📔설명
숫자형, 문자형, 날짜형 컬럼 인덱스가 가공됐을 때 튜닝하는 방법을 알아보자
🍔WHERE절의 인덱스 컬럼이 가공된 경우
--튜닝 전
create index emp_sal on emp(sal);
select /*+gatehr_plan_statistics */ ename, sal*12
from emp
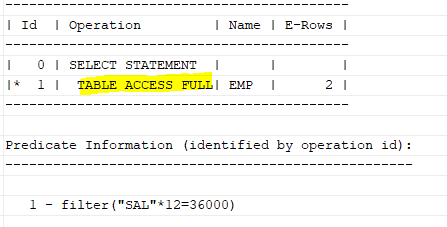
where sal*12=36000;where절의 sal이 가공이 되어서 (*12) 인덱스를 사용할 수 없다.
그러므로 full table scan을 하게 된다.
--튜닝 후
select /*+gatehr_plan_statistics */ ename, sal*12
from emp
where sal=36000/12;
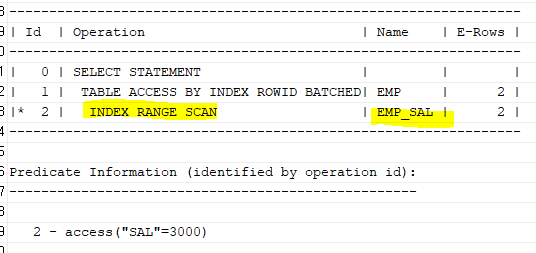
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'ALLSTATS LAST'));위의 sql처럼 36000의 상수를 12로 나눠서 sal 인덱스를 사용할 수 있도록 하자
create index emp_job on emp(job);
select /*+gatehr_plan_statistics */ ename, job
from emp
where substr(job,1,5)='SALES';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'ALLSTATS LAST'));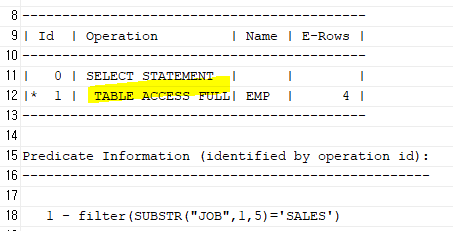
문자형 컬럼일 경우 substr(컬럼,1,5)와 같은 경우 대신 like를 사용하자!
select /*+gather_plan_statistics */ ename, job
from emp
where job like 'SALES%';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'ALLSTATS LAST'));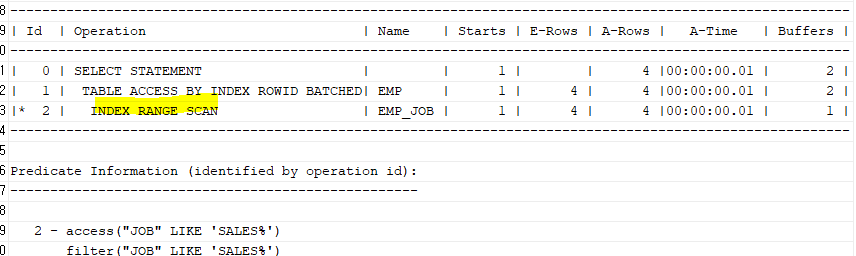
create index emp_hiredate on emp(hiredate);
select /*+gather_plan_statistics */ ename, hiredate
from emp
where to_char(hiredate,'RRRR')='1981';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'ALLSTATS LAST'));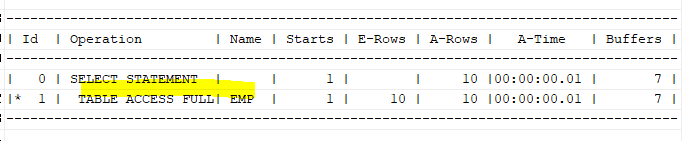
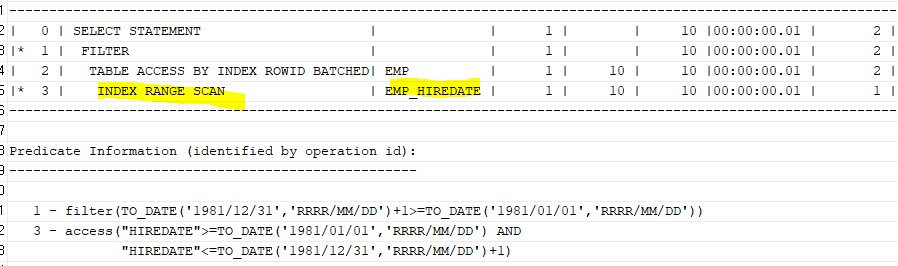
날짜형 컬럼일 경우 1981년도일 경우를 추출하는 것은
between to_date('1981/01/01','RRRR/MM/DD') and to_date('1981/12/31','RRRR/MM/DD')+1로 하자!
+1을 붙이는 이유는 to_date('1981/12/31','RRRR/MM/DD')는 12/31일 00시 00분 00초 까지 이기 때문이다.
select /*+gather_plan_statistics */ ename, hiredate
from emp
where hiredate between to_date('1981/01/01','RRRR/MM/DD') and to_date('1981/12/31','RRRR/MM/DD')+1;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'ALLSTATS LAST'));