해당 글은 다음 글과 그림을 참고하였습니다.
Heys, Howard. (2001). A Tutorial on Linear and Differential Cryptanalysis. Cryptologia. 26. 10.1080/0161-110291890885.
- 서론
암호해독에는 여러 가지 방식이 있는데 그 중 DC (Differential Cryptanalysis) 일명 차분 분석이 존재한다.
차분 분석을 이용하면 마스터 키를 복구할 수 있게 된다.
어떻게?
전제가 한 가지 필요하다.
임의의 함수와 암호화 함수가 구별이 되어야 한다.
그리고 해당 글에서는 SPN (substitution permutation network)를 토대로 설명한다.
그 특성을 이끌어내는데 차분을 사용하는 것이 차분 분석이다.
입력차분, 출력차분을 이용하게 되는데 문자 그대로
입력차분은 입력값들의 XOR 값, 출력차분은 출력값들의 XOR 값이다.
그리고 어떤 입력차분을 사용했을 때 어떤 출력차분이 나올 확률이 차분 확률이다.
(Latex으로 과제하다보니 이제 잘 쓴다^^ 역시 뭐든 배워두니 편한듯)
그러면 이 차분 확률은 어떻게 구할까?
차분 경로를 구해서 해당 경로의 확률들을 곱해 최종 확률을 구한다.
그러면 차분 경로는 어떻게 구할까?
DDT (Differential Distribution Table) 일명 차분분포표를 사용한다.
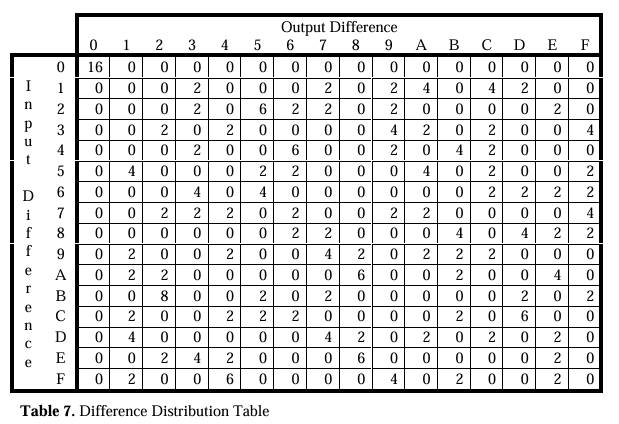
예를 들어 입력 차분이 1일 때, 출력 차분이 3인 경우가 2번, 7인 경우가 2번, 9인 경우가 2번, A인 경우가 4번, C인 경우가 4번, D인 경우가 2번이라면 위의 표처럼 완성할 수 있다.
코드로 표현하면 다음과 같다.
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++) {
ddt[i ^ j][s_box[i] ^ s_box[j]] += 1;
}
}그럼 차분 경로는 어떤 걸로 선택해야 할까?
확률이 높을 수록 좋은 경로다.
여기서 질문이 한 가지 생긴다.
"저 DDT는 s-box 한 번 지날 때에 대한 입력 차분과 출력 차분이잖아요. 그런데 우리는 여러 라운드를 지나고 permutation도 진행하는데 그럼 확률을 어떻게 계산해요?"
매우 좋은 질문이다. 각 단계별로 살펴보자.
(1) S-BOX
S-BOX의 경우에는 을 각 S-BOX에 대해 구한 후 모두 곱해주면 된다.
(2) Permutation
Permutation Layer는 선형연산이기 때문에 해당 사건이 일어날 확률이 1이다.
(3) 라운드키 Addition Layer
라운드키 addition은 xor이고 xor은 두 번 연산되면 1과 동일하기 때문에 신경쓰지 않아도 된다.
(4) 라운드 함수
한 라운드의 확률은 S-BOX에 의해서만 결정된다.
그러면 가장 큰 확률을 가지는 경로를 구했다면, 이제 무엇을 해야 할까?
우리의 목표는 마스터키를 구하는 것이다.
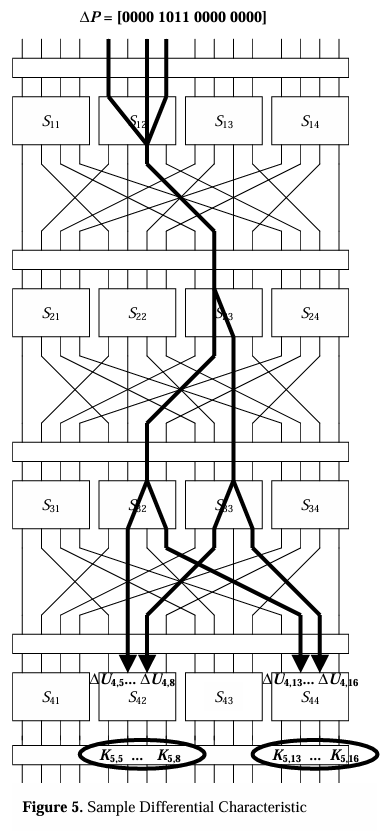
이번에 사용한 toy cipher는 48bit 마스터키를 16bit짜리 키 3개로 나눈 후 xor 연산을 통해 6개의 round key를 생성한다.
그래서 마지막 를 먼저 DC를 통해 구할 것이다. 그 이후는 경로가 정해지기 때문에 brute-forcing으로 진행할 수 있다.
- 차분 경로
차분 경로는 dfs를 통해 구했다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
int s_box[16] = { 11, 5, 6, 10, 9, 12, 7, 1, 2, 14, 13, 0, 4, 3, 8, 15 };
int p_box[16] = { 8, 5, 2, 15, 4, 9, 14, 3, 0, 13, 6, 11, 12, 1, 10, 7 };
int ddt[16][16] = { 0, };
#define MAX_ROUNDS 5
typedef struct {
int input_diff;
int round_diffs[MAX_ROUNDS];
double probability;
} DiffPath;
DiffPath best_path;
double best_probability = 0.0;
void make_ddt() {
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++) {
ddt[i ^ j][s_box[i] ^ s_box[j]] += 1;
}
}
printf("Difference Distribution Table (DDT):\n");
printf(" | ");
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++) {
printf("%2X ", j);
}
printf("\n---+");
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++) {
printf("---");
}
printf("\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
printf("%2X | ", i);
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++) {
printf("%2d ", ddt[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
int apply_permutation(int diff) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
if (diff & (1 << i)) {
result |= (1 << p_box[i]);
}
}
return result;
}
double sbox_probability(int input_diff, int output_diff) {
return (double)ddt[input_diff][output_diff] / 16.0;
}
double calculate_round_probability(int input_diff, int output_diff) {
double prob = 1.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nibble_in_diff = (input_diff >> (i * 4)) & 0xF;
int nibble_out_diff = (output_diff >> (i * 4)) & 0xF;
if (nibble_in_diff != 0) {
double nibble_prob = sbox_probability(nibble_in_diff, nibble_out_diff);
if (nibble_prob == 0) {
return 0.0;
}
prob *= nibble_prob;
}
else if (nibble_out_diff != 0) {
return 0.0;
}
}
return prob;
}
void dfs(int current_diff, int round, double current_prob, int path[MAX_ROUNDS]) {
if (round >= MAX_ROUNDS) {
if (current_prob >= best_probability) {
best_probability = current_prob;
best_path.input_diff = path[0];
best_path.probability = current_prob;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_ROUNDS; i++) {
best_path.round_diffs[i] = path[i];
}
printf("New best path found! Probability: %e (2 ^ %f)\n", current_prob, log2(current_prob));
printf("Input diff: 0x%04X\n", path[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_ROUNDS; i++) {
printf("Round %d diff: 0x%04X\n", i + 1, path[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return;
}
if (current_prob <= best_probability) {
return;
}
for (int n0 = 0; n0 < 16; n0++) {
int in0 = (current_diff >> 0) & 0xF;
if ((in0 == 0 && n0 == 0) || (in0 != 0 && ddt[in0][n0] > 0)) {
for (int n1 = 0; n1 < 16; n1++) {
int in1 = (current_diff >> 4) & 0xF;
if ((in1 == 0 && n1 == 0) || (in1 != 0 && ddt[in1][n1] > 0)) {
for (int n2 = 0; n2 < 16; n2++) {
int in2 = (current_diff >> 8) & 0xF;
if ((in2 == 0 && n2 == 0) || (in2 != 0 && ddt[in2][n2] > 0)) {
for (int n3 = 0; n3 < 16; n3++) {
int in3 = (current_diff >> 12) & 0xF;
if ((in3 == 0 && n3 == 0) || (in3 != 0 && ddt[in3][n3] > 0)) {
int sbox_out_diff = n0 | (n1 << 4) | (n2 << 8) | (n3 << 12);
int perm_out_diff = apply_permutation(sbox_out_diff);
double round_prob = calculate_round_probability(current_diff, sbox_out_diff);
if (round_prob > 0) {
path[round] = perm_out_diff;
dfs(perm_out_diff, round + 1, current_prob * round_prob, path);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
void find_path() {
printf("Searching for highest probability differential paths...\n\n");
best_probability = 0.0;
memset(&best_path, 0, sizeof(best_path));
int current_path[MAX_ROUNDS] = { 0 };
for (int i = 1; i <= 0xFFFF; i++) {
current_path[0] = i;
dfs(i, 1, 1.0, current_path);
if (i % 32 == 0) {
printf("Processed 0x%04X input differences, current best probability: %e (2 ^ %f)\n", i, best_probability, log2(best_probability));
}
}
printf("\n=== BEST DIFFERENTIAL PATH ===\n");
printf("Input Difference: 0x%04X\n", best_path.input_diff);
printf("Overall Probability: %e (2^%f)\n", best_path.probability, log2(best_path.probability));
int current_diff = best_path.input_diff;
for (int round = 0; round < MAX_ROUNDS; round++) {
int sbox_out = 0;
printf("Round %d:\n", round + 1);
printf(" Input difference: 0x%04X\n", current_diff);
printf(" Output difference: 0x%04X\n", best_path.round_diffs[round]);
current_diff = best_path.round_diffs[round];
}
}
int main() {
make_ddt();
find_path();
return 0;
}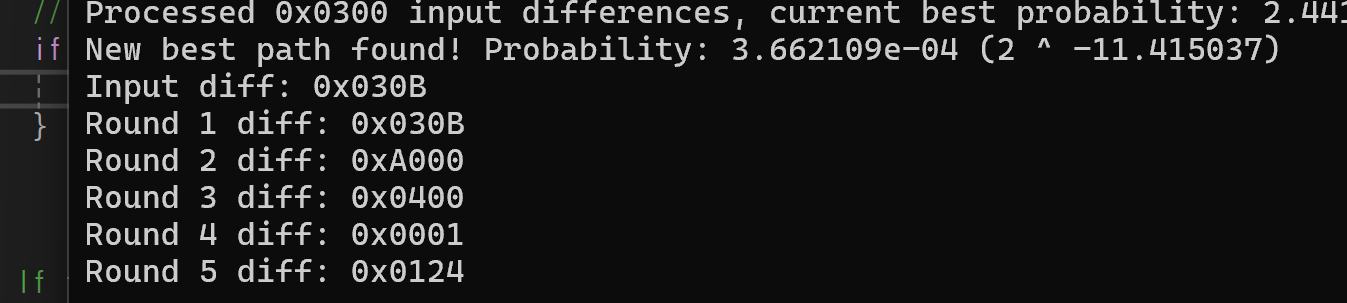
이렇게 경로를 구할 수 있다.
해당 확률을 가지는 다른 경로도 많으며 이는 다음 단계에서 키를 쉽게 구하기 위해 사용될 예정이다.
하지만 너무 많아서 제일 처음 나온 결과만 캡처했다.
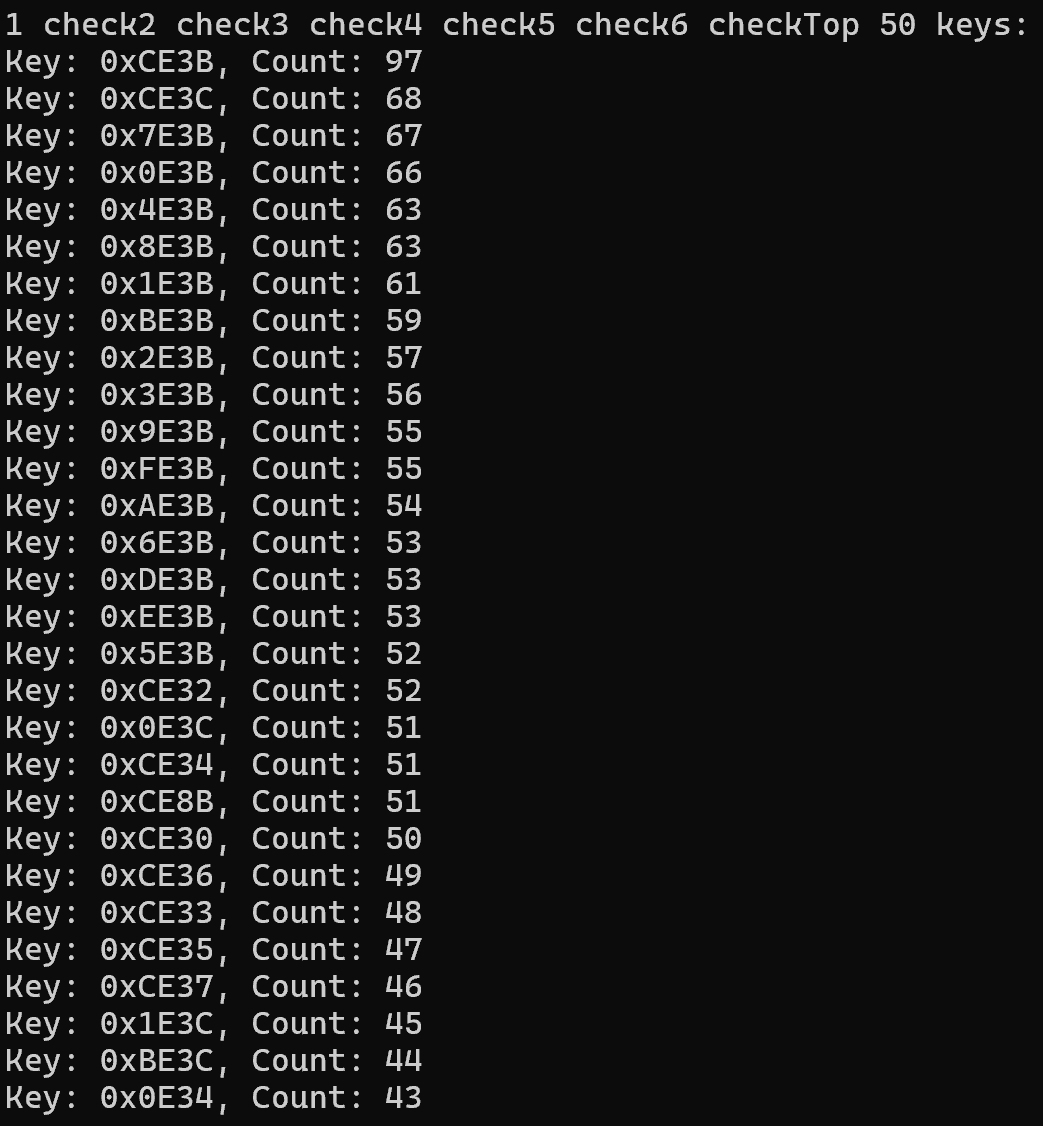
- COUNT
처음에는 하나의 경로만 이용해서 카운트했는데, 너무 차이가 안 나서 총 6개의 경로를 통해 카운트하였다.
카운트는 차분을 만족하는 경우 +1 해준다.
그러면 카운트가 가장 높은 키가 올바른 키라는 것을 알 수 있다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "caltoy.h"
int inv_s_box[16] = { 11, 7, 8, 13, 12, 1, 2, 6, 14, 4, 3, 0, 5, 10, 9, 15 };
pt_t plain_pair[65536][2];
ct_t cipher_pair[65536][2];
int idx = 0;
int key_cnt[0x10000] = { 0, };
void make_pair(pt_t diff) {
pt_t p1, p2;
ct_t c1, c2;
int chk[0xffff] = { 0, };
for (p1 = 0; p1 <= 0xffff; p1++)
{
//printf("plaintext: 0x%04X\n", p1);
p2 = p1 ^ diff;
if (chk[p1] == 0 && chk[p2] == 0) {
chk[p1] = 1;
chk[p2] = 1;
}
else {
if (p1 == 0xffff) {
break;
}
continue;
}
caltoy_enc(&c1, p1);
caltoy_enc(&c2, p2);
plain_pair[idx][0] = p1;
plain_pair[idx][1] = p2;
cipher_pair[idx][0] = c1;
cipher_pair[idx][1] = c2;
idx++;
if (p1 == 0xffff) {
break;
}
}
}
ct_t decrypt(ct_t cipher, rk_t key) {
cipher = cipher ^ key;
return inv_s_box[cipher & 0xf] | (inv_s_box[(cipher & 0xf0) >> 4] << 4) | (inv_s_box[(cipher & 0xf00) >> 8] << 8) | (inv_s_box[(cipher & 0xf000) >> 12] << 12);
}
void find_rk5(ct_t diff) {
for (rk_t key = 0x0000; key <= 0xffff; key++) {
//printf("0x%04X\n", key);
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i++) {
ct_t result = decrypt(cipher_pair[i][0], key) ^ decrypt(cipher_pair[i][1], key);
if (result == diff) {
key_cnt[key] += 1;
}
}
if (key == 0xffff) {
break;
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
printf("%d check\n", 1);
idx = 0;
make_pair(0x030B);
find_rk5(0x0480);
printf("%d check\n", 2);
idx = 0;
make_pair(0x040B);
find_rk5(0x8004);
printf("%d check\n", 3);
idx = 0;
make_pair(0x050B);
find_rk5(0x1480);
printf("%d check\n", 4);
idx = 0;
make_pair(0x070B);
find_rk5(0x0482);
printf("%d check\n", 5);
idx = 0;
make_pair(0x050B);
find_rk5(0x0124);
printf("%d check\n", 6);
idx = 0;
make_pair(0x040B);
find_rk5(0x1482);
/*
for (int i = 0; i <= 0xffff; i++) {
printf("Key 0x%04X: %d\n", i, key_cnt[i]);
}
*/
int top_keys[50] = { 0 };
int top_counts[50] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 0x10000; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 50; j++) {
if (key_cnt[i] > top_counts[j]) {
for (int k = 49; k > j; k--) {
top_keys[k] = top_keys[k - 1];
top_counts[k] = top_counts[k - 1];
}
top_keys[j] = i;
top_counts[j] = key_cnt[i];
break;
}
}
}
printf("Top 50 keys:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
printf("Key: 0x%04X, Count: %d\n", top_keys[i], top_counts[i]);
}
return 0;
}
- 전수조사
나머지 k0, k1은 전수조사를 통해 구했다.
DC로 구해보려고 했으나 너무 카운트 차이가 안 나서 전수조사를 이용했다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "caltoy.h"
int s_box[16] = { 11, 5, 6, 10, 9, 12, 7, 1, 2, 14, 13, 0, 4, 3, 8, 15 };
int p_box[16] = { 8, 5, 2, 15, 4, 9, 14, 3, 0, 13, 6, 11, 12, 1, 10, 7 };
ct_t apply_sbox(pt_t p) {
return s_box[p & 0xf] | (s_box[(p & 0xf0) >> 4] << 4) | (s_box[(p & 0xf00) >> 8] << 8) | (s_box[(p & 0xf000) >> 12] << 12);
}
ct_t apply_pbox(pt_t p) {
ct_t result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
if (p & (1 << i)) {
result |= (1 << p_box[i]);
}
}
return result;
}
void encrypt(ct_t* out, pt_t in, rk_t rk0, rk_t rk1, rk_t rk2, rk_t rk3, rk_t rk4, rk_t rk5) {
in = in ^ rk0;
in = apply_sbox(in);
in = apply_pbox(in);
in = in ^ rk1;
in = apply_sbox(in);
in = apply_pbox(in);
in = in ^ rk2;
in = apply_sbox(in);
in = apply_pbox(in);
in = in ^ rk3;
in = apply_sbox(in);
in = apply_pbox(in);
in = in ^ rk4;
in = apply_sbox(in);
*out = in ^ rk5;
return;
}
int main() {
rk_t k0, k1;
rk_t k2 = 0x9b6e;
rk_t rk0, rk1, rk2, rk3, rk4, rk5;
rk2 = k2 ^ 0x2222;
rk5 = k2 ^ 0x5555;
rk_t keys[0xffff][2];
int idx = 0;
for (k0 = 0x0000; k0 <= 0xffff; k0++) {
// printf("k0: 0x%04X\n", k0);
if (k0 % 0x1000 == 0) {
printf("k0: 0x%04X\n", k0);
}
rk0 = k0 ^ 0x0000;
rk3 = k0 ^ 0x3333;
for (k1 = 0x0000; k1 <= 0xffff; k1++) {
rk1 = k1 ^ 0x1111;
rk4 = k1 ^ 0x4444;
int chk = 1;
for (pt_t plain = 0x0000; plain <= 0xffff; plain += 0x100) {
ct_t cipher, real_cipher;
caltoy_enc(&real_cipher, plain);
encrypt(&cipher, plain, rk0, rk1, rk2, rk3, rk4, rk5);
if (cipher != real_cipher) {
chk = 0;
break;
}
if (plain == 0xff00) {
break;
}
}
if (chk == 1) {
printf("k0: 0x%04X, k1: 0x%04X\n", k0, k1);
keys[idx][0] = k0;
keys[idx][1] = k1;
idx++;
}
if (k1 == 0xffff) {
break;
}
}
if (k0 == 0xffff) {
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i++) {
printf("k0: 0x%04X, k1: 0x%04X\n", keys[i][0], keys[i][1]);
}
}SPN에서 DC 적용 toy cipher 끝!