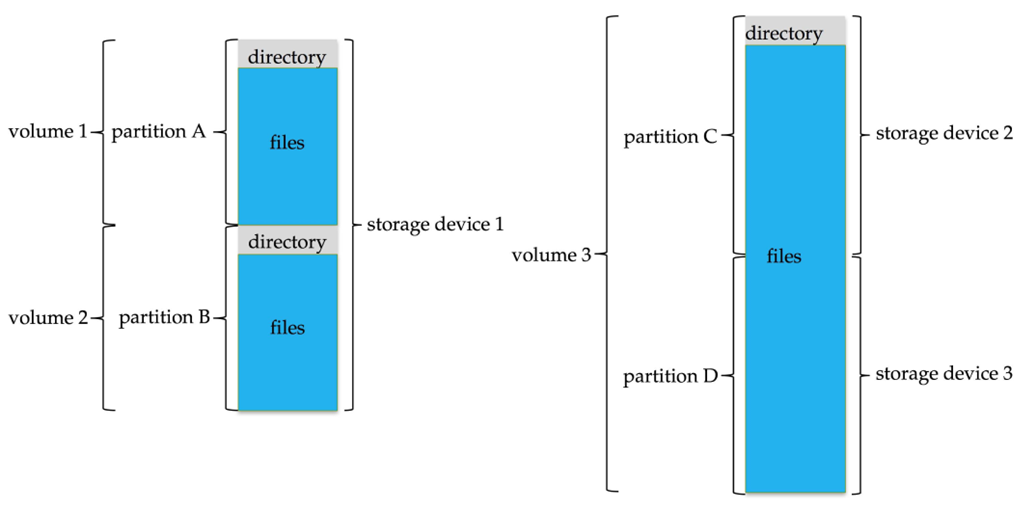
- General-purpose computers can have multiple storage devices
- Devices can be sliced into partitions, which hold volumes
- Volumes can span multiple partitions
- Each volume usually formatted into a file system
- (#) of file systems varies, typically dozens available to choose from
Typical storage device organization:
- 범용 시스템에 여러 개의 저장 장치가 있을 수 있다.
- 장치를 볼륨을 저장하는 파티션으로 분할할 수 있다.
- 볼륨이 여러 파티션에 걸쳐 있을 수 있다.
- 각 볼륨은 일반적으로 파일 시스템으로 포맷된다.
- 파일 시스템의 수는 다양하며, 일반적으로 수십 개의 파일 시스템 중에서 선택할 수 있다.
일반적인 스토리지 장치 구성:
File-System Mounting
Example Mount Points and File Systems - Solaris

Partitions and Mounting
- Partition can be a volume containing a file system (“cooked”) or raw – just a sequence of blocks with no file system
- Boot block can point to boot volume or boot loader set of blocks that contain enough code to know how to load the kernel from the file system
- Or a boot management program for multi-os booting
- Root partition contains the OS, other partitions can hold other Oses, other file systems, or be raw
- Mounted at boot time
- Other partitions can mount automatically or manually on mount points - location at which they can be accessed
- At mount time, file system consistency checked
- Is all metadata correct?
- If not, fix it, try again
- If yes, add to mount table, allow access
- Is all metadata correct?
- 파티션은 파일 시스템("조리된") 또는 원시 블록을 포함하는 볼륨일 수 있다. 파일 시스템이 없는 일련의 블록일 뿐이다.
- 부트 블록은 파일 시스템에서 커널을 로드하는 방법을 알기에 충분한 코드를 포함하는 부트 볼륨 또는 부트 로더 블록 집합을 가리킬 수 있다.
- 또는 다중 OS 부팅을 위한 부팅 관리 프로그램
- 루트 파티션에 OS가 포함되어 있으며, 다른 파티션은 다른 Oes, 다른 파일 시스템을 보유하거나 원시 파티션일 수 있다.
- 부팅 시 마운트됨
- 다른 파티션은 마운트 지점에 자동 또는 수동으로 마운트할 수 있다. 이 지점에서 액세스할 수 있다.
- 마운트 시 파일 시스템 일관성 확인
- 모든 메타데이터가 올바른가?
- 그렇지 않으면 수정하고 다시 시도하십시오.
- "예"인 경우 마운트 테이블에 추가하고 액세스
- 모든 메타데이터가 올바른가?
File Systems and Mounting
(a) Unix-like file system directory tree
(b) Unmounted file system
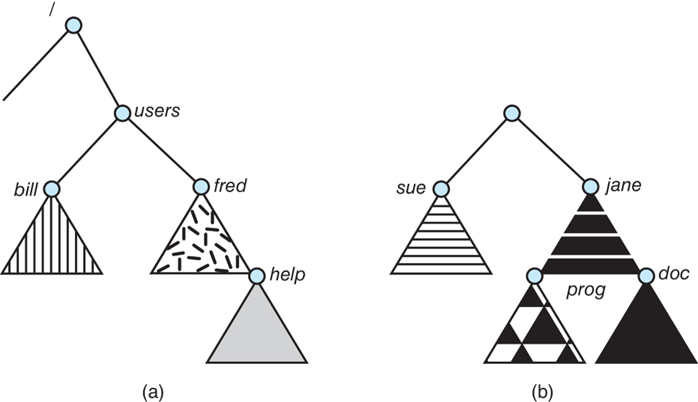
After mounting (b) into the existing directory tree
File Sharing
- Allows multiple users / systems access to the same files
- Permissions / protection must be implement and accurate
- Most systems provide concepts of owner, group member
- Must have a way to apply these between systems
- 여러 사용자/시스템이 동일한 파일에 액세스할 수 있도록 허용
- 사용 권한/보호가 구현되고 정확해야 함
- 대부분의 시스템은 소유자, 그룹 구성원의 개념을 제공한다.
- 시스템 간에 이를 적용할 수 있는 방법이 있어야 한다.
Virtual File Systems
- Virtual File Systems (VFS) on Unix provide an object-oriented way of implementing file systems
- VFS allows the same system call interface (the API) to be used for different types of file systems
- Separates file-system generic operations from implementation details
- Implementation can be one of many file systems types, or network file system
- Implements vnodes which hold inodes or network file details
- Then dispatches operation to appropriate file system implementation routines
- 유닉스의 VFS(Virtual File Systems)는 파일 시스템을 구현하는 객체 지향 방식을 제공한다.
- VFS를 사용하면 동일한 시스템 호출 인터페이스(API)를 다른 유형의 파일 시스템에 사용할 수 있다.
- 파일 시스템 일반 작업과 구현 세부 정보를 구분한다.
- 구현은 다양한 파일 시스템 유형 또는 네트워크 파일 시스템 중 하나일 수 있다.
- inode 또는 네트워크 파일 세부 정보를 포함하는 vnode 구현한다.
- 그런 다음 적절한 파일 시스템 구현 루틴에 작업을 디스패치한다.
- The API is to the VFS interface, rather than any spcific type of file system
- API는 특정 유형의 파일 시스템이 아닌 VFS 인터페이스에 적용됩니다.
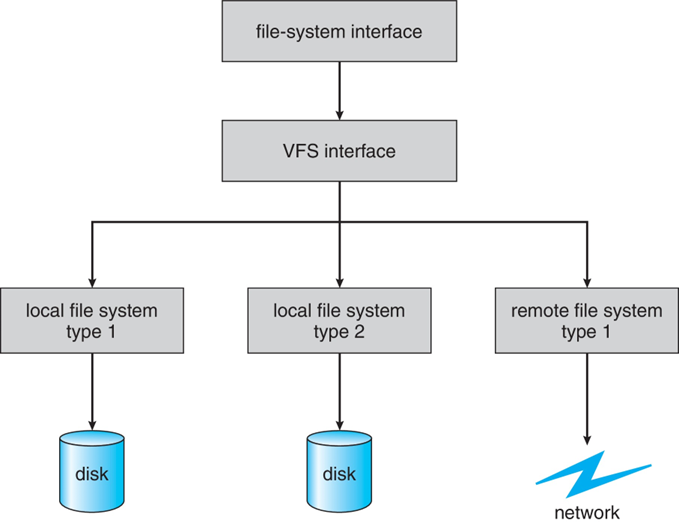
Virtual File System Implementation
- For example, Linux has four object types:
- inode, file, superblock, dentry
- VFS defines set of operations on the objects that must be implemented
- Every object has a pointer to a function table
- Function table has addresses of routines to implement that function on that object
- For example:
- • int open(. . .)—Open a file
- • int close(. . .)—Close an already-open file
- • ssize t read(. . .)—Read from a file
- • ssize t write(. . .)—Write to a file
- • int mmap(. . .)—Memory-map a file
- Every object has a pointer to a function table
- 예를 들어 리눅스에는 네 가지 개체 유형이 있다.
- inode, file, superblock, dentry
- VFS는 구현해야 하는 개체에 대한 작업 집합을 정의한다.
- 모든 개체에는 함수 테이블에 대한 포인터가 있다.
- 함수 테이블에는 해당 개체에 해당 함수를 구현하기 위한 루틴의 주소가 있다.
- 예:
- • int open(...)—파일 열기
- • int close(...)—이미 열려 있는 파일 닫기
- • ssize tread(. . .)—파일에서 읽기
- • ssize write( . . . )—파일에 쓰기
- • int mmap(. . .)—메모리 맵 파일
- 모든 개체에는 함수 테이블에 대한 포인터가 있다.
Remote File Systems
- Sharing of files across a network
- First method involved manually sharing each file – programs like ftp
- Second method uses a distributed file system (DFS)
- Remote directories visible from local machine
- Third method – World Wide Web
- A bit of a revision to first method
- Use browser to locate file/files and download /upload
- Anonymous access doesn’t require authentication
- 네트워크를 통한 파일 공유
- 각 파일을 수동으로 공유하는 첫 번째 방법 – ftp와 같은 프로그램
- 두 번째 방법은 분산 파일 시스템(DFS)을 사용한다.
- 로컬 컴퓨터에서 볼 수 있는 원격 디렉터리
- 세 번째 방법 – World Wide Web
- 첫 번째 방법을 약간 수정함
- 브라우저를 사용하여 파일/파일 찾기 및 다운로드/업로드
- 익명 액세스에 인증이 필요하지 않음
Client-Server Model
- Sharing between a server (providing access to a file system via a network protocol) and a client (using the protocol to access the remote file system)
- Identifying each other via network ID can be spoofed, encryption can be performance expensive
- NFS an example
- User auth info on clients and servers must match (UserIDs for example)
- Remote file system mounted, file operations sent on behalf of user across network to server
- Server checks permissions, file handle returned
- Handle used for reads and writes until file closed
- 서버(네트워크 프로토콜을 통해 파일 시스템에 대한 액세스 제공)와 클라이언트(프로토콜을 사용하여 원격 파일 시스템에 액세스) 간의 공유
- 네트워크 ID를 통해 서로를 식별하는 것은 스푸핑될 수 있으며 암호화는 성능 비용이 많이 들 수 있다.
- NFS의 예
- 클라이언트 및 서버의 사용자 인증 정보가 일치해야 한다(예: 사용자 ID).
- 원격 파일 시스템 마운트, 사용자 대신 네트워크를 통해 서버로 파일 작업 전송
- 서버 검사 권한, 파일 핸들 반환
- 파일을 닫을 때까지 읽기 및 쓰기에 사용되는 핸들
Distributed Information Systems
- Aka distributed naming services, provide unified access to info needed for remote computing
- Domain name system (DNS) provides host-name-to-network-address translations for the Internet
- Others like network information service (NIS) provide user-name, password, userID, group information
- Microsoft’s common Internet file system (CIFS) network info used with user auth to create network logins that server uses to allow to deny access
- Active directory distributed naming service
- Kerberos-derived network authentication protocol
- Industry moving toward lightweight directory-access protocol (LDAP) as secure distributed naming mechanism
- 원격 컴퓨팅에 필요한 정보에 대한 통합 액세스를 제공하는 분산 명명 서비스
- 도메인 이름 시스템(DNS)은 인터넷을 위한 호스트 이름에서 네트워크 주소로 변환을 제공한다.
- 네트워크 정보 서비스(NIS)와 같은 다른 것들은 사용자 이름, 암호, 사용자 ID, 그룹 정보를 제공한다.
- 서버가 액세스 거부에 사용하는 네트워크 로그인을 만들기 위해 사용자 인증과 함께 사용되는 Microsoft의 CIFS(Common Internet File System) 네트워크 정보
- Active Directory 분산 명명 서비스
- Kerberos 파생 네트워크 인증 프로토콜
- 업계에서 안전한 분산 이름 지정 메커니즘으로 LDAP(Lightweight Directory-Access Protocol)를 채택하고 있다.
Consistency Semantics
- Important criteria for evaluating file sharing-file systems
- Specify how multiple users are to access shared file simultaneously
- When modifications of data will be observed by other users
- Directly related to process synchronization algorithms, but atomicity across a network has high overhead (see Andrew File System)
- The series of accesses between file open and closed called file session
- UNIX semantics
- Writes to open file immediately visible to others with file open
- One mode of sharing allows users to share pointer to current I/O location in file
- Single physical image, accessed exclusively, contention causes process delays
- Session semantics (Andrew file system (OpenAFS))
- Writes to open file not visible during session, only at close
- Can be several copies, each changed independently
- 파일 공유 파일 시스템 평가를 위한 중요 기준
- 여러 사용자가 동시에 공유 파일에 액세스하는 방법 지정
- 다른 사용자가 데이터 수정을 관찰할 수 있는 경우
- 프로세스 동기화 알고리즘과 직접적으로 관련되지만 네트워크 전체의 원자성은 오버헤드가 높다(Andrew File System 참조).
- 열린 파일과 닫힌 파일 사이의 일련의 액세스를 호출한 파일 세션
- UNIX 의미론
- 파일을 연 상태에서 다른 사용자가 바로 볼 수 있는 파일 열기에 쓰기
- 한 가지 공유 모드를 통해 사용자는 파일의 현재 I/O 위치에 대한 포인터를 공유할 수 있다.
- 단일 물리적 이미지, 단독 액세스, 경합으로 인해 프로세스 지연 발생
- 세션 의미론(Andrew 파일 시스템(OpenAFS))
- 세션 중에는 열려 있는 파일에 쓰기가 표시되지 않으며, 닫을 때만 표시된다.
- 각각 독립적으로 변경된 여러 복사본일 수 있다.
NFS
The Sun Network File System (NFS)
- An implementation and a specification of a software system for accessing remote files across LANs (or WANs)
- The implementation originally part of SunOS operating system, now industry standard / very common
- Can use unreliable datagram protocol (UDP/IP) or TCP/IP, over Ethernet or other network
- LAN(또는 WAN)을 통해 원격 파일에 액세스하기 위한 소프트웨어 시스템의 구현 및 사양
- 이 구현은 원래 SunOS 운영 체제의 일부였지만, 현재는 업계 표준/매우 일반적이다.
- 이더넷 또는 다른 네트워크를 통해 신뢰할 수 없는 데이터그램 프로토콜(UDP/IP) 또는 TCP/IP를 사용할 수 있다.
- Interconnected workstations viewed as a set of independent machines with independent file systems, which allows sharing among these file systems in a transparent manner
- A remote directory is mounted over a local file system directory
- The mounted directory looks like an integral subtree of the local file system, replacing the subtree descending from the local directory
- Specification of the remote directory for the mount operation is nontransparent; the host name of the remote directory has to be provided
- Files in the remote directory can then be accessed in a transparent manner
- Subject to access-rights accreditation, potentially any file system (or directory within a file system), can be mounted remotely on top of any local directory
- A remote directory is mounted over a local file system directory
- 상호 연결된 워크스테이션은 독립적인 파일 시스템을 갖춘 독립적인 시스템의 집합으로 보이며, 이를 통해 이러한 파일 시스템 간에 투명한 방식으로 공유 가능
- 원격 디렉터리가 로컬 파일 시스템 디렉터리에 마운트됨
- 마운트된 디렉터리는 로컬 디렉터리에서 내려오는 하위 트리를 대체하는 로컬 파일 시스템의 통합 하위 트리처럼 보인다.
- 마운트 작업에 대한 원격 디렉터리의 사양이 투명하지 않습니다. 원격 디렉터리의 호스트 이름을 제공해야 한다.
- 그러면 원격 디렉터리의 파일에 투명한 방식으로 액세스할 수 있다.
- 접근 권한 인증에 따라, 잠재적으로 모든 파일 시스템(또는 파일 시스템 내의 디렉토리)을 모든 로컬 디렉토리 위에 원격으로 마운트할 수 있다.
- 원격 디렉터리가 로컬 파일 시스템 디렉터리에 마운트됨
- NFS is designed to operate in a heterogeneous environment of different machines, operating systems, and network architectures; the NFS specifications independent of these media
- This independence is achieved through the use of RPC primitives built on top of an External Data Representation (XDR) protocol used between two implementation-independent interfaces
- The NFS specification distinguishes between the services provided by a mount mechanism and the actual remote-file-access services
- NFS는 서로 다른 시스템, 운영 체제 및 네트워크 아키텍처의 이기종 환경에서 작동하도록 설계되었다. NFS 사양은 이러한 미디어와 무관하다.
- 이러한 독립성은 두 개의 구현 독립적인 인터페이스 사이에서 사용되는 외부 데이터 표현(XDR) 프로토콜 위에 구축된 RPC 원시 요소의 사용을 통해 달성된다.
- NFS 사양은 마운트 메커니즘에서 제공하는 서비스와 실제 원격 파일 액세스 서비스를 구분한다.
Three Independent File Systems
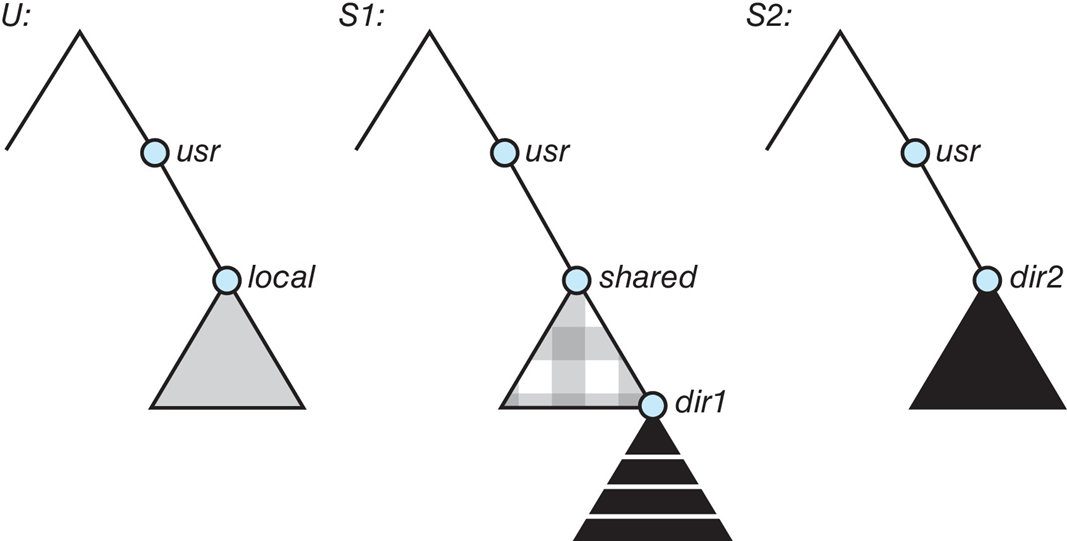
Mounting in NFS
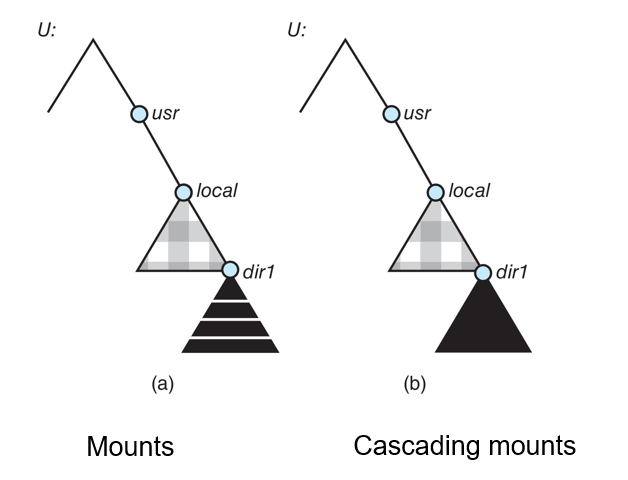
NFS Mount Protocol
- Establishes initial logical connection between server and client
- Mount operation includes name of remote directory to be mounted and name of server machine storing it
- Mount request is mapped to corresponding RPC and forwarded to mount server running on server machine
- Export list – specifies local file systems that server exports for mounting, along with names of machines that are permitted to mount them
- Following a mount request that conforms to its export list, the server returns a file handle—a key for further accesses
- File handle – a file-system identifier, and an inode number to identify the mounted directory within the exported file system
- The mount operation changes only the user’s view and does not affect the server side
- 서버와 클라이언트 간의 초기 논리적 연결을 설정한다.
- 마운트 작업에는 마운트할 원격 디렉터리의 이름과 이를 저장하는 서버 시스템의 이름이 포함된다.
- 마운트 요청이 해당 RPC에 매핑되고 서버 시스템에서 실행 중인 마운트 서버로 전달된다.
- 목록 내보내기 - 서버가 마운트를 위해 내보낼 로컬 파일 시스템과 마운트가 허용된 시스템 이름을 지정한다.
- 내보내기 목록과 일치하는 마운트 요청에 따라 서버는 추가 액세스를 위한 키인 파일 핸들을 반환한다.
- 파일 핸들 – 파일 시스템 식별자 및 내보낸 파일 시스템 내에 마운트된 디렉토리를 식별하는 아이노드 번호
- 마운트 작업은 사용자 보기만 변경되고 서버 측에는 영향을 주지 않는다.
NFS Protocol
- Provides a set of remote procedure calls for remote file operations. The procedures support the following operations:
- searching for a file within a directory
- reading a set of directory entries
- manipulating links and directories
- accessing file attributes
- reading and writing files
- NFS servers are stateless; each request has to provide a full set of arguments (NFS V4 is newer, less used – very different, stateful)
- Modified data must be committed to the server’s disk before results are returned to the client (lose advantages of caching)
- The NFS protocol does not provide concurrency-control mechanisms
- 원격 파일 작업에 대한 일련의 원격 프로시저 호출을 제공합니다. 이 절차는 다음 작업을 지원한다.
- 디렉터리 내에서 파일 검색
- 디렉터리 항목 집합 읽기
- 링크 및 디렉터리 조작
- 파일 특성 액세스
- 파일 읽기 및 쓰기
- NFS 서버는 상태 비저장 상태이며, 각 요청은 전체 인수 집합을 제공해야 한다(NFS V4는 최신 버전이고 사용률이 낮으며 매우 다르며 상태 저장).
- 수정된 데이터는 결과가 클라이언트에 반환되기 전에 서버의 디스크에 커밋되어야 한다(캐싱의 이점 상실).
- NFS 프로토콜은 동시성 제어 메커니즘을 제공하지 않는다.
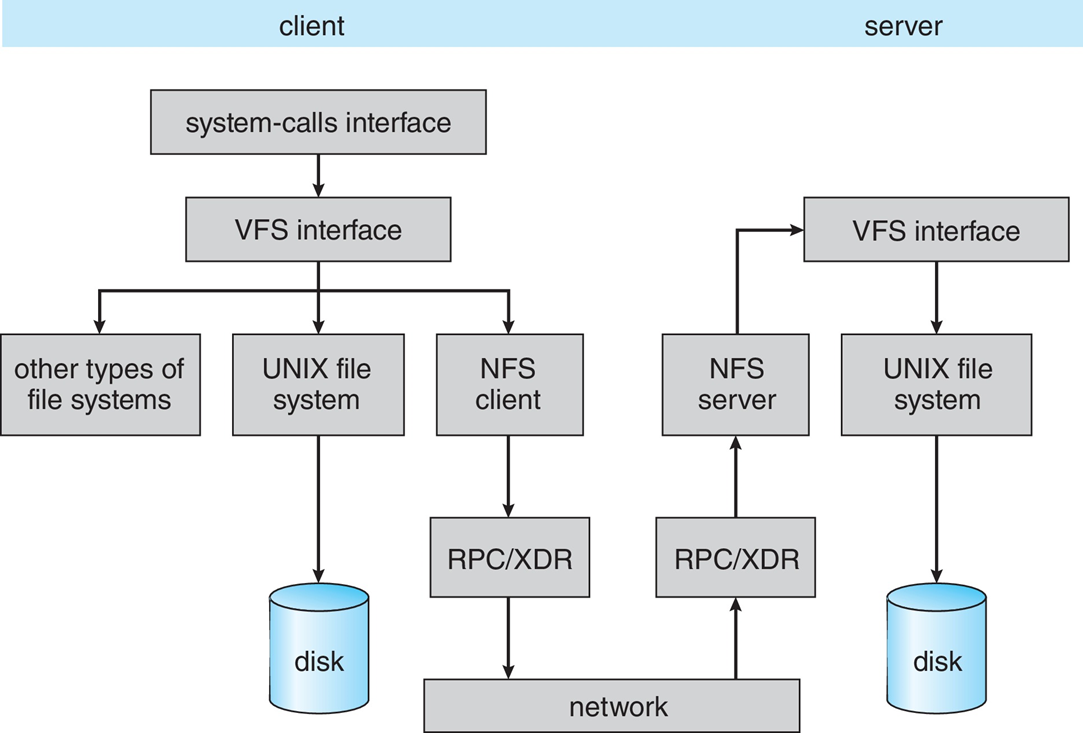
Three Major Layers of NFS Architecture
- UNIX file-system interface (based on the open, read, write, and close calls, and file descriptors)
- Virtual File System (VFS) layer – distinguishes local files from remote ones, and local files are further distinguished according to their file-system types
- The VFS activates file-system-specific operations to handle local requests according to their file-system types
- Calls the NFS protocol procedures for remote requests
- NFS service layer – bottom layer of the architecture
- Implements the NFS protocol
- UNIX 파일 시스템 인터페이스(개방, 읽기, 쓰기 및 닫기 호출 및 파일 설명자 기반)
- VFS(Virtual File System) 계층 – 로컬 파일을 원격 파일과 구별하고 파일 시스템 유형에 따라 로컬 파일을 더욱 구분한다.
- VFS는 파일 시스템 유형에 따라 로컬 요청을 처리하기 위해 파일 시스템별 작업을 활성화한다.
- 원격 요청에 대해 NFS 프로토콜 절차를 호출한다.
- NFS 서비스 계층 – 아키텍처의 맨 아래 계층
- NFS 프로토콜 구현
Schematic View of NFS Architecture
NFS Path-Name Translation
- Performed by breaking the path into component names and performing a separate NFS lookup call for every pair of component name and directory vnode
- To make lookup faster, a directory name lookup cache on the client’s side holds the vnodes for remote directory names
- 경로를 구성 요소 이름으로 나누고 구성 요소 이름과 디렉토리 vnode의 모든 쌍에 대해 별도의 NFS 조회 호출을 수행하는 방식으로 수행된다.
- 더 빠르게 조회할 수 있도록 클라이언트 측의 디렉토리 이름 조회 캐시는 원격 디렉토리 이름에 대한 vnode를 유지한다.
NFS Remote Operations
- Nearly one-to-one correspondence between regular UNIX system calls and the NFS protocol RPCs (except opening and closing files)
- NFS adheres to the remote-service paradigm, but employs buffering and caching techniques for the sake of performance
- File-blocks cache – when a file is opened, the kernel checks with the remote server whether to fetch or revalidate the cached attributes
- Cached file blocks are used only if the corresponding cached attributes are up to date
- File-attribute cache – the attribute cache is updated whenever new attributes arrive from the server
- Clients do not free delayed-write blocks until the server confirms that the data have been written to disk
- 일반 UNIX 시스템 호출과 NFS 프로토콜 RPC 간의 거의 일대일 대응(파일 열기 및 닫기 제외)
- NFS는 원격 서비스 패러다임을 고수하지만 성능을 위해 버퍼링 및 캐슁 기술을 채택한다.
- 파일 차단 캐시 – 파일이 열리면 커널이 원격 서버에서 캐시된 속성을 가져오거나 다시 확인할지 여부를 확인한다.
- 캐시된 파일 블록은 해당 캐시된 속성이 최신인 경우에만 사용된다.
- 파일 속성 캐시 – 서버에서 새 속성이 도착할 때마다 속성 캐시가 업데이트된다.
- 서버가 데이터가 디스크에 기록되었음을 확인할 때까지 클라이언트는 지연-쓰기 블록을 해제하지 않는다.