
본 시리즈는 프로그래밍 자료구조의 개념을 정리하고 실습을 진행해보는 시리즈입니다.
- 실습은 다음과 같은 개발환경 및 버전에서 진행하였습니다.
- IDE : IntelliJ IDEA (Ultimate Edition)
- Java : JDK 21 (corretto-21)
- Python : 3.9 (conda env)
자료구조 - LinkedList
0. 서론: LinkedList란?
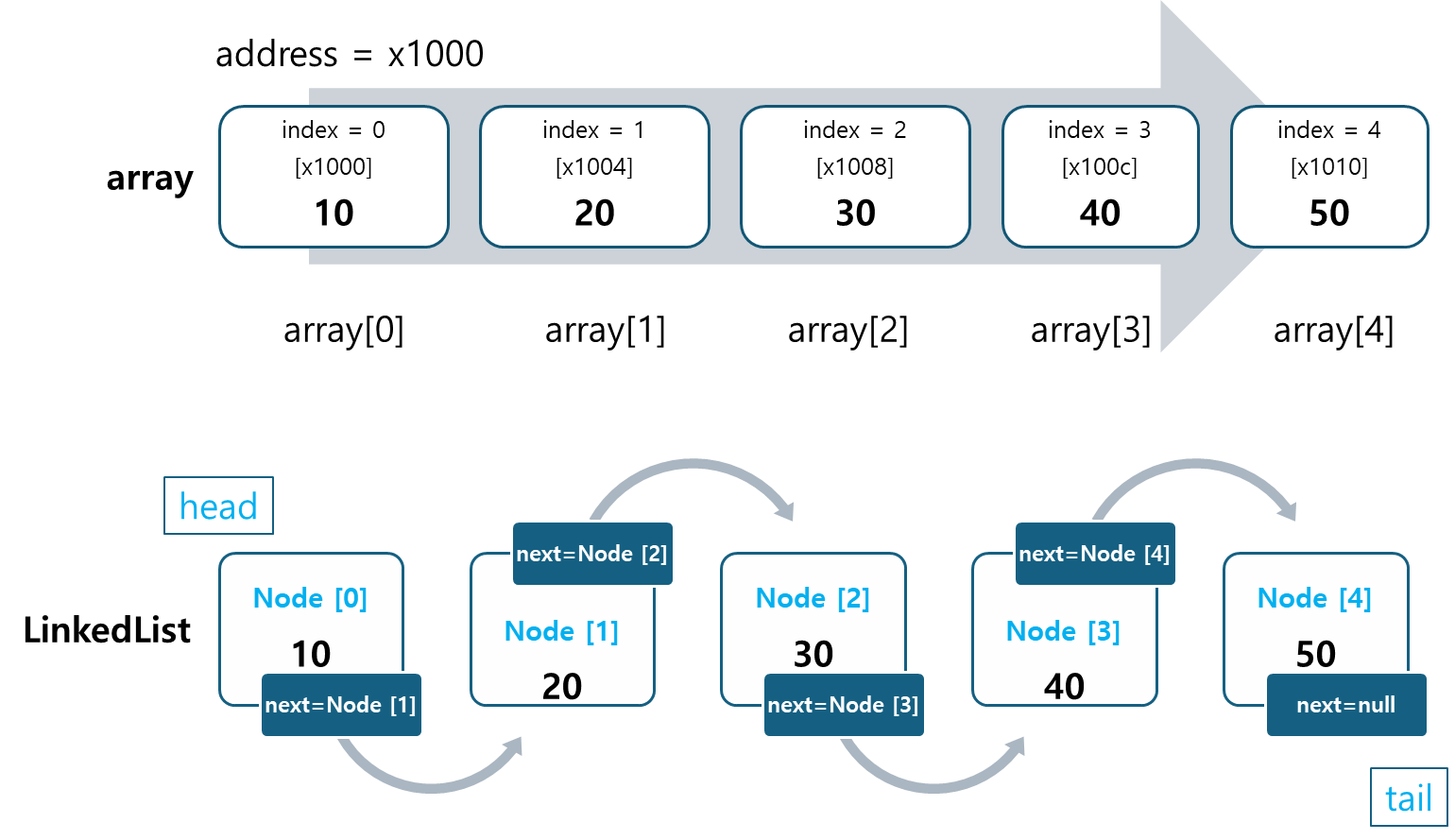
배열과의 차이점
- 배열과 달리 연결 리스트(LinkedList)는 각 요소가 노드(Node)로 연결된 선형 자료구조입니다.
- 노드는 데이터와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터로 구성되며, 필요에 따라 동적으로 크기를 확장할 수 있습니다.
- 배열은 인덱스를 통한 빠른 접근이 필요한 경우 적합하지만, 크기가 고정적이라 삽입/삭제가 빈번하게 발생하는 경우 비효율적입니다.
- 반면, LinkedList는 빈번한 삽입/삭제가 필요할 때 유리하지만, 요소 접근 속도가 느리다는 단점이 있습니다.
LinkedList 장점
- 중간 삽입/삭제가 배열보다 효율적입니다.
- 배열은 데이터를 이동해야 하는 반면, 연결 리스트는 연결된 링크만 수정하면 됩니다.
- 빈번한 삽입/삭제가 필요할 때 상당히 유리합니다.
LinkedList 단점
- 인덱스를 통한 직접 접근이 불가능하여, 특정 위치의 요소를 조회하려면 순차적으로 탐색해야 합니다.
- 추가적으로, 연결 리스트는 포인터를 유지해야 하므로, 메모리 사용량이 배열보다 더 큽니다.
Python과 Java의 연결리스트
- Python에서는 기본적으로
LinkedList를 제공하지 않으므로, 직접Node와LinkedList클래스를 구현해야 합니다. - 반면, Java에서는
java.util.LinkedList클래스를 통해 이미 구현된 연결 리스트를 사용할 수 있으며, 이는 이중 연결 리스트로 구현되어 있습니다.
1. LinkedList 개념과 기본 구현
연결 리스트는 크게 단일 연결 리스트(Singly Linked List), 이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List), 원형 연결 리스트(Circular Linked List)로 분류됩니다.
- 단일 연결 리스트(Singly Linked List): 각 노드가 하나의 다음 노드만 가리키며 연결됩니다.
- 앞에서부터 순차적으로 탐색해야 하며, 단방향으로만 움직일 수 있습니다.
- 이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List): 각 노드가 다음 노드와 이전 노드를 가리키며 연결됩니다.
- 양방향 탐색이 가능하여, 삽입/삭제 시 양방향으로 더 효율적으로 동작할 수 있습니다.
- 원형 연결 리스트(Circular Linked List): 마지막 노드가 첫 번째 노드를 가리켜서 리스트의 끝이 다시 처음과 연결됩니다.
- 순환형 데이터 처리나 리소스 관리 등에 사용되지만, 일반적으로는 많이 사용되지 않습니다.
Python과 Java에서의 LinkedList
- Python에서는
LinkedList를 기본적으로 제공하지 않기 때문에 직접 구현해야 합니다. - Java에서는
java.util.LinkedList클래스를 통해 이미 구현된 연결 리스트를 바로 사용할 수 있습니다.
참고: 이번 포스팅에서는 단일 연결 리스트와 이중 연결 리스트의 구조와 구현 방법에 집중하며, 원형 연결 리스트는 자세히 다루지 않습니다.
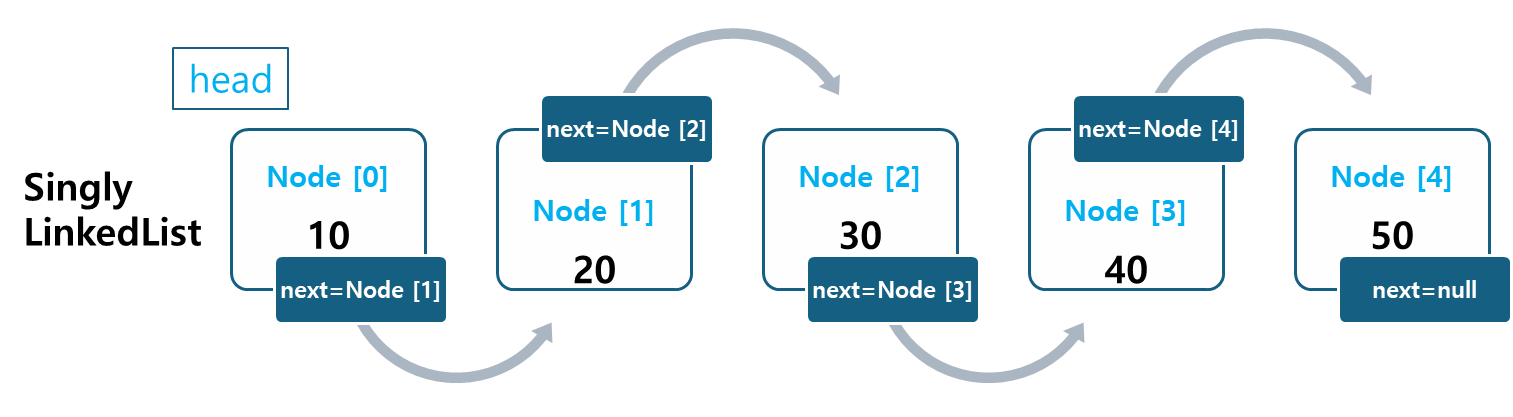
1.1 단일 연결 리스트(Singly Linked List)
단일 연결 리스트는 각 노드가 하나의 다음 노드만 가리키며 연결되는 단방향 자료구조입니다.
- 처음과 마지막 노드를 제외하고, 모든 노드는 하나의 참조만 가집니다.
- 노드는 데이터를 저장하고, 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터로 구성됩니다.
특징
- 삽입/삭제가 중간에 일어나는 경우, 배열보다 효율적입니다.
- 순차 탐색을 해야 하기 때문에, 인덱스를 통한 접근은 비효율적입니다.
Java에서의 LinkedList 사용 예시
Java의 LinkedList는 사실 이중 연결 리스트로 구현되어 있지만, 단일 연결 리스트처럼 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 아래 코드는 Java의
LinkedList를 이용한 단일 연결 리스트처럼 사용하는 예입니다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(10); // 끝에 추가 (O(1))
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(1, 15); // 중간 삽입 (O(n))
System.out.println(list); // [10, 15, 20, 30]
list.remove(2); // 중간 삭제 (O(n))
System.out.println(list); // [10, 15, 30]
}
}Python에서의 단일 연결 리스트 구현 예시
Python에서는 LinkedList가 내장되어 있지 않기 때문에, 직접 Node와 SinglyLinkedList 클래스를 구현해야 합니다.
- 아래 코드는 Python에서 단일 연결 리스트를 직접 구현한 예시입니다.
Node클래스는 데이터와 다음 노드를 가리키는 참조를 저장하며,SinglyLinkedList클래스는 노드를 관리하는 구조입니다.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SinglyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
# 끝에 노드를 추가하는 연산은 O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 가집니다.
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
else:
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def insert_at(self, index, data):
# 인덱스 위치에 노드를 삽입하는 연산은 O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 가집니다.
if index == 0:
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
for i in range(index - 1):
if current is None:
raise IndexError("Index out of bounds")
current = current.next
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" -> ")
current = current.next
print("None")
# 실습
slist = SinglyLinkedList()
slist.append(10)
slist.append(20)
slist.append(30)
slist.display() # 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> None
- 이외에도 탐색(search), 삭제(pop, remove) 등도 구현할 순 있는데, 이건 뒤에서 다시 다루도록 하겠습니다.
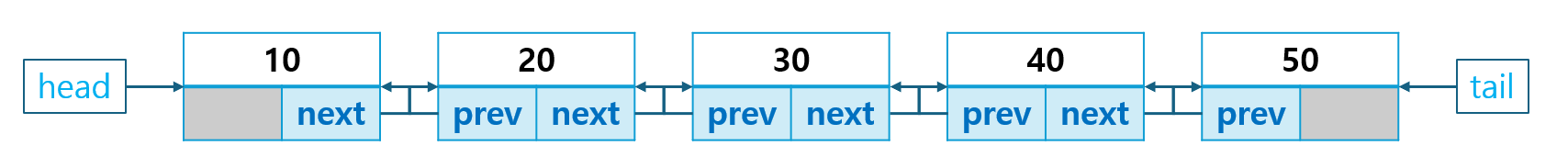
1.2 이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List)
이중 연결 리스트는 각 노드가 다음 노드와 이전 노드를 모두 가리킵니다.
- 양방향 탐색이 가능하여, 앞뒤로 쉽게 이동할 수 있는 구조입니다.
- 노드가 추가되거나 삭제될 때 앞이나 뒤에서 빠르게 처리할 수 있어 효율적입니다.
Java에서의 이중 연결 리스트 사용 예시
- Java의
LinkedList는 기본적으로이중 연결 리스트로 구현되어 있습니다. - 아래 코드는 Java의
LinkedList를 사용한 이중 연결 리스트 예제입니다.
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(10); // 끝에 추가 (O(1))
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.addFirst(5); // 맨 앞에 삽입 (O(1)) -> [5, 10, 20, 30]
list.removeLast(); // 끝에서 삭제 (O(1)) -> [5, 10, 20]
System.out.println(list); // [5, 10, 20]addFirst()는 첫 번째 위치에 노드를 삽입하고,removeLast()는 마지막 노드를 삭제합니다.- 이 두 연산은 이중 연결 리스트의 양방향 탐색 기능 덕분에 O(1)의 시간 복잡도로 처리됩니다.
Python에서의 이중 연결 리스트 구현 예시
- 단일 연결 리스트와 거의 동일하지만, 삽입된 노드의 prev와 기존 tail의 연결만 추가적으로 처리해줍니다.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def append(self, data):
# 끝에 노드를 추가하는 연산은 O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 가집니다.
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
else:
self.tail.next = new_node # 기존 tail의 다음 노드로 연결
new_node.prev = self.tail # 새 노드의 이전 노드를 기존 tail로 연결
self.tail = new_node # tail을 새로운 노드로 업데이트
def remove_last(self):
# 마지막 노드를 삭제하는 연산 (O(1))
if not self.tail:
raise IndexError("List is empty")
elif self.head == self.tail:
self.head = None
self.tail = None
else:
self.tail = self.tail.prev
self.tail.next = None
def display(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" <-> ")
current = current.next
print("None")
# 실습
dlist = DoublyLinkedList()
dlist.append(10)
dlist.append(20)
dlist.append(30)
dlist.display() # 10 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> None
dlist.remove_last()
dlist.display() # 10 <-> 20 <-> None1.3 단일 연결리스트 & 이중 연결리스트 비교
- 단일 연결 리스트는 각 노드가 하나의 다음 노드만 가리키며 연결되는 단방향 리스트입니다.
- 이중 연결 리스트는 각 노드가 다음 노드와 이전 노드를 모두 가리키며, 양방향 탐색이 가능합니다.
시간복잡도 비교
| 자료구조 | 끝에서 삽입 | 중간 삽입 | 끝에서 삭제 | 중간 삭제 | 탐색 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 단일 연결 리스트 | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
| 이중 연결 리스트 | O(1) | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
- 단일 연결 리스트:
- 끝에서 삽입하는 연산은 O(1)이지만, 중간 삽입 및 삭제는 노드를 하나씩 순차적으로 찾아야 하므로 O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 가집니다.
- 끝에서 삭제할 때도 이전 노드를 찾기 위해 전체 리스트를 탐색해야 하므로 O(n)이 소요됩니다.
- 이중 연결 리스트:
- 삽입 및 삭제 시 앞과 뒤에서는 O(1)로 빠르게 처리할 수 있지만, 중간 삽입 및 중간 삭제는 삭제할 노드를 찾기 위해 O(n)의 시간이 소요됩니다.
2-1. 양방향 LinkedList 직접 구현해보기 - Java
- Java에서 기본적으로 제공하는
LinkedList를 사용해도 무방하지만, 이번엔 직접 구현해보며 원리를 파악해보도록 하겠습니다.
2-1.1 LinkedList 생성
- 먼저
Node클래스를 정의하고, 각 노드는data,next,prev필드를 가집니다. - 그리고
DoublyLinkedList클래스에서head와tail노드를 관리합니다.
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
Node head;
Node tail;
public DoublyLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
}2-1.2 데이터 추가/삽입
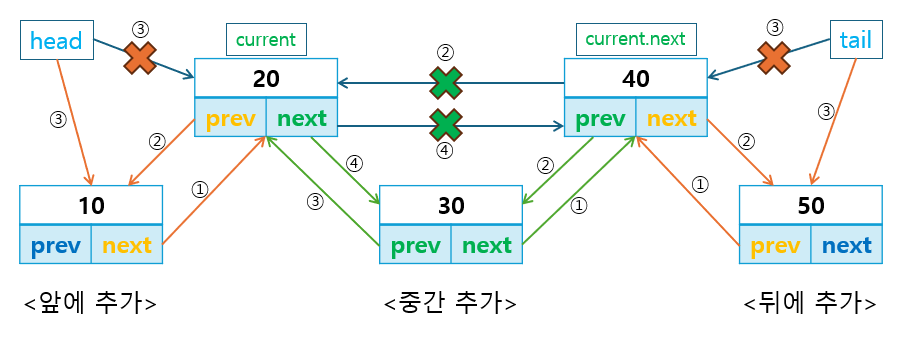
데이터를 앞/뒤 또는 중간에 삽입하는 메서드를 작성합니다.
addFirst()메서드는 리스트의 앞에 노드를 삽입하고,addLast()메서드는 리스트의 뒤에 노드를 삽입하며,insertAt()메서드는 중간에 데이터를 삽입합니다.
class DoublyLinkedList {
// 기존 생성자 생략...
// 리스트의 앞에 노드를 추가하는 메서드
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = head;
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
}
// 리스트의 뒤에 노드를 추가하는 메서드
public void addLast(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (tail == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}
}
// 특정 인덱스에 노드를 삽입하는 메서드
public void insertAt(int index, int data) {
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
Node newNode = new Node(data);
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
if (current == null) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index out of bounds");
}
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
if (current.next != null) {
current.next.prev = newNode;
}
newNode.prev = current;
current.next = newNode;
if (newNode.next == null) {
tail = newNode;
}
}
}2-1.3 데이터 삭제
삭제 연산은 앞/뒤 또는 특정 위치에서 노드를 삭제합니다.
removeFirst()는 리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 삭제하고,removeLast()는 리스트의 마지막 노드를 삭제하며,removeAt()는 특정 위치의 노드를 삭제합니다.
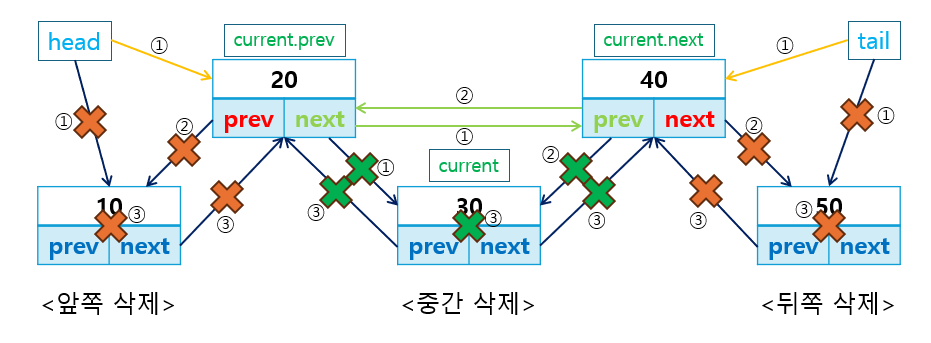
class DoublyLinkedList {
// 기존 생성 및 삽입 메서드 생략...
// 리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 삭제하는 메서드
public void removeFirst() {
if (head == null) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("List is empty");
}
if (head == tail) {
head = tail = null;
} else {
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
}
}
// 리스트의 마지막 노드를 삭제하는 메서드
public void removeLast() {
if (tail == null) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("List is empty");
}
if (head == tail) {
head = tail = null;
} else {
tail = tail.prev;
tail.next = null;
}
}
// 특정 인덱스의 노드를 삭제하는 메서드
public void removeAt(int index) {
if (index == 0) {
removeFirst();
return;
}
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
if (current == null) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index out of bounds");
}
current = current.next;
}
if (current == tail) {
removeLast();
} else {
current.prev.next = current.next;
if (current.next != null) {
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
}
}
}
- 참고로 구현한
removeAt메서드는 중간에 노드를 삭제할 때O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 가집니다.- 중간에 있는 노드를 찾는 과정에서 순차 탐색을 해야 하므로, 삭제할 노드의 위치에 따라 성능이 크게 달라질 수 있습니다.
- 그래서 삭제 연산을 최적화하려면, 중간 삽입/삭제가 빈번히 발생하는 경우 다른 자료구조를 고려하는 것이 좋습니다.
2-1.4 탐색/출력
리스트를 순방향 또는 역방향으로 탐색하면서 데이터를 출력하는 메서드를 작성합니다.
class DoublyLinkedList {
// 기존 생성, 삽입, 삭제 메서드 생략...
// 리스트의 모든 노드를 순방향으로 출력하는 메서드
public void displayForward() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " <-> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("None");
}
// 리스트의 모든 노드를 역방향으로 출력하는 메서드
public void displayBackward() {
Node current = tail;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " <-> ");
current = current.prev;
}
System.out.println("None");
}
}2-1.5 테스트 코드 실행
- 이제
DoublyLinkedList클래스의 모든 주요 연산이 구현되었습니다.- 각 연산이 어떻게 동작하는지 확인하기 위해 테스트 코드를 추가하여 실행해 봅시다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList list = new DoublyLinkedList();
list.addLast(10);
list.addLast(20);
list.addLast(30);
list.displayForward(); // 10 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> None
list.addFirst(5);
list.displayForward(); // 5 <-> 10 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> None
list.removeAt(2);
list.displayForward(); // 5 <-> 10 <-> 30 <-> None
list.insertAt(2, 15);
list.displayForward(); // 5 <-> 10 <-> 15 <-> 30 <-> None
list.displayBackward(); // 30 <-> 15 <-> 10 <-> 5 <-> None
}
}2-2. 양방향 LinkedList 직접 구현해보기 - Python
- 이번에는 Python에서 양방향 LinkedList를 직접 구현해보겠습니다.
- Java와 비슷한 방식으로
Node와DoublyLinkedList클래스를 정의하여 각 노드의data,prev,next를 관리합니다.
2-2.1 LinkedList 생성
먼저 Node 클래스를 정의하고, DoublyLinkedList 클래스에서 head와 tail 노드를 관리합니다.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None2-2.2 데이터 추가/삽입
다음으로, 앞/뒤 또는 중간에 데이터를 삽입하는 메서드를 작성합니다.
add_first()는 리스트의 앞에 노드를 삽입하고,add_last()는 리스트의 뒤에 노드를 삽입하며,insert_at()는 중간에 데이터를 삽입합니다.
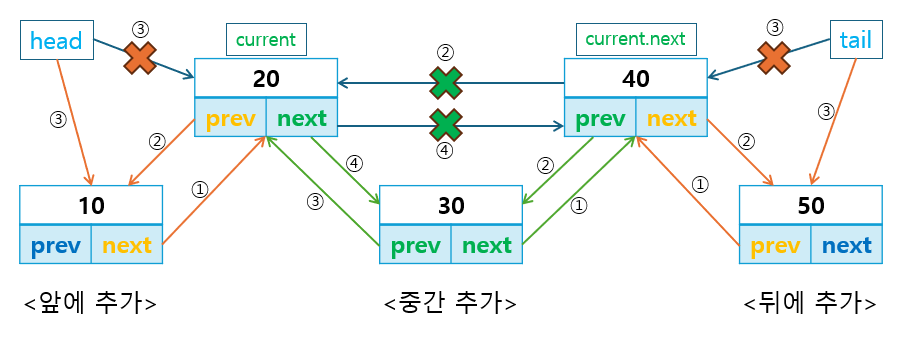
class DoublyLinkedList:
# 기존 생성자 생략...
# 리스트의 앞에 노드를 추가하는 메서드
def add_first(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.tail = new_node
else:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
# 리스트의 뒤에 노드를 추가하는 메서드
def add_last(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.tail is None:
self.head = self.tail = new_node
else:
self.tail.next = new_node
new_node.prev = self.tail
self.tail = new_node
# 특정 인덱스에 노드를 삽입하는 메서드
def insert_at(self, index, data):
if index == 0:
self.add_first(data)
return
new_node = Node(data)
current = self.head
for _ in range(index - 1):
if current is None:
raise IndexError("Index out of bounds")
current = current.next
new_node.next = current.next
if current.next is not None:
current.next.prev = new_node
new_node.prev = current
current.next = new_node
if new_node.next is None:
self.tail = new_node2-2.3 데이터 삭제
데이터 삭제 연산도 앞/뒤 또는 특정 위치에서 노드를 삭제하는 메서드를 작성합니다.
remove_first()는 리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 삭제하고,remove_last()는 리스트의 마지막 노드를 삭제하며,remove_at()는 특정 위치의 노드를 삭제합니다.
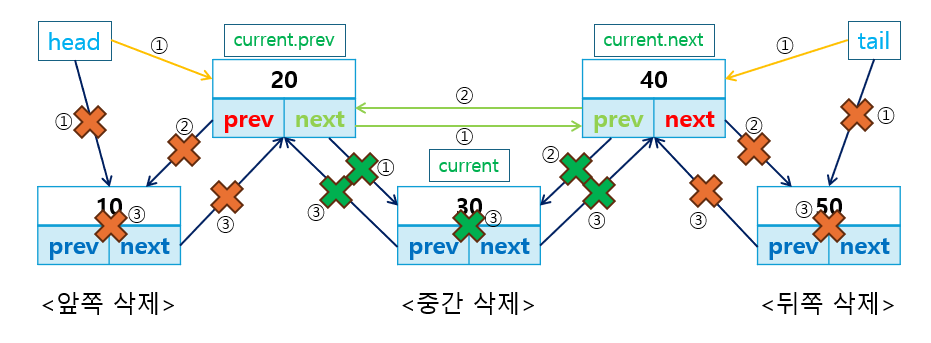
class DoublyLinkedList:
# 기존 생성자 및 삽입 메서드 생략...
# 리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 삭제하는 메서드
def remove_first(self):
if self.head is None:
raise IndexError("List is empty")
if self.head == self.tail:
self.head = self.tail = None
else:
self.head = self.head.next
self.head.prev = None
# 리스트의 마지막 노드를 삭제하는 메서드
def remove_last(self):
if self.tail is None:
raise IndexError("List is empty")
if self.head == self.tail:
self.head = self.tail = None
else:
self.tail = self.tail.prev
self.tail.next = None
# 특정 인덱스의 노드를 삭제하는 메서드
def remove_at(self, index):
if index == 0:
self.remove_first()
return
current = self.head
for _ in range(index):
if current is None:
raise IndexError("Index out of bounds")
current = current.next
if current == self.tail:
self.remove_last()
else:
current.prev.next = current.next
if current.next is not None:
current.next.prev = current.prev2-2.4 탐색/출력
- 리스트의 데이터를 순방향 또는 역방향으로 탐색하며 출력하는 메서드를 작성합니다.
class DoublyLinkedList:
# 기존 생성, 삽입, 삭제 메서드 생략...
# 리스트의 모든 노드를 순방향으로 출력하는 메서드
def display_forward(self):
current = self.head
while current:
print(current.data, end=" <-> ")
current = current.next
print("None")
# 리스트의 모든 노드를 역방향으로 출력하는 메서드
def display_backward(self):
current = self.tail
while current:
print(current.data, end=" <-> ")
current = current.prev
print("None")
2-2.5 테스트 코드 실행
- 이제
DoublyLinkedList클래스의 모든 주요 연산이 구현되었습니다.- 이를 테스트하기 위한 코드를 작성하여 실행해봅시다.
# 테스트
dlist = DoublyLinkedList()
dlist.add_last(10)
dlist.add_last(20)
dlist.add_last(30)
dlist.display_forward() # 10 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> None
dlist.add_first(5)
dlist.display_forward() # 5 <-> 10 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> None
dlist.remove_at(2)
dlist.display_forward() # 5 <-> 10 <-> 30 <-> None
dlist.display_backward() # 30 <-> 10 <-> 5 <-> None3. LinkedList 활용 및 최적화
3.1 고급 활용과 변형: 원형 연결 리스트(Circular LinkedList)
원형 연결 리스트는 마지막 노드가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키는 구조로, 연결 리스트의 끝과 처음이 연결된 순환형 구조입니다.
- 이 자료구조는 특정 상황에서 메모리와 연산의 효율성을 극대화하기 위해 사용됩니다.
원형 연결 리스트의 주요 특징:
- 단방향 원형 리스트: 마지막 노드의
next가 첫 번째 노드를 가리킴. - 이중 원형 리스트: 마지막 노드의
next가 첫 번째 노드를, 첫 번째 노드의prev가 마지막 노드를 가리킴.
원형 연결 리스트 활용 예시:
- 리소스 관리: 원형 구조는 일정한 자원을 반복적으로 사용할 때 유리합니다.
- 예를 들어, 프로세스 관리에서 라운드 로빈 스케줄링(Round Robin Scheduling)에서 사용됩니다. (일단 이런게 있구나 하고 넘어가셔도 됩니다)
- 순환 버퍼: 데이터 스트림의 연속적 처리나 네트워크 패킷의 저장을 위한 버퍼 관리에 적합합니다.
원형 연결 리스트 구현 예시: Java
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class CircularLinkedList {
Node head = null;
Node tail = null;
public void addLast(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = head; // 원형 구조
} else {
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = head;
}
}
public void display() {
Node current = head;
if (head != null) {
do {
System.out.print(current.data + " -> ");
current = current.next;
} while (current != head);
System.out.println("(head)");
}
}
}원형 연결 리스트 구현 예시: Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def add_last(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = self.tail = new_node
self.tail.next = self.head # 원형 구조
else:
self.tail.next = new_node
self.tail = new_node
self.tail.next = self.head
def display(self):
current = self.head
if self.head is not None:
while True:
print(current.data, end=" -> ")
current = current.next
if current == self.head:
break
print("(head)")3.2 Queue/Deque로서의 LinkedList 활용
Queue와 Deque는 자료구조에서 자주 사용하는 개념입니다.
- Queue는 FIFO(First In First Out) 방식으로, Deque는 양쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 가능한 자료구조입니다. (다음 포스팅부터 Stack/Queue/Deque를 정리할 예정입니다)
Java에서의 활용
Java의 LinkedList는 Queue와 Deque 인터페이스를 구현하고 있으므로, 간단한 코드로 Queue와 Deque로 활용할 수 있습니다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Deque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Queue로 LinkedList 사용
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(10);
queue.add(20);
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 10 출력
// Deque로 LinkedList 사용
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.addFirst(5);
deque.addLast(10);
System.out.println(deque.removeFirst()); // 5 출력
System.out.println(deque.removeLast()); // 10 출력
}
}Python에서의 활용
Python에서는 collections.deque를 사용하여 큐와 덱의 기능을 사용할 수 있습니다.
- Python에서
collections.deque는 양방향 큐로 동작하며, 양쪽 끝에서 삽입/삭제가 O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 가집니다.- 이는
LinkedList보다 효율적인 구현이기 때문에, Python에서는 대부분의 경우deque를 사용하는 것이 더 좋은 선택입니다. - 또한,
deque는 리스트 연산보다 메모리 사용량도 적어 성능이 매우 뛰어납니다.
- 이는
from collections import deque
# Queue로 deque 사용
queue = deque()
queue.append(10)
queue.append(20)
print(queue.popleft()) # 10 출력
# Deque로 deque 사용
deque_obj = deque()
deque_obj.appendleft(5)
deque_obj.append(10)
print(deque_obj.popleft()) # 5 출력
print(deque_obj.pop()) # 10 출력3.3 성능 최적화 및 트레이드오프
연결 리스트의 메모리 사용량 분석
- 연결 리스트는 각 노드가 추가적인 포인터(
next,prev)를 유지해야 하므로, 노드 수가 많아질수록 배열에 비해 메모리 사용량이 더 커집니다.- 각 노드는 데이터를 저장할 뿐만 아니라 포인터 필드를 저장해야 하므로, 노드 수가 많을수록 메모리 사용량이 증가합니다.
- 예를 들어, 100개의 요소를 가진
LinkedList는 100개의 데이터 필드뿐만 아니라 100개의 추가 포인터 필드를 유지해야 합니다. 반면, 배열은 하나의 연속된 메모리 블록에 모든 데이터를 저장하므로, 포인터에 대한 추가 비용이 들지 않습니다.
- 메모리 트레이드오프: 대량의 데이터가 있을 때 메모리 효율성이 중요하다면, 배열이 더 유리할 수 있습니다.
LinkedList vs ArrayList 성능 비교 (Java에만 해당되는 내용)
Java에서 LinkedList와 ArrayList는 모두 동일한 List 인터페이스를 구현한 구현체이지만, 각기 다른 상황에서 적합한 성능을 보여줍니다.
- 여기선 삽입/삭제와 탐색 성능 차이를 알아보겠습니다.
| 자료구조 | 삽입 시간 복잡도 | 삭제 시간 복잡도 | 탐색 시간 복잡도 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | O(n) (중간) | O(n) (중간) | O(1) (인덱스 접근) |
| LinkedList | O(1) (앞/뒤) | O(1) (앞/뒤) | O(n) (순차 탐색) |
ArrayList는 인덱스 접근이 빠르지만, 중간 삽입/삭제 시 모든 요소를 이동해야 하므로 성능이 떨어집니다.LinkedList는 중간 삽입/삭제 시 포인터만 변경하면 되므로 유리하지만, 탐색 속도가 느리다는 단점이 있습니다.
다만, 실무에서는 대부분의 경우 ArrayList가 LinkedList보다 더 나은 성능을 제공합니다.
- 이는 Java에서
ArrayList가 내부적으로 고속 복사 메서드인System.arraycopy를 사용하기 때문입니다. - 그래서 중간 삽입 및 삭제에서도
ArrayList는 데이터 블록을 통째로 복사하는 방식으로 상대적으로 빠르게 처리할 수 있습니다.
따라서 대용량 데이터를 처리할 때도 LinkedList보다 ArrayList가 더 효율적인 경우가 많습니다.
3.4 언제 ArrayList를 사용하고, 언제 LinkedList를 사용할까?
ArrayList는 읽기/탐색이 빈번한 경우 적합합니다. 특히 대규모 데이터를 순차적으로 접근할 때 유리합니다.LinkedList는 대용량 데이터의 삽입/삭제가 빈번한 경우 적합하며, 특히 양방향 탐색이나 큐/덱 구조에서 유리합니다.
참고 : 굳이 이렇게 분류했지만, 실무에서는 일반적으로 ArrayList가 LinkedList보다 훨씬 더 좋은 성능을 나타내기 때문에 List 자료형이 필요한 경우 ArrayList를 쓰면 된다고 생각하시면 됩니다.
마무리
이번 포스팅에서는 LinkedList의 구조와 구현 방법에 대해 자세히 알아보았습니다.
- 단일 연결 리스트와 이중 연결 리스트의 차이점과 각각의 장단점, 그리고 원형 연결 리스트와 Queue/Deque로서의 활용 방법을 살펴보았습니다.
Java의 경우 실제 개발에서는 대용량 데이터를 처리할 때는 ArrayList를 사용하는 것이 대부분 더 적합합니다.
- 다만 앞쪽이나 뒤쪽으로 대량의 데이터 삽입과 삭제가 빈번한 경우에는 LinkedList 또는 deque를 사용하는 것이 유리할 수 있습니다.
다음 포스팅부터는 Stack/Queue/Deque 자료구조와 그 활용에 대해 다루어 보도록 하겠습니다.
