USACO 2020 Feb Gold 3
Problem

Solution
Yes, it is a Gold 3, but no need to fret! Let's start with some trivial test cases provided by the problem. How can we solve the problem when the graph forms a star?
Let vertex be the root of the star, and be the number of edges in each branch. Trivially, , and to go even further, if is the number of such that , . If not, the partition is not possible because elements in has to be paired with and vice versa.
Let's combine this property with tree DP. We can define as following.
Even though the subtree itself may not be partitioned, it can be redeemed further up in the the tree as vertex 8 does in the following figure.
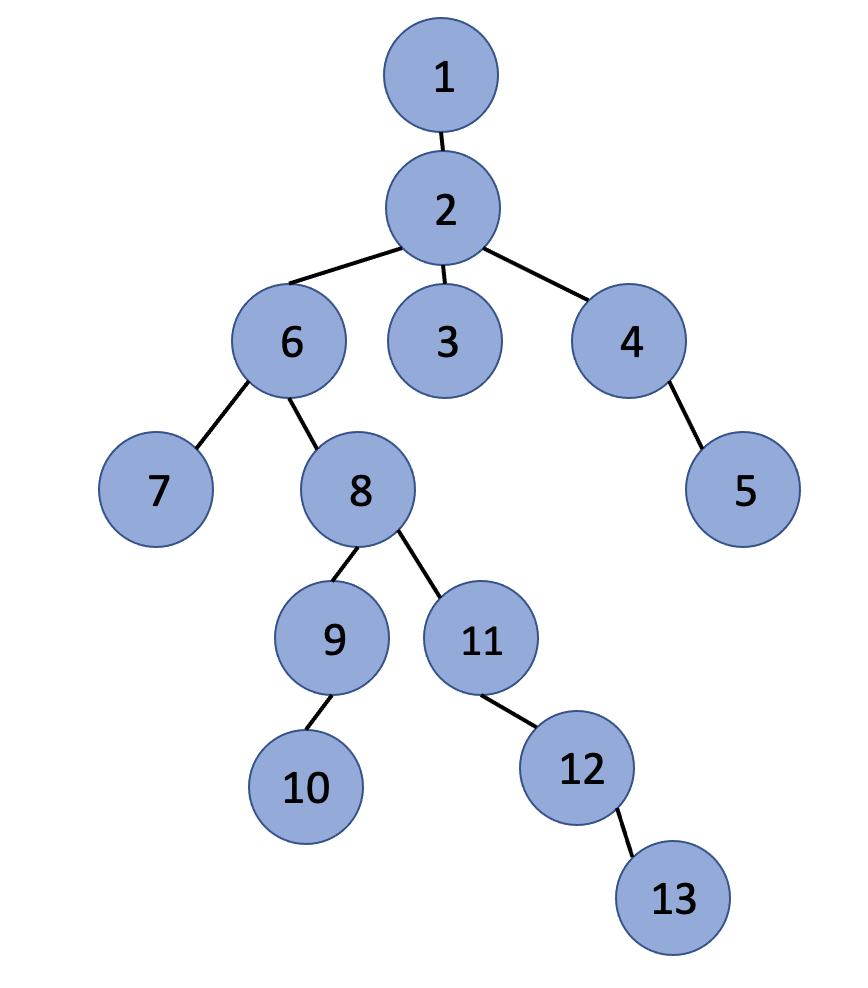
As seen in the figure, will return 2 but this 2 will be later solved in by the edge between 6 and 8.
I used multiset to implement the solve function of DP (not sure if this is the ideal approach since it is risky for TLE).
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int N, dp[100010], K, ans[100010], mark[100010];
vector <int> graph[100010], son[100010];
int solve(int x){
multiset<int> s;
int &r=dp[x];
if(r!=-1) return r;
else{
r=0;
for(int nxt : son[x]){
if(solve(nxt)==-2){
r=-2;
}
else{
int val=(1+solve(nxt))%K;
if(val!=0){
if(s.count(K-val)>0)
s.erase(s.find(K-val));
else s.insert(val);
}
}
}
if(r!=-2){
if(s.size()==0) r=0;
else if(s.size()==1) r=*s.begin();
else r=-2;
}
}
return r;
}
void dfs(int v){
mark[v]=1;
for(int nxt : graph[v])
if(mark[nxt]==0){
son[v].push_back(nxt);
dfs(nxt);
}
}
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin >> N;
for(int i=1; i<N; i++){
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1);
for(int i=1; i<N; i++){
if((N-1)%i!=0){
ans[i]=0;
continue;
}
K=i;
fill(&dp[0], &dp[100010], -1);
solve(1);
if(dp[1]==0)
ans[i]=1;
else ans[i]=0;
}
for(int i=1; i<N; i++)
cout << ans[i];
return 0;
}
