EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
In this paper, we systematically study model scaling and identify that carefully balancing network depth, width, and resolution can lead to better performance.
New scaling method : uniformly scales all dimensions of depth/width/resolution using a simple yet highly effective compound coefficient.
1. Introduction
기존의 ConvNets를 scaling up 하는 방법
- depth
- width
- image resolution
CNN은 보통 fixed resource budget으로 개발된 후, resource가 더 충분해졌을 때 scaled up 되곤 한다.
Is there a principled method to scale up ConvNets that can achieve better accuracy and efficiency?
network width/depth/resolution의 모든 차원의 balance가 굉장히 중요하다.
놀랍게도, 이 balance는 각각 일정한 비율로 scaling 하는 것으로 달성할 수 있다.
compound scaling method : uniformly scales network width, depth, and resolution with a set of fixed scaling coefficients
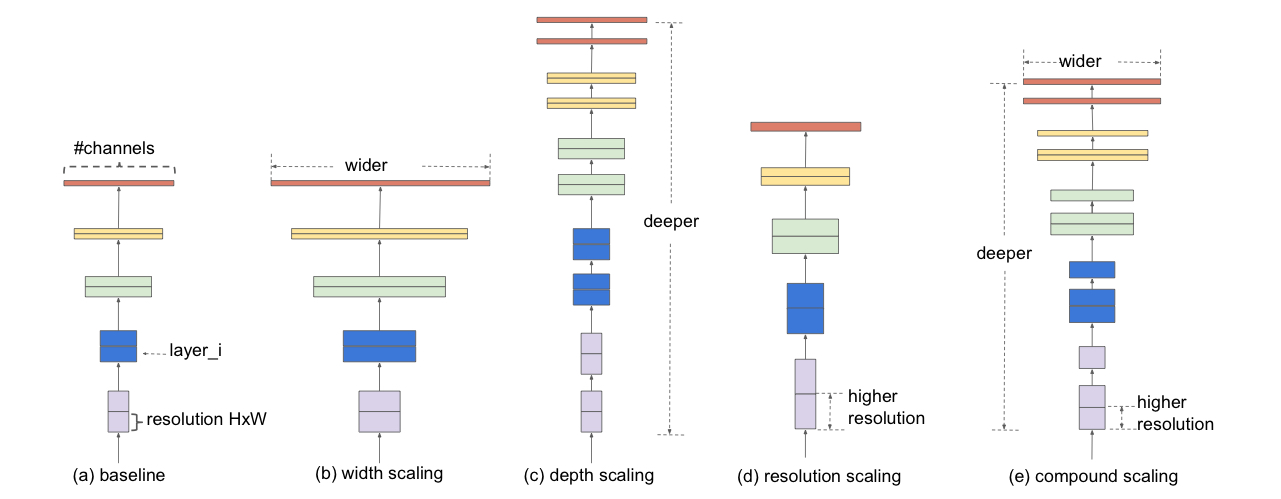
만약 만큼의 computational resources를 얻고 싶다면,
depth를 만큼, width를 만큼 ,image size를 만큼 증가시키면 된다. α,β,γ는 constant coefficients로 original small model의 small grid search로 정해진다.
모델을 키우거나 복잡하게 만드는 것이 항상 좋은 결과를 내는 것은 아니고, 처음 설계한 네트워크 구조가 얼마나 잘 만들어졌는지가 매우 중요하다. 그래서 더 좋은 시작점을 찾기 위해 Neural Architecture Search를 써서 기본이 되는 새로운 모델 구조를 자동으로 찾아낸다. 이 구조를 기반으로 크기를 키워가며 EfficientNets를 만든다.
2. Related Work
ConvNet Accuracy
Although higher accuracy is critical for many applications, we have already hit the hardware memory limit, and thus further accuracy gain needs better efficiency.
ConvNet Efficiency
It is unclear how to apply these techniques for larger models.
In this paper, we aim to study model efficiency for super large ConvNets the surpass sate-of-the-art accuracy.
-> 이를 위하여 model scaling에 의존한다.
Model Scaling
Bigger input image size will help accuracy with the overhead of more FLOPS.
FLOPS
Floating Point Operations Per Seconds
연산량을 나타내는 지표 ( 컴퓨터 성능 측정 단위 )
사진 크기가 커지면, 정확도는 높아지지만 처리시간이 늘거나 하드웨어 자원이 더 많이 필요하다.
3. Compound Model Scaling
3.1. Problem Formulation
ConvNet Layer :
- : operator ( 연산자 )
- : output tensor ( 결과값 )
- : input tensor ( 입력값 )
- : tensor shape ( 데이터 구조 )
ConvNet 은 합성된 레이어들의 리스트로 표현될 수 있다.
: = ... ()
ConvNet 레이어들은 보통 같은 아키텍처를 가진 여러 레이어들이 있는 Multiple stage로 분할된다.
따라서, ConvNet을
=
- : stage 에서 가 번 반복되었다.
ConvNet은 best layer architecture 를 찾는 것이 목표이며, model scaling은 baseline network에 초기 정의된 를 바꾸지 않으면서, network Length , width, and/or resolution을 확장시키는 것을 시도한다.

주어진 자원 (리소스) 제약 하에서 가장 높은 정확도를 달성하는 것이 목표이다.
3.2. Scaling Dimensions
Problem : the optimal depend on each other and the values change under different resource constraints.
Due to this difficulty, conventional methods mostly scale ConvNets in one one these dimensions.
제약 조건 아래에 d,w,r이 dependent 하기 때문에 풀기 어렵다, 일반적으로 세 차원 중 하나만 scale 하는 방법이 많다.
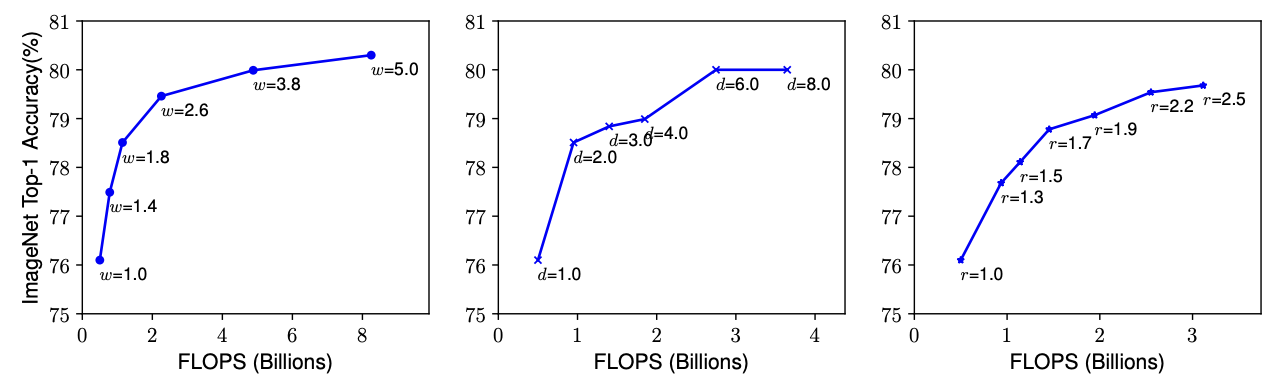
- Depth ()
Depper ConvNet can capture richer and more complex features, and generalize well on new tasks.
하지만!! Deeper Networks are also more difficult to train due to the vanishing gradient problem
: skip connection, batch normalization 등의 해결 방법이 있지만, 아주 깊은 경우에 효과가 없음
Vanishing gradient problem (기울기 소실 문제)
: 역전파 (Backpropagation) 중에 기울기 (gradient)가 점점 작아져서, 앞 쪽(초기층) 레이어가 학습되지 않는 문제
-
Width ()
Scaling network width is commonly used for small size models.
Wider networks tend to be able to capture more fine-grained features and are easier to train.
하지만!! Extremely wide but shallow networks tend to have difficulties in capturing higher level features. -
Resolution ()
With higher resolution input images, ConvNets can potentially capture more fine-grained patterns.
Indeed higher resolutions improve accuracy, but the accuracy gain diminishes for very high resolutions.
위의 분석을 통한
Observation 1 : " Scaling up any dimension of network width, depth, or resolution improves accuracy, but the accuracy gain diminishes for bigger models. "
= 모델을 더 깊거나 넓게 만들거나 입력 해상도를 높이면 정확도는 올라가지만, 일정 크기 이상부터는 성능 향상이 점점 적어진다.
3.3. Compound Scaling
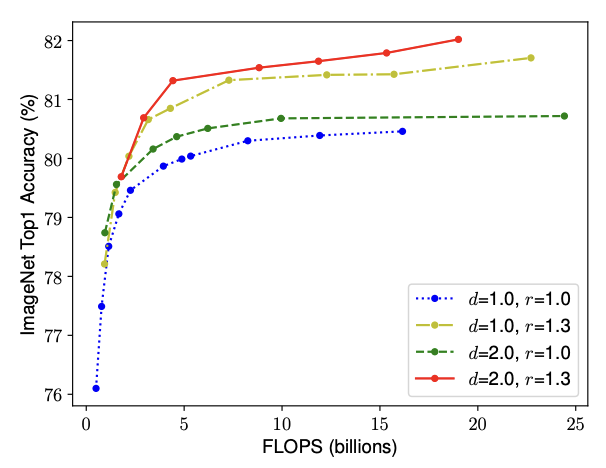
The intuition suggest that we need to coordinate and balance different scaling dimensions rather than conventional single-dimension scaling.
한 방향보다는 조화롭게 키우는 것이 중요하다.
We compare width scaling under differnet network depths and resolutions.
depth와 resolutions을 다르게 한 상태로 width scaling을 진행해보았다.
위의 그래프를 통하여,
Obeservation 2 : " In order to pursue better accuracy and efficiency, it is critical to balance all dimensions of network width, depth, and resolution during ConvNet scaling. "
= 정확도와 연산 효율을 동시에 높이려면, CNN을 키울 때 너비·깊이·해상도를 골고루 조절하는 것이 핵심이다.
논문에서 new compound scaling method를 제안한다.
which use a compound coefficient to uniformly scales network width, depth, and resolution in a principled way :
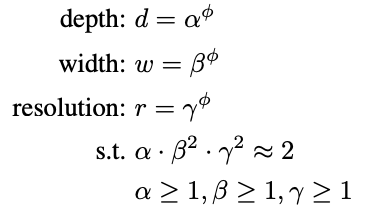
is a user-specified coefficient that controls how many more resources are available for model scaling, while specify how to assign these extra resources to network width, depth, and resolutions respectively.
ø는 모델을 얼마나 키울지를 정하는 사용자 설정 값이고,
α, β, γ는 그 자원을 너비·깊이·해상도 중 어디에 얼마나 분배할지를 나타낸다.
Notably, the FLOPS of a regular convolution op is proportional to .
FLOPS: 연산량 (Floating Point Operations per Second)
Conv 연산량은 보통 다음에 비례함:
- : 네트워크 깊이 (레이어 수)
- : 채널 수가 늘어나면 입력·출력 채널 간 곱이 많아짐 → 제곱
- : 해상도 커질수록 처리해야 할 픽셀 수가 제곱으로 증가
4. EfficientNet Architecture
Model Scaling does not change layer operations in baseline network, having a good baseline network is also critical.
existing ConvNet를 시용하여 scaling method를 평가하겠지만, scaling method의 효과를 더 잘 입증시키기 위하여, mobile-size baseline인 EfficientNet을 개발?했다.
We develop out baseline network by leveraging a multi-objective nerual architecture search that optimizes both accuracy and FLOPS.
정확도와 효율성(FLOPS)을 동시에 고려한 NAS(신경망 구조 자동 설계)를 사용해, 효율적이고 성능 좋은 기준 모델을 설계했다.
We optimize FLOPS rather than latency since we are not targeting any specific hardware device.
Latency : 지연시간
실제 모델이 입력 → 출력까지 걸리는 시간
어떤 모델은 FLOPS는 많아도, 하드웨어 최적화가 잘되어 있으면 latency는 짧을 수도 있다.
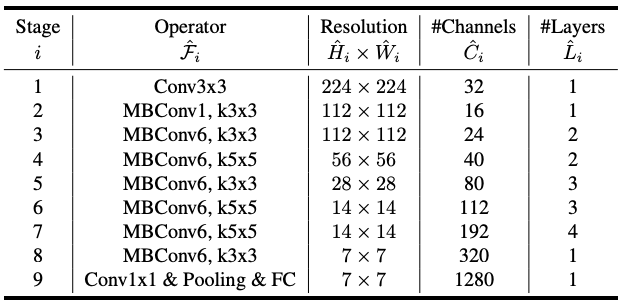
^ EfficientNet-B0 baseline network
Starting from the baseline EfficientNet-B0 , we apply our compound scaling method to scale it up with two steps:
- STEP 1 : 우선 자원()이 2배라고 가정하고, 가장 좋은 너비·깊이·해상도 비율(α, β, γ)을 찾음
- STEP 2 : 그 비율을 고정한 상태에서, 를 늘리며 EfficientNet-B1 ~ B7을 생성
- : 모델 확장 크기 조절 계수 (얼마나 키울지)
- : 각각 너비(width), 깊이(depth), 해상도(resolution)에 자원을 어떻게 배분할지를 조절
- : 연산량이 2배 늘어나는 조건을 만족시키는 scaling 균형 공식
Our method sloves the cost issue by only doing search once on the small baseline netwrok (step 1) , and then use the same scaling coefficents of all other methods (step 2).
5. Experiments
We will first evaluate our scaling method on existing ConvNets and the new proposed EfficientNets.
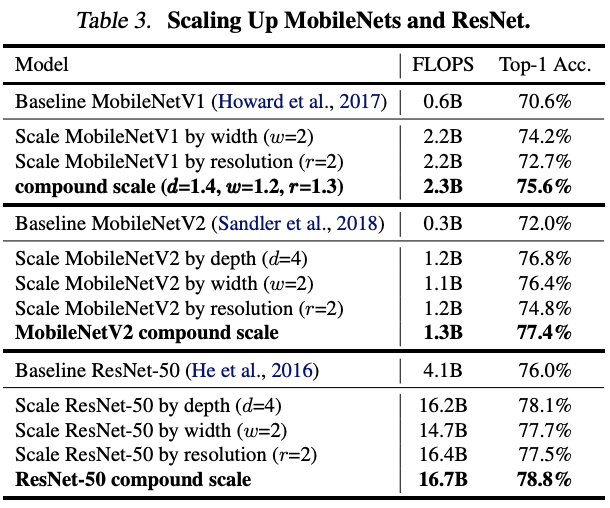
5.1. Scaling Up MobileNets and ResNets
Compared to other single-dimension scaling methods, our compound scaling method improves the accuracy on all these models.
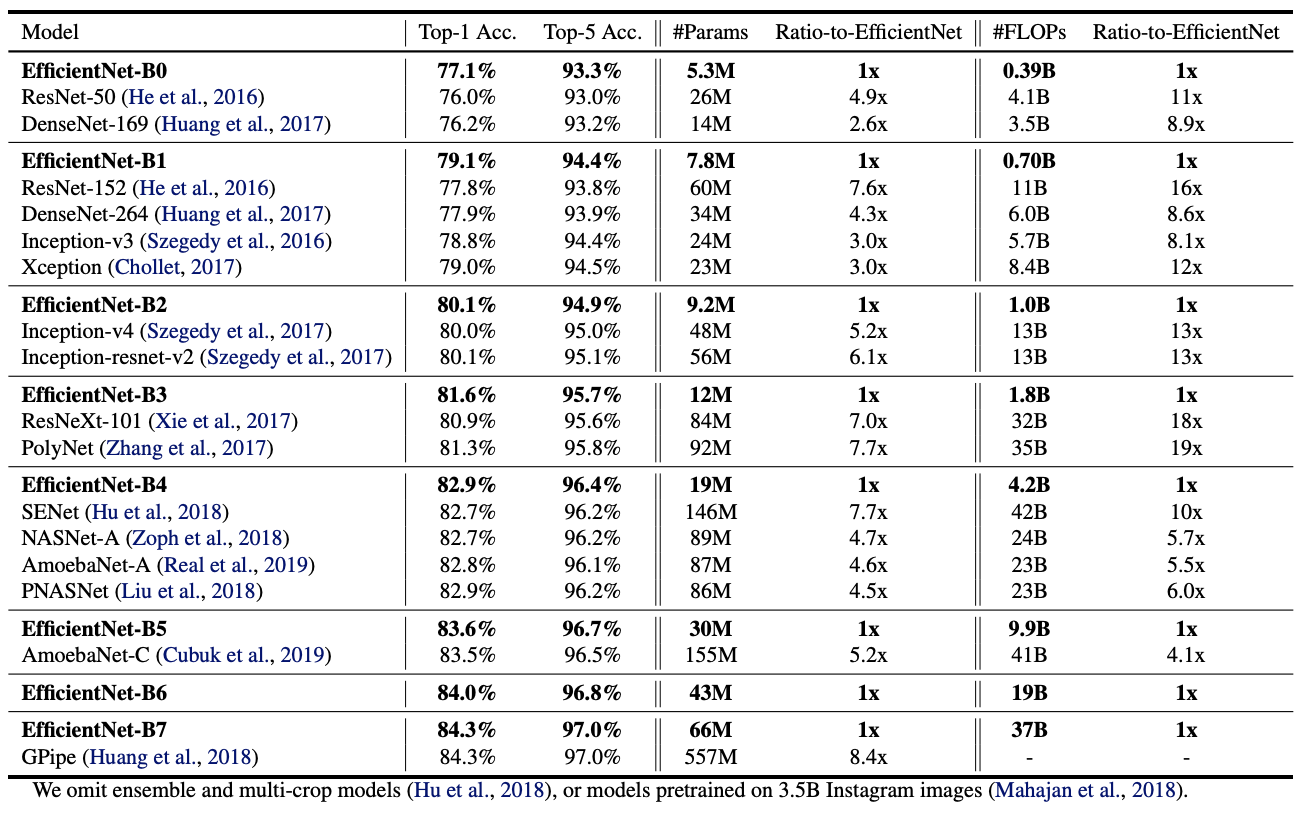
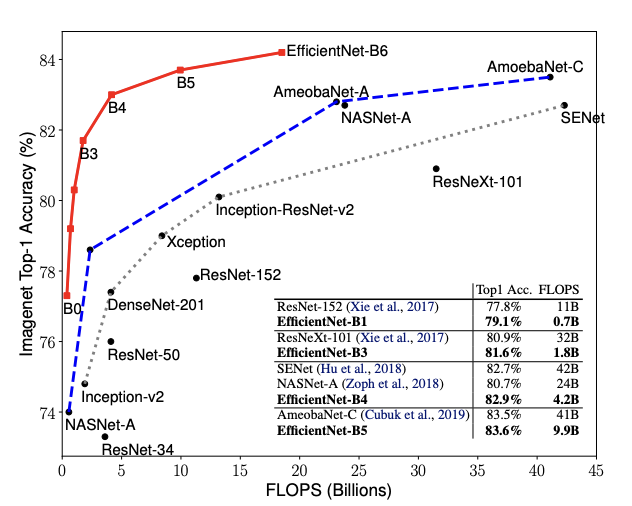
5.2. ImageNet Results for EfficientNet
As commonly known that bigger models need more regularization, we linearly increase dropout ratio from 0.2 for EfficientNet-B0 to 0.5 for B7.
모델이 클수록 과적합을 방지하기 위해 정규화를 더 강하게 적용해야 하므로, EfficientNet에서는 드롭아웃 비율을 B0에서는 0.2로 작게, B7처럼 큰 모델에서는 0.5까지 점점 늘려서 적용한다.
^ Shows the performance of all EfficientNet models that are scaled from the same baseline EfficientNet-B0.
Our EfficientNet models generally use an order of magnitude fewer parameters and FLOPS than other ConvNets with similar accuracy.
더 적은 parameter와 FLOP으로도 비슷한 성능을 보였다.
Our EfficientNet models are not only small, but also computational cheaper.
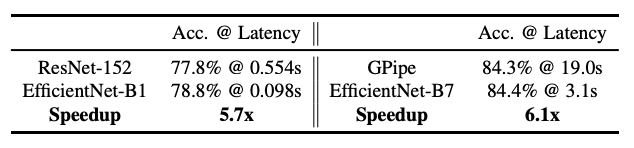
To validate the latency, we have also measured the inference latency for a few representative ConvNets on a real CPU.
결과적으로는 엄청 빨랐다..~
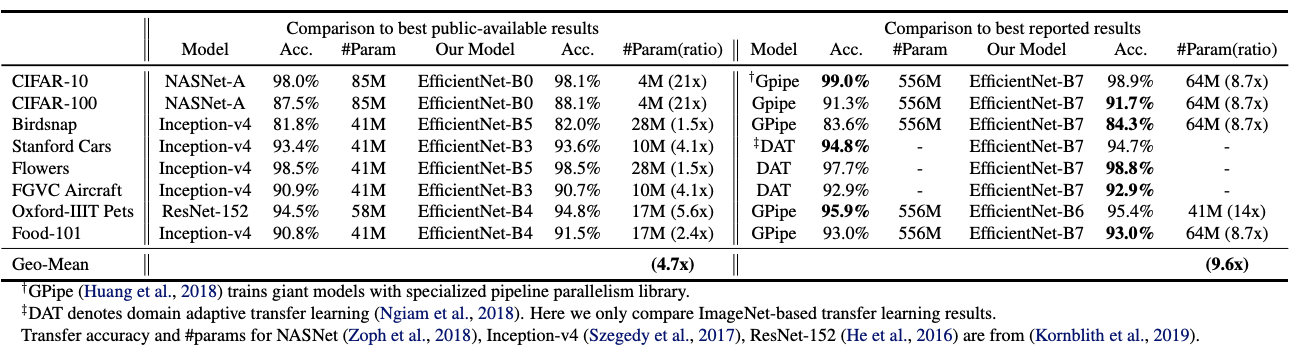
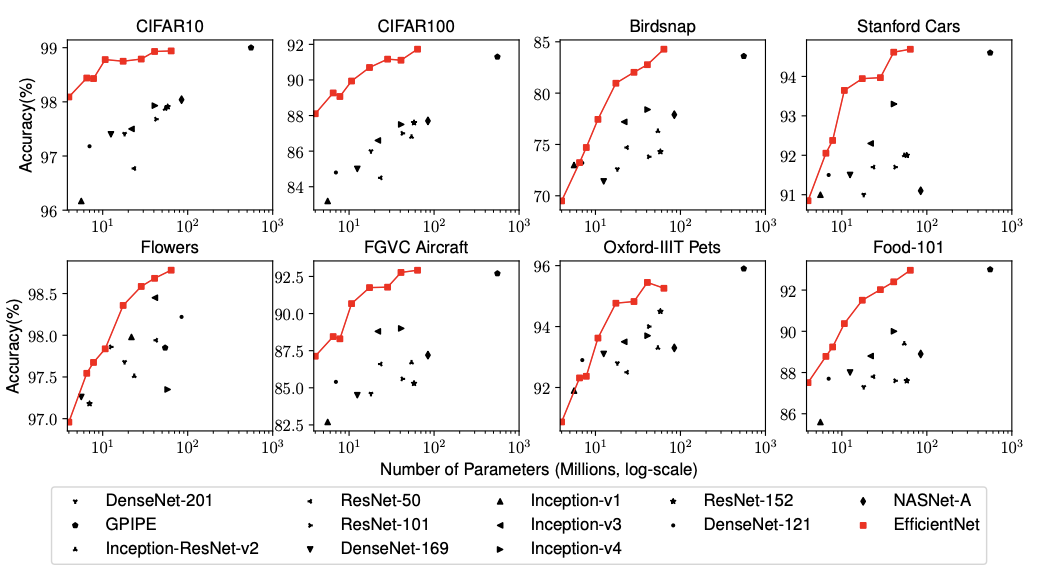
5.3. Transfer Learning Results for EfficientNet
We have also evaluated our EfficientNet on a list of commonly used transfer learning datasets.
역시나 성능이 좋았다..~
6. Discussion
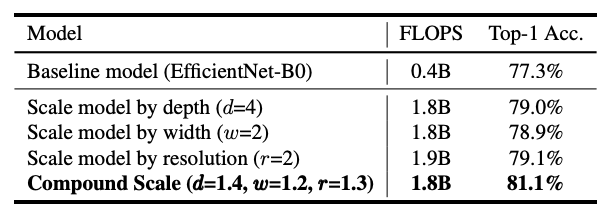
EfficientNet archiecture의 scaling method와 우리의 scaling method를 구분하기 위해서,,
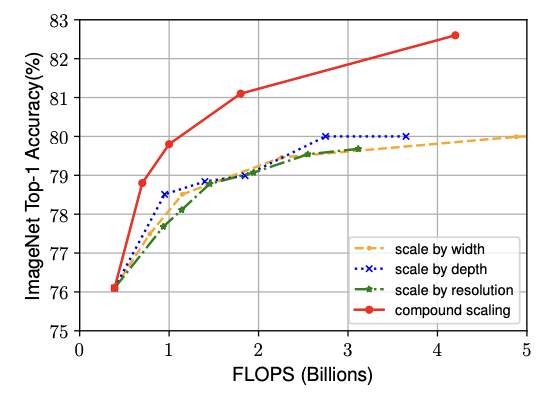
^ Compares the ImageNet performance of different scaling methods for the sane EfficientNet-B0 baseline network.
^ Compares the class activation map for a few representative models with different scaling methods.
The model with compound scaling tends to focus on more relevant regions with more object details, while other models are either lack of object details or unable to capture all objects in the images.
Compound Scaling을 한 모델은 이미지에서 중요한 부분을 더 잘 보고, 더 많은 객체 정보를 잘 담는다.
하지만 일반적인(단일 확장 기반의) 모델들은 중요한 디테일을 놓치거나, 아예 일부 객체를 인식하지 못하는 문제가 있다.
7. Conclusion
Carefully balancing network width, depth, and resolution is an important but missing piece, preventing us from better accuracy and efficiency.
우리는 네트워크의 너비(width), 깊이(depth), 해상도(resolution)를 균형 있게 조정하는 것이 정확도(accuracy)와 효율성(efficiency)을 더 향상시키지 못하게 막는 중요하지만 간과된 요소(missing piece)임을 확인했다.
Powered by this compound scaling method, we demonstrate that a mobile-size EfficientNet model can be scaled up very effectively.
이 복합 스케일링(compound scaling) 방법을 바탕으로, 우리는 모바일 크기의 EfficientNet 모델도 매우 효과적으로 확장할 수 있음을 보여준다.
