문제 링크
문제 설명
가장 기본적인 BFS DFS 문제 중 하나이다.
간략하게 문제를 설명하자면
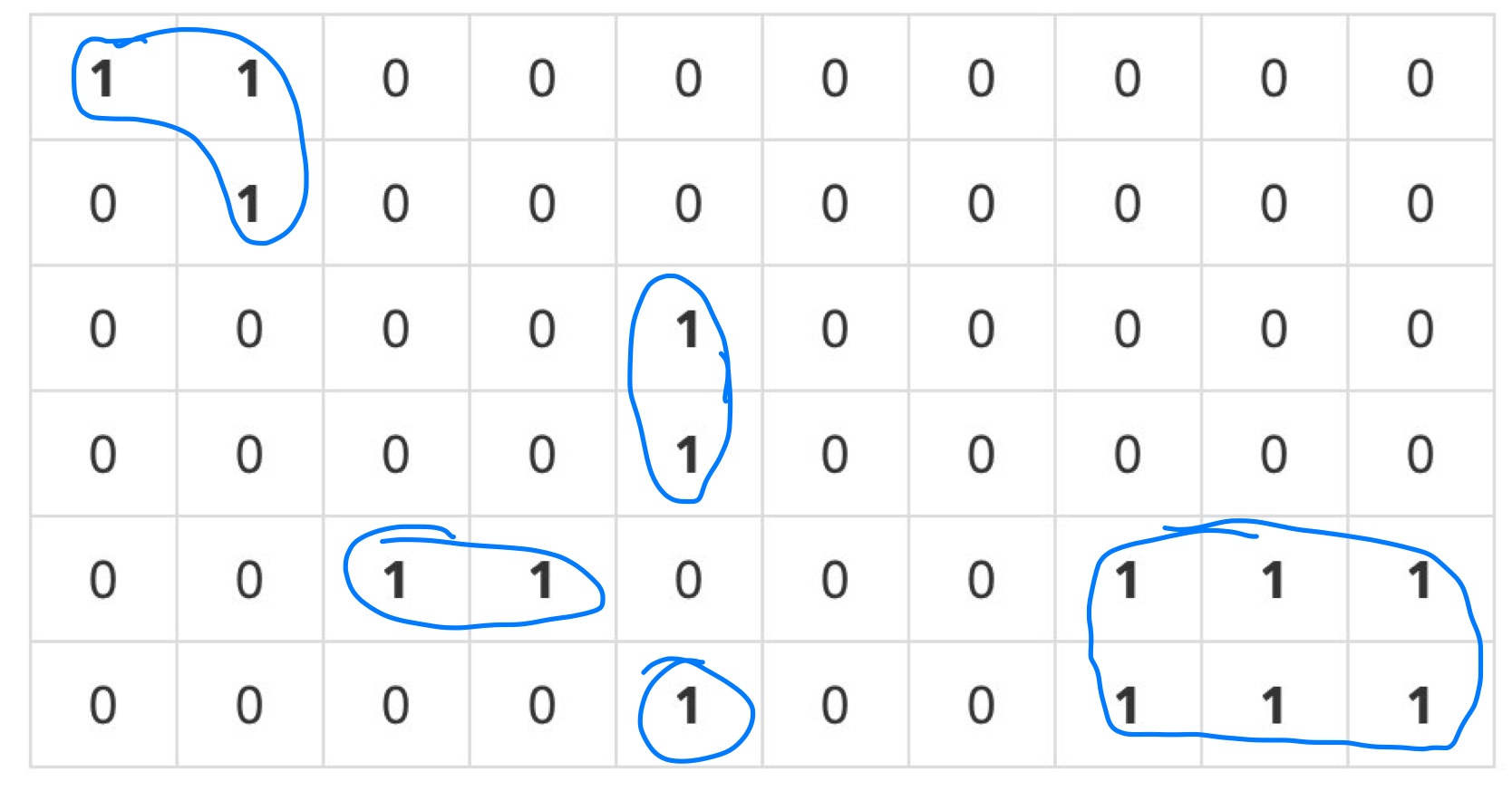
위와 같은 Map이 있을 때 서로 인접한(상하좌우) 1들을 하나의 그룹으로 볼 때, 총 몇개의 그룹이 나오는지 보는 문제이다.
그렇다면 위의 표를 기준으로 봤을 때 정답은 5가 되는 것이다.
풀이 과정
- 0과 1로 이루어진 map을 만든다.
- map의 X와 Y를 돌며 1인 경우를 찾는다.
- BFS 혹은 DFS를 사용하여 인접한 1까지 한번에 체크한다.
- 위의 과정을 테스트 횟수만큼 반복
풀이는 위와 같은 순서로 진행
map 생성 코드
let fs = require("fs");
let input = fs.readFileSync("./input.text").toString().trim().split("\n");
let N = parseInt(input.shift());
let Answer = 0;
var SIZE = input.shift().split(' ').map(Number);
var map = new Array(SIZE[0]);
for (let i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
map[i] = new Array(SIZE[1]).fill(0);
}
for (let i = 0; i < SIZE[2]; i++) {
const [LocX, LocY] = input.shift().split(" ").map(Number);
map[LocX][LocY] = 1;
}BFS(너비 우선 탐색) 함수 코드
const BFS = (nowX, nowY) => {
let LocQueue = [];
let dx = [1, -1, 0, 0];
let dy = [0, 0, 1, -1];
LocQueue.push([nowX, nowY]);
while (LocQueue.length) {
const [X, Y] = LocQueue.shift();
map[X][Y] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
const nextX = X + dx[i];
const nextY = Y + dy[i];
if (nextY >= SIZE[1] || nextX >= SIZE[0] || nextX <0 || nextY < 0) continue;
if (map[nextX][nextY] === 1) {
LocQueue.push([nextX, nextY]);
}
}
}
};전체 코드
const BFS = (nowX, nowY) => {
let LocQueue = [];
let dx = [1, -1, 0, 0];
let dy = [0, 0, 1, -1];
LocQueue.push([nowX, nowY]);
while (LocQueue.length) {
const [X, Y] = LocQueue.shift();
map[X][Y] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
const nextX = X + dx[i];
const nextY = Y + dy[i];
if (nextY >= SIZE[1] || nextX >= SIZE[0] || nextX <0 || nextY < 0) continue;
if (map[nextX][nextY] === 1) {
LocQueue.push([nextX, nextY]);
}
}
}
};
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
let Answer = 0;
var SIZE = input.shift().split(' ').map(Number);
var map = new Array(SIZE[0]);
for (let i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
map[i] = new Array(SIZE[1]).fill(0);
}
for (let i = 0; i < SIZE[2]; i++) {
const [LocX, LocY] = input.shift().split(" ").map(Number);
map[LocX][LocY] = 1;
}
for (let i = 0; i < SIZE[0]; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < SIZE[1]; j++) {
if (map[i][j] === 1) {
BFS(i, j);
Answer++;
}
}
}
console.log(Answer);
}그런데 위와 같이 했을 때 시간초과가 나게 된다.
그래서 BFS가 아니라 DFS를 사용하여 다시 풀어보게 되었다.
DFS(깊이 우선 탐색) 함수 코드
function DFS(X, Y) {
let dx = [1, -1, 0, 0];
let dy = [0, 0, 1, -1];
map[X][Y] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
const nextX = X + dx[i];
const nextY = Y + dy[i];
if (nextY < SIZE[1] && nextX < SIZE[0] && nextX >= 0 && nextY >= 0){
if (map[nextX][nextY] === 1) {
DFS(nextX, nextY);
}
}
}
}전체 코드
let input = require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin").toString().trim().split("\n");
let N = input.shift();
function DFS(X, Y) {
let dx = [1, -1, 0, 0];
let dy = [0, 0, 1, -1];
map[X][Y] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {
const nextX = X + dx[i];
const nextY = Y + dy[i];
if (nextY < SIZE[1] && nextX < SIZE[0] && nextX >= 0 && nextY >= 0){
if (map[nextX][nextY] === 1) {
DFS(nextX, nextY);
}
}
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
let Answer = 0;
var SIZE = input.shift().split(' ').map(Number);
var map = new Array(SIZE[0]);
for (let i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
map[i] = new Array(SIZE[1]).fill(0);
}
for (let i = 0; i < SIZE[2]; i++) {
const [LocX, LocY] = input.shift().split(" ").map(Number);
map[LocX][LocY] = 1;
}
for (let i = 0; i < SIZE[0]; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < SIZE[1]; j++) {
if (map[i][j] === 1) {
DFS(i, j);
Answer++;
}
}
}
console.log(Answer);
}이렇게 탐색하는 부분만 DFS로 바꿔주니 시간초과 문제가 해결되고 통과할 수 있었다.
후기
솔직히 말하면 아직까지도 왜 두 코드에서 시간 차이가 나는지 정확하게는 모르겠다.
DFS의 풀이가 인접 행렬이 아닌 인접 리스트 방식으로 할 경우 DFS는 O(n + e)이고 BFS는 O(n^2) 라고 하지만
위의 풀이의 경우 인접 행렬을 사용했고 두 풀이 모두 시간 복잡도는 O(행의 수 * 열의 수)가 나오는데 왜 차이가 있는지 모르겠다.

